Featured
-
-
Article |
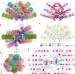 Structure of phycobilisome from the red alga Griffithsia pacifica
Structure of phycobilisome from the red alga Griffithsia pacifica
Single-particle cryo-electron microscopy is used to resolve the structure of the phycobilisome, a 16.8-megadalton light-harvesting megacomplex, from the red alga Griffithsia pacifica at a resolution of 3.5 Å.
- Jun Zhang
- , Jianfei Ma
- & Sen-Fang Sui
-
Letter |
 Cryo-electron microscopy structure of the lysosomal calcium-permeable channel TRPML3
Cryo-electron microscopy structure of the lysosomal calcium-permeable channel TRPML3
A cryo-electron microscopy structure shows that the mucolipin domain of the lysosomal calcium channel TRPML3 binds phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate and gates the channel.
- Marscha Hirschi
- , Mark A. Herzik Jr
- & Seok-Yong Lee
-
Article |
 Human TRPML1 channel structures in open and closed conformations
Human TRPML1 channel structures in open and closed conformations
Two structures of human transient receptor potential mucolipin 1 (TRPML1), in the closed and agonist-bound open states, have been resolved by electron cryo-microscopy.
- Philip Schmiege
- , Michael Fine
- & Xiaochun Li
-
Letter |
 Nucleosome–Chd1 structure and implications for chromatin remodelling
Nucleosome–Chd1 structure and implications for chromatin remodelling
A cryo-electron microscopy structure of the chromatin remodelling factor Chd1 bound to a nucleosome leads to a model for DNA translocation by its ATPase motor.
- Lucas Farnung
- , Seychelle M. Vos
- & Patrick Cramer
-
Letter |
 Structure of mammalian endolysosomal TRPML1 channel in nanodiscs
Structure of mammalian endolysosomal TRPML1 channel in nanodiscs
The structure of mouse transient receptor potential mucolipin 1 (TRPML1), a cation channel located within endosomal and lysosomal membranes, is resolved using single-particle electron cryo-microscopy.
- Qingfeng Chen
- , Ji She
- & Youxing Jiang
-
Letter |
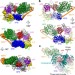 The cryo-electron microscopy structure of human transcription factor IIH
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of human transcription factor IIH
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of the ten-subunit human transcription factor IIH, revealing the molecular architecture of the TFIIH core complex, the detailed structures of its constituent XPB and XPD ATPases, and how the core and kinase subcomplexes of TFIIH are connected.
- Basil J. Greber
- , Thi Hoang Duong Nguyen
- & Eva Nogales
-
Article |
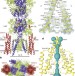 Channel opening and gating mechanism in AMPA-subtype glutamate receptors
Channel opening and gating mechanism in AMPA-subtype glutamate receptors
The structures of AMPA receptors in complex with auxiliary proteins are resolved by cryo-electron microscopy, and reveal conformational and permeation pathway changes that are associated with activation and desensitization of ionotropic glutamate receptors.
- Edward C. Twomey
- , Maria V. Yelshanskaya
- & Alexander I. Sobolevsky
-
Letter |
 Open and closed structures reveal allostery and pliability in the HIV-1 envelope spike
Open and closed structures reveal allostery and pliability in the HIV-1 envelope spike
New high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structures of the HIV-1 envelope protein provide a detailed description and understanding of how the HIV-1 fusion machinery functions and how it changes its structure over time to convert from the pre-fusion to the fusion-intermediate conformation.
- Gabriel Ozorowski
- , Jesper Pallesen
- & Andrew B. Ward
-
Letter |
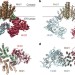 Cryo-EM structure of the protein-conducting ERAD channel Hrd1 in complex with Hrd3
Cryo-EM structure of the protein-conducting ERAD channel Hrd1 in complex with Hrd3
The structure of yeast Hrd1 in complex with Hrd3 shows that Hrd1 forms an aqueous cavity with a lateral seal within the endoplasmic reticulum membrane, shedding light on how misfolded proteins are transported out of the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Stefan Schoebel
- , Wei Mi
- & Maofu Liao
-
Article |
 Cryo-EM structures of tau filaments from Alzheimer’s disease
Cryo-EM structures of tau filaments from Alzheimer’s disease
High-resolution structures of tau filaments shed light on the ultrastructure of neurofibrillary lesions in Alzheimer’s disease.
- Anthony W. P. Fitzpatrick
- , Benjamin Falcon
- & Sjors H. W. Scheres
-
Letter |
 Electron cryo-microscopy structure of the mechanotransduction channel NOMPC
Electron cryo-microscopy structure of the mechanotransduction channel NOMPC
Single-particle electron cryo-microscopy analysis of the mechanotransduction channel NOMPC reveals that it contains a bundle of four helical spring-shaped ankyrin repeat domains that undergo motion, potentially allowing mechanical movement of the cytoskeleton to be coupled to the opening of the channel.
- Peng Jin
- , David Bulkley
- & Yifan Cheng
-
Article |
 Structure of the human multidrug transporter ABCG2
Structure of the human multidrug transporter ABCG2
The structure of human ABCG2 bound to an inhibitory antibody using cryo-electron microscopy, representing the first high-resolution structural data of a human multidrug transporter.
- Nicholas M. I. Taylor
- , Ioannis Manolaridis
- & Kaspar P. Locher
-
Article |
 Cryo-EM structure of the activated GLP-1 receptor in complex with a G protein
Cryo-EM structure of the activated GLP-1 receptor in complex with a G protein
The structure of the GLP-1 receptor complexed with its ligand offers insight into the mechanism of class B G-protein-coupled receptor activation.
- Yan Zhang
- , Bingfa Sun
- & Georgios Skiniotis
-
Article |
 Ensemble cryo-EM elucidates the mechanism of translation fidelity
Ensemble cryo-EM elucidates the mechanism of translation fidelity
Structural ensembles of the 70S ribosome bound to cognate or near-cognate charged tRNAs in complex with EF-Tu illustrate the crucial role of the nucleotide G530 in decoding of mRNA, and demonstrate that translational fidelity results from direct control of GTPase by the decoding centre.
- Anna B. Loveland
- , Gabriel Demo
- & Andrei A. Korostelev
-
Article |
 Structure of a pre-catalytic spliceosome
Structure of a pre-catalytic spliceosome
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of the yeast spliceosome in a pre-catalytic state provides insights into the molecular events leading to formation of the spliceosome active site.
- Clemens Plaschka
- , Pei-Chun Lin
- & Kiyoshi Nagai
-
Article |
 Phase-plate cryo-EM structure of a class B GPCR–G-protein complex
Phase-plate cryo-EM structure of a class B GPCR–G-protein complex
Volta phase-plate cryo-electron microscopy reveals the structure of the full-length calcitonin receptor in complex with its peptide ligand and Gαsβγ.
- Yi-Lynn Liang
- , Maryam Khoshouei
- & Patrick M. Sexton
-
Article |
 Mechanism of chromatin remodelling revealed by the Snf2-nucleosome structure
Mechanism of chromatin remodelling revealed by the Snf2-nucleosome structure
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Snf2 chromatin remodeller bound to a nucleosome and a proposed mechanism for DNA translocation by Snf2 are presented.
- Xiaoyu Liu
- , Meijing Li
- & Zhucheng Chen
-
Article |
 Mediator structure and rearrangements required for holoenzyme formation
Mediator structure and rearrangements required for holoenzyme formation
Cryo-electron microscopy maps of the fission yeast Mediator complex and of a Mediator–RNA polymerase II holoenzyme reveal how changes in the Med14 subunit enable large-scale rearrangements of the Mediator structure that are essential for holoenzyme formation.
- Kuang-Lei Tsai
- , Xiaodi Yu
- & Francisco J. Asturias
-
Article |
 Structure of a eukaryotic cyclic-nucleotide-gated channel
Structure of a eukaryotic cyclic-nucleotide-gated channel
The first high-resolution (3.5 Å) structure of a full-length cyclic-nucleotide-gated channel, revealing an unconventional, voltage-insensitive voltage-sensor domain and a unique coupling mechanism between cyclic-nucleotide-binding and pore-opening.
- Minghui Li
- , Xiaoyuan Zhou
- & Jian Yang
-
Letter |
 Structure of a spliceosome remodelled for exon ligation
Structure of a spliceosome remodelled for exon ligation
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of a yeast spliceosome stalled before mature RNA formation provides insight into the mechanism of exon ligation.
- Sebastian M. Fica
- , Chris Oubridge
- & Kiyoshi Nagai
-
Letter |
 Structural basis of co-translational quality control by ArfA and RF2 bound to ribosome
Structural basis of co-translational quality control by ArfA and RF2 bound to ribosome
The structure of the bacterial ribosome in complex with the ArfA and the release factor RF2 shows how ArfA recruits RF2 to terminate translation of messenger RNAs that lack a stop codon in the ribosome.
- Fuxing Zeng
- , Yanbo Chen
- & Hong Jin
-
Article |
 Cryo-EM structure of a human spliceosome activated for step 2 of splicing
Cryo-EM structure of a human spliceosome activated for step 2 of splicing
The cryo-EM structure of the splicing intermediate known as the C* complex from human.
- Karl Bertram
- , Dmitry E. Agafonov
- & Reinhard Lührmann
-
Article |
 Structure of a CLC chloride ion channel by cryo-electron microscopy
Structure of a CLC chloride ion channel by cryo-electron microscopy
Some CLC proteins are channels that conduct chloride ions passively, whereas others are active co-transporters, a difference that has been hard to understand given their high degree of sequence homology; now, cryo-electron microscopy is used to determine the structure of a mammalian CLC channel, shedding light on this question.
- Eunyong Park
- , Ernest B. Campbell
- & Roderick MacKinnon
-
Letter |
 In situ structures of the genome and genome-delivery apparatus in a single-stranded RNA virus
In situ structures of the genome and genome-delivery apparatus in a single-stranded RNA virus
A high-resolution structure of the bacteriophage MS2 sheds light on the structure of the genome and how the genome is delivered into a bacterium.
- Xinghong Dai
- , Zhihai Li
- & Ren Sun
-
Article |
 Cryo-EM structure of the open high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel
Cryo-EM structure of the open high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel
Two complementary studies present the full-length high-resolution structure of a Slo1 channel in the presence or absence of Ca2+ ions, in which an unconventional allosteric voltage-sensing mechanism regulates the Ca2+ sensor in addition to the voltage sensor’s direct action on the pore.
- Xiao Tao
- , Richard K. Hite
- & Roderick MacKinnon
-
Letter |
 Near-atomic-resolution cryo-EM analysis of the Salmonella T3S injectisome basal body
Near-atomic-resolution cryo-EM analysis of the Salmonella T3S injectisome basal body
The authors report the structure of the assembled membrane spanning ring forming proteins of the Salmonella Typhimurium injectisome basal body, including the first atomic structure of a member of the secretin family of outer-membrane pores.
- L. J. Worrall
- , C. Hong
- & N. C. J. Strynadka
-
Article |
 Structural basis for gating the high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel
Structural basis for gating the high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel
Two complementary studies present the full-length high-resolution structure of a Slo1 channel in the presence or absence of Ca2+ ions, in which an unconventional allosteric voltage-sensing mechanism regulates the Ca2+ sensor in addition to the voltage sensor’s direct action on the pore.
- Richard K. Hite
- , Xiao Tao
- & Roderick MacKinnon
-
Letter |
 Mechanistic insights into the alternative translation termination by ArfA and RF2
Mechanistic insights into the alternative translation termination by ArfA and RF2
The structure of the bacterial 70S ribosome in complex with ArfA, the release factor RF2, a short non-stop mRNA and a cognate P-site tRNA is presented, revealing how ArfA and RF2 facilitate alternative translation termination of the non-stop ribosomal complex using a stop-codon surrogate mechanism.
- Chengying Ma
- , Daisuke Kurita
- & Ning Gao
-
Letter |
 Structural basis for ArfA–RF2-mediated translation termination on mRNAs lacking stop codons
Structural basis for ArfA–RF2-mediated translation termination on mRNAs lacking stop codons
The structure of the bacterial ribosome stalled on a truncated mRNA in complex with ArfA and the release factor RF2 is presented, revealing how ArfA recruits RF2 to the ribosome and induces conformational changes within RF2 to enable translation termination in the absence of a stop codon.
- Paul Huter
- , Claudia Müller
- & Daniel N. Wilson
-
Article |
 The pathway to GTPase activation of elongation factor SelB on the ribosome
The pathway to GTPase activation of elongation factor SelB on the ribosome
The structures of several states on the pathway of SelB-mediated delivery of selenocysteine-specific tRNA to the ribosome in Escherichia coli reveal the mechanism of UGA stop codon recoding to selenocysteine and show how codon recognition triggers activation of translational GTPases.
- Niels Fischer
- , Piotr Neumann
- & Holger Stark
-
Letter |
 Structure of RNA polymerase I transcribing ribosomal DNA genes
Structure of RNA polymerase I transcribing ribosomal DNA genes
Structures of budding yeast RNA polymerase I in a catalytically active conformation are presented and confirmed by visualizing processive transcription along ribosomal DNA genes; they support a general model for transcription elongation in which contracted and expanded polymerase conformations are associated with active and inactive states, respectively.
- Simon Neyer
- , Michael Kunz
- & Achilleas S. Frangakis
-
Letter |
 Atomic model for the membrane-embedded VO motor of a eukaryotic V-ATPase
Atomic model for the membrane-embedded VO motor of a eukaryotic V-ATPase
The structure of the VO subcomplex of yeast V-ATPase, solved by electron cryomicroscopy, reveals a new subunit and suggests a mechanism for the translocation of protons across membranes.
- Mohammad T. Mazhab-Jafari
- , Alexis Rohou
- & John L. Rubinstein
-
Article |
 The architecture of the mammalian respirasome
The architecture of the mammalian respirasome
Respirasomes are supercomplexes of mitochondrial electron transport chain complexes that are responsible for cellular respiration and energy production; a cryo-electron microscopy structural study of the respirasome is presented.
- Jinke Gu
- , Meng Wu
- & Maojun Yang
-
Letter |
 Structural basis of kainate subtype glutamate receptor desensitization
Structural basis of kainate subtype glutamate receptor desensitization
The high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of the kainate receptor GluK2 subtype in its desensitized state is reported, which reveals that desensitization is attained by establishing a ring-like structure in the ligand-binding domains.
- Joel R. Meyerson
- , Sagar Chittori
- & Sriram Subramaniam
-
Article |
 Structure of the voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1.1 at 3.6 Å resolution
Structure of the voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1.1 at 3.6 Å resolution
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of the rabbit voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1.1 complex at a nominal resolution of 3.6 ångströms.
- Jianping Wu
- , Zhen Yan
- & Nieng Yan
-
Article |
 Molecular basis of APC/C regulation by the spindle assembly checkpoint
Molecular basis of APC/C regulation by the spindle assembly checkpoint
A high-resolution structure of a complex between the anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C) and the mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC) reveals how MCC interacts with and represses APC/C by obstructing substrate recognition and suppressing E3 ligase activity.
- Claudio Alfieri
- , Leifu Chang
- & David Barford
-
Letter |
 Structure of mammalian respiratory complex I
Structure of mammalian respiratory complex I
Electron cryomicroscopy structures are provided for all core and supernumerary protein subunits of mammalian complex I, a 45-subunit enzyme that powers eukaryotic respiration.
- Jiapeng Zhu
- , Kutti R. Vinothkumar
- & Judy Hirst
-
Letter |
 The structural basis of modified nucleosome recognition by 53BP1
The structural basis of modified nucleosome recognition by 53BP1
A cryo-electron microscopy structure of the DNA damage repair protein 53BP1 bound to a nucleosome illuminates the way 53BP1 recognizes two types of histone modifications (a methyl group and a ubiquitin moiety), and provides insight into the highly specified recognition and recruitment of 53BP1 to modified chromatin.
- Marcus D. Wilson
- , Samir Benlekbir
- & Daniel Durocher
-
Article |
 Cryo-EM structure of the spliceosome immediately after branching
Cryo-EM structure of the spliceosome immediately after branching
Cryo-EM reveals the configuration of substrate pre-mRNA within the active spliceosome and suggests how remodelling occurs prior to exon ligation.
- Wojciech P. Galej
- , Max E. Wilkinson
- & Kiyoshi Nagai
-
Letter |
 Architecture of fully occupied GluA2 AMPA receptor–TARP complex elucidated by cryo-EM
Architecture of fully occupied GluA2 AMPA receptor–TARP complex elucidated by cryo-EM
The cryo-electron microscopy structure of the homomeric GluA2 AMPA receptor in the presence of TARP γ2 subunits is reported, which reveals that TARPs are arranged around the ion channel domain and underneath the ligand-binding domains, poised to modulate receptor activity.
- Yan Zhao
- , Shanshuang Chen
- & Eric Gouaux
-
Letter |
 Cryo-EM structure of a human cytoplasmic actomyosin complex at near-atomic resolution
Cryo-EM structure of a human cytoplasmic actomyosin complex at near-atomic resolution
The first high-resolution structure of a human actomyosin complex reveals the interface between F-actin and myosin in near-atomic detail.
- Julian von der Ecken
- , Sarah M. Heissler
- & Stefan Raunser
-
Letter |
 The bacteriophage ϕ29 tail possesses a pore-forming loop for cell membrane penetration
The bacteriophage ϕ29 tail possesses a pore-forming loop for cell membrane penetration
Structural and functional studies of the tail knob protein of bacteriophage ϕ29 shed light on how the phage breaches the membrane barrier and ejects its DNA genome into the host cell.
- Jingwei Xu
- , Miao Gui
- & Ye Xiang
-
Letter |
 Diverse roles of assembly factors revealed by structures of late nuclear pre-60S ribosomes
Diverse roles of assembly factors revealed by structures of late nuclear pre-60S ribosomes
The cryo-electron microscopy structures of yeast nucleoplasmic pre-60S ribosomal particles give insight into the function of multiple assembly factors in ribosome biogenesis.
- Shan Wu
- , Beril Tutuncuoglu
- & Ning Gao
-
Article |
 Structure of spinach photosystem II–LHCII supercomplex at 3.2 Å resolution
Structure of spinach photosystem II–LHCII supercomplex at 3.2 Å resolution
A high-resolution structural study sheds light on processes of energy transfer within the photosynthetic water-splitting machinery of plants.
- Xuepeng Wei
- , Xiaodong Su
- & Zhenfeng Liu
-
Article |
 Structure of the T4 baseplate and its function in triggering sheath contraction
Structure of the T4 baseplate and its function in triggering sheath contraction
A tour-de-force of structural biology solves the structure of the macromolecular injection machinery used to deliver a phage genome into a bacterium.
- Nicholas M. I. Taylor
- , Nikolai S. Prokhorov
- & Petr G. Leiman
-
Article |
 TRPV1 structures in nanodiscs reveal mechanisms of ligand and lipid action
TRPV1 structures in nanodiscs reveal mechanisms of ligand and lipid action
Cryo-electron microscopy has undergone a resolution revolution—here, this method has been combined with lipid nanodisc technology to solve structures of TRPV1, the receptor for capsaicin, in a membrane bilayer, revealing mechanisms of lipid and ligand regulation.
- Yuan Gao
- , Erhu Cao
- & Yifan Cheng
-
Article |
 Near-atomic resolution visualization of human transcription promoter opening
Near-atomic resolution visualization of human transcription promoter opening
Cryo-electron microscopy structural models of the human pre-initiation complex at all major steps of transcription initiation at near atomic-level resolution are presented, providing new mechanistic insights into the processes of promoter melting and transcription-bubble formation, as well as an almost complete proposed structural model of all of the pre-initiation complex components and their interactions with DNA.
- Yuan He
- , Chunli Yan
- & Eva Nogales
-
Article |
 Transcription initiation complex structures elucidate DNA opening
Transcription initiation complex structures elucidate DNA opening
The cryo-electron microscopy structures of yeast initiation complexes containing the transcription factors TBP, TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIIE, and TFIIF and containing either closed or open promoter DNA are reported, providing mechanistic insights into DNA opening and template-strand loading.
- C. Plaschka
- , M. Hantsche
- & P. Cramer
-
Letter |
 Ribosome-dependent activation of stringent control
Ribosome-dependent activation of stringent control
The structure of a bacterial ribosome–RelA complex reveals that RelA, a protein recruited to the ribosome in the case of scarce amino acids, binds in a different location to translation factors, and that this binding event suppresses auto-inhibition to activate synthesis of the (p)ppGpp secondary messenger, thus initiating stringent control.
- Alan Brown
- , Israel S. Fernández
- & V. Ramakrishnan

 Structures of transcription pre-initiation complex with TFIIH and Mediator
Structures of transcription pre-initiation complex with TFIIH and Mediator