Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access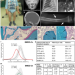 A neomorphic variant in SP7 alters sequence specificity and causes a high-turnover bone disorder
A neomorphic variant in SP7 alters sequence specificity and causes a high-turnover bone disorder
SP7 is a transcription factor required for osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. A neomorphic mutation in SP7 was found to alter DNA binding specificity, causing a complex skeletal disorder in both mice and humans.
- Julian C. Lui
- , Adalbert Raimann
- & Jeffrey Baron
-
Article
| Open Access A de novo paradigm for male infertility
A de novo paradigm for male infertility
Germline de novo mutations can impact individual fitness, but their role in human male infertility is understudied. Trio-based exome sequencing identifies many new candidate genes affecting male fertility, including an essential regulator of male germ cell pre-mRNA splicing.
- M. S. Oud
- , R. M. Smits
- & J. A. Veltman
-
Article
| Open Access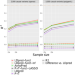 Incorporating functional priors improves polygenic prediction accuracy in UK Biobank and 23andMe data sets
Incorporating functional priors improves polygenic prediction accuracy in UK Biobank and 23andMe data sets
Incorporating functional information has shown promise for improving polygenic risk prediction of complex traits. Here, the authors describe polygenic prediction method LDpred-funct, and demonstrate its utility across 21 heritable traits in the UK Biobank.
- Carla Márquez-Luna
- , Steven Gazal
- & Alkes L. Price
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of limb-specific Lmx1b auto-regulatory modules with Nail-patella syndrome pathogenicity
Identification of limb-specific Lmx1b auto-regulatory modules with Nail-patella syndrome pathogenicity
Nail-patella syndrome (NPS) is characterized by nail dysplasia, absent/hypoplastic patellae, chronic kidney disease, and glaucoma and can be caused by haploinsufficiency of LMX1B; however, not all patients harbor pathogenic LMX1B mutations. Here the authors show that loss-of-function variations in upstream enhancer sequences are responsible for a limb specific form of human NPS.
- Endika Haro
- , Florence Petit
- & Kerby C. Oberg
-
Article
| Open Access Mesomelic dysplasias associated with the HOXD locus are caused by regulatory reallocations
Mesomelic dysplasias associated with the HOXD locus are caused by regulatory reallocations
Mesomelic dysplasia, a severe shortening and bending of the limb, has been linked to rearrangements in the HoxD cluster in humans and mice. Here the authors engineer a 1 Mb inversion including the HoxD gene cluster and use this model to provide a mechanistic framework to understand and unify the molecular origins of human mesomelic dysplasia associated with 2q31.
- Christopher Chase Bolt
- , Lucille Lopez-Delisle
- & Denis Duboule
-
Article
| Open Access Overexpression of human BAG3P209L in mice causes restrictive cardiomyopathy
Overexpression of human BAG3P209L in mice causes restrictive cardiomyopathy
An amino acid exchange (P209L) in the human co-chaperone BAG3 gives rise to severe childhood restrictive cardiomyopathy. Here the authors describe humanized transgenic mouse models which phenocopy the disease and provide insight into the pathogenic mechanisms.
- Kenichi Kimura
- , Astrid Ooms
- & Michael Hesse
-
Article
| Open Access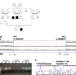 Deletion of CTCF sites in the SHH locus alters enhancer–promoter interactions and leads to acheiropodia
Deletion of CTCF sites in the SHH locus alters enhancer–promoter interactions and leads to acheiropodia
Acheiropodia is associated with homozygous deletions in the LMBR1 gene around ZRS, an enhancer regulating SHH during limb development, but how these deletions lead to this phenotype is unknown. Here the authors use whole-genome sequencing, ChIP-seq, 4C-seq and DNA FISH to show that alterations in CTCF motifs are responsible via altered enhancer–promoter interactions.
- Aki Ushiki
- , Yichi Zhang
- & Nadav Ahituv
-
Article
| Open Access Deficiency of TMEM53 causes a previously unknown sclerosing bone disorder by dysregulation of BMP-SMAD signaling
Deficiency of TMEM53 causes a previously unknown sclerosing bone disorder by dysregulation of BMP-SMAD signaling
Sclerosing bone disorder (SBD) includes a broad spectrum of monogenic diseases characterised by increased bone density. Here, the authors describe a previously unknown SBD in four families caused by mutations in TMEM53 and demonstrate the role this protein plays in BMP signalling during bone formation.
- Long Guo
- , Aritoshi Iida
- & Shiro Ikegawa
-
Article
| Open Access Impaired eIF5A function causes a Mendelian disorder that is partially rescued in model systems by spermidine
Impaired eIF5A function causes a Mendelian disorder that is partially rescued in model systems by spermidine
eIF5A is critical for protein synthesis but has not yet been associated with congenital human disease. Here, the authors show that EIF5A variants cause a Mendelian disorder via reduced eIF5A-ribosome interactions and this phenotype is partially corrected by spermidine supplementation in yeast and zebrafish.
- Víctor Faundes
- , Martin D. Jennings
- & Siddharth Banka
-
Article
| Open Access Detection of aberrant splicing events in RNA-seq data using FRASER
Detection of aberrant splicing events in RNA-seq data using FRASER
Aberrant splicing is a major contributor to rare disease, but detection accuracy using current methods is limited. Here, the authors develop an algorithm that detects aberrant splicing and intron retention events from RNA-seq data and apply it to diagnosis in mitochondrial disease.
- Christian Mertes
- , Ines F. Scheller
- & Julien Gagneur
-
Article
| Open Access PCM1 is necessary for focal ciliary integrity and is a candidate for severe schizophrenia
PCM1 is necessary for focal ciliary integrity and is a candidate for severe schizophrenia
The role of ciliary/centriolar components in the postnatal brain is unclear. Here, the authors show via ablation of Pcm1 in mice that degenerative ciliary/centriolar phenotypes induce neuroanatomical and behavioral changes. Sequencing of PCM1 in human cohorts and zebrafish in vivo complementation suggests PCM1 mutations can contribute to schizophrenia.
- Tanner O. Monroe
- , Melanie E. Garrett
- & Nicholas Katsanis
-
Article
| Open Access LSH mediates gene repression through macroH2A deposition
LSH mediates gene repression through macroH2A deposition
The human ICF 4 syndrome is caused by mutation of the chromatin remodeller LSH. Here, the authors show that LSH depletion disrupts the ability of histone variant macroH2A to insert into chromatin and silence transcription.
- Kai Ni
- , Jianke Ren
- & Kathrin Muegge
-
Article
| Open Access Common schizophrenia risk variants are enriched in open chromatin regions of human glutamatergic neurons
Common schizophrenia risk variants are enriched in open chromatin regions of human glutamatergic neurons
Here, the authors perform ATAC-seq on four distinct cell populations from three different regions of the human brain, finding that chromatin accessibility varies greatly by cell type and less by brain region. This study reveals differences in biological function and gene regulation, as well as overlap of genetic variants associated with schizophrenia and other neuropsychiatric traits.
- Mads E. Hauberg
- , Jordi Creus-Muncunill
- & Panos Roussos
-
Article
| Open Access NEMF mutations that impair ribosome-associated quality control are associated with neuromuscular disease
NEMF mutations that impair ribosome-associated quality control are associated with neuromuscular disease
Defective protein quality control is a key feature of neurodegeneration. Here, the authors show that mutations in Nemf/NEMF, a component of the Ribosome-associated Quality Control complex, have a neurodegenerative effect in mice and may underlie neuromuscular disease in seven unrelated families.
- Paige B. Martin
- , Yu Kigoshi-Tansho
- & Gregory A. Cox
-
Article
| Open Access Mutations in COMP cause familial carpal tunnel syndrome
Mutations in COMP cause familial carpal tunnel syndrome
Familial carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is common, but causal genes are not characterized. Here the authors report two CTS-related mutations in two large families that impair secretion of COMP in tenocytes, leading to ER stress-induced unfolded protein response, inflammation and fibrosis in patients and mouse models.
- Chunyu Li
- , Ni Wang
- & Bo Gao
-
Article
| Open Access A universal and independent synthetic DNA ladder for the quantitative measurement of genomic features
A universal and independent synthetic DNA ladder for the quantitative measurement of genomic features
Standard units of measurement are required for a quantitative description of the genome. Here, the authors present a universal synthetic DNA ladder that can measure genetic abundance in next-generation sequencing libraries.
- Andre L. M. Reis
- , Ira W. Deveson
- & Tim R. Mercer
-
Article
| Open Access Exome sequencing of familial high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma reveals heterogeneity for rare candidate susceptibility genes
Exome sequencing of familial high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma reveals heterogeneity for rare candidate susceptibility genes
Around half of the heritability underpinning familial high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma remains unidentified. Here, the authors show that extremely rare protein encoding loss-of-function variants, with a high degree of genetic heterogeneity, may account for some of this missing heritability.
- Deepak N. Subramanian
- , Magnus Zethoven
- & Ian G. Campbell
-
Article
| Open Access Extracellular nanovesicles for packaging of CRISPR-Cas9 protein and sgRNA to induce therapeutic exon skipping
Extracellular nanovesicles for packaging of CRISPR-Cas9 protein and sgRNA to induce therapeutic exon skipping
Expression of Cas9 and gRNA from viral vectors in vivo may cause off-target activity. Here the authors present NanoMEDIC, which uses nanovesicles to transiently deliver editing machinery to hard-to-transfect cells.
- Peter Gee
- , Mandy S. Y. Lung
- & Akitsu Hotta
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association and multi-omic analyses reveal ACTN2 as a gene linked to heart failure
Genome-wide association and multi-omic analyses reveal ACTN2 as a gene linked to heart failure
Heart failure has a heterogeneous etiology and the genetic underpinnings are not well understood. Here, Arvanitis et al. perform GWAS meta-analysis including 10,976 heart failure cases and 437,573 controls, identify new loci near ABO and ACTN2 and show that deletion of a ACTN2 enhancer leads to reduced ACTN2 expression in differentiating cardiomyocytes.
- Marios Arvanitis
- , Emmanouil Tampakakis
- & Alexis Battle
-
Article
| Open Access Human FCHO1 deficiency reveals role for clathrin-mediated endocytosis in development and function of T cells
Human FCHO1 deficiency reveals role for clathrin-mediated endocytosis in development and function of T cells
FCH domain only 1 (FCHO1) is a key molecule involved in clathrin-mediated endocytosis (CME). Here, the authors report homozygous FCHO1 mutations in individuals with variable T and B cell lymphopenia, which are associated with loss-of-function of FCHO1 and impaired formation of clathrin-coated pits in T cells.
- Marcin Łyszkiewicz
- , Natalia Ziętara
- & Christoph Klein
-
Article
| Open Access Human and mouse essentiality screens as a resource for disease gene discovery
Human and mouse essentiality screens as a resource for disease gene discovery
Discovery of causal variants for monogenic disorders has been facilitated by whole exome and genome sequencing, but does not provide a diagnosis for all patients. Here, the authors propose a Full Spectrum of Intolerance to Loss-of-Function (FUSIL) categorization that integrates gene essentiality information to aid disease gene discovery.
- Pilar Cacheiro
- , Violeta Muñoz-Fuentes
- & Coleen Kane
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular signatures of aneuploidy-driven adaptive evolution
Molecular signatures of aneuploidy-driven adaptive evolution
Aneuploidy (abnormal chromosome number) can enable rapid adaptation to stress conditions, but it also entails fitness costs from gene imbalance. Here, the authors experimentally evolve yeast while forcing maintenance of aneuploidy to identify the mechanisms that promote tolerance of aneuploidy.
- Alaattin Kaya
- , Marco Mariotti
- & Vadim N. Gladyshev
-
Article
| Open Access Loss-of-function mutations in UDP-Glucose 6-Dehydrogenase cause recessive developmental epileptic encephalopathy
Loss-of-function mutations in UDP-Glucose 6-Dehydrogenase cause recessive developmental epileptic encephalopathy
UDP-glucuronic acid is a component of the extracellular matrix. Here, the authors report biallelic variants in the gene encoding UDP-Glucose 6-Dehydrogenase (UGDH) in individuals affected by developmental epileptic encephalopathies that impair UGDH stability, oligomerization, or enzymatic activity in vitro.
- Holger Hengel
- , Célia Bosso-Lefèvre
- & Bruno Reversade
-
Article
| Open Access Intronic ATTTC repeat expansions in STARD7 in familial adult myoclonic epilepsy linked to chromosome 2
Intronic ATTTC repeat expansions in STARD7 in familial adult myoclonic epilepsy linked to chromosome 2
Familial cortical myoclonic tremor (FAME) has so far been mapped to regions on chromosome 2, 3, 5 and 8 and pentameric repeat expansions in SAMD12 were identified as cause of FAME1. Here, Corbett et al. identify ATTTT/ATTTC repeat expansions in intron 1 of STARD7 in individuals with FAME2.”
- Mark A. Corbett
- , Thessa Kroes
- & Jozef Gecz
-
Article
| Open Access Trisomy 21 activates the kynurenine pathway via increased dosage of interferon receptors
Trisomy 21 activates the kynurenine pathway via increased dosage of interferon receptors
Down syndrome (DS) is caused by trisomy 21 (T21), but the underlying etiology of the related immune and neurological dysfunction is unclear. Here, the authors show that T21 activates the kynurenine pathway via increased interferon receptor copy number, which could contribute to DS pathophysiology.
- Rani K. Powers
- , Rachel Culp-Hill
- & Joaquin M. Espinosa
-
Article
| Open Access GWAS of mosaic loss of chromosome Y highlights genetic effects on blood cell differentiation
GWAS of mosaic loss of chromosome Y highlights genetic effects on blood cell differentiation
Mosaic loss of chromosome Y (mLOY) is associated with age and smoking but also genetic factors play a role. Here, Terao et al. perform GWAS for mLOY in 95,380 Japanese men and identify 46 loci that overlap with hematopoietic stem cell enhancers and transcription factor binding sites critical for hematopoiesis.
- Chikashi Terao
- , Yukihide Momozawa
- & Yoichiro Kamatani
-
Article
| Open Access Human genome-edited hematopoietic stem cells phenotypically correct Mucopolysaccharidosis type I
Human genome-edited hematopoietic stem cells phenotypically correct Mucopolysaccharidosis type I
Mucopolysaccharidosis type I (MPSI) is a lysosomal storage disease caused by insufficient iduronidase (IDUA) activity. Here, the authors use an ex vivo genome editing approach to overexpress IDUA in human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and show it can phenotypically correct MSPI in mouse model.
- Natalia Gomez-Ospina
- , Samantha G. Scharenberg
- & Matthew H. Porteus
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association study identifies 14 previously unreported susceptibility loci for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in Japanese
Genome-wide association study identifies 14 previously unreported susceptibility loci for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in Japanese
Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) is a common pediatric disease leading to spinal deformities. Here, the authors report GWAS followed by genome-wide meta-analysis in up to 79,211 Japanese individuals, identifying 20 genetic loci for AIS, 14 of which were previously unreported, and perform in vitro validation for rs1978060.
- Ikuyo Kou
- , Nao Otomo
- & Shiro Ikegawa
-
Article
| Open Access Clinically-relevant postzygotic mosaicism in parents and children with developmental disorders in trio exome sequencing data
Clinically-relevant postzygotic mosaicism in parents and children with developmental disorders in trio exome sequencing data
Systematic analysis of postzygotic mosaicism (PZM) is difficult due to challenges in detecting such events. Here, Wright et al. analyse trio exome sequencing data from blood and saliva of 4,293 probands with developmental disorders from the DDD Study and estimate that >3% of causative de novo mutations result from PZM.
- C. F. Wright
- , E. Prigmore
- & M. E. Hurles
-
Article
| Open Access Comprehensive analysis of coding variants highlights genetic complexity in developmental and epileptic encephalopathy
Comprehensive analysis of coding variants highlights genetic complexity in developmental and epileptic encephalopathy
Many causative genes are known for epileptic or developmental and epileptic encephalopathies (EE/DEE) yet a genetic diagnosis cannot be made for many patients. Here, the authors analyse whole exome sequencing data from a Japanese case−control cohort to identify common, rare and ultra-rare coding variants associated with EE/DEE.
- Atsushi Takata
- , Mitsuko Nakashima
- & Naomichi Matsumoto
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible and scalable diagnostic filtering of genomic variants using G2P with Ensembl VEP
Flexible and scalable diagnostic filtering of genomic variants using G2P with Ensembl VEP
Diagnostic filtering is an important step to analyze the functional and clinical significance of the large number of genetic variants identified from next-generation genome sequencing data. Here, the authors develop a flexible and scalable system for diagnostic filtering of genetic variants using G2P with Ensembl VEP.
- Anja Thormann
- , Mihail Halachev
- & David R. FitzPatrick
-
Review Article
| Open Access Humanising the mouse genome piece by piece
Humanising the mouse genome piece by piece
Generation of transgenic mice has become routine in studying gene function and disease mechanisms, but often this is not enough to fully understand human biology. Here, the authors review the current state of the art of targeted genomic humanisation strategies and their advantages over classic approaches.
- Fei Zhu
- , Remya R. Nair
- & Thomas J. Cunningham
-
Article
| Open Access The BIN1 rs744373 SNP is associated with increased tau-PET levels and impaired memory
The BIN1 rs744373 SNP is associated with increased tau-PET levels and impaired memory
The BIN1 SNP rs744373 is associated with higher CSF tau and phosphorylated tau levels. Here the authors show, using PET imaging, that this SNP is associated with tau accumulation in the brain as well as impaired memory in older individuals without dementia.
- Nicolai Franzmeier
- , Anna Rubinski
- & Ansgar J. Furst
-
Article
| Open Access Homozygous frameshift mutations in FAT1 cause a syndrome characterized by colobomatous-microphthalmia, ptosis, nephropathy and syndactyly
Homozygous frameshift mutations in FAT1 cause a syndrome characterized by colobomatous-microphthalmia, ptosis, nephropathy and syndactyly
Loss of the cadherin FAT1 has been associated with nephropathy and epithelial cell adhesion defects. Here, the authors report five families with a syndromic form of coloboma associated with homozygous frameshift variants in FAT1 and recapitulate the phenotype in mutant mice and zebrafish.
- Najim Lahrouchi
- , Aman George
- & Abdelaziz Sefiani
-
Article
| Open Access Recessive mutations in muscle-specific isoforms of FXR1 cause congenital multi-minicore myopathy
Recessive mutations in muscle-specific isoforms of FXR1 cause congenital multi-minicore myopathy
FXR1P is a RNA binding protein involved in muscle development. Here, the authors show that mutations in FXR1 exon 15, which is alternatively spliced in muscle, cause multi-minicore myopathy in humans and in mouse models.
- María Cristina Estañ
- , Elisa Fernández-Núñez
- & Victor L. Ruiz-Perez
-
Article
| Open Access Biallelic mutations in valyl-tRNA synthetase gene VARS are associated with a progressive neurodevelopmental epileptic encephalopathy
Biallelic mutations in valyl-tRNA synthetase gene VARS are associated with a progressive neurodevelopmental epileptic encephalopathy
Valyl-tRNA synthetase (VARS) charges valyl-tRNA with the amino acid valine, required for translation. Here, the authors describe a progressive epileptic encephalopathy in individuals from five families carrying biallelic mutations in the VARS gene that leave the enzyme activity partially intact.
- Jennifer Friedman
- , Desiree E. Smith
- & Joseph G. Gleeson
-
Article
| Open Access Biallelic VARS variants cause developmental encephalopathy with microcephaly that is recapitulated in vars knockout zebrafish
Biallelic VARS variants cause developmental encephalopathy with microcephaly that is recapitulated in vars knockout zebrafish
tRNAs are linked with their cognate amino acid by aminoacyl tRNA synthetases (ARS). Here, the authors report a developmental encephalopathy associated with biallelic VARS variants (valyl-tRNA synthetase) that lead to loss of function, as determined by several in vitro assays and a vars knockout zebrafish model.
- Aleksandra Siekierska
- , Hannah Stamberger
- & Peter De Jonghe
-
Article
| Open Access Distinct adaptive mechanisms drive recovery from aneuploidy caused by loss of the Ulp2 SUMO protease
Distinct adaptive mechanisms drive recovery from aneuploidy caused by loss of the Ulp2 SUMO protease
Transient aneuploidy enables cells to survive sudden environmental changes before longterm cellular adaptations are established. Here, the authors show that yeast cells respond to the acute loss of Ulp2 SUMO protease by rapid induction of aneuploidy, and reveal predictable long-term adaptation mechanisms that restore euploidy.
- Hong-Yeoul Ryu
- , Francesc López-Giráldez
- & Mark Hochstrasser
-
Article
| Open Access BAFopathies’ DNA methylation epi-signatures demonstrate diagnostic utility and functional continuum of Coffin–Siris and Nicolaides–Baraitser syndromes
BAFopathies’ DNA methylation epi-signatures demonstrate diagnostic utility and functional continuum of Coffin–Siris and Nicolaides–Baraitser syndromes
Mutations in genes encoding subunits of the BAF complex can cause Coffin–Siris and Nicolaides–Baraitser syndromes. Here the authors identify overlapping DNA methylation signatures in individuals with subtypes of these two syndromes that suggest a functional link and can be used to diagnose subjects with unclear clinical presentations.
- Erfan Aref-Eshghi
- , Eric G. Bend
- & Bekim Sadikovic
-
Article
| Open Access CHD3 helicase domain mutations cause a neurodevelopmental syndrome with macrocephaly and impaired speech and language
CHD3 helicase domain mutations cause a neurodevelopmental syndrome with macrocephaly and impaired speech and language
Chromodomain Helicase DNA-binding (CHD) proteins have been implicated in neurodevelopmental processes. Here, the authors identify missense variants in CHD3 that disturb its chromatin remodeling activities and cause a neurodevelopmental disorder with macrocephaly and speech and language impairment.
- Lot Snijders Blok
- , Justine Rousseau
- & Philippe M. Campeau
-
Article
| Open Access Variants in exons 5 and 6 of ACTB cause syndromic thrombocytopenia
Variants in exons 5 and 6 of ACTB cause syndromic thrombocytopenia
Genetic variants in ACTB and ACTG1 have been associated with Baraitser-Winter Cerebrofrontofacial syndrome. Here, the authors report of a syndromic thrombocytopenia caused by variants in ACTB exons 5 or 6 that compromise the organization and coupling of the cytoskeleton, leading to impaired platelet maturation.
- Sharissa L. Latham
- , Nadja Ehmke
- & Nataliya Di Donato
-
Article
| Open Access Germline pathogenic variants of 11 breast cancer genes in 7,051 Japanese patients and 11,241 controls
Germline pathogenic variants of 11 breast cancer genes in 7,051 Japanese patients and 11,241 controls
Association between variants in 11 different genes and breast cancer risk has been established and sequencing of these genes is recommended to provide personalized diagnosis, therapy, and surveillance for the high-risk patients and their relatives. Here the authors analyse the frequency of germline pathogenic mutations in these genes specifically in a Japanese population.
- Yukihide Momozawa
- , Yusuke Iwasaki
- & Michiaki Kubo
-
Article
| Open Access SLC10A7 mutations cause a skeletal dysplasia with amelogenesis imperfecta mediated by GAG biosynthesis defects
SLC10A7 mutations cause a skeletal dysplasia with amelogenesis imperfecta mediated by GAG biosynthesis defects
The majority of skeletal dysplasia are caused by pathogenic variants in genes required for glycosaminoglycan (GAG) metabolism. Here, Dubail et al. identify genetic variants in the solute carrier family protein SLC10A7 in families with skeletal dysplasia and amelogenesis imperfecta that disrupt GAG synthesis.
- Johanne Dubail
- , Céline Huber
- & Valérie Cormier-Daire
-
Article
| Open Access FoxM1 repression during human aging leads to mitotic decline and aneuploidy-driven full senescence
FoxM1 repression during human aging leads to mitotic decline and aneuploidy-driven full senescence
Evidence for mitotic decline in aged cells and for aneuploidy-driven progression into full senescence is limited. Here, the authors find that in aged cells, mitotic gene repression leads to increased chromosome mis-segregation and aneuploidy that triggers permanent cell cycle arrest and full senescence.
- Joana Catarina Macedo
- , Sara Vaz
- & Elsa Logarinho
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic deficiency of NOD2 confers resistance to invasive aspergillosis
Genetic deficiency of NOD2 confers resistance to invasive aspergillosis
NOD2 has been shown to be crucial for immune recognition of Aspergillus infection. Here the authors show that a common NOD2 genetic variant associated with Crohn’s disease is associated with reduced risk of disease due to enhanced antifungal activates of monocytes and macrophages.
- Mark S. Gresnigt
- , Cristina Cunha
- & Frank L. van de Veerdonk
-
Article
| Open Access Dual origin of relapses in retinoic-acid resistant acute promyelocytic leukemia
Dual origin of relapses in retinoic-acid resistant acute promyelocytic leukemia
Historical acute promyelocytic leukemia patients treated with retinoic acid and chemotherapy sometimes did relapse. Here the authors performed exome sequencing on 64 patient's samples from diagnosis/relapse/remission and show relapse associates either with cooperating oncogenes at diagnosis, or with unexpected persistence of ancestral pre-leukemic clones.
- Jacqueline Lehmann-Che
- , Cécile Bally
- & Hugues de Thé
-
Article
| Open Access The multiple myeloma risk allele at 5q15 lowers ELL2 expression and increases ribosomal gene expression
The multiple myeloma risk allele at 5q15 lowers ELL2 expression and increases ribosomal gene expression
ELL2 was recently discovered as a susceptibility gene for multiple myeloma (MM). Here, they show that the MM risk allele lowers ELL2 expression in plasma cells, that it also upregulates gene sets related to ribosome biogenesis, and that one of the linked variants reduces binding of MAFF/G/K family transcription factors.
- Mina Ali
- , Ram Ajore
- & Björn Nilsson
-
Article
| Open Access Characterization of the enhancer and promoter landscape of inflammatory bowel disease from human colon biopsies
Characterization of the enhancer and promoter landscape of inflammatory bowel disease from human colon biopsies
Many SNPs associated with inflammatory bowel disease are located in non-coding genomic regions. Here, the authors perform CAGE-sequencing on descending colon biopsies of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis patients to map transcription start sites and enhancer activity for analysis of regulatory regions.
- Mette Boyd
- , Malte Thodberg
- & Albin Sandelin
-
Article
| Open Access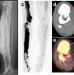 Somatic activating mutations in MAP2K1 cause melorheostosis
Somatic activating mutations in MAP2K1 cause melorheostosis
Melorheostosis is characterized by bone overgrowth and associated with pain and functional impairment. Here, the authors use whole exome sequencing to identify somatic mutations in MAP2K1 in affected bone of melorheostosis patients which is associated with increased proliferation but delayed differentiation of cultured osteoblasts.
- Heeseog Kang
- , Smita Jha
- & Timothy Bhattacharyya

 Population-level deficit of homozygosity unveils CPSF3 as an intellectual disability syndrome gene
Population-level deficit of homozygosity unveils CPSF3 as an intellectual disability syndrome gene