Review Article |
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial membrane-binding proteins stimulate oxygenation of stem cells during engineering of large cartilage tissue
Artificial membrane-binding proteins stimulate oxygenation of stem cells during engineering of large cartilage tissue
Avoiding central cell necrosis at the centre of large engineered tissue constructs is an important issue forin vitrotissue engineering. Here, the authors demonstrate that this problem may be overcome by oxygenating human mesenchymal stem cells with artificial membrane-binding proteins.
- James P. K. Armstrong
- , Rameen Shakur
- & Anthony P. Hollander
-
Article |
 Predictive modelling-based design and experiments for synthesis and spinning of bioinspired silk fibres
Predictive modelling-based design and experiments for synthesis and spinning of bioinspired silk fibres
Reproducing many naturally occurring silk fibres—such as spider silk—remains a challenge. Here, the authors develop a predictive modelling approach to understand and design the artificial synthesis and fibre-spinning processes, which are tested in the laboratory to create de novobioinspired silk fibres.
- Shangchao Lin
- , Seunghwa Ryu
- & Markus J. Buehler
-
Article
| Open Access Structural optimization of 3D-printed synthetic spider webs for high strength
Structural optimization of 3D-printed synthetic spider webs for high strength
Spider webs have some intriguing mechanical properties, but understanding of the properties is limited to individual silk fibres. Here, the authors create mimics of spider web using 3D techniques, which enables them to acquire knowledge of mechanical strength of the entire synthetic web.
- Zhao Qin
- , Brett G. Compton
- & Markus J. Buehler
-
Article |
 Reinforcement of hydrogels using three-dimensionally printed microfibres
Reinforcement of hydrogels using three-dimensionally printed microfibres
Hydrogels are commonly used materials for tissue engineering, but they can lack the structural properties required for load-bearing and mechanical applications. Here, the authors prepare a polycaprolactone scaffold using melt-electrospinning to reinforce a gelatin methacrylamide hydrogel.
- Jetze Visser
- , Ferry P.W. Melchels
- & Jos Malda
-
Article
| Open Access Superlattices assembled through shape-induced directional binding
Superlattices assembled through shape-induced directional binding
Controlling self-assembly of nanoparticles into superlattices is an important approach to build functional materials. Here, Lu et al. use directional binding provided by DNA-encoded polyhedral blocks—cubes or octahedrons—to guide spherical nanoparticles into clusters and three-dimensional lattices.
- Fang Lu
- , Kevin G. Yager
- & Oleg Gang
-
Article |
 Protease-degradable electrospun fibrous hydrogels
Protease-degradable electrospun fibrous hydrogels
Electrospinning is a useful method of biomaterial fabrication, but a lack of bioactivity in the final construct can limit their application as mimics for biological matrices. Here, the authors fabricate a degradable electrospun scaffold as an in vitro and in vivomimic of the extracellular matrix.
- Ryan J. Wade
- , Ethan J. Bassin
- & Jason A. Burdick
-
Article
| Open Access Abiotic ligation of DNA oligomers templated by their liquid crystal ordering
Abiotic ligation of DNA oligomers templated by their liquid crystal ordering
Some oligomers exhibit liquid-crystal-like ordering in concentrated aqueous solutions. Here, Fraccia et al. show that this kind of ordering can further facilitate DNA ligation in a way similar to a catalytic process that arises from a hierarchical self-assembly, namely liquid crystal autocatalysis.
- Tommaso P. Fraccia
- , Gregory P. Smith
- & Tommaso Bellini
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration of asymmetric electron conduction in pseudosymmetrical photosynthetic reaction centre proteins in an electrical circuit
Demonstration of asymmetric electron conduction in pseudosymmetrical photosynthetic reaction centre proteins in an electrical circuit
Photosynthetic reaction centres have been proposed for applications in bioelectronics. Here, the authors examine electron transport through the reaction centre from R. sphaeroidesusing conductive AFM, observing asymmetric conductance along only one cofactor wire under an applied bias.
- Muhammad Kamran
- , Vincent M. Friebe
- & Michael R. Jones
-
Article
| Open Access A highly conspicuous mineralized composite photonic architecture in the translucent shell of the blue-rayed limpet
A highly conspicuous mineralized composite photonic architecture in the translucent shell of the blue-rayed limpet
Mollusks have evolved an exquisite diversity of complex mineralized shells for protection. One such example, the blue-rayed limpet, incorporates a vivid display of blue lines, which originate from the interference of light in a nano-periodic photonic architecture buried within the animal's translucent shell.
- Ling Li
- , Stefan Kolle
- & Mathias Kolle
-
Article |
 Self-assembled hydrogels utilizing polymer–nanoparticle interactions
Self-assembled hydrogels utilizing polymer–nanoparticle interactions
Mouldable hydrogels find a variety of applications in the biomedical industry. Here, Appel et al. show a method to fabricate hydrogels through a self-assembly process based on the interaction between biopolymers and functional nanoparticles for multistage drug delivery in vivo.
- Eric A. Appel
- , Mark W. Tibbitt
- & Robert Langer
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of erosion of nanostructured porous silicon drug carriers in neoplastic tissues
Mechanism of erosion of nanostructured porous silicon drug carriers in neoplastic tissues
The degradation of materials used in biological applications has an important bearing on their long term performance. Here, the authors show how porous silicon nanoparticle degradation can be accelerated in vivothrough the influence of local tissue pathology, likely influencing drug delivery performance.
- Adi Tzur-Balter
- , Zohar Shatsberg
- & Natalie Artzi
-
Article
| Open Access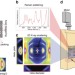 Osmotic pressure induced tensile forces in tendon collagen
Osmotic pressure induced tensile forces in tendon collagen
Water is an important component of collagen in tendons, bone and extracellular matrix, but its role in the mechanical function of protein is poorly understood. Here, the authors study the effects of osmotic pressure on contraction in collagen, suggesting that collagen could function as a mechanical actuator.
- Admir Masic
- , Luca Bertinetti
- & Peter Fratzl
-
Article
| Open Access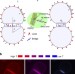 Volume and porosity thermal regulation in lipid mesophases by coupling mobile ligands to soft membranes
Volume and porosity thermal regulation in lipid mesophases by coupling mobile ligands to soft membranes
DNA-functionalized particles can aggregate into materials with programmable morphology, but the response of these materials to external stimuli is limited. Here, the authors demonstrate how the structure of DNA-liposome aggregates can be controlled by changing temperature.
- Lucia Parolini
- , Bortolo M. Mognetti
- & Lorenzo Di Michele
-
Article |
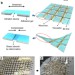 A strain-absorbing design for tissue–machine interfaces using a tunable adhesive gel
A strain-absorbing design for tissue–machine interfaces using a tunable adhesive gel
Biocompatibility is a limiting factor in the use of electronic sensors in physiological applications. Here, the authors present a flexible and conductive polymer gel as an adhesive interface material for electronic biosensors, also demonstrating in vivoheart attachment and monitoring.
- Sungwon Lee
- , Yusuke Inoue
- & Takao Someya
-
Article
| Open Access Structural reorganization of cylindrical nanoparticles triggered by polylactide stereocomplexation
Structural reorganization of cylindrical nanoparticles triggered by polylactide stereocomplexation
A polymer stereocomplex can possess quite different properties to its constituent homopolymers. Here, the authors prepare stereocomplex micelles of amphiphilic block-copolymers via crystallization-driven self-assembly, and observe a change from cylindrical to mixed spherical micelle morphology.
- Liang Sun
- , Anaïs Pitto-Barry
- & Andrew P. Dove
-
Article |
 Stretchable silicon nanoribbon electronics for skin prosthesis
Stretchable silicon nanoribbon electronics for skin prosthesis
An integrated electronic platform with site-specific sensitivity is highly needed for medical applications. Here, Kim et al.report a stretchable prosthetic skin composed of ultrathin single crystalline silicon nanoribbon array, which can sense strain, pressure and temperature spontaneously.
- Jaemin Kim
- , Mincheol Lee
- & Dae-Hyeong Kim
-
Article |
 Bio-inspired networks for optoelectronic applications
Bio-inspired networks for optoelectronic applications
Biological systems, subject to evolutionary optimization over millions of years, have been a source of ingenious solutions in many areas of science. Here, Han et al. develop transparent electrodes inspired by two such systems: a leaf venation and a spider’s web.
- Bing Han
- , Yuanlin Huang
- & Jinwei Gao
-
Article |
 Semi-permeable coatings fabricated from comb-polymers efficiently protect proteins in vivo
Semi-permeable coatings fabricated from comb-polymers efficiently protect proteins in vivo
The attachment of polymers to protein molecules is known to shield them from biological breakdown. Here, the authors apply this concept to an asparaginase, in order to prevent its deactiviation by host immune responses during leukaemia treatment.
- Mi Liu
- , Pål Johansen
- & Marc A. Gauthier
-
Article
| Open Access Mind-controlled transgene expression by a wireless-powered optogenetic designer cell implant
Mind-controlled transgene expression by a wireless-powered optogenetic designer cell implant
Brain–machine interfaces offer the possibility of controlling prosthetic devices using changes in brain activity. Folcher et al.couple such a system wirelessly to an optogenetic implant in mice to control expression of a transgene, demonstrating its potential for mind-controlled drug delivery.
- Marc Folcher
- , Sabine Oesterle
- & Martin Fussenegger
-
Article |
 CD95 and CD95L promote and protect cancer stem cells
CD95 and CD95L promote and protect cancer stem cells
The death receptor CD95/Fas induces apoptosis of many normal cells but prevents necrotic death of cancer cells. Here the authors demonstrate that CD95 activation promotes a cancer stem cell (CSC) phenotype, and that CSCs but not differentiated cancer cells are resistant to CD95-mediated apoptosis and depend on CD95 signalling to prevent necrosis.
- Paolo Ceppi
- , Abbas Hadji
- & Marcus E. Peter
-
Article |
 Biologically inspired pteridine redox centres for rechargeable batteries
Biologically inspired pteridine redox centres for rechargeable batteries
Bio-inspired organic materials are a promising class of battery electrodes. Here, the authors present the use of the redox centre of pteridine derivatives, essential constituents in cellular energy metabolism, in lithium and sodium battery systems, and show some excellent electrochemical performance.
- Jihyun Hong
- , Minah Lee
- & Kisuk Kang
-
Article |
 Bioinspired copper catalyst effective for both reduction and evolution of oxygen
Bioinspired copper catalyst effective for both reduction and evolution of oxygen
The conversion between water and oxygen is an important process in electrochemical devices, but is hindered by the large activation energy. Here, the authors report a copper-based catalyst capable of catalyzing both oxygen reduction and evolution, and identify the hydroxyl radical as the common intermediate.
- Jiong Wang
- , Kang Wang
- & Xing-Hua Xia
-
Article |
 Stimuli-sensitive intrinsically disordered protein brushes
Stimuli-sensitive intrinsically disordered protein brushes
Polymer brush surface coatings are important biomaterials for the reduction of biomolecule and cell adhesion. Here, the authors use a recombinantly expressed, intrinsically disordered protein to form a stimuli-responsive and enzyme-active polymer brush surface.
- Nithya Srinivasan
- , Maniraj Bhagawati
- & Sanjay Kumar
-
Article |
 Direct visualization of flow-induced conformational transitions of single actin filaments in entangled solutions
Direct visualization of flow-induced conformational transitions of single actin filaments in entangled solutions
Semi-flexible polymers are an important structural building block in living cells, which possess unique mechanical properties. Here, the authors visualize the shear-induced conformational transition of actin filaments as a model system to study cell formation in cytoplasmic flows.
- Inka Kirchenbuechler
- , Donald Guu
- & M. Paul Lettinga
-
Article |
 Programmable biofilm-based materials from engineered curli nanofibres
Programmable biofilm-based materials from engineered curli nanofibres
Bacterial cells use a self-generated extracellular matrix of various biomolecules in order to form biofilms and promote their stability. Here, the authors present a method for genetically controlling the composition of this extracellular matrix to yield more functional biofilms.
- Peter Q. Nguyen
- , Zsofia Botyanszki
- & Neel S. Joshi
-
Article |
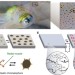 Cephalopod-inspired design of electro-mechano-chemically responsive elastomers for on-demand fluorescent patterning
Cephalopod-inspired design of electro-mechano-chemically responsive elastomers for on-demand fluorescent patterning
Cephalopods change colour by mechanically activating chromatophores via muscle contraction. Here, the authors use a similar concept for flexible displays, where electric field control over elastomer strain allows activation of mechanophores and provides on-demand and variable fluorescent patterns.
- Qiming Wang
- , Gregory R. Gossweiler
- & Xuanhe Zhao
-
Article |
 A toolbox of oligopeptide-modified polymers for tailored elastomers
A toolbox of oligopeptide-modified polymers for tailored elastomers
Biological systems are capable of building diverse structures starting from a limited number of chemical building blocks. Here, the authors show that polymers terminated with oligopeptides display assembly behaviour dependent on peptide length, and blends allow tailoring of a variety of material properties.
- Emmanuel Croisier
- , Su Liang
- & Holger Frauenrath
-
Article |
 Bioreactor droplets from liposome-stabilized all-aqueous emulsions
Bioreactor droplets from liposome-stabilized all-aqueous emulsions
Bioreactors need to separate the internal environment from the bulk, while also allowing entry and exit of substrate and product. Here, the authors make highly uniform, semipermeable droplets using an aqueous two-phase system, and show potential as microreactors based on a ribozyme cleavage reaction.
- Daniel C. Dewey
- , Christopher A. Strulson
- & Christine D. Keating
-
Article |
 Photoinitiated charge separation in a hybrid titanium dioxide metalloporphyrin peptide material
Photoinitiated charge separation in a hybrid titanium dioxide metalloporphyrin peptide material
Peptides can be used as templates for the synthesis of dye-sensitised semiconducting materials. Here, the authors design two peptides that give excellent and sequence specific control over the spatial arrangement of the semiconducting materials with respect to the dye molecule.
- H. Christopher Fry
- , Yuzi Liu
- & Tijana Rajh
-
Article |
 Lipid tail protrusions mediate the insertion of nanoparticles into model cell membranes
Lipid tail protrusions mediate the insertion of nanoparticles into model cell membranes
Gold nanoparticles coated with amphiphilic ligands can spontaneously insert into lipid bilayers, reducing hydrophobic interactions. Here, the authors show the key step in this process is similar to vesicle fusion: lipid tails from the bilayer protrude into water before encountering the nanoparticle.
- Reid C. Van Lehn
- , Maria Ricci
- & Alfredo Alexander-Katz
-
Article |
 Morphogenesis of filaments growing in flexible confinements
Morphogenesis of filaments growing in flexible confinements
Growing polymer chains are often confined within vesicles in biological systems. Here, the authors study how material properties such as friction, flexibility and thickness affect confined polymer filaments when they grow beyond their equilibrium size, identifying four unique morphologies.
- R. Vetter
- , F. K. Wittel
- & H. J. Herrmann
-
Article |
 Synergistic roles for lipids and proteins in the permanent adhesive of barnacle larvae
Synergistic roles for lipids and proteins in the permanent adhesive of barnacle larvae
Using their unique bioadhesives, barnacles can adhere to a great variety of surfaces. Here, Gohad et al.show that the barnacle larval bioadhesive contains lipids and phosphoproteins that are organized in a complex structure and work together to maximize adhesion.
- Neeraj V. Gohad
- , Nick Aldred
- & Andrew S. Mount
-
Article |
 High-power biofuel cell textiles from woven biscrolled carbon nanotube yarns
High-power biofuel cell textiles from woven biscrolled carbon nanotube yarns
Biofuel cells can be used as power sources for implantable biomedical devices, but suffer from limited power and lifetime. Here, Kwon et al.fabricate biscrolled carbon nanotube yarn electrodes, and demonstrate high fuel cell performances when used for glucose energy harvesting.
- Cheong Hoon Kwon
- , Sung-Ho Lee
- & Seon Jeong Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink
Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink
The application of 3D printing to biomaterials presents interesting possibilities for tissue engineering. Here, the authors show that a printing medium derived from an extracellular matrix can be applied to printing tissue analogues with enhanced cell compatibility.
- Falguni Pati
- , Jinah Jang
- & Dong-Woo Cho
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrodynamic alignment and assembly of nanofibrils resulting in strong cellulose filaments
Hydrodynamic alignment and assembly of nanofibrils resulting in strong cellulose filaments
Nanofibrils isolated from wood have potential as building blocks for materials, but in order to obtain high performance, control of the assembly process is needed. Here, the authors report a method to process nanofibrils using microfluidics, giving filaments with aligned fibrils and high strength.
- Karl M. O. Håkansson
- , Andreas B. Fall
- & L. Daniel Söderberg
-
Article
| Open Access Multiscale structural gradients enhance the biomechanical functionality of the spider fang
Multiscale structural gradients enhance the biomechanical functionality of the spider fang
Fangs are segments of the spider mouthparts, which are used to inject venom into prey and are required to sustain large mechanical loads. Here, the authors perform experiment-driven simulations, so to understand the correlation between the multiscale structural gradients and the biomechanical function of the fang.
- Benny Bar-On
- , Friedrich G. Barth
- & Yael Politi
-
Article
| Open Access Bio-inspired detoxification using 3D-printed hydrogel nanocomposites
Bio-inspired detoxification using 3D-printed hydrogel nanocomposites
Nanoparticles capable of selectively binding target chemicals have potential for detoxification processes, but can lead to accumulation in the liver. Here the authors show a 3D-printed device containing functional nanoparticles, allowing the detox potential to be realised while holding the particles in place.
- Maling Gou
- , Xin Qu
- & Shaochen Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental orthotopic transplantation of a tissue-engineered oesophagus in rats
Experimental orthotopic transplantation of a tissue-engineered oesophagus in rats
Patients with oesophageal diseases may require surgical removal and replacement of the oesophagus. Here the authors seed mesenchymal stromal cells on a decellularized rat oesophagus and show that this bioengineered tissue construct restores swallowing function after transplantation into rats.
- Sebastian Sjöqvist
- , Philipp Jungebluth
- & Paolo Macchiarini
-
Article |
 Tyrosine-mediated two-dimensional peptide assembly and its role as a bio-inspired catalytic scaffold
Tyrosine-mediated two-dimensional peptide assembly and its role as a bio-inspired catalytic scaffold
It is well known that the interplay between molecular ordering and interface geometry can determine the morphology of two-dimensional systems. Here, the authors report facet formation in water droplets, driven by peptide assembly, and investigate the structural and sequence motifs that affect this behaviour.
- Hyung-Seok Jang
- , Jung-Ho Lee
- & Yoon-Sik Lee
-
Article |
 The use of silk-based devices for fracture fixation
The use of silk-based devices for fracture fixation
Current bone fracture repair options include metallic and resorbable systems, both of which suffer from various issues and limitations. Here, the authors demonstrate resorbable and biocompatible silk bone screws, via in vivotesting.
- Gabriel S. Perrone
- , Gary G. Leisk
- & David L. Kaplan
-
Article |
 3D multifunctional integumentary membranes for spatiotemporal cardiac measurements and stimulation across the entire epicardium
3D multifunctional integumentary membranes for spatiotemporal cardiac measurements and stimulation across the entire epicardium
Tools for cardiac physiological mapping are important for basic and clinical cardiac research. Here the authors use 3D printing to create a thin, elastic silicone sheath that fits tightly around the entire epicardium and contains sensors to measure a variety of physiological parameters of the beating heart ex vivo.
- Lizhi Xu
- , Sarah R. Gutbrod
- & John A. Rogers
-
Article |
 Hybrid carbon nanotube yarn artificial muscle inspired by spider dragline silk
Hybrid carbon nanotube yarn artificial muscle inspired by spider dragline silk
Artificial muscles composed of carbon nanotube yarns have previously demonstrated fast, large-angle rotations. Here, the authors infiltrate carbon nanotube yarns with a paraffin wax and polystyrene-based copolymer mixture, achieving stable 9,800 r.p.m. rotation without apparent oscillation.
- Kyoung-Yong Chun
- , Shi Hyeong Kim
- & Seon Jeong Kim
-
Article |
 A cortical–spinal prosthesis for targeted limb movement in paralysed primate avatars
A cortical–spinal prosthesis for targeted limb movement in paralysed primate avatars
Brain–machine interfaces are being investigated for recovery of motor function after paralysis. Shanechi et al.present a neural prosthesis that decodes premotor neuronal activity in an alert monkey to activate spinal neurons and muscles that produce target-directed movements in a sedated monkey or avatar.
- Maryam M. Shanechi
- , Rollin C. Hu
- & Ziv M. Williams
-
Article |
 Cell death versus cell survival instructed by supramolecular cohesion of nanostructures
Cell death versus cell survival instructed by supramolecular cohesion of nanostructures
Self-assembly is a promising route for creating new functional biomaterials. Here, the authors find that subtle modifications to intermolecular interactions within supramolecular nanofibres can cause the disruption of lipid membranes and impart cytotoxicity or allow cells to survive.
- Christina J. Newcomb
- , Shantanu Sur
- & Samuel I. Stupp
-
Article |
 Textured fluorapatite bonded to calcium sulphate strengthen stomatopod raptorial appendages
Textured fluorapatite bonded to calcium sulphate strengthen stomatopod raptorial appendages
The raptorial appendages of stomatopods are known to inflict large impact forces at high speeds, while exhibiting large damage tolerance. Here, the authors study the structure, distribution and nanomechanical properties of mineral phases in stomatopod's clubs, finding that calcium sulphate is co-localized with crystalline fluorapatite.
- Shahrouz Amini
- , Admir Masic
- & Ali Miserez
-
Article
| Open Access Dehydration and crystallization of amorphous calcium carbonate in solution and in air
Dehydration and crystallization of amorphous calcium carbonate in solution and in air
The crystallization of amorphous calcium carbonate is a widely studied process. Here, the authors probe the mechanism and show that transformation to calcite is preceded by dehydration, even in solution, and that loss of the final water fraction triggers crystallization.
- Johannes Ihli
- , Wai Ching Wong
- & Fiona C. Meldrum
-
Article |
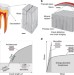 Overcoming the brittleness of glass through bio-inspiration and micro-architecture
Overcoming the brittleness of glass through bio-inspiration and micro-architecture
Glass is well known to be a brittle material, with fracture occurring soon after crack nucleation. Here, inspired by natural architectures, the authors report the laser patterning of features within an oxide glass, leading to a two order of magnitude improvement in fracture toughness.
- M. Mirkhalaf
- , A. Khayer Dastjerdi
- & F. Barthelat
-
Article |
 Artificial synapse network on inorganic proton conductor for neuromorphic systems
Artificial synapse network on inorganic proton conductor for neuromorphic systems
Realizing artificial synapses that mirror those found in the brain is a major challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate the fabrication of a laterally coupled oxide-based artificial synapse via a self-assembling process.
- Li Qiang Zhu
- , Chang Jin Wan
- & Qing Wan
-
Article |
 Forced protein unfolding leads to highly elastic and tough protein hydrogels
Forced protein unfolding leads to highly elastic and tough protein hydrogels
Protein-based hydrogels are of great interest for many biomedical applications. Here, the authors demonstrate the use of mechanical labile proteins to initiate large-scale forced unfolding in order to engineer the mechanical properties of protein-based biomaterials.
- Jie Fang
- , Alexander Mehlich
- & Hongbin Li

 The role of mechanics in biological and bio-inspired systems
The role of mechanics in biological and bio-inspired systems