Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Pannexin 1 channels regulate leukocyte emigration through the venous endothelium during acute inflammation
Pannexin 1 channels regulate leukocyte emigration through the venous endothelium during acute inflammation
Endothelial cell activation by inflammation requires extracellular ATP release. Here the authors show that TNF-α induces Src-family kinase-dependent ATP release by Pannexin1 channels in endothelial cells, and that Pannexin1 is required for leukocyte adhesion and emigration into the inflamed tissue.
- Alexander W. Lohman
- , Igor L. Leskov
- & Brant E. Isakson
-
Article
| Open Access CD163 interacts with TWEAK to regulate tissue regeneration after ischaemic injury
CD163 interacts with TWEAK to regulate tissue regeneration after ischaemic injury
CD163 is a glycoprotein receptor expressed on the surface of macrophages. Here, the authors demonstrate that a soluble form of CD163 can act as a decoy receptor for the pro inflammatory cytokine TWEAK, thereby revealing a new mechanism for the regulation of tissue repair after ischaemic injury.
- Hirokuni Akahori
- , Vinit Karmali
- & Aloke V. Finn
-
Article
| Open Access Multicohort analysis of the maternal age effect on recombination
Multicohort analysis of the maternal age effect on recombination
The question of whether recombination rate increases with maternal age is controversial, with conflicting prior evidence. Here, Martin et al.analyse nine cohorts in the largest SNP-based analysis of this question and find a small positive increase with maternal age in the number of crossovers.
- Hilary C. Martin
- , Ryan Christ
- & Peter Donnelly
-
Article
| Open Access Nonsynaptic junctions on myelinating glia promote preferential myelination of electrically active axons
Nonsynaptic junctions on myelinating glia promote preferential myelination of electrically active axons
The myelin sheath on vertebrate axons is critical for neural impulse transmission, but whether electrically active axons are preferentially myelinated by glial cells, is not clear. Here the authors show that cultured oligodendrocytes preferentially myelinate electrically active axons via a mechanism dependent on nonsynaptic vesicular release of glutamate.
- Hiroaki Wake
- , Fernando C. Ortiz
- & R. Douglas Fields
-
Article |
 Arf6 regulates tumour angiogenesis and growth through HGF-induced endothelial β1 integrin recycling
Arf6 regulates tumour angiogenesis and growth through HGF-induced endothelial β1 integrin recycling
Targetting tumour angiogenesis is a useful strategy to reduce tumour burden; however, the clinical benefits of anti-angiogenetic drugs are modest. Here, the authors show that HGFR signalling, which contributes to tumour angiogenesis, requires Arf6 and that blocking Arf6 can lead to reduced tumour growth in mice.
- Tsunaki Hongu
- , Yuji Funakoshi
- & Yasunori Kanaho
-
Article
| Open Access Harmonic force spectroscopy measures load-dependent kinetics of individual human β-cardiac myosin molecules
Harmonic force spectroscopy measures load-dependent kinetics of individual human β-cardiac myosin molecules
Single molecule methods for measuring load dependence are fundamental for molecular motor research. Here, Sung et al. introduce harmonic force spectroscopy, a method that randomly applies varying loads at high frequency, allowing the determination of load dependent parameters of human β-cardiac myosin at physiological ATP concentration.
- Jongmin Sung
- , Suman Nag
- & James A. Spudich
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and vascular function of MEKK3–cerebral cavernous malformations 2 complex
Structure and vascular function of MEKK3–cerebral cavernous malformations 2 complex
The protein kinase MEKK3 interacts with CCM2, which is associated with the predominantly cerebrovascular CCM disease. Here the authors use structural, biochemical, cell biology and in vivotechniques to show that regulation of Rho signalling by the CCM2:MEKK3 complex is needed to maintain neurovascular integrity.
- Oriana S. Fisher
- , Hanqiang Deng
- & Bing Su
-
Article
| Open Access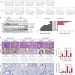 Truncating mutation in the autophagy gene UVRAG confers oncogenic properties and chemosensitivity in colorectal cancers
Truncating mutation in the autophagy gene UVRAG confers oncogenic properties and chemosensitivity in colorectal cancers
Some colon carcinomas with microsatellite instability carry a frameshift mutation in a tumour suppressor UVRAG. Here the authors show that mutant UVRAG triggers colorectal cancer by antagonizing the activity of normal UVRAG in autophagy and chromosomal stability, but also sensitizes the cancer to DNA damage-inducing chemotherapeutic drugs.
- Shanshan He
- , Zhen Zhao
- & Chengyu Liang
-
Article
| Open Access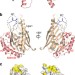 Structural and mechanistic insights into phospholipid transfer by Ups1–Mdm35 in mitochondria
Structural and mechanistic insights into phospholipid transfer by Ups1–Mdm35 in mitochondria
Phospholipid trafficking between membranes is essential to maintain the structural integrity and function of membrane-bound cellular compartments. Here the authors establish the structural basis for transport of phosphatidic acid between the outer and inner membranes of the mitochondria by the Ups1–Mdm35 lipid-transport complex.
- Yasunori Watanabe
- , Yasushi Tamura
- & Toshiya Endo
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative interactome analysis reveals a chemoresistant edgotype
Quantitative interactome analysis reveals a chemoresistant edgotype
Changes in protein–protein interactions result in changes to cellular phenotype. Here the authors use crosslinking mass spectrometry to derive a quantitative protein interaction network in drug-sensitive and -resistant HeLa cells, and uncover a chemoresistant ‘edgotype’.
- Juan D. Chavez
- , Devin K. Schweppe
- & James E. Bruce
-
Article
| Open Access RETRACTED ARTICLE: An apoptosis-enhancing drug overcomes platinum resistance in a tumour-initiating subpopulation of ovarian cancer
RETRACTED ARTICLE: An apoptosis-enhancing drug overcomes platinum resistance in a tumour-initiating subpopulation of ovarian cancer
Despite normalization of the CA125 serum biomarker at the completion of carboplatin therapy the vast majority of patients with high grade serous ovarian cancers relapse. Here, Janzen et al., identify a sub-population of tumor cells that are CA125 negative, cancer initiating and platinum resistant but readily eliminated with the addition of apoptosis enhancing drugs to carboplatin.
- D. M. Janzen
- , E. Tiourin
- & S. Memarzadeh
-
Article
| Open Access RTN1 mediates progression of kidney disease by inducing ER stress
RTN1 mediates progression of kidney disease by inducing ER stress
ER stress is associated with the pathogenesis of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and new CKD therapies are needed. Here the authors show that expression of Rtn1 can control severity of renal disease and that inhibition of its expression can attenuate ER stress and CKD.
- Ying Fan
- , Wenzhen Xiao
- & John C. He
-
Article
| Open Access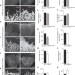 PTEN mediates Notch-dependent stalk cell arrest in angiogenesis
PTEN mediates Notch-dependent stalk cell arrest in angiogenesis
During the formation of vascular sprouts, Notch activation inhibits proliferation of the stalk ECs via unknown mechanism. Here the authors show that PTEN represents a critical mediator of Notch anti-proliferative response in stalk cells via its phosphatase-dependent and -independent activity.
- Helena Serra
- , Iñigo Chivite
- & Mariona Graupera
-
Article
| Open Access Actin nucleation by WH2 domains at the autophagosome
Actin nucleation by WH2 domains at the autophagosome
Autophagy is a catabolic process whereby cellular components are degraded by the autophagosome, but the role of the actin cytoskeleton is not clear. Here Coutts and La Thangue show that the actin nucleator JMY is recruited to the autophagosome via binding LC3, and promotes actin nucleation that is required for autophagosome maturation.
- Amanda S. Coutts
- & Nicholas B. La Thangue
-
Article
| Open Access Loss of ATM accelerates pancreatic cancer formation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition
Loss of ATM accelerates pancreatic cancer formation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition
Mutations in the serine/threonine kinase ataxia teleangiectasia mutated (ATM) have been linked to pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cohorts. Here Russellet al. show that loss of ATM induces a greater number of proliferative precursor lesions in a mouse model, recapitulating many features of human PDAC subtypes.
- Ronan Russell
- , Lukas Perkhofer
- & Alexander Kleger
-
Article |
 An MTCH2 pathway repressing mitochondria metabolism regulates haematopoietic stem cell fate
An MTCH2 pathway repressing mitochondria metabolism regulates haematopoietic stem cell fate
Changes in the metabolic state of stem cells can trigger a shift from quiescence into cell cycle entry. Here Maryanovichet al. identify mitochondrial carrier homolog 2 (MCH2) as a negative regulator of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in haematopoietic stem cells, maintaining their homeostasis.
- Maria Maryanovich
- , Yehudit Zaltsman
- & Atan Gross
-
Article
| Open Access 14-3-3ζ coordinates adipogenesis of visceral fat
14-3-3ζ coordinates adipogenesis of visceral fat
14-3-3 family proteins are adaptor proteins involved in various cellular functions. Here Lim et al. show that 14-3-3ζ regulates adipogenesis in vitro, and the formation of visceral fat in mice, by reducing autophagic degradation of the adipogenic master transcription factor C/EBP-δ.
- Gareth E. Lim
- , Tobias Albrecht
- & James D. Johnson
-
Article
| Open Access Legionella suppresses the host unfolded protein response via multiple mechanisms
Legionella suppresses the host unfolded protein response via multiple mechanisms
The bacterium Legionella pneumophila, a causative agent of severe pneumonia, replicates inside an endoplasmic reticulum-like organelle in the host cells. Here, Treacy-Abarca and Mukherjee show that the pathogen dampens the host’s unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway by multiple mechanisms.
- Sean Treacy-Abarca
- & Shaeri Mukherjee
-
Article |
 Redefining the concept of protease-activated receptors: cathepsin S evokes itch via activation of Mrgprs
Redefining the concept of protease-activated receptors: cathepsin S evokes itch via activation of Mrgprs
Sensory neurons that mediate histamine-independent itch express Mas-related G protein coupled receptors (Mrgprs). Here, Reddy et al.show that the cysteine protease cathepsin S cleaves and activates MrgpcrC11 without the generation of a tethered ligand, in contrast to other protease activated receptors.
- Vemuri B. Reddy
- , Shuohao Sun
- & Ethan A. Lerner
-
Article
| Open Access MCM8-9 complex promotes resection of double-strand break ends by MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 complex
MCM8-9 complex promotes resection of double-strand break ends by MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 complex
The MCM8-9 complex is required for repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). Here, the authors show that MCM8-9 is required for the nuclease activity of the MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 complex (MRN) and stabilizes its association with DNA damage sites, promoting resection of DSB ends.
- Kyung Yong Lee
- , Jun-Sub Im
- & Anindya Dutta
-
Article |
 Perinuclear tethers license telomeric DSBs for a broad kinesin- and NPC-dependent DNA repair process
Perinuclear tethers license telomeric DSBs for a broad kinesin- and NPC-dependent DNA repair process
Damaged DNA is often targeted to nuclear pore complexes for repair. Here, the authors show that kinesin-14 mediates this process ensuring error-prone repair, while perinuclear telomere attachment licenses damaged telomeric loci for this repair and kinesin-14 blocks senescence in the absence of telomerase.
- Daniel K.C. Chung
- , Janet N.Y. Chan
- & Karim Mekhail
-
Article
| Open Access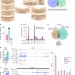 MEG3 long noncoding RNA regulates the TGF-β pathway genes through formation of RNA–DNA triplex structures
MEG3 long noncoding RNA regulates the TGF-β pathway genes through formation of RNA–DNA triplex structures
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) regulate gene expression by association with chromatin. Here, the authors show that lncRNA MEG3regulates the TGF-β pathway by bridging the interactions between polycomb repressive complex 2 and the distal regulatory elements of the TGF-β pathway genes via formation of RNA–DNA triplexes.
- Tanmoy Mondal
- , Santhilal Subhash
- & Chandrasekhar Kanduri
-
Article
| Open Access Highly condensed chromatins are formed adjacent to subtelomeric and decondensed silent chromatin in fission yeast
Highly condensed chromatins are formed adjacent to subtelomeric and decondensed silent chromatin in fission yeast
The level of chromatin condensation and gene expression is believed to be inversely correlated. Here the authors show that the transcriptionally silent telomere regions are flanked by highly condensed chromatin, and are less condensed than euchromatin in the interphase of Schizosaccharomyces pombe.
- Atsushi Matsuda
- , Yuji Chikashige
- & Yasushi Hiraoka
-
Article
| Open Access Intrinsically disordered proteins drive membrane curvature
Intrinsically disordered proteins drive membrane curvature
Proteins that bend membranes often contain curvature-promoting structural motifs such as wedges or crescent-shaped domains. Busch et al.report that intrinsically disordered domains can also drive membrane curvature and provide evidence that steric pressure driven by protein crowding mediates this effect.
- David J. Busch
- , Justin R. Houser
- & Jeanne C. Stachowiak
-
Article |
 Thrombin-dependent intravascular leukocyte trafficking regulated by fibrin and the platelet receptors GPIb and PAR4
Thrombin-dependent intravascular leukocyte trafficking regulated by fibrin and the platelet receptors GPIb and PAR4
Thrombin is a key proinflammatory protease regulating leukocyte trafficking at sites of vascular injury. Here the authors show that balanced thrombin interactions with platelet proteins PAR4, GPIbα and fibrin plays a major role in regulating this process.
- Zane S. Kaplan
- , Alessandro Zarpellon
- & Shaun P. Jackson
-
Article
| Open Access Repression of arterial genes in hemogenic endothelium is sufficient for haematopoietic fate acquisition
Repression of arterial genes in hemogenic endothelium is sufficient for haematopoietic fate acquisition
The first haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells arise from the hemogenic endothelium of arterial vascular beds. Here the authors describe the mechanism that regulates the endothelial-to-haematopoietic transition and show that Sox17 and Notch1, genes critical to arterial endothelium identity, are also crucial repressors of haematopoietic fate.
- Carlos O. Lizama
- , John S. Hawkins
- & Ann C. Zovein
-
Article |
 HDAC6 and RhoA are novel players in Abeta-driven disruption of neuronal polarity
HDAC6 and RhoA are novel players in Abeta-driven disruption of neuronal polarity
Retracted neurites and disorganized actin filaments are major components of senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles—hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease. Here the authors show that soluble ß-amyloid impairs action potential firing by disrupting actin and microtubule filaments through the inhibition of HDAC6 and activation of RhoA.
- Hanako Tsushima
- , Marco Emanuele
- & Evelina Chieregatti
-
Article
| Open Access Snf1/AMP-activated protein kinase activates Arf3p to promote invasive yeast growth via a non-canonical GEF domain
Snf1/AMP-activated protein kinase activates Arf3p to promote invasive yeast growth via a non-canonical GEF domain
Snf1p is the yeast homologue of AMP-activated protein kinase, a key regulator of cellular energy homeostasis. Here, Hsu et al.identify Snf1p as a non-canonical guanine nucleotide-exchange factor for the Arf3p GTPase, regulating the yeast invasive response to glucose depletion.
- Jia-Wei Hsu
- , Kuan-Jung Chen
- & Fang-Jen S. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access A draft network of ligand–receptor-mediated multicellular signalling in human
A draft network of ligand–receptor-mediated multicellular signalling in human
Cell-to-cell communication relies upon interactions between secreted ligands and cell surface receptors. Here, Ramilowski et al.present a draft cell-to-cell communication network based on expression of ligand-receptor pairs in 144 different human cell types.
- Jordan A. Ramilowski
- , Tatyana Goldberg
- & Alistair R. R. Forrest
-
Article
| Open Access STAT3 regulated ARF expression suppresses prostate cancer metastasis
STAT3 regulated ARF expression suppresses prostate cancer metastasis
IL6-STAT3 signaling is activated in prostate cancer, however inhibiting this pathway has not lead to a survival advantage in patients. Here, Pencik et al.show that loss of the IL6-STAT3 axis in mice and humans leads to metastasis due to loss of ARF, unravelling STAT3 and ARF as potential prognostic markers in prostate cancer.
- Jan Pencik
- , Michaela Schlederer
- & Lukas Kenner
-
Article
| Open Access DOT1L cooperates with the c-Myc-p300 complex to epigenetically derepress CDH1 transcription factors in breast cancer progression
DOT1L cooperates with the c-Myc-p300 complex to epigenetically derepress CDH1 transcription factors in breast cancer progression
DOT1L is an anti-cancer therapeutic target in leukaemia but has a poorly understood role in solid tumours. Here the authors show that DOT1L expression is associated with poor survival and aggressive cancers by helping to epigenetically activate the epithelial-mesenchymal transition during breast cancer progression.
- Min-Hyung Cho
- , Ji-Hye Park
- & Gu Kong
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphorylation status determines the opposing functions of Smad2/Smad3 as STAT3 cofactors in TH17 differentiation
Phosphorylation status determines the opposing functions of Smad2/Smad3 as STAT3 cofactors in TH17 differentiation
TGF-ß and IL-6 are the essential cytokines for mediating the differentiation of IL-17-producing CD4+ T helper cells (TH17). Here, Yoon et al. provide more insights into this process and describe the opposing roles of TGFß-signalling intermediates Smad2 and Smad3 as STAT3 cofactors in Th17 differentiation.
- Jeong-Hwan Yoon
- , Katsuko Sudo
- & Mizuko Mamura
-
Article
| Open Access Functional genomics identifies negative regulatory nodes controlling phagocyte oxidative burst
Functional genomics identifies negative regulatory nodes controlling phagocyte oxidative burst
Phagocytes employ multiple bactericidal mechanisms to kill microorganisms, including the generation of toxic superoxide and other reactive oxygen species. Here the authors utilize a multi-omics approach to identify and characterize new regulatory nodes implicated in mucosal immunity that control phagocyte oxidative burst.
- Daniel B. Graham
- , Christine E. Becker
- & Ramnik J. Xavier
-
Article
| Open Access Tyrosine glycosylation of Rho by Yersinia toxin impairs blastomere cell behaviour in zebrafish embryos
Tyrosine glycosylation of Rho by Yersinia toxin impairs blastomere cell behaviour in zebrafish embryos
Yersinia ruckeri is the source of redmouth disease in fish. Here the authors analysed the Yersiniatoxin Afp18 and show that it acts to inhibit RhoA activation by glycosylating a distinct tyrosine residue inducing a signalling incompetent structural conformation.
- Thomas Jank
- , Stephanie Eckerle
- & Klaus Aktories
-
Article |
 E2F1-dependent miR-421 regulates mitochondrial fragmentation and myocardial infarction by targeting Pink1
E2F1-dependent miR-421 regulates mitochondrial fragmentation and myocardial infarction by targeting Pink1
Inhibition of mitochondrial fragmentation can block or delay cell death. Here the authors show that the signalling axis E2F1-miR-421-Pink1 represents a major regulator of mitochondrial fission and cardiomyocyte death, identifying potential therapeutic targets for treatment of heart failure.
- Kun Wang
- , Lu-Yu Zhou
- & Pei-Feng Li
-
Article
| Open Access PI3K/AKT activation induces PTEN ubiquitination and destabilization accelerating tumourigenesis
PI3K/AKT activation induces PTEN ubiquitination and destabilization accelerating tumourigenesis
Mutations and post-translational modifications of the PI3K/AKT pathway inhibitor PTEN are a feature of many cancers, but these have not been associated with cervical cancer. Here, the authors identify a PI3K/AKT-mediated ubiquitination degradation pathway of PTEN that occurs in patients with cervical cancer.
- Min-Sik Lee
- , Man-Hyung Jeong
- & Jaewhan Song
-
Article
| Open Access Inside-out Ca2+ signalling prompted by STIM1 conformational switch
Inside-out Ca2+ signalling prompted by STIM1 conformational switch
Depletion of calcium from intracellular stores induces interaction between the endoplasmic reticulum STIM1 protein and the plasma membrane ORAI1 channel that facilitates cellular calcium entry. Here Ma et al. characterize a STIM1 gain-of-function mutant and propose a conformational switch that controls ORAI1 gating.
- Guolin Ma
- , Ming Wei
- & Yubin Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access An autoinhibitory mechanism modulates MAVS activity in antiviral innate immune response
An autoinhibitory mechanism modulates MAVS activity in antiviral innate immune response
The cellular protein RIG-I detects viral RNA and activates another protein, MAVS, which then forms filaments and stimulates an antiviral pathway. Here, the authors identify different regions within MAVS involved in activating transcription factors IRF3 and NF-κB, and in MAVS self-inhibition.
- Yuheng Shi
- , Bofeng Yuan
- & Fajian Hou
-
Article
| Open Access Downregulation of N-terminal acetylation triggers ABA-mediated drought responses in Arabidopsis
Downregulation of N-terminal acetylation triggers ABA-mediated drought responses in Arabidopsis
N-terminal acetylation is a common protein modification in eukaryotes. Here the authors show that in Arabidopsis, N-terminal acetylation is decreased by drought stress, that abundance of an N-terminal acetyltransferase is reduced by abscisic acid and that constitutive downregulation can confer drought resistance.
- Eric Linster
- , Iwona Stephan
- & Markus Wirtz
-
Article
| Open Access Deactivation of excitatory neurons in the prelimbic cortex via Cdk5 promotes pain sensation and anxiety
Deactivation of excitatory neurons in the prelimbic cortex via Cdk5 promotes pain sensation and anxiety
The medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) is implicated in pain regulation, yet the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. Here the authors establish a critical role for mPFC in regulating pain sensation and pain-related anxiety, mediated by activation of the cyclin-dependent kinase 5 signalling pathway.
- Guo-Qiang Wang
- , Cheng Cen
- & Yun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access D2HGDH regulates alpha-ketoglutarate levels and dioxygenase function by modulating IDH2
D2HGDH regulates alpha-ketoglutarate levels and dioxygenase function by modulating IDH2
IDH1- and IDH2-mutant cancer cells aberrantly accumulate D2-hydroxyglutarate (D2-HG). Here, Lin et al. find loss-of-function mutations in D2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase (D2HGDH), which converts D2-HG to alpha-ketoglutarate (α-KG), in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas and show that D2HGDH via α-KG regulates the expression and activity of IDH2.
- An-Ping Lin
- , Saman Abbas
- & Ricardo C. T. Aguiar
-
Article
| Open Access Interneuron- and GABAA receptor-specific inhibitory synaptic plasticity in cerebellar Purkinje cells
Interneuron- and GABAA receptor-specific inhibitory synaptic plasticity in cerebellar Purkinje cells
Rebound potentiation (RP), a form of inhibitory plasticity in the cerebellum, is characterized by an increase in GABAergic synaptic currents. Here the authors demonstrate that RP is both interneuron input-specific and GABAAreceptor subunit-specific and serves to regulate Purkinje cell firing patterns.
- Qionger He
- , Ian Duguid
- & Trevor G. Smart
-
Article
| Open Access Locking GTPases covalently in their functional states
Locking GTPases covalently in their functional states
The cellular function of small GTPases is regulated by switching between active (GTP-bound) and inactive (GDP-bound) states. Here the authors develop nucleotide analogues that can be covalently linked to GTPases via a strategically placed cysteine residue to lock the target GTPase in defined activation states.
- David Wiegandt
- , Sophie Vieweg
- & Roger S. Goody
-
Article
| Open Access Parallel circuits control temperature preference in Drosophila during ageing
Parallel circuits control temperature preference in Drosophila during ageing
The capacity for thermoregulation deteriorates with age, particularly in cold environments. Here the authors demonstrate inDrosophilathat age-related changes in cold avoidance result from a shift in the relative contribution of two parallel mushroom body circuits that are modulated by dopamine.
- Hsiang-Wen Shih
- , Chia-Lin Wu
- & Ann-Shyn Chiang
-
Article
| Open Access An actin-dependent spindle position checkpoint ensures the asymmetric division in mouse oocytes
An actin-dependent spindle position checkpoint ensures the asymmetric division in mouse oocytes
In mammalian oocytes, the meiotic spindle is assembled close to the centre of the cell and relocates to the cell periphery prior to chromosome segregation. Here Metchat et al. show that anaphase is delayed until the spindle is positioned close to the cell cortex, providing evidence for a spindle position checkpoint.
- Aïcha Metchat
- , Manuel Eguren
- & Jan Ellenberg
-
Article
| Open Access SUMOylation of synapsin Ia maintains synaptic vesicle availability and is reduced in an autism mutation
SUMOylation of synapsin Ia maintains synaptic vesicle availability and is reduced in an autism mutation
Synapsins anchor synaptic vesicles (SVs) to the actin cytoskeleton to establish the reserve vesicle pool. Here Tanget al. show that SUMOylation of synapsin 1a enhances its interaction with SVs to promote efficient reclustering following stimulation, and a mutation linked to autism and epilepsy leads to defective SUMOylation.
- Leo T. -H. Tang
- , Tim J. Craig
- & Jeremy M. Henley
-
Article
| Open Access RC3H1 post-transcriptionally regulates A20 mRNA and modulates the activity of the IKK/NF-κB pathway
RC3H1 post-transcriptionally regulates A20 mRNA and modulates the activity of the IKK/NF-κB pathway
The RNA-binding protein RC3H1/ROQUIN1 promotes the degradation of mRNA by binding to a consensus CDE present in the 3′UTR. Here the authors expand the set of consensus sequences through which RCH31 binds and regulates mRNA encoding members of the DNA damage response and IKK/NF-κB pathway.
- Yasuhiro Murakawa
- , Michael Hinz
- & Markus Landthaler
-
Article
| Open Access Self-organizing human cardiac microchambers mediated by geometric confinement
Self-organizing human cardiac microchambers mediated by geometric confinement
Organogenesis is orchestrated by biochemical and biophysical stimuli. Here, Ma et al. generate a micro-patterned surface that provides mechanical cues which, when combined with biochemical signals, drive human pluripotent stem cells’ differentiation into beating cardiac microchambers resembling primitive hearts.
- Zhen Ma
- , Jason Wang
- & Kevin E. Healy
-
Article
| Open Access 9-O-Acetylation of sialic acids is catalysed by CASD1 via a covalent acetyl-enzyme intermediate
9-O-Acetylation of sialic acids is catalysed by CASD1 via a covalent acetyl-enzyme intermediate
9-O-Acetylation is one of the most common modifications of sialic acids, implicated in sialoglycan recognition and ganglioside biology. Here, the authors show that the key enzyme for the biosynthesis of 9-O-acetylated sialoglycans is CASD1, which uses CMP-activated sialic acid as acceptor substrate.
- Anna-Maria T. Baumann
- , Mark J. G. Bakkers
- & Martina Mühlenhoff
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Autophagy
- Cell adhesion
- Cell death
- Cell division
- Cell growth
- Cell migration
- Cell polarity
- Cell signalling
- Cellular imaging
- Chromosomes
- Circadian rhythms
- Cytoskeleton
- Glycobiology
- Mechanisms of disease
- Membrane trafficking
- Nuclear organization
- Nuclear transport
- Organelles
- Post-translational modifications
- Protein folding
- Protein transport
- Proteolysis
- Senescence

 Turning terminally differentiated skeletal muscle cells into regenerative progenitors
Turning terminally differentiated skeletal muscle cells into regenerative progenitors