Featured
-
-
Article |
 A monomeric red fluorescent protein with low cytotoxicity
A monomeric red fluorescent protein with low cytotoxicity
Fluorescent proteins are widely used to image cellular structures. Here, Shemiakina and colleagues develop an enhanced version of a red fluorescent protein that is monomeric and less cytotoxic, thereby improving the quality of images that can be obtained in the red part of the visible spectrum.
- I.I. Shemiakina
- , G.V. Ermakova
- & D. Shcherbo
-
Article |
 Engineering RNA endonucleases with customized sequence specificities
Engineering RNA endonucleases with customized sequence specificities
Sequence-specific DNA endonucleases have found numerous applications in biology, but similar manipulations of RNA have been limited by the lack of suitable enzymes. These authors combine a cleavage domain with a designable binding domain and demonstrate the resulting RNA endonuclease's utilityin vitroand in cells.
- Rajarshi Choudhury
- , Yihsuan S. Tsai
- & Zefeng Wang
-
Article |
 Imaging the post-fusion release and capture of a vesicle membrane protein
Imaging the post-fusion release and capture of a vesicle membrane protein
Rapid synaptic transmission requires efficient recycling of synaptic vesicle membrane proteins. Sochackiet al.use live cell, electron and super-resolution microscopy to visualize exocytosis of vesicular transporters and their rapid recapture in clathrin-rich microdomains in the plasma membrane.
- Kem A. Sochacki
- , Ben T. Larson
- & Justin W. Taraska
-
Article |
 Identifying the preferred RNA motifs and chemotypes that interact by probing millions of combinations
Identifying the preferred RNA motifs and chemotypes that interact by probing millions of combinations
Identifying molecules that bind to RNA is difficult because information about RNA–ligand interactions is limited. Tran and Disney report a solution-based screening method that can probe large numbers of RNA motif-small molecule interactions to identify privileged RNA structures and chemical spaces that interact.
- Tuan Tran
- & Matthew D. Disney
-
Article |
 Protein encapsulation within synthetic molecular hosts
Protein encapsulation within synthetic molecular hosts
Protein encapsulation in molecular cages has the potential to alter protein function and aid crystallization. Here, ubiquitin is encapsulated within a giant coordination cage; the protein is attached to a bidentate ligand, and the cage self-assembles upon addition of capping ligands and Pd(II) ions.
- Daishi Fujita
- , Kosuke Suzuki
- & Makoto Fujita
-
Article
| Open Access A kinase inhibitor screen identifies small-molecule enhancers of reprogramming and iPS cell generation
A kinase inhibitor screen identifies small-molecule enhancers of reprogramming and iPS cell generation
The efficiency of reprogramming somatic cells to induced pluripotent stem cells is low. To enhance reprogramming efficiency, Li and Rana used a chemical screen and identified several kinase inhibitors that enhance reprogramming, and show that blocking Aurora A, p38 and inositiol triphosphate 3-kinase signalling is important for this process.
- Zhonghan Li
- & Tariq M. Rana
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of an inhibitory restraint of seizure activity in humans
Evidence of an inhibitory restraint of seizure activity in humans
Seizure activity in the brain is characterized by the recruitment of cortical neuronal activity. Schevon and colleagues study seizure activity in human subjects and find that the recruitment of neurons is hypersynchronous and that there is an intrinsic restraint on the propagation of this activity.
- Catherine A. Schevon
- , Shennan A. Weiss
- & Andrew J. Trevelyan
-
Article |
 Real-time in vivo imaging of the beating mouse heart at microscopic resolution
Real-time in vivo imaging of the beating mouse heart at microscopic resolution
Microscopic imaging techniques have a high spatio-temporal resolution but, in living animals, are hampered by cardiac and respiratory motion. This paper describes a microscopic setup that allows fluorescent confocal imaging of the beating mouse heart over a period of several hours.
- Sungon Lee
- , Claudio Vinegoni
- & Ralph Weissleder
-
Article |
 Biocompatibility of a genetically encoded calcium indicator in a transgenic mouse model
Biocompatibility of a genetically encoded calcium indicator in a transgenic mouse model
Calcium-sensing fluorescent proteins such as TN-XXL are valuable tools for studying cellular function but, when expressed in mice, may affect animal physiology and behaviour. The authors of this paper create transgenic mice expressing TN-XXL and show that long-term expression of TN-XXL is tolerated well.
- Stephan Direnberger
- , Marsilius Mues
- & Oliver Griesbeck
-
Article |
 Imaging enzyme-triggered self-assembly of small molecules inside live cells
Imaging enzyme-triggered self-assembly of small molecules inside live cells
Supramolecular interactions allow some small molecules to self-assemble into nanofibres and hydrogels in aqueous environments. Gaoet al.report a hydrogelator that forms fluorescent nanofibres within cells, leading to the visualization of their self-assembly at the endoplasmic reticulum.
- Yuan Gao
- , Junfeng Shi
- & Bing Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Active learning framework with iterative clustering for bioimage classification
Active learning framework with iterative clustering for bioimage classification
Semi-automated imaging systems help with the task of classifying large numbers of biological images. This study presents a novel framework—CARTA—with an active learning algorithm combined with a genetic algorithm, whose applications include the classification of magnetic resonance imaging of cancer cells.
- Natsumaro Kutsuna
- , Takumi Higaki
- & Seiichiro Hasezawa
-
Article
| Open Access Non-transgenic genome modifications in a hemimetabolous insect using zinc-finger and TAL effector nucleases
Non-transgenic genome modifications in a hemimetabolous insect using zinc-finger and TAL effector nucleases
Hemimetabolous insects comprise many pests but introducing targeted mutations into these species has been difficult. This paper reports efficient targeted mutagenesis, and the generation of homozygous knockouts, in crickets based on zinc finger nucleases or transcription activator-like effector nucleases.
- Takahito Watanabe
- , Hiroshi Ochiai
- & Taro Mito
-
Article
| Open Access Proteomic screen reveals Fbw7 as a modulator of the NF-κB pathway
Proteomic screen reveals Fbw7 as a modulator of the NF-κB pathway
Fbw7 is a ubiquitin-ligase, which targets several oncoproteins for proteolysis, and is therefore important for the control and prevention of tumorigenesis. In this study, Arabi and colleagues carry out a proteomic screen of the targets of Fbw7, and identify Nuclear Factor of κ-B2 as a substrate.
- Azadeh Arabi
- , Karim Ullah
- & Olle Sangfelt
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance and site-directed in utero electroporation by a triple-electrode probe
High-performance and site-directed in utero electroporation by a triple-electrode probe
In uteroelectroporation allows the labelling of specific populations of neurons in the developing mouse brain. The authors of this paper present a simple modification of this method that increases labelling efficiency and allows, for the first time, transfection of Purkinje cells in the rat cerebellum.
- Marco dal Maschio
- , Diego Ghezzi
- & Laura Cancedda
-
Article
| Open Access Switching of myosin-V motion between the lever-arm swing and Brownian search-and-catch
Switching of myosin-V motion between the lever-arm swing and Brownian search-and-catch
The motor protein myosin-V transports cargo along actin filaments, but the biophysical mechanisms by which myosin-V generates force are unclear. Here, optical tweezers and a DNA handle are used to study the forces generated by myosin-V: the mechanism of force generation is found to depend on the load applied.
- Keisuke Fujita
- , Mitsuhiro Iwaki
- & Toshio Yanagida
-
Article
| Open Access Deep-tissue focal fluorescence imaging with digitally time-reversed ultrasound-encoded light
Deep-tissue focal fluorescence imaging with digitally time-reversed ultrasound-encoded light
Fluorescence imaging is important for biomedical research and applications, but the turbidity of biological material prohibits deep tissue study. By combining ultrasound-encoding with digital time-reversal, Wanget al.perform focussed fluorescence imaging at a tissue depth of 2.5mm.
- Ying Min Wang
- , Benjamin Judkewitz
- & Changhuei Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Microscopic magnetic stimulation of neural tissue
Microscopic magnetic stimulation of neural tissue
Electrical stimulation is used to treat a range of neurological diseases, but there are limitations that reduce its benefits. Bonmassar and colleagues show that magnetic stimulation delivered by small coils, close to the targeted neural tissue, can also be used to activate neurons and with fewer limitations.
- Giorgio Bonmassar
- , Seung Woo Lee
- & John T. Gale
-
Article |
 Visualizing specific protein glycoforms by transmembrane fluorescence resonance energy transfer
Visualizing specific protein glycoforms by transmembrane fluorescence resonance energy transfer
A common post-translational modification is the attachment of sugars, but proteins with different sugar chains, known as glycoforms, are hard to distinguish. Here, the authors use transmembrane fluorescence resonance energy transfer to visualize specific glycoforms of the membrane protein GLUT4 in living cells.
- Yoshimi Haga
- , Kumiko Ishii
- & Tadashi Suzuki
-
Article |
 Reliable detection of subclonal single-nucleotide variants in tumour cell populations
Reliable detection of subclonal single-nucleotide variants in tumour cell populations
The detection of subclonal variants in heterogeneous cancer specimens is a challenge due to errors that occur during sequencing. In this study, a statistical algorithm and a sequencing strategy are reported that circumvent this issue and can accurately detect variants at a frequency as low as 1/10,000.
- Moritz Gerstung
- , Christian Beisel
- & Niko Beerenwinkel
-
Article
| Open Access Combinatorial targeting and discovery of ligand-receptors in organelles of mammalian cells
Combinatorial targeting and discovery of ligand-receptors in organelles of mammalian cells
Phage display screening can unravel protein–protein interactions, but its application has been mainly restricted to the cell surface. Here, a phage-based reagent is introduced that allows the targeting of combinatorial peptides to cell organelles, providing a tool for the discovery of intracellular ligand-receptors.
- Roberto Rangel
- , Liliana Guzman-Rojas
- & Wadih Arap
-
Article |
 Nanodomain Ca2+ of Ca2+ channels detected by a tethered genetically encoded Ca2+ sensor
Nanodomain Ca2+ of Ca2+ channels detected by a tethered genetically encoded Ca2+ sensor
Calcium nanodomains arise from the cytoplasmic mouth of calcium channels but have not been directly visualized. In this study, the nanodomain of the CaV2.2 calcium channel is imaged using total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy and a genetically encoded calcium sensor attached to the carboxy terminus.
- Lai Hock Tay
- , Ivy E. Dick
- & David T. Yue
-
Article
| Open Access Neural circuits in the brain that are activated when mitigating criminal sentences
Neural circuits in the brain that are activated when mitigating criminal sentences
Jurors can be influenced by mitigating circumstances when deciding on sentences for committed crimes. Yamadaet al. show that feelings of sympathy created by mitigating circumstances activate moral conflict regions of the brain that predict individual differences in the severity of the sentence.
- Makiko Yamada
- , Colin F. Camerer
- & Hidehiko Takahashi
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-guided evolution of cyan fluorescent proteins towards a quantum yield of 93%
Structure-guided evolution of cyan fluorescent proteins towards a quantum yield of 93%
Cyan variants of green fluorescent protein (CFPs) are widely used as donors in FRET experiments. Here, a new CFP, mTurquoise2, is developed, which displays a high-fluorescence quantum yield and a long mono-exponential fluorescence lifetime.
- Joachim Goedhart
- , David von Stetten
- & Antoine Royant
-
Article
| Open Access Infrared light excites cells by changing their electrical capacitance
Infrared light excites cells by changing their electrical capacitance
Pulsed infrared laser light can directly stimulate nerves and muscles, but the underlying biophysical mechanism has remained enigmatic. This study reveals that infrared pulses depolarize target cells by reversibly altering the electrical capacitance of the plasma membrane.
- Mikhail G. Shapiro
- , Kazuaki Homma
- & Francisco Bezanilla
-
Article
| Open Access Intracellular temperature mapping with a fluorescent polymeric thermometer and fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy
Intracellular temperature mapping with a fluorescent polymeric thermometer and fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy
Intracellular temperature mapping has not previously been achieved. Now, a fluorescent polymeric thermometer has been developed that can be used in combination with fluorescence-lifetime imaging microscopy to allow thermometry with spatial and temperature resolutions of 200 nm and 0.18–0.58 ° C.
- Kohki Okabe
- , Noriko Inada
- & Seiichi Uchiyama
-
Article |
 Mapping of H3N2 influenza antigenic evolution in China reveals a strategy for vaccine strain recommendation
Mapping of H3N2 influenza antigenic evolution in China reveals a strategy for vaccine strain recommendation
Influenza vaccines are updated frequently to accommodate changing influenza antigenicity. Here, the authors develop a new computational method for predicting the antigenicity of H3N2 influenza strains based on the HA sequence.
- Xiangjun Du
- , Libo Dong
- & Taijiao Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Draft genome sequence and genetic transformation of the oleaginous alga Nannochloropsis gaditana
Draft genome sequence and genetic transformation of the oleaginous alga Nannochloropsis gaditana
Algae show much promise in the production of biofuels owing to their high photoautotrophic biomass and lipid production rates. In this study, the draft genome ofNannochloropsis gaditanaCCMP526 and a method for the transformation of this alga are reported, facilitating the investigation of lipid synthesis and biofuel production.
- Randor Radakovits
- , Robert E. Jinkerson
- & Matthew C. Posewitz
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional analysis of ribonucleoprotein complexes in influenza A virus
Three-dimensional analysis of ribonucleoprotein complexes in influenza A virus
The influenza A virus genome consists of eight RNA segments, which permits genetic reassortment and contributes to the emergence of novel strains with pandemic potential. Here, electron tomography is used to study the three-dimensional structure of ribonucleoprotein complexes within progeny virions.
- Takeshi Noda
- , Yukihiko Sugita
- & Yoshihiro Kawaoka
-
Article |
 Biomedical photoacoustics beyond thermal expansion using triggered nanodroplet vaporization for contrast-enhanced imaging
Biomedical photoacoustics beyond thermal expansion using triggered nanodroplet vaporization for contrast-enhanced imaging
A dual-contrast agent has been developed for combined ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging. This agent uses vaporization for ultrasound contrast enhancement and photoacoustic signal generation, providing significantly higher signals than thermal expansion, the most commonly used photoacoustic mechanism.
- Katheryne Wilson
- , Kimberly Homan
- & Stanislav Emelianov
-
Article |
 Programmable multivalent display of receptor ligands using peptide nucleic acid nanoscaffolds
Programmable multivalent display of receptor ligands using peptide nucleic acid nanoscaffolds
Multivalent display of integrin antagonists enhances their efficacy, but current synthetic scaffolds used to display ligands are limited in range and precision. Englundet al. develop a new scaffold to study the multivalent effects of integrin antagonists across wide ranges of ligand number, density, and 3D arrangement.
- Ethan A. Englund
- , Deyun Wang
- & Daniel H. Appella
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic quorum-sensing circuit to control consortial biofilm formation and dispersal in a microfluidic device
Synthetic quorum-sensing circuit to control consortial biofilm formation and dispersal in a microfluidic device
Engineered biofilms have applications in biorefineries. Here, Honget al. engineer bacteria to produce a combination of dispersal proteins and quorum sensing factors, and show that one dispersing bacterium can eliminate a biofilm formed by a colonizing bacterium.
- Seok Hoon Hong
- , Manjunath Hegde
- & Thomas K. Wood
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-based mutagenesis reveals the albumin-binding site of the neonatal Fc receptor
Structure-based mutagenesis reveals the albumin-binding site of the neonatal Fc receptor
Albumin transport proteins circulate in the blood and are protected from degradation by interaction with the neonatal Fc receptor. Andersenet al. investigate the albumin binding site of the neonatal Fc receptor and find pH sensitive ionic networks at the binding interface.
- Jan Terje Andersen
- , Bjørn Dalhus
- & Inger Sandlie
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide functional screening of miR-23b as a pleiotropic modulator suppressing cancer metastasis
Genome-wide functional screening of miR-23b as a pleiotropic modulator suppressing cancer metastasis
microRNAs are known to be deregulated in cancer. Using a screen for microRNAs that alter cell migration, Zhanget al. show that mir-23b blocks cell migration in vitro and in vivoand is reduced in expression in human colon cancer, suggesting a therapeutic potential for this microRNA.
- Hanshuo Zhang
- , Yang Hao
- & Jianzhong Jeff Xi
-
Article |
 Metabolomic high-content nuclear magnetic resonance-based drug screening of a kinase inhibitor library
Metabolomic high-content nuclear magnetic resonance-based drug screening of a kinase inhibitor library
Metabolism is altered in many diseases, and monitoring metabolic changes during treatment could facilitate investigations into treatment efficacy and cellular responses. This study reports an NMR-based method to screen the metabolic responses of mammalian cells to drugs.
- Stefano Tiziani
- , Yunyi Kang
- & Giovanni Paternostro
-
Article |
 Genetic dissection of axon regeneration via in vivo electroporation of adult mouse sensory neurons
Genetic dissection of axon regeneration via in vivo electroporation of adult mouse sensory neurons
Dorsal root ganglion neurons can regenerate after injury, but the mechanisms underlying axon regrowth are unclear. To address this, an electroporation transfection method is developed that can alter the gene expression of dorsal root ganglion cells in a living adult mouse, providing a tool to study axon regeneration.
- Saijilafu
- , Eun-Mi Hur
- & Feng-Quan Zhou
-
Article |
 Super-resolution surface mapping using the trajectories of molecular probes
Super-resolution surface mapping using the trajectories of molecular probes
Surface characterization of soft materialsin situis challenging due to the importance of non-covalent interactions. Now, a new chemical imaging method is reported that generates images of surface interactions by combining many molecular probe trajectories.
- Robert Walder
- , Nathaniel Nelson
- & Daniel K. Schwartz
-
Article |
 Electrosensory ampullary organs are derived from lateral line placodes in bony fishes
Electrosensory ampullary organs are derived from lateral line placodes in bony fishes
Ampullary organs are involved in electroreception, but whether these are derived from placodes, thickened ectoderm, is unclear. In this study, the ampullary organs of the primitive ray-finned fish,Polyodon spathula, are shown to develop from lateral line placodes, suggesting that this is the ancestral state in bony fishes.
- Melinda S. Modrell
- , William E. Bemis
- & Clare V.H. Baker
-
Article |
 Reprogramming within hours following nuclear transfer into mouse but not human zygotes
Reprogramming within hours following nuclear transfer into mouse but not human zygotes
The generation of human cell lines using somatic cell nuclear transfer has been difficult to achieve. In this study, Egliet al. show that while mouse eggs reprogram somatic cells within hours, human eggs arrest after nuclear transfer which may be due to a lack of genome transcription.
- Dieter Egli
- , Alice E. Chen
- & Kevin Eggan
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association mapping reveals a rich genetic architecture of complex traits in Oryza sativa
Genome-wide association mapping reveals a rich genetic architecture of complex traits in Oryza sativa
Understanding the genetics and physiology of domesticated species is important for crop improvement. By studying natural variation and the phenotypic traits of 413 diverse accessions of rice, Zhao et al. identify many common genetic variants that influence quantitative traits such as seed size and flowering time.
- Keyan Zhao
- , Chih-Wei Tung
- & Susan R. McCouch
-
Article
| Open Access A segmental genomic duplication generates a functional intron
A segmental genomic duplication generates a functional intron
The appearance of a new intron that splits an exon without disrupting the corresponding peptide sequence is a rare event in vertebrate genomes. Hellstenet al.demonstrate that, under certain circumstances, a functional intron can be produced in a single step by segmental genomic duplication.
- Uffe Hellsten
- , Julie L. Aspden
- & Daniel S. Rokhsar
-
Article |
 Discovery of lost diversity of paternal horse lineages using ancient DNA
Discovery of lost diversity of paternal horse lineages using ancient DNA
Modern female horses are genetically diverse but male horses are relatively homogenous. Lippoldet al. sequence the Y chromosome of nine ancient horses and detect diversity in the ancestral paternal lineage, demonstrating ancient Y-chromosomal DNA sequencing can provide insights into evolution.
- Sebastian Lippold
- , Michael Knapp
- & Michael Hofreiter
-
Article
| Open Access Freely orbiting magnetic tweezers to directly monitor changes in the twist of nucleic acids
Freely orbiting magnetic tweezers to directly monitor changes in the twist of nucleic acids
Rotational motion and torsional strain affects DNA replication, transcription and repair. Lipfertet al. have developed a new technique that uses freely orbiting magnetic tweezers to measure equilibrium fluctuations and determine the twist of tethered nucleic acid molecules.
- Jan Lipfert
- , Matthew Wiggin
- & Nynke H. Dekker
-
Article |
 Detection of focal adhesion kinase activation at membrane microdomains by fluorescence resonance energy transfer
Detection of focal adhesion kinase activation at membrane microdomains by fluorescence resonance energy transfer
The focal adhesion kinase has a role in cell adhesion and migration. In this study, a fluorescent resonance energy transfer biosensor is designed to monitor focal adhesion kinase activity at membrane microdomains, revealing that the mechanisms that activate focal adhesion kinase are stimulus dependent.
- Jihye Seong
- , Mingxing Ouyang
- & Yingxiao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access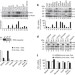 Toxicity modelling of Plk1-targeted therapies in genetically engineered mice and cultured primary mammalian cells
Toxicity modelling of Plk1-targeted therapies in genetically engineered mice and cultured primary mammalian cells
Polo-like kinase 1 is a key regulator of mitosis and is a candidate for drug development to treat cancer. Here, reduced expression of polo-like kinase 1 in adult mice has a minor impact on animal physiology, suggesting that polo-like kinase 1 inhibitors may be useful in the killing of tumour cells while sparing normal cells.
- Monika Raab
- , Sven Kappel
- & Klaus Strebhardt
-
Article |
 A photoconvertible fluorescent reporter to track chaperone-mediated autophagy
A photoconvertible fluorescent reporter to track chaperone-mediated autophagy
Soluble cytosolic proteins can be degraded in lysosomes by chaperone-mediated autophagy, however, the current method to measure this process requires isolation of lysosomes. Now, a fluorescent reporter is described that can measure this type of autophagy in intact cells.
- Hiroshi Koga
- , Marta Martinez-Vicente
- & Ana Maria Cuervo
-
Article |
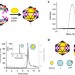 A synthetic icosahedral DNA-based host–cargo complex for functional in vivo imaging
A synthetic icosahedral DNA-based host–cargo complex for functional in vivo imaging
Encapsulating molecules within supramolecular frameworks for potential biological application is challenging. Bhatiaet al. incorporate a fluorescent polymer within an icosahedral DNA nanocapsule, and show that it can be used to target specific cells in vivoand map pH spatially and temporally.
- Dhiraj Bhatia
- , Sunaina Surana
- & Yamuna Krishnan
-
Article |
 The neural circuits and sensory channels mediating harsh touch sensation in Caenorhabditis elegans
The neural circuits and sensory channels mediating harsh touch sensation in Caenorhabditis elegans
The mechanisms by which animals distinguish between harsh and gentle touch are unclear. UsingCaenorhabditis elegansas a model system, the authors identify neural circuits and touch-sensitive ion channels that are required for harsh touch sensation.
- Wei Li
- , Lijun Kang
- & X.Z. Shawn Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting sites of ADAR editing in double-stranded RNA
Predicting sites of ADAR editing in double-stranded RNA
ADAR enzymes edit double-stranded RNA, converting adenosines to inosines, and are essential for neuronal function. Eggingtonet al. quantify edit sites in RNA using a Sanger sequencing protocol and use the resulting data to develop algorithms to predict RNA edit sites.
- Julie M. Eggington
- , Tom Greene
- & Brenda L. Bass
-
Article
| Open Access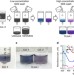 Large-scale single-chirality separation of single-wall carbon nanotubes by simple gel chromatography
Large-scale single-chirality separation of single-wall carbon nanotubes by simple gel chromatography
Large-scale separation of single-wall carbon nanotubes into populations of single chirality is a significant challenge in the practical application of nanotubes. Now, using multicolumn gel chromatography, the large-scale separation of 13 different carbon nanotube species is achieved.
- Huaping Liu
- , Daisuke Nishide
- & Hiromichi Kataura
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Analytical biochemistry
- Behavioural methods
- Bioinformatics
- Biological models
- Biophysical methods
- Cytological techniques
- Electrophysiology
- Epigenetics analysis
- Experimental organisms
- Gene delivery
- Gene expression analysis
- Genetic engineering
- Genetic techniques
- Genomic analysis
- High-throughput screening
- Imaging
- Immunological techniques
- Isolation, separation and purification
- Lab-on-a-chip
- Mass spectrometry
- Metabolomics
- Microbiology techniques
- Microscopy
- Molecular engineering
- Nanobiotechnology
- Optogenetics
- Proteomic analysis
- Sensors and probes
- Sequencing
- Software
- Optical spectroscopy
- Structure determination

 Diminishing returns and tradeoffs constrain the laboratory optimization of an enzyme
Diminishing returns and tradeoffs constrain the laboratory optimization of an enzyme