Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Regulating protein corona on nanovesicles by glycosylated polyhydroxy polymer modification for efficient drug delivery
Regulating protein corona on nanovesicles by glycosylated polyhydroxy polymer modification for efficient drug delivery
The dynamic protein corona hinders the uptake of nanocarriers in desired target cell populations, limiting their bench-to-bedside translation. Here the authors reveal that the modification of hydroxyl and amino functional groups on nanovesicles can rationally regulate the composition of protein coronas to improve the efficiency of targeted drug delivery.
- Yunqiu Miao
- , Lijun Li
- & Yong Gan
-
Article
| Open Access Antiviral fibrils of self-assembled peptides with tunable compositions
Antiviral fibrils of self-assembled peptides with tunable compositions
In this work, the authors report the use of a computationally and rationally designed self-assembling peptide that has robust antiviral capability with demonstrated specificity in binding to SARS-CoV-2 and inhibition of viral entry into human cells.
- Joseph Dodd-o
- , Abhishek Roy
- & Vivek Kumar
-
Article
| Open Access Replicating shear-mediated self-assembly of spider silk through microfluidics
Replicating shear-mediated self-assembly of spider silk through microfluidics
Native spider silk has desirable mechanical properties, but these are challenging to replicate in an artificial material. Here, the authors report the use of a microfluidic system to create continuous fibers based on recombinant spidroin.
- Jianming Chen
- , Arata Tsuchida
- & Keiji Numata
-
Article
| Open Access Building block aspect ratio controls assembly, architecture, and mechanics of synthetic and natural protein networks
Building block aspect ratio controls assembly, architecture, and mechanics of synthetic and natural protein networks
Fibrous networks constructed from high aspect ratio protein building blocks are ubiquitous in nature, but the functional advantage of such building blocks over globular proteins is not understood. Here, using shear rheology and small-angle neutron scattering, the authors characterise the mechanical and structural properties of photochemically crosslinked protein L and fibrin networks and show that aspect ratio is a crucial property that defines network architecture and mechanics.
- Matt D. G. Hughes
- , Sophie Cussons
- & Lorna Dougan
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis of robust underwater glues from common proteins via unfolding-aggregating strategy
Synthesis of robust underwater glues from common proteins via unfolding-aggregating strategy
Underwater adhesive proteins greatly inspired the development of underwater glue but except for specific proteins it is believed that abundant common proteins cannot be converted into underwater glue. Here, the authors demonstrate, using bovine serum albumin as model protein, that unfolded common proteins exhibit high affinity to surfaces and strong internal cohesion via amyloid-like aggregation in water.
- Yongchun Liu
- , Ke Li
- & Peng Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Self-anticoagulant sponge for whole blood auto-transfusion and its mechanism of coagulation factor inactivation
Self-anticoagulant sponge for whole blood auto-transfusion and its mechanism of coagulation factor inactivation
Current methods for auto-transfusion often result in disturbances to the patient’s blood homeostasis, leading to an increased bleeding risk. Here, the authors develop heparin-mimicking self-anticoagulant sponges for safe and convenient whole blood auto-transfusion, and study underlying mechanisms.
- Tao Xu
- , Haifeng Ji
- & Changsheng Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Transforming sustainable plant proteins into high performance lubricating microgels
Transforming sustainable plant proteins into high performance lubricating microgels
Demand for plant proteins is increasing, but these often give an astringent sensation due to poor lubrication performance. Here, the authors report the development of plantprotein microgels with improved lubricity with potential in sustainable foods.
- Ben Kew
- , Melvin Holmes
- & Anwesha Sarkar
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic control of self-assembly and disassembly in organic materials
Magnetic control of self-assembly and disassembly in organic materials
Organic molecules and materials are generally insensitive or weakly sensitive to magnetic fields due to their small diamagnetic force. Here, the authors show a strategy to amplify the magnetic responsiveness of self-assembled peptide nanostructures by synergistically combining the concepts of perfect α-helix and rod-coil supramolecular building blocks
- You-jin Jung
- , Hyoseok Kim
- & Yong-beom Lim
-
Article
| Open Access Collagen breaks at weak sacrificial bonds taming its mechanoradicals
Collagen breaks at weak sacrificial bonds taming its mechanoradicals
Collagen is an important structural protein in connective tissue, but the effect of location and type of micro-ruptures in the structure on the overall tissue is not well understood. Here, the authors use scale-bridging simulations to determine the breakage points in collagen, and how the failure mode helps to prevent material ageing
- Benedikt Rennekamp
- , Christoph Karfusehr
- & Frauke Gräter
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogel oxygen reservoirs increase functional integration of neural stem cell grafts by meeting metabolic demands
Hydrogel oxygen reservoirs increase functional integration of neural stem cell grafts by meeting metabolic demands
Injectable biomimetic hydrogels hold significant promise for tissue engineering applications. Here, the authors present a hybrid myoglobin:peptide hydrogel to overcome a critical oxygen shortage following neural stem cell transplantation, thus increasing cell survival and integration.
- Y. Wang
- , E. R. Zoneff
- & D. R. Nisbet
-
Article
| Open Access Volumetric additive manufacturing of pristine silk-based (bio)inks
Volumetric additive manufacturing of pristine silk-based (bio)inks
Volumetric additive manufacturing of protein scaffolds has a wide range of possible biomedical applications. Here the authors report on the bioprinting of unmodified silk sericin and silk fibroin inks with shape-memory and tuneable mechanical properties and demonstrate the potential of the inks in different applications.
- Maobin Xie
- , Liming Lian
- & Yu Shrike Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Micro and nano-scale compartments guide the structural transition of silk protein monomers into silk fibers
Micro and nano-scale compartments guide the structural transition of silk protein monomers into silk fibers
By following morphological changes in supramolecular assemblies of silkworm silk, the authors find that while the initial steps of secretion and storage inside the silk gland follow the micelle theory of silk assembly, a phase rearrangement occurs inside microscale spherical structures that gives rise to the formation of nanoscale spherical assemblies.
- D. Eliaz
- , S. Paul
- & U. Shimanovich
-
Article
| Open Access Design of synthetic collagens that assemble into supramolecular banded fibers as a functional biomaterial testbed
Design of synthetic collagens that assemble into supramolecular banded fibers as a functional biomaterial testbed
Molecular level control is required to capture the folding and supramolecular assembly of collagen in mimetic materials. Here, the authors report on the creation of a synthetic collagen which assembles into banded fibers, recaptures structural properties of natural collagen and which can act as a testbed for design and experimentation
- Jinyuan Hu
- , Junhui Li
- & Fei Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Ectopic expression of sericin enables efficient production of ancient silk with structural changes in silkworm
Ectopic expression of sericin enables efficient production of ancient silk with structural changes in silkworm
Transgenic modification of silkworms has the potential to engineer new silks with a wider range of properties. Here, the authors engineered the expression of the outer layer sericin SER3 in the inner fibroin layer generating a new silk with higher production efficiency and resistance to alkaline conditions.
- Xuedong Chen
- , Yongfeng Wang
- & Shiqing Xu
-
Article
| Open Access A de novo matrix for macroscopic living materials from bacteria
A de novo matrix for macroscopic living materials from bacteria
Engineered living materials (ELMs) embed living cells in a biopolymer matrix to create novel materials with tailored functions. In this work, the authors engineered bacteria to grow novel macroscopic materials that can be reshaped, functionalized, and used to filter contaminated water while also showing that the stiffness of these materials can be tuned through genetic changes.
- Sara Molinari
- , Robert F. Tesoriero Jr.
- & Caroline M. Ajo-Franklin
-
Article
| Open Access Spidroin N-terminal domain forms amyloid-like fibril based hydrogels and provides a protein immobilization platform
Spidroin N-terminal domain forms amyloid-like fibril based hydrogels and provides a protein immobilization platform
Recombinant spider silks are of interest but the multimodal and aggregation-prone nature of them is a limitation. Here, the authors report on a miniature spidroin based on the N-terminal domain which forms a hydrogel at 37 °C which allows for ease of production and fusion protein modification to generate functional biomaterials.
- Tina Arndt
- , Kristaps Jaudzems
- & Anna Rising
-
Article
| Open Access Protein secondary structure in spider silk nanofibrils
Protein secondary structure in spider silk nanofibrils
Secondary fibril structure is a key component of the mechanical properties of protein materials like silk, yet, limited information is known about the internal structure of these protein fibrils. Here, the authors report on the use of polarised Raman and FTIR spectroscopy to study silk materials and identify six distinct secondary structures.
- Qijue Wang
- , Patrick McArdle
- & Hannes C. Schniepp
-
Article
| Open Access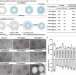 Nanoparticle elasticity affects systemic circulation lifetime by modulating adsorption of apolipoprotein A-I in corona formation
Nanoparticle elasticity affects systemic circulation lifetime by modulating adsorption of apolipoprotein A-I in corona formation
Nanoparticle elasticity is known to affect physiological fate but how this occurs is largely unknown. Here, the authors report on a study using nanoparticles differing in elasticity alone to show a difference in the protein corona, in particular apolipoprotein A-1 absorption, corresponds to differences in circulation time.
- Mingyang Li
- , Xinyang Jin
- & Lihua Yang
-
Article
| Open Access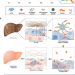 Fibroblast activation protein activated antifibrotic peptide delivery attenuates fibrosis in mouse models of liver fibrosis
Fibroblast activation protein activated antifibrotic peptide delivery attenuates fibrosis in mouse models of liver fibrosis
Activated hepatic stellate cells contribute towards the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis, and overexpress fibroblast activation protein. Here the authors report a targeted peptide-delivery system in which fibroblast activation protein liberates the antifibrotic peptide melittin, and demonstrate the approach attenuates fibrosis in mouse models of liver fibrosis.
- Jaiwoo Lee
- , Junho Byun
- & Yu-Kyoung Oh
-
Article
| Open Access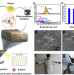 Liquid metal-tailored gluten network for protein-based e-skin
Liquid metal-tailored gluten network for protein-based e-skin
E-skins currently suffer from issues to do with the predominantly non-biological materials they are made from. Here, the authors report on a gluten network which is cross-linked with EGaIn liquid metal to make a self-healing, biocompatible, biodegradable, stretchable and conductive material which is demonstrated as a movement strain sensor.
- Bin Chen
- , Yudong Cao
- & Mingxin Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Protein nanowires with tunable functionality and programmable self-assembly using sequence-controlled synthesis
Protein nanowires with tunable functionality and programmable self-assembly using sequence-controlled synthesis
Bacterial hairs called pili become highly-conductive electric wires upon addition of both natural and synthetic amino acids conjugated with gold nanoparticles. Here the authors use computationally-guided ordering further increasing their conductivity, thus yielding genetically-programmable materials.
- Daniel Mark Shapiro
- , Gunasheil Mandava
- & Farren J. Isaacs
-
Article
| Open Access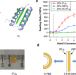 Engineering shape memory and morphing protein hydrogels based on protein unfolding and folding
Engineering shape memory and morphing protein hydrogels based on protein unfolding and folding
Engineering shape memory and morphing materials achieved considerable progress in polymer-based systems, but protein-based shape memory and morphing materials remain less investigated. Here, the authors report the engineering of protein-based shape memory and morphing hydrogels using protein folding-unfolding as a general mechanism to trigger shape morphing in protein-bilayer structures.
- Qingyuan Bian
- , Linglan Fu
- & Hongbin Li
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering Bacillus subtilis for the formation of a durable living biocomposite material
Engineering Bacillus subtilis for the formation of a durable living biocomposite material
Despite the advances in engineered living materials (ELMs), the diversity of ELMs especially those that are capable of autonomous self-fabrication and regeneration, is low. Here, the authors engineer a resilient ELM biocomposite using Bacillus subtilis and secreted EutM proteins as selfassembling scaffold building blocks.
- Sun-Young Kang
- , Anaya Pokhrel
- & Claudia Schmidt-Dannert
-
Article
| Open Access One-step construction of circularized nanodiscs using SpyCatcher-SpyTag
One-step construction of circularized nanodiscs using SpyCatcher-SpyTag
Circularised nanodiscs (cNDs) are able to stabilise large lipid bilayer patches and are used for structural and functional studies. Current techniques to build cNDs have numerous steps and low yields; here the authors report a single step construction method using the SpyCatcher-SpyTag system.
- Shanwen Zhang
- , Qian Ren
- & Huan Bao
-
Article
| Open Access Microbial production of megadalton titin yields fibers with advantageous mechanical properties
Microbial production of megadalton titin yields fibers with advantageous mechanical properties
Here, the authors engineer microbial production of muscle titin fibers with highly desirable mechanical properties and provide structural analyses that explain the molecular mechanisms underlying high performance of this polymer with potential uses in biomedicine and textile industries, among others.
- Christopher H. Bowen
- , Cameron J. Sargent
- & Fuzhong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled self-assembly of plant proteins into high-performance multifunctional nanostructured films
Controlled self-assembly of plant proteins into high-performance multifunctional nanostructured films
Green use of plant derived proteins in functional materials has been limited by inefficient methods to control micro and nanoscale structure. Here, the authors use nanoscale assembly of water-insoluble plant proteins to make meter scale films with comparable properties to conventional plastics.
- Ayaka Kamada
- , Marc Rodriguez-Garcia
- & Tuomas P. J. Knowles
-
Article
| Open Access Self-sustained green neuromorphic interfaces
Self-sustained green neuromorphic interfaces
For bio-inspired neuromorphic interfaces to emulate biological signal processing and self-sustainability, the mismatch between sensing and computing signals must be addressed. Here, the authors report sensor-driven, integrated neuromorphic systems with signal matching at the biological level.
- Tianda Fu
- , Xiaomeng Liu
- & Jun Yao
-
Review Article
| Open Access Protein nanofibrils for next generation sustainable water purification
Protein nanofibrils for next generation sustainable water purification
Water scarcity is a rapidly spreading global challenge but water purification technologies are often not sustainable. Here, the authors review the research on water purification technologies based on protein nanofibrils as a green and affordable solution to alleviate a water crisis.
- Mohammad Peydayesh
- & Raffaele Mezzenga
-
Article
| Open Access Design of multi-scale protein complexes by hierarchical building block fusion
Design of multi-scale protein complexes by hierarchical building block fusion
De novo design of self-assembling protein nanostructures and materials is of significant interest, however design of complex, multi-component assemblies is challenging. Here, the authors present a stepwise hierarchical approach to build such assemblies using helical repeat and helical bundle proteins as building blocks, and provide an in-depth structural characterization of the resulting assemblies.
- Yang Hsia
- , Rubul Mout
- & David Baker
-
Article
| Open Access Surface chemistry-mediated modulation of adsorbed albumin folding state specifies nanocarrier clearance by distinct macrophage subsets
Surface chemistry-mediated modulation of adsorbed albumin folding state specifies nanocarrier clearance by distinct macrophage subsets
Polymeric nanocarriers used for drug delivery are often coated by albumin in vivo influencing the therapeutic outcomes. Here, the authors engineer the surface chemistry of a nanocarrier to either stabilize or denature the structure of adsorbed albumin, resulting in evasion or clearance by macrophages.
- Michael P. Vincent
- , Sharan Bobbala
- & Evan A. Scott
-
Article
| Open Access Structural analysis of cross α-helical nanotubes provides insight into the designability of filamentous peptide nanomaterials
Structural analysis of cross α-helical nanotubes provides insight into the designability of filamentous peptide nanomaterials
Peptide-based filamentous assemblies are successfully used for generation of structurally ordered materials, but their de novo design and structural characterization is challenging. Here, the authors provide a strategy for the design of self-assembling peptide nanotubes based on modifications of an arginine clasp interaction motif, and report the cryo-EM structures of seven designed nanotubes.
- Fengbin Wang
- , Ordy Gnewou
- & Vincent P. Conticello
-
Article
| Open Access Behavior control of membrane-less protein liquid condensates with metal ion-induced phase separation
Behavior control of membrane-less protein liquid condensates with metal ion-induced phase separation
Mimetic membrane-less organelles are of interest for the range of biochemical processes which can be spatio-temporally organized using them. Here, the authors report on a protein condensate system formed by metal ion induced clustering and demonstrate control over condensate properties.
- Kibeom Hong
- , Daesun Song
- & Yongwon Jung
-
Article
| Open Access Development of A4 antibody for detection of neuraminidase I223R/H275Y-associated antiviral multidrug-resistant influenza virus
Development of A4 antibody for detection of neuraminidase I223R/H275Y-associated antiviral multidrug-resistant influenza virus
Rapid detection of antiviral resistant strains is important for effective clinical treatment. Here the authors develop an antibody which specifically binds to multidrug-resistant influenza virus and demonstrated detection in a number of different systems using the antibody.
- Kyeonghye Guk
- , Hyeran Kim
- & Juyeon Jung
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanoradicals in tensed tendon collagen as a source of oxidative stress
Mechanoradicals in tensed tendon collagen as a source of oxidative stress
The existence, nature and biological relevance of mechanoradicals in proteins are unknown. Here authors show that mechanical stress on collagen produces radicals and subsequently reactive oxygen species and suggest that collagen I evolved as a radical sponge against mechano-oxidative damage.
- Christopher Zapp
- , Agnieszka Obarska-Kosinska
- & Frauke Gräter
-
Article
| Open Access Polychromatic solar energy conversion in pigment-protein chimeras that unite the two kingdoms of (bacterio)chlorophyll-based photosynthesis
Polychromatic solar energy conversion in pigment-protein chimeras that unite the two kingdoms of (bacterio)chlorophyll-based photosynthesis
The spectra of light used by photosynthetic organisms are determined by their pigmentation colour palettes. Here Liu et al. show that a genetically-encoded chimera of light-harvesting proteins from plants and reaction centres from purple bacteria allows for polychromatic solar energy harvesting.
- Juntai Liu
- , Vincent M. Friebe
- & Michael R. Jones
-
Article
| Open Access Complex microparticle architectures from stimuli-responsive intrinsically disordered proteins
Complex microparticle architectures from stimuli-responsive intrinsically disordered proteins
The production of microparticles with complex geometries for biotechnological use historically requires sophisticated fabrication techniques. Here, the authors create complex particle geometries by exploiting the metastable region of the phase diagram of thermally responsive intrinsically disordered proteins within microdroplets.
- Stefan Roberts
- , Vincent Miao
- & Ashutosh Chilkoti
-
Article
| Open Access Single particles as resonators for thermomechanical analysis
Single particles as resonators for thermomechanical analysis
Eliminating the need for cleanroom fabrication for thermomechanical characterization of organic samples in a biomedical setting remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose the use of a single drug and collagen particles as resonators, enabling direct measurements on a material during thermal cycling.
- Peter Ouma Okeyo
- , Peter Emil Larsen
- & Anja Boisen
-
Article
| Open Access Disordered protein-graphene oxide co-assembly and supramolecular biofabrication of functional fluidic devices
Disordered protein-graphene oxide co-assembly and supramolecular biofabrication of functional fluidic devices
Self-organising systems have huge potential in device design and fabrication; however, demonstrations of this are limited. Here, the authors report on a combination of disordered proteins and graphene oxide which allows spatio-temporal patterning and demonstrate the fabrication of microfluidic devices.
- Yuanhao Wu
- , Babatunde O. Okesola
- & Alvaro Mata
-
Article
| Open Access Long-living and highly efficient bio-hybrid light-emitting diodes with zero-thermal-quenching biophosphors
Long-living and highly efficient bio-hybrid light-emitting diodes with zero-thermal-quenching biophosphors
Bio-hybrid LEDs (HLED) are an environmental friendly alternative to LEDs based on inorganic phosphors but achieving long term is challenging. Here, the authors present a long-living Bio-HLED based on a zero-thermal-quenching biophosphor design and investigate the photo-induced heat generation and dissipation processes.
- Anna Espasa
- , Martina Lang
- & Rubén D. Costa
-
Article
| Open Access Polypeptide templating for designer hierarchical materials
Polypeptide templating for designer hierarchical materials
Despite recent progress in directed assembly of protein molecules into well-defined nanostructures, bridging materials fabrication from nano- to macroscale remains a challenge. Here, using silk fibroin as an example, the authors demonstrate templated crystallization to drive hierarchical materials growth from disordered molecules all the way up to centimeter scale.
- Hui Sun
- & Benedetto Marelli
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered E. coli Nissle 1917 for the delivery of matrix-tethered therapeutic domains to the gut
Engineered E. coli Nissle 1917 for the delivery of matrix-tethered therapeutic domains to the gut
Anti-inflammatory treatments for gastrointestinal diseases can often have detrimental side effects. Here the authors engineer E. coli Nissle 1917 to create a fibrous matrix that has a protective effect in DSS-induced colitis mice.
- Pichet Praveschotinunt
- , Anna M. Duraj-Thatte
- & Neel S. Joshi
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogen bond guidance and aromatic stacking drive liquid-liquid phase separation of intrinsically disordered histidine-rich peptides
Hydrogen bond guidance and aromatic stacking drive liquid-liquid phase separation of intrinsically disordered histidine-rich peptides
Liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) of intrinsically disordered proteins plays an important part in the formation of extracellular biological materials. Here, the authors show that repeats of the peptide motif GHGLY are necessary for the LLPS of pH-responsive histidine-rich squid beak proteins.
- Bartosz Gabryelczyk
- , Hao Cai
- & Ali Miserez
-
Article
| Open Access Packaging and delivering enzymes by amorphous metal-organic frameworks
Packaging and delivering enzymes by amorphous metal-organic frameworks
For packaging enzymes into metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), crystalline MOFs are usually used. Here, the authors encapsulated enzymes in amorphous MOFs a via one-pot co-precipitation process under ambient condition, which led to higher enzymatic activity than in a corresponding crystalline MOF composite.
- Xiaoling Wu
- , Hua Yue
- & Jun Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Active DNA unwinding and transport by a membrane-adapted helicase nanopore
Active DNA unwinding and transport by a membrane-adapted helicase nanopore
Active translocation of DNA through nanopores usually needs enzyme assistance. Here authors present a nanopore derived from helicase E1 of bovine papillomavirus (BPV) which acts as a conductive pore embedded in lipid membrane to allow the translocation of ssDNA and unwinding of dsDNA.
- Ke Sun
- , Changjian Zhao
- & Jia Geng
-
Article
| Open Access Transforming protein-polymer conjugate purification by tuning protein solubility
Transforming protein-polymer conjugate purification by tuning protein solubility
Therapeutic proteins are often conjugated with polymers, but separating the conjugate from unconjugated protein and free polymer is a major challenge. Here, the authors discover that proteins conjugated to charged or zwitterionic polymers maintain solubility in 100% ammonium sulfate, greatly simplifying purification.
- Stefanie L. Baker
- , Aravinda Munasinghe
- & Alan J. Russell
-
Article
| Open Access Covalently-assembled single-chain protein nanostructures with ultra-high stability
Covalently-assembled single-chain protein nanostructures with ultra-high stability
De novo protein nanostructures are typically assembled via top-down approaches. Here, the authors developed a bottom-up approach, using split inteins to ligate multiple copies of a three-helix bundle to create 2D triangular and square-shaped structures with high stability.
- Wenqin Bai
- , Cameron J. Sargent
- & Fuzhong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Multifunctional and biodegradable self-propelled protein motors
Multifunctional and biodegradable self-propelled protein motors
Several factors have limited the potential/application of self-propelled chemical motors. Here, to address some of these concerns, the authors report on the development of squid-derived biodegradable motors, which use an anaesthetic metabolite for propulsion and demonstrate a range of different applications.
- Abdon Pena-Francesch
- , Joshua Giltinan
- & Metin Sitti
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial coiled coil biomineralisation protein for the synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles
Artificial coiled coil biomineralisation protein for the synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles
Proteins have been used in the synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles but issues with aggregation limit this application. Here, the authors report on the synthesis of coiled proteins that display the active loop of the natural proteins to avoid aggregation and investigate the application in nanoparticle synthesis.
- Andrea E. Rawlings
- , Lori A. Somner
- & Sarah S. Staniland
-
Article
| Open Access Topologically-guided continuous protein crystallization controls bacterial surface layer self-assembly
Topologically-guided continuous protein crystallization controls bacterial surface layer self-assembly
Bacteria assemble the surface layer (S-layer), a crystalline protein coat surrounding the curved surface, using protein self-assembly. Here authors image native and purified RsaA, the S-layer protein from C. crescentus, and show that protein crystallization alone is sufficient to assemble and maintain the S-layer in vivo.
- Colin J. Comerci
- , Jonathan Herrmann
- & W. E. Moerner

 Impact of PEG sensitization on the efficacy of PEG hydrogel-mediated tissue engineering
Impact of PEG sensitization on the efficacy of PEG hydrogel-mediated tissue engineering