Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Tension can directly suppress Aurora B kinase-triggered release of kinetochore-microtubule attachments
Tension can directly suppress Aurora B kinase-triggered release of kinetochore-microtubule attachments
Tension stabilizes properly attached microtubules to kinetochores during chromosome segregation, and lack of tension leads to release. Here the authors show that tension directly suppresses Aurora B kinase mediated destabilization of reconstituted kinetochore-microtubule attachments, likely ensuring accurate chromosome segregation.
- Anna K. de Regt
- , Cordell J. Clark
- & Sue Biggins
-
Article
| Open Access The methyl phosphate capping enzyme Bmc1/Bin3 is a stable component of the fission yeast telomerase holoenzyme
The methyl phosphate capping enzyme Bmc1/Bin3 is a stable component of the fission yeast telomerase holoenzyme
There exists a remarkable evolutionary breadth of telomerase holoenzyme components among eukaryotes. Here the authors report that the fission yeast methyl phosphate capping enzyme Bin3/Bmc1 regulates telomerase activity by promoting holoenzyme formation.
- Jennifer Porat
- , Moaine El Baidouri
- & Mark A. Bayfield
-
Article
| Open Access A putative cap binding protein and the methyl phosphate capping enzyme Bin3/MePCE function in telomerase biogenesis
A putative cap binding protein and the methyl phosphate capping enzyme Bin3/MePCE function in telomerase biogenesis
Most eukaryotes maintain telomeres using a specialized reverse transcriptase. Here the authors report that Thc1 (Telomerase Holoenzyme Component 1) and Bmc1 (Bin3/MePCE 1) form a complex with Pof8, a constitutive member of telomerase in fission yeast.
- Diego J. Páez-Moscoso
- , David V. Ho
- & Peter Baumann
-
Article
| Open Access Recruitment of two Ndc80 complexes via the CENP-T pathway is sufficient for kinetochore functions
Recruitment of two Ndc80 complexes via the CENP-T pathway is sufficient for kinetochore functions
The kinetochores contain multiple protein interaction networks. Takenoshita et al. analyzed the complicated networks using the genetic method and revealed that two copies of Ndc80 complexes on CENP-T are sufficient for kinetochore functions.
- Yusuke Takenoshita
- , Masatoshi Hara
- & Tatsuo Fukagawa
-
Article
| Open Access A Mediator-cohesin axis controls heterochromatin domain formation
A Mediator-cohesin axis controls heterochromatin domain formation
The link between 3D genome architecture and gene expression is still far from resolved. Here the authors show that loss of the CDK catalytic subunit of the Mediator complex results in heterochromatic silencing, which can be rescued by stabilization of cohesin on chromatin.
- Judith H. I. Haarhuis
- , Robin H. van der Weide
- & Elzo de Wit
-
Article
| Open Access Somatic PMK-1/p38 signaling links environmental stress to germ cell apoptosis and heritable euploidy
Somatic PMK-1/p38 signaling links environmental stress to germ cell apoptosis and heritable euploidy
Here the authors show that elimination of germ cells carrying damaged genomes is regulated by intestinal stress signalling in nematodes. Failure of the intestinal signalling results in stress-induced aneuploidy indicating that environmental stress impacts inheritance.
- Najmeh Soltanmohammadi
- , Siyao Wang
- & Björn Schumacher
-
Article
| Open Access Hematopoiesis under telomere attrition at the single-cell resolution
Hematopoiesis under telomere attrition at the single-cell resolution
The molecular mechanisms that drive hematopoietic stem cell functional decline under conditions of telomere shortening are not completely understood. Here the authors demonstrate that hematopoietic stem cells with short telomeres induced by mutations affecting telomerase complex genes undergo differentiation towards megakaryopoiesis through the activation of the IFI16-mediated interferon response.
- Natthakan Thongon
- , Feiyang Ma
- & Simona Colla
-
Article
| Open Access CENP-V is required for proper chromosome segregation through interaction with spindle microtubules in mouse oocytes
CENP-V is required for proper chromosome segregation through interaction with spindle microtubules in mouse oocytes
Chromosome segregation is essential to avoid aneuploidy, yet in mammalian oocytes it progressively fails in an age-dependent manner. Here the authors identify CENP-V as a microtubule binding and bundling protein crucial to faithful oocyte meiosis, and present Cenp-V−/− oocytes as revealing age-dependent weakening of the spindle assembly checkpoint.
- Dalileh Nabi
- , Hauke Drechsler
- & Mariola Chacón
-
Article
| Open Access A compendium of chromatin contact maps reflecting regulation by chromatin remodelers in budding yeast
A compendium of chromatin contact maps reflecting regulation by chromatin remodelers in budding yeast
The effect of ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers on 3D genome organization has not been well studied. Here the authors employ in situ Hi-C with an auxin-inducible degron system to degrade chromatin remodelers in yeast to find that the 3D structure of chromatin collapses in their absence. The chromatin remodeling can modulate 3D architecture depending on chromosomal context and cell cycle stage.
- Hyelim Jo
- , Taemook Kim
- & Daeyoup Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Spatiotemporal coordination of the RSF1-PLK1-Aurora B cascade establishes mitotic signaling platforms
Spatiotemporal coordination of the RSF1-PLK1-Aurora B cascade establishes mitotic signaling platforms
During cell division, chromosome alignment is engendered by connection of microtubules to kinetochores, coordinated by Aurora B and PLK1. Here, the authors show that the RSF1-PLK1 axis creates an activating phosphorylation on T236 in the GT motif of Aurora B and this is indispensable for Aurora B activation.
- Ho-Soo Lee
- , Sunwoo Min
- & Hyeseong Cho
-
Article
| Open Access Distinct functions of POT1 proteins contribute to the regulation of telomerase recruitment to telomeres
Distinct functions of POT1 proteins contribute to the regulation of telomerase recruitment to telomeres
Mammalian shelterin proteins POT1 and TPP1 form a stable heterodimer that protects telomere ends. The authors exploit the observation that mice have two POT1 paralogs, enabling functional dissections to shed important light on the mechanistic basis for human POT1 functions.
- Peili Gu
- , Shuting Jia
- & Sandy Chang
-
Article
| Open Access USP11 controls R-loops by regulating senataxin proteostasis
USP11 controls R-loops by regulating senataxin proteostasis
DNA:RNA hybrids (R-loops) are products of transcription that impact genome integrity and gene expression. Here the authors reveal a mechanism for regulating R-loops in a ubiquitination-dependent manner controlled by the activities of USP11 and KEAP1
- Mateusz Jurga
- , Arwa A. Abugable
- & Sherif F. El-Khamisy
-
Article
| Open Access MAD2L2 dimerization and TRIP13 control shieldin activity in DNA repair
MAD2L2 dimerization and TRIP13 control shieldin activity in DNA repair
MAD2L2 — a member of the shieldin complex — is known to play important roles in DNA repair. Here the authors demonstrate how MAD2L2 dimerization mediated through SHLD2 participates in shieldin assembly and function.
- Inge de Krijger
- , Bastian Föhr
- & Jacqueline J. L. Jacobs
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial rearrangement of the Streptomyces venezuelae linear chromosome during sporogenic development
Spatial rearrangement of the Streptomyces venezuelae linear chromosome during sporogenic development
Streptomyces bacteria have a linear chromosome and a complex life cycle, including development of multi-genomic hyphae that differentiate into mono-genomic exospores. Here, Szafran et al. show that the chromosome of Streptomyces venezuelae undergoes substantial remodelling during sporulation, from an ‘open’ to a ‘closed’ conformation.
- Marcin J. Szafran
- , Tomasz Małecki
- & Dagmara Jakimowicz
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamics of the compartmentalized Streptomyces chromosome during metabolic differentiation
Dynamics of the compartmentalized Streptomyces chromosome during metabolic differentiation
Streptomyces bacteria have a linear chromosome, with core genes located in the central region and gene clusters for specialized metabolite biosynthesis found in the ‘arms’. Here, Lioy et al. show that such chromosome structure correlates with genetic compartmentalization, and the onset of metabolic differentiation is accompanied by a rearrangement of chromosome architecture.
- Virginia S. Lioy
- , Jean-Noël Lorenzi
- & Stéphanie Bury-Moné
-
Article
| Open Access Bisection of the X chromosome disrupts the initiation of chromosome silencing during meiosis in Caenorhabditis elegans
Bisection of the X chromosome disrupts the initiation of chromosome silencing during meiosis in Caenorhabditis elegans
During meiosis, sex chromosomes show silenced gene expression that is disrupted when translocated to autosomes. Here, the authors engineer C. elegans with bisected X chromosomes and see active transcription in gonads, indicating continuity of sex chromosomes promotes silencing.
- Yisrael Rappaport
- , Hanna Achache
- & Yonatan B. Tzur
-
Article
| Open Access A prometaphase mechanism of securin destruction is essential for meiotic progression in mouse oocytes
A prometaphase mechanism of securin destruction is essential for meiotic progression in mouse oocytes
Securin inhibits the protease separase and must be removed before anaphase to ensure timely chromosome segregation. Here, the authors define a mechanism of securin destruction in prometaphase I in mouse oocytes and demonstrate its importance for successful meiotic progression.
- Christopher Thomas
- , Benjamin Wetherall
- & Suzanne Madgwick
-
Article
| Open Access RPA shields inherited DNA lesions for post-mitotic DNA synthesis
RPA shields inherited DNA lesions for post-mitotic DNA synthesis
Single-stranded DNA during DNA replication and repair in S/G2 needs protection by replication protein A (RPA). Here the authors reveal that RPA also shields inherited single-stranded DNA in G1, representing replication remnants from the previous cell cycle, to allow for post-mitotic DNA synthesis.
- Aleksandra Lezaja
- , Andreas Panagopoulos
- & Matthias Altmeyer
-
Article
| Open Access TERRA transcription destabilizes telomere integrity to initiate break-induced replication in human ALT cells
TERRA transcription destabilizes telomere integrity to initiate break-induced replication in human ALT cells
TERRA RNA has previously been linked to Alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT). Here the authors developed a tool to rapidly inhibit TERRA transcription from different chromosome ends in an ALT cell line to show that TERRA transcription actively promotes break induced replication (BIR) and destabilizes telomere integrity in ALT cells.
- Bruno Silva
- , Rajika Arora
- & Claus M. Azzalin
-
Article
| Open Access BRCA1 binds TERRA RNA and suppresses R-Loop-based telomeric DNA damage
BRCA1 binds TERRA RNA and suppresses R-Loop-based telomeric DNA damage
BRCA1-mediated resolution of R-loops has previously been described. Here the authors reveal a functional association of BRCA1 with TERRA RNA at telomeres, which develops in an R-loop-, and a cell cycle-dependent manner.
- Jekaterina Vohhodina
- , Liana J. Goehring
- & David M. Livingston
-
Article
| Open Access HiC-DC+ enables systematic 3D interaction calls and differential analysis for Hi-C and HiChIP
HiC-DC+ enables systematic 3D interaction calls and differential analysis for Hi-C and HiChIP
The genome-wide investigation of chromatin organization enables insights into global gene expression control. Here, the authors present a computationally efficient method for the analysis of chromatin organization data and use it to recover principles of 3D organization across conditions.
- Merve Sahin
- , Wilfred Wong
- & Christina S. Leslie
-
Article
| Open Access RTEL1 influences the abundance and localization of TERRA RNA
RTEL1 influences the abundance and localization of TERRA RNA
Long non coding RNA TERRA transcripts can form R-loops at chromosome ends. Here, the authors reveal a role for the helicase RTEL in affecting TERRA levels and localization.
- Fiorella Ghisays
- , Aitor Garzia
- & John H. J. Petrini
-
Article
| Open Access The impact of chromosomal fusions on 3D genome folding and recombination in the germ line
The impact of chromosomal fusions on 3D genome folding and recombination in the germ line
How mammalian genomes are packaged and the heritability of structural variations in genome folding is incomplete. Here, the authors investigate the impact of chromosomal fusions on three-dimensional genome topology and meiotic recombination, highlighting the implications of large-scale genome reorganizations on genome function, evolution, and fertility.
- Covadonga Vara
- , Andreu Paytuví-Gallart
- & Aurora Ruiz-Herrera
-
Article
| Open Access Guiding functions of the C-terminal domain of topoisomerase IIα advance mitotic chromosome assembly
Guiding functions of the C-terminal domain of topoisomerase IIα advance mitotic chromosome assembly
Topoisomerase IIα (topo IIα) is critical for mitotic chromatid assembly. Here the authors report a refinement of the mitotic chromatid reconstitution assay and provide novel insights into the C-terminal domain (CTD) of topo IIα.
- Keishi Shintomi
- & Tatsuya Hirano
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of MRX inhibition by Rif2 at telomeres
Mechanism of MRX inhibition by Rif2 at telomeres
Different proteins localised at telomeres ensure chromosome end stability to prevent double strand-end break recognition. Here the authors provide new insight into how in S. cerevisiae the interaction between Rif2 and Rad50 inhibits MRX functions at telomeres.
- Florian Roisné-Hamelin
- , Sabrina Pobiega
- & Stéphane Marcand
-
Article
| Open Access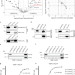 The double-stranded DNA-binding proteins TEBP-1 and TEBP-2 form a telomeric complex with POT-1
The double-stranded DNA-binding proteins TEBP-1 and TEBP-2 form a telomeric complex with POT-1
Telomeres, tandem repeats at the ends of linear chromosomes, have evolved to deal with the end replication and end protection. Using a proteomics approach, the authors identify TEBP-1 and TEBP-2, two double-stranded binding proteins which together are required for fertility. Despite being paralogs, they have distinct individual effects on telomere dynamics; TEBP-1 and TEBP-2 are part of a telomeric complex also containing POT-1.
- Sabrina Dietz
- , Miguel Vasconcelos Almeida
- & Falk Butter
-
Article
| Open Access Mutations inhibiting KDM4B drive ALT activation in ATRX-mutated glioblastomas
Mutations inhibiting KDM4B drive ALT activation in ATRX-mutated glioblastomas
Alternative Lengthening of Telomeres (ALT) is a telomere maintenance pathway utilised in 15% of cancers that have been associated with mutations in ATRX. Here the authors reveal a functional role of histone demethylases KDM4B in regulating ALT activation.
- M. Udugama
- , L. Hii
- & L. H. Wong
-
Article
| Open Access Structural variant evolution after telomere crisis
Structural variant evolution after telomere crisis
Telomere crisis has been shown to induce chromothripsis and breakage fusion bridge (BFB) cycles in vitro. Here, the authors show that telomere crisis generates a much broader spectrum of structural variations, implying that cancers without chromothripsis and BFB cycles could have emerged from telomere crisis.
- Sally M. Dewhurst
- , Xiaotong Yao
- & Marcin Imieliński
-
Article
| Open Access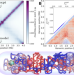 Learning the distribution of single-cell chromosome conformations in bacteria reveals emergent order across genomic scales
Learning the distribution of single-cell chromosome conformations in bacteria reveals emergent order across genomic scales
The order and variability of bacterial chromosome organization, contained within the distribution of chromosome conformations, are unclear. Here, the authors develop a fully data-driven maximum entropy approach to extract single-cell 3D chromosome conformations from Hi-C experiments on the model organism Caulobacter crescentus.
- Joris J. B. Messelink
- , Muriel C. F. van Teeseling
- & Chase P. Broedersz
-
Article
| Open Access Bi-allelic MCM10 variants associated with immune dysfunction and cardiomyopathy cause telomere shortening
Bi-allelic MCM10 variants associated with immune dysfunction and cardiomyopathy cause telomere shortening
Minichromosome maintenance protein 10 (MCM10) is critical for eukaryotic DNA replication. Here, by modelling MCM10 variants in human cell lines, the authors reveal a mechanism of MCM10-associated disease, finding that loss of MCM10 function constrains telomerase activity.
- Ryan M. Baxley
- , Wendy Leung
- & Anja-Katrin Bielinsky
-
Article
| Open Access Pre-mitotic genome re-organisation bookends the B cell differentiation process
Pre-mitotic genome re-organisation bookends the B cell differentiation process
During differentiation, chromosome conformation is remodelled to support lineage-specific transcriptional programs. Here, the authors characterise chromosome conformational changes in B lymphocytes as they differentiate into plasma cells, and provide evidence that chromosome reconfiguration occurs prior to DNA replication and mitosis and guides gene expression that controls differentiation.
- Wing Fuk Chan
- , Hannah D. Coughlan
- & Rhys S. Allan
-
Article
| Open Access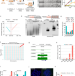 Telomeres reforged with non-telomeric sequences in mouse embryonic stem cells
Telomeres reforged with non-telomeric sequences in mouse embryonic stem cells
Telomeres can be maintained by a telomerase-independent mechanism called an alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT). Here the authors use mouse Terc (telomerase RNA) knockout embryonic cells and provide longitudinal analysis of ALT telomeres maintained with non-telomeric sequences.
- Chuna Kim
- , Sanghyun Sung
- & Junho Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Metabolic regulation of telomere silencing by SESAME complex-catalyzed H3T11 phosphorylation
Metabolic regulation of telomere silencing by SESAME complex-catalyzed H3T11 phosphorylation
Pyruvate kinase phosphorylates histone H3T11 (H3pT11) and represses gene expression by forming a large complex SESAME (Serine-responsive SAM-containing Metabolic Enzyme). Here the authors show that SESAME-catalyzed H3pT11 regulates telomere silencing by promoting Sir2 binding at telomeres and preventing autophagy-mediated Sir2 degradation.
- Shihao Zhang
- , Xilan Yu
- & Shanshan Li
-
Article
| Open Access Oncogenic herpesvirus KSHV triggers hallmarks of alternative lengthening of telomeres
Oncogenic herpesvirus KSHV triggers hallmarks of alternative lengthening of telomeres
~15% of cancers induce alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT) to activate telomere maintenance. Here, the authors reveal that infection with Kaposi’s sarcoma herpesvirus (KSHV) induces acquisition of ALT-like features in previously non-ALT cell lines.
- Timothy P. Lippert
- , Paulina Marzec
- & Simon J. Boulton
-
Article
| Open Access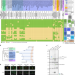 Bridgin connects the outer kinetochore to centromeric chromatin
Bridgin connects the outer kinetochore to centromeric chromatin
The kinetochore is a multi-complex structure that helps attach chromosomes to spindle microtubules, ensuring accurate chromosome segregation during cell division. Kinetochores are thought to be evolutionarily conserved, but which components are conserved is unclear. Here, the authors report that some members of the fungal phylum of Basidomycota lack many conventional kinetochore linker proteins. Instead, they possess a human Ki67-like protein that bridges the outer part of the kinetochore to centromere DNA, which may compensate for the loss of a conventional linker.
- Shreyas Sridhar
- , Tetsuya Hori
- & Kaustuv Sanyal
-
Article
| Open Access Radiation-induced DNA damage and repair effects on 3D genome organization
Radiation-induced DNA damage and repair effects on 3D genome organization
Genomic aberrations disrupting chromosome spatial domains can lead to disease. Here, the authors investigate the impact of DNA damage response and repair on 3D genome folding, comparing wild type cells and ataxia telangiectasia mutated patient cells, and characterise both cell type-specific and shared changes to genome organization during the response to damage.
- Jacob T. Sanders
- , Trevor F. Freeman
- & Rachel Patton McCord
-
Article
| Open Access Microcephalin 1/BRIT1-TRF2 interaction promotes telomere replication and repair, linking telomere dysfunction to primary microcephaly
Microcephalin 1/BRIT1-TRF2 interaction promotes telomere replication and repair, linking telomere dysfunction to primary microcephaly
Primary microcephaly is a clinical feature of several human telomere disorder syndromes. Here the authors reveal a role of Microcephalin 1 in promoting telomere replication and repair.
- Alessandro Cicconi
- , Rekha Rai
- & Sandy Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis of CTCF binding polarity in genome folding
Molecular basis of CTCF binding polarity in genome folding
The boundaries of topologically associating domains (TADs) arise from the ability of the CTCF protein to stop extrusion of chromatin loops by cohesin. Here the authors find that CTCF positions cohesin through its N-terminus but does not control its overall binding dynamics on chromatin, and show how the orientation of CTCF binding sites translates into genome folding patterns.
- Elphège P. Nora
- , Laura Caccianini
- & Benoit G. Bruneau
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanisms of telomerase inhibition by oxidized and therapeutic dNTPs
Mechanisms of telomerase inhibition by oxidized and therapeutic dNTPs
Telomerase enzymes add telomeric repeats to the end of linear chromosomes. Here the authors reveal mechanisms by which oxidized dNTPs and therapeutic dNTPs inhibit telomerase-mediated telomere elongation.
- Samantha L. Sanford
- , Griffin A. Welfer
- & Patricia L. Opresko
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplex flow magnetic tweezers reveal rare enzymatic events with single molecule precision
Multiplex flow magnetic tweezers reveal rare enzymatic events with single molecule precision
Single molecule force measurements have shed light on dynamic biological events, but rare events escape notice owing to low throughput of the methods. Here, the authors combine an array of magnetic tweezers with lateral flow to increase throughput 100-fold, and detect rare DNA breaks induced by gyrase.
- Rohit Agarwal
- & Karl E. Duderstadt
-
Article
| Open Access Helicase LSH/Hells regulates kinetochore function, histone H3/Thr3 phosphorylation and centromere transcription during oocyte meiosis
Helicase LSH/Hells regulates kinetochore function, histone H3/Thr3 phosphorylation and centromere transcription during oocyte meiosis
Centromeres are the sites of kinetochore and inner centromere formation, which can be epigenetically regulated. Here, the authors reveal a role for the lymphocyte specific helicase LSH/Hells associated with pericentric heterochromatin formation in centromere stability and chromosome segregation at meiotic kinetochores.
- Claudia Baumann
- , Wei Ma
- & Rabindranath De La Fuente
-
Article
| Open Access Chromosome drives via CRISPR-Cas9 in yeast
Chromosome drives via CRISPR-Cas9 in yeast
Self-propagating drives allow for non-Mendelian inheritance. Here the authors use CRISPR to build a chromosome drive, showing elimination of entire chromosomes, endoreduplication of desired chromosomes and enabling preferential transmissions of complex genetic traits on a chromosomal scale in yeast.
- Hui Xu
- , Mingzhe Han
- & Ying-Jin Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access Surveillance of cohesin-supported chromosome structure controls meiotic progression
Surveillance of cohesin-supported chromosome structure controls meiotic progression
Meiosis-specific cohesins and the synaptonemal complex are essential for meiotic chromosome structure and function. Here the authors show that continued surveillance of these chromosome structures controls meiotic progression by regulating CHK-2, a master regulator of pairing and recombination.
- Maikel Castellano-Pozo
- , Sarai Pacheco
- & Enrique Martinez-Perez
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying proteins bound to native mitotic ESC chromosomes reveals chromatin repressors are important for compaction
Identifying proteins bound to native mitotic ESC chromosomes reveals chromatin repressors are important for compaction
Epigenetic information is transmitted from mother to daughter cells through mitosis. Here, the authors isolate native chromosomes from metaphase-arrested cells and perform LC-MS/MS to identify chromosome-bound proteins in pluripotent stem cells during mitosis and reveal that PRC2, DNA methylation and Mecp2 are required to maintain chromosome compaction.
- Dounia Djeghloul
- , Bhavik Patel
- & Amanda G. Fisher
-
Article
| Open Access DONSON and FANCM associate with different replisomes distinguished by replication timing and chromatin domain
DONSON and FANCM associate with different replisomes distinguished by replication timing and chromatin domain
Eukaryotic replisomes are multiprotein complexes. Here the authors reveal two distinct stressed replisomes, associated with DONSON and FANCM, displaying a bias in replication timing and chromatin domain.
- Jing Zhang
- , Marina A. Bellani
- & Michael M. Seidman
-
Article
| Open Access Topoisomerase 1 prevents replication stress at R-loop-enriched transcription termination sites
Topoisomerase 1 prevents replication stress at R-loop-enriched transcription termination sites
While R-loops can alter cell homeostasis, it is unclear what determines their toxicity. Here, the authors, by using Top1 knockdown as a tool to enhance the formation of R-loops at certain genomic sites, reveal and characterize a proportion of R-loops that are more toxic to the cell by causing DNA damage.
- Alexy Promonet
- , Ismaël Padioleau
- & Philippe Pasero
-
Article
| Open Access Persistent telomere cohesion protects aged cells from premature senescence
Persistent telomere cohesion protects aged cells from premature senescence
Telomere function is regulated by the telomere repeat binding proteins TRF1 and TRF2. Here the authors show that decreased levels of TRF1 proteins at shortened telomeres in aged human cells results in persistent telomere cohesion, protecting from premature senescence.
- Kameron Azarm
- , Amit Bhardwaj
- & Susan Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Proline-rich protein PRR19 functions with cyclin-like CNTD1 to promote meiotic crossing over in mouse
Proline-rich protein PRR19 functions with cyclin-like CNTD1 to promote meiotic crossing over in mouse
Crossing over is a critical process during meiosis, although the regulation of this process still remains somewhat elusive. Here, the authors show that PRR19 partners with CNTD1 to enable formation of crossover-specific recombination complexes in mouse germ cells.
- Anastasiia Bondarieva
- , Kavya Raveendran
- & Attila Tóth
-
Article
| Open Access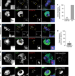 Spt6 is a maintenance factor for centromeric CENP-A
Spt6 is a maintenance factor for centromeric CENP-A
CENP-A is a stable centromere mark, although active transcription poses a potential threat for retaining CENP-A through chromatin remodeling and nucleosome eviction. Here, the authors show that maintenance of the centromeric mark is preserved by Spt6, which recycles CENP-A nucleosomes.
- Georg O. M. Bobkov
- , Anming Huang
- & Patrick Heun

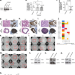 TGS1 mediates 2,2,7-trimethyl guanosine capping of the human telomerase RNA to direct telomerase dependent telomere maintenance
TGS1 mediates 2,2,7-trimethyl guanosine capping of the human telomerase RNA to direct telomerase dependent telomere maintenance