Featured
-
-
Article |
 Optofluidic laser for dual-mode sensitive biomolecular detection with a large dynamic range
Optofluidic laser for dual-mode sensitive biomolecular detection with a large dynamic range
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays are common biological analyses, but they can be hindered by non-specific binding and background interference. Here, the authors present an optofluidic laser-based ELISA technique with low detection limits and in the presence of significant non-specific binding.
- Xiang Wu
- , Maung Kyaw Khaing Oo
- & Xudong Fan
-
Article
| Open Access The stimulus-evoked population response in visual cortex of awake monkey is a propagating wave
The stimulus-evoked population response in visual cortex of awake monkey is a propagating wave
Propagating waves of cortical neuronal activity are implicated in various cognitive processes and have been observed in anaesthetised animals. Here, the authors demonstrate the existence of propagating waves in awake monkeys during visual stimulation, and show that they are mediated by horizontal fibres in the cortex.
- Lyle Muller
- , Alexandre Reynaud
- & Alain Destexhe
-
Article |
 Targeted genomic rearrangements using CRISPR/Cas technology
Targeted genomic rearrangements using CRISPR/Cas technology
Genomic rearrangements have important functional consequences for cancer. Here, Choi and Meyerson use CRISPR/Cas technology to generate translocations and inversions that are known drivers of lung cancer, and demonstrate the utility of this technology for studying the role of genomic rearrangements in disease.
- Peter S. Choi
- & Matthew Meyerson
-
Article |
 A red-shifted fluorescent substrate for aldehyde dehydrogenase
A red-shifted fluorescent substrate for aldehyde dehydrogenase
Aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH)-expressing stem cells can be stained and sorted using a green fluorescent substrate. Minn et al.synthesise a red-shifted fluorescent ALDH probe and demonstrate sorting and microscopic staining of cells in the presence of a green fluorescent marker.
- Il Minn
- , Haofan Wang
- & Martin G. Pomper
-
Article |
 Imaging neural spiking in brain tissue using FRET-opsin protein voltage sensors
Imaging neural spiking in brain tissue using FRET-opsin protein voltage sensors
Genetically encoded optical voltage sensors measure the electrical activity of various tissues with limited effectiveness, due to the sensors’ suboptimal performance metrics. Gong et al.create a sensor with increased brightness, fast kinetics and improved dynamic ranges when compared with previous sensors.
- Yiyang Gong
- , Mark J. Wagner
- & Mark J. Schnitzer
-
Article
| Open Access Correlated optical and isotopic nanoscopy
Correlated optical and isotopic nanoscopy
Secondary ion mass spectrometry is effective for imaging cellular turnover, but it cannot identify subcellular structures such as organelles. Here the authors show a method for correlating this technique with high-resolution fluorescence microscopy, enabling the measurement of turnover in cellular compartments.
- Sinem K. Saka
- , Angela Vogts
- & Johannes T. Wessels
-
Article |
 An RNA-seq method for defining endoribonuclease cleavage specificity identifies dual rRNA substrates for toxin MazF-mt3
An RNA-seq method for defining endoribonuclease cleavage specificity identifies dual rRNA substrates for toxin MazF-mt3
MazF toxins inhibit bacterial growth by cleaving single-stranded RNA at specific sequences. Here, the authors describe a new genome-wide approach, MORE RNA-seq, for defining MazF cleavage specificity, and show that MazF-mt3 cleaves 23S and 16S ribosomal RNAs.
- Jason M. Schifano
- , Irina O. Vvedenskaya
- & Nancy A Woychik
-
Article |
 Estimating the effective density of engineered nanomaterials for in vitro dosimetry
Estimating the effective density of engineered nanomaterials for in vitro dosimetry
The assessment of nanomaterial toxicity can be hampered by difficulties in determining cell dosage. Here, the authors present a simple method for determination of nanomaterial agglomerate density in liquid media, enabling accurate calculation of dose delivered to cells in an in vitrosystem.
- Glen DeLoid
- , Joel M. Cohen
- & Philip Demokritou
-
Article |
 One-step pipetting and assembly of encoded chemical-laden microparticles for high-throughput multiplexed bioassays
One-step pipetting and assembly of encoded chemical-laden microparticles for high-throughput multiplexed bioassays
High-throughput screening allows for the rapid assessment of biochemical compounds and processes, but with increasing scale comes increasing costs. Here, the authors use an array of lithographically encoded hydrogel microparticles as a more accessible screening technique.
- Su Eun Chung
- , Jiyun Kim
- & Sunghoon Kwon
-
Article |
 A TAL effector repeat architecture for frameshift binding
A TAL effector repeat architecture for frameshift binding
Transcription activator-like effectors (TALEs) of pathogenic bacteria activate target genes in host plants to support infection. Here, the authors show that TALEs with single natural repeats of aberrant length tolerate one base pair deletions and may enable the bacteria to overcome natural plant resistance.
- Annekatrin Richter
- , Jana Streubel
- & Jens Boch
-
Article |
 Microfluidic probe for single-cell analysis in adherent tissue culture
Microfluidic probe for single-cell analysis in adherent tissue culture
Cellular heterogeneity is a feature of diverse disease processes, yet is masked in typical biochemical assays. Sarkar et al.develop a microfluidic device to access the contents of single cells in adherent culture, allowing biochemical measurements to be connected with phenotypic information.
- Aniruddh Sarkar
- , Sarah Kolitz
- & Jongyoon Han
-
Article |
 Surrogate reporter-based enrichment of cells containing RNA-guided Cas9 nuclease-induced mutations
Surrogate reporter-based enrichment of cells containing RNA-guided Cas9 nuclease-induced mutations
RNA-guided endonucleases (RGENs) are promising tools for genome editing, although their limited activity poses a challenge. Here the authors use surrogate reporters to achieve enrichment of cells containing RGEN-induced mutations up to 11-fold, which could help facilitate the use of RGENs in biomedical research.
- Suresh Ramakrishna
- , Seung Woo Cho
- & Hyongbum Kim
-
Article |
 A sensitive two-photon probe to selectively detect monoamine oxidase B activity in Parkinson’s disease models
A sensitive two-photon probe to selectively detect monoamine oxidase B activity in Parkinson’s disease models
Monoamine oxidase B is an enzyme that is unusually active in Parkinson’s disease, a feature that makes it an ideal diagnostic biomarker. Here, Li et al. create a highly specific fluorogenic probe that can selectively detect monoamine oxidase B activity in vivoto effectively diagnose Parkinson’s disease.
- Lin Li
- , Cheng-Wu Zhang
- & Shao Q. Yao
-
Article |
 Integrated circuit-based electrochemical sensor for spatially resolved detection of redox-active metabolites in biofilms
Integrated circuit-based electrochemical sensor for spatially resolved detection of redox-active metabolites in biofilms
The direct detection of metabolites secreted by cells can indicate how cellular dynamics affects population development. Here, the authors present an integrated circuit-based method for electrochemical imaging of redox-active signalling molecules with spatial resolution within bacterial colonies.
- Daniel L. Bellin
- , Hassan Sakhtah
- & Kenneth L. Shepard
-
Article |
 Synthetic polymers enable non-vitreous cellular cryopreservation by reducing ice crystal growth during thawing
Synthetic polymers enable non-vitreous cellular cryopreservation by reducing ice crystal growth during thawing
Cryopreservation is the method of choice for extending the lifespan of biological samples, although high concentrations of potentially toxic additives are required. Here, the authors show that polymers that mimic antifreeze proteins can enhance cell cryopreservation at only 0.1 wt% concentration.
- Robert C. Deller
- , Manu Vatish
- & Matthew I. Gibson
-
Article |
 Iridium oxide nanotube electrodes for sensitive and prolonged intracellular measurement of action potentials
Iridium oxide nanotube electrodes for sensitive and prolonged intracellular measurement of action potentials
Nanoelectrode intracellular recording of action potential may be used to study cell electrophysiology. Here, the authors demonstrate vertical nanotube electrodes which improve recording quality and duration, as the cell membrane wraps the nanotubes surfaces and protrudes into their hollow centres.
- Ziliang Carter Lin
- , Chong Xie
- & Bianxiao Cui
-
Article
| Open Access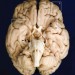 Postmortem examination of patient H.M.’s brain based on histological sectioning and digital 3D reconstruction
Postmortem examination of patient H.M.’s brain based on histological sectioning and digital 3D reconstruction
Studies on Patient H.M. showed that bilateral resection of the hippocampus results in impaired consolidation of long-term memory. Annese et al.create a digital map of Henry Molaison’s brain and find that a significant portion of the posterior hippocampus is actually histologically intact.
- Jacopo Annese
- , Natalie M. Schenker-Ahmed
- & Suzanne Corkin
-
Article
| Open Access Clonal culturing of human embryonic stem cells on laminin-521/E-cadherin matrix in defined and xeno-free environment
Clonal culturing of human embryonic stem cells on laminin-521/E-cadherin matrix in defined and xeno-free environment
Laminin-511 and its cell-binding domain support long-term self-renewal of human pluripotent stem cells in xeno-free culture conditions. Here the authors show that a xeno-free culture matrix consisting of a full-length laminin-521 and the cell–cell adhesion protein E-cadherin supports clonal expansion of human embryonic stem cells.
- Sergey Rodin
- , Liselotte Antonsson
- & Karl Tryggvason
-
Article |
 Biomimetic virus-based colourimetric sensors
Biomimetic virus-based colourimetric sensors
Colour changes in response to external stimuli are common in nature, from turkey skin to butterfly wings. Here, inspired by this behaviour, the authors have developed a sensor capable of providing an individual colour response to specific target chemicals using genetically engineered viruses.
- Jin-Woo Oh
- , Woo-Jae Chung
- & Seung-Wuk Lee
-
Article |
 Genotyping with CRISPR-Cas-derived RNA-guided endonucleases
Genotyping with CRISPR-Cas-derived RNA-guided endonucleases
Cas9 RNA-guided engineered nucleases (RGENs) induce site-specific DNA cleavages in cultured cells and organisms and are used widely as genome-editing tools. Here, the authors develop an RGEN-based technology to genotype both RGEN-induced mutations and cancer-associated mutations in human cell lines.
- Jong Min Kim
- , Daesik Kim
- & Jin-Soo Kim
-
Article |
 Diversity-oriented synthesis as a tool for identifying new modulators of mitosis
Diversity-oriented synthesis as a tool for identifying new modulators of mitosis
Diversity-oriented synthesis is a useful tool to synthesize libraries of structurally complex molecules. Here, the authors show the utility of this method by ultimately identifying a compound causing mitotic arrest and cancer cell death.
- Brett M. Ibbeson
- , Luca Laraia
- & David R. Spring
-
Article
| Open Access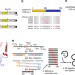 Drawing a high-resolution functional map of adeno-associated virus capsid by massively parallel sequencing
Drawing a high-resolution functional map of adeno-associated virus capsid by massively parallel sequencing
Adeno-associated viruses (AAV) are promising gene transfer vectors for human gene therapy. Here, the authors report a high-throughput, sequencing-based method for characterizing amino acid function in AAV capsids and highlight the potential of this method for improving capsid design.
- Kei Adachi
- , Tatsuji Enoki
- & Hiroyuki Nakai
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging of molecular surface dynamics in brain slices using single-particle tracking
Imaging of molecular surface dynamics in brain slices using single-particle tracking
Lateral diffusion of transmembrane signalling molecules is implicated in neuronal communication but imaging in tissue is limited by poor temporal resolution. Here, the authors use quantum dots to label lipids and adhesion molecules, allowing them to track single-molecule motions in subcellular compartments.
- B. Biermann
- , S. Sokoll
- & M. Heine
-
Article |
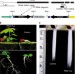 Phytochrome RNAi enhances major fibre quality and agronomic traits of the cotton Gossypium hirsutum L
Phytochrome RNAi enhances major fibre quality and agronomic traits of the cotton Gossypium hirsutum L
Improving the quality of cotton fibres is important for agriculture and fibre length is influenced by far-red light. Here, the authors knock down the red/far-red photoreceptor Phytocrome A1 of cotton and show that this enhances cotton fibre length.
- Ibrokhim Y. Abdurakhmonov
- , Zabardast T. Buriev
- & Alan E. Pepper
-
Article |
 Efficient genome engineering by targeted homologous recombination in mouse embryos using transcription activator-like effector nucleases
Efficient genome engineering by targeted homologous recombination in mouse embryos using transcription activator-like effector nucleases
Genetically engineered mice are an important aspect of human disease research. Here, the authors use artificial transcription activator-like effector-nucleases to generate a mouse line with a conditionally targeted allele and suggest that this method can be easily adapted to any gene in the mouse genome.
- Daniel Sommer
- , Annika E. Peters
- & Marc Beyer
-
Article |
 Familial Alzheimer’s mutations within APPTM increase Aβ42 production by enhancing accessibility of ε-cleavage site
Familial Alzheimer’s mutations within APPTM increase Aβ42 production by enhancing accessibility of ε-cleavage site
In Alzheimer’s disease, familial mutations of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) can increase the production of the toxic cleavage product Aß42. Here, Chen et al. show that mutations within the transmembrane domain of APP favour Aß42 production by increasing the accessibility of the ε-cleavage site.
- Wen Chen
- , Eric Gamache
- & Chunyu Wang
-
Article |
 Engineering protein thermostability using a generic activity-independent biophysical screen inside the cell
Engineering protein thermostability using a generic activity-independent biophysical screen inside the cell
Methods to improve protein stability are important in the biopharmaceutical industry. Here, the authors describe a high-throughput screen to increase protein thermostability and identify thermostable variants from a broad range of proteins.
- Ignacio Asial
- , Yue Xiang Cheng
- & Tobias Cornvik
-
Article |
 Determination of in vivo RNA structure in low-abundance transcripts
Determination of in vivo RNA structure in low-abundance transcripts
RNA is central to many cellular functions, but in vivo structures of most RNAs are unknown. Here Kwok et al. present a universally applicable method, DMS/SHAPE-LMPCR, to identify structures of low-abundance transcripts in living cells, which reveals important features that are uniquely present in vivo.
- Chun Kit Kwok
- , Yiliang Ding
- & Philip C Bevilacqua
-
Article |
 A quantitative telomeric chromatin isolation protocol identifies different telomeric states
A quantitative telomeric chromatin isolation protocol identifies different telomeric states
The protein composition of telomeres changes during development, aging, tumourigenesis and in telomere syndromes. Here, the authors develop a quantitative telomeric chromatin isolation protocol (QTIP) to analyse and quantitatively compare telomeric chromatin of different cell populations.
- Larissa Grolimund
- , Eric Aeby
- & Joachim Lingner
-
Article |
 Using synthetic templates to design an unbiased multiplex PCR assay
Using synthetic templates to design an unbiased multiplex PCR assay
Immunosequencing enables cost-effective sequencing of repertoires of immune cells, but it often suffers from amplification biases when attempting cell quantification. Here, the authors present a powerful multiplex PCR assay that allows for quantitative and unbiased analysis of frequency of different T cell receptors.
- Christopher S. Carlson
- , Ryan O. Emerson
- & Harlan Robins
-
Article
| Open Access Visualization and targeted disruption of protein interactions in living cells
Visualization and targeted disruption of protein interactions in living cells
Screens for protein–protein interactions and for drugs that disrupt them typically use in vitro assays which fail to capture the complexity of the cell’s interior. By fixing proteins to distinct cellular locations, Herce et al.demonstrate a fluorescent-three-hybrid approach to probe such interactions in their cellular contexts.
- Henry D. Herce
- , Wen Deng
- & M. Cristina Cardoso
-
Article |
 Programming adaptive control to evolve increased metabolite production
Programming adaptive control to evolve increased metabolite production
Cells can adapt rapidly to survive and efficiently exploit constantly changing environments by varying their mutation rate. Here the authors construct an in silicosystem to modulate mutation rate, and demonstrate that this method can be used in the laboratory to create specific phenotypes.
- Howard H. Chou
- & Jay D. Keasling
-
Article |
 Real-time in vivo imaging of invasive- and biomaterial-associated bacterial infections using fluorescently labelled vancomycin
Real-time in vivo imaging of invasive- and biomaterial-associated bacterial infections using fluorescently labelled vancomycin
Invasive and biomaterial-associated infections in humans are often difficult to diagnose and treat. Here, the authors demonstrate that real-time in vivodetection and imaging of these bacterial infections can be successfully performed with fluorescently labelled vancomycin.
- Marleen van Oosten
- , Tina Schäfer
- & Gooitzen M. van Dam
-
Article
| Open Access Zinc-finger nickase-mediated insertion of the lysostaphin gene into the beta-casein locus in cloned cows
Zinc-finger nickase-mediated insertion of the lysostaphin gene into the beta-casein locus in cloned cows
Zinc-finger nickases are programmable nucleases that can be used to generate site-specific single-strand breaks in DNA. Liu et al. use this technology to insert an antimicrobial gene into the endogenous beta-casein locus in cloned cows, with the aim of providing protection against mastitis.
- Xu Liu
- , Yongsheng Wang
- & Yong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data
Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data
Tumour biopsies contain contaminating normal cells and these can influence the analysis of tumour samples. In this study, Yoshihara et al.develop an algorithm based on gene expression profiles from The Cancer Genome Atlas to estimate the number of contaminating normal cells in tumour samples.
- Kosuke Yoshihara
- , Maria Shahmoradgoli
- & Roel G.W. Verhaak
-
Article |
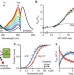 Imaging energy status in live cells with a fluorescent biosensor of the intracellular ATP-to-ADP ratio
Imaging energy status in live cells with a fluorescent biosensor of the intracellular ATP-to-ADP ratio
The ratio between ATP and ADP within the cell is a key indicator of metabolic status. Tantama et al. describe a ratiometric, genetically encoded fluorescent sensor for ATP:ADP that is now optimized for mammalian cells, and demonstrate that it can detect physiological changes in energy consumption and production.
- Mathew Tantama
- , Juan Ramón Martínez-François
- & Gary Yellen
-
Article |
 A peptide probe for targeted brown adipose tissue imaging
A peptide probe for targeted brown adipose tissue imaging
Current methods to image brown adipose tissue rely on radioactive tracers and specialized imaging equipment. Here Azhdarinia et al.report a peptide-based probe that selectively binds to the vascular endothelium of brown adipose tissue and allows the near-infrared imaging of brown fat in mice.
- Ali Azhdarinia
- , Alexes C. Daquinag
- & Mikhail G. Kolonin
-
Article |
 Activation of the central nervous system induced by micro-magnetic stimulation
Activation of the central nervous system induced by micro-magnetic stimulation
Magnetic stimulation is used therapeutically for neurological disorders, but its effectiveness is hindered by efficacy and safety limitations due to large device sizes. Here the authors show that sub-millimetre, micro-magnetic coils effectively stimulate hamster cochlear neurons, with minimal side effects.
- Hyun-Joo Park
- , Giorgio Bonmassar
- & John T. Gale
-
Article
| Open Access A nanopore machine promotes the vectorial transport of DNA across membranes
A nanopore machine promotes the vectorial transport of DNA across membranes
Transport of DNA molecules across lipid membranes requires protein conduits such as the nuclear pore complex. Franceschiniet al.engineer an artificial sequence-selective DNA transporter by attaching gating oligonucleotides to a bacterial nanopore.
- Lorenzo Franceschini
- , Misha Soskine
- & Giovanni Maglia
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing influenza virus infection in living mice
Visualizing influenza virus infection in living mice
Mouse models of influenza infection that permit monitoring of infection in living animals are scarce. Here Pan et al. describe an engineered influenza virus expressing luciferase, which enables real-time in vivovisualization of viral infection and assessment of antiviral drugs.
- Weiqi Pan
- , Zhenyuan Dong
- & Ling Chen
-
Article |
 Non-invasive in vivo assessment of IDH1 mutational status in glioma
Non-invasive in vivo assessment of IDH1 mutational status in glioma
The metabolic reaction catalysed by the isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) enzyme is commonly perturbed in some glioma subtypes due to gain-of-function mutations in the IDH1 gene. Here, Chaumeil et al.present a method that detects mutant IDH1 activity by measuring the levels of different hyperpolarized metabolites produced by wild-type and mutant IDH1.
- Myriam M. Chaumeil
- , Peder E. Z. Larson
- & Sabrina M. Ronen
-
Article |
 A comprehensive multiscale framework for simulating optogenetics in the heart
A comprehensive multiscale framework for simulating optogenetics in the heart
Optogenetics can be used to induce an electrical response in cardiac cells and could become an alternative to electrical cardiac pacing. Here, Boyleet al.present a modelling framework for cardiac optogenetics and explore how optogenetic stimulation might be used to alter cardiac function.
- Patrick M. Boyle
- , John C. Williams
- & Natalia A. Trayanova
-
Article |
 In vivo imaging and histochemistry are combined in the cryosection labelling and intravital microscopy technique
In vivo imaging and histochemistry are combined in the cryosection labelling and intravital microscopy technique
Imaging cells within live animals is important in biomedical research, but this process is limited by the availability of probes. Ritsma et al.combine intravital microscopy with immunohistochemistry to increase the panel of available reagents and examine the role of T cells in the migration of breast cancer cells.
- Laila Ritsma
- , Nienke Vrisekoop
- & Jacco van Rheenen
-
Article
| Open Access High-speed panoramic light-sheet microscopy reveals global endodermal cell dynamics
High-speed panoramic light-sheet microscopy reveals global endodermal cell dynamics
Systematic large-scale analysis of embryonic development requires the processing of large amounts of microscopy data. Here Schmid et al.solve this problem by developing a high-speed imaging system that projects zebrafish embryos onto a ‘world map’ in real time, revealing characteristic migration patterns in the early endoderm.
- Benjamin Schmid
- , Gopi Shah
- & Jan Huisken
-
Article |
 Rare-earth-doped biological composites as in vivo shortwave infrared reporters
Rare-earth-doped biological composites as in vivo shortwave infrared reporters
The short-wavelength infrared spectral region is of interest for bio-imaging applications as biological tissue is transparent to such light. Here Naczynski et al. fabricate rare-earth-based nanomaterials and demonstrate multispectral, real-time short-wavelength infrared in-vivoimaging.
- D. J. Naczynski
- , M. C. Tan
- & P. V. Moghe
-
Article |
 Tracking axonal action potential propagation on a high-density microelectrode array across hundreds of sites
Tracking axonal action potential propagation on a high-density microelectrode array across hundreds of sites
Optical techniques that are used to study neuronal action potential propagation are limited by phototoxicity and photobleaching. Here the authors describe a microelectrode system that allows simultaneous stimulation and recordings of action potential propagation across hundreds of sites in cultured neurons.
- Douglas J. Bakkum
- , Urs Frey
- & Andreas Hierlemann
-
Article |
 Genome-scale proteome quantification by DEEP SEQ mass spectrometry
Genome-scale proteome quantification by DEEP SEQ mass spectrometry
The complexity and dynamic range of mammalian proteomes has stymied comprehensive protein quantification for the past twenty years. Zhou et al. develop DEEP SEQ mass spectrometry and use it to quantify a murine stem cell proteome to a depth equivalent to RNA-seq-based ribosome profiling.
- Feng Zhou
- , Yu Lu
- & Jarrod A. Marto
-
Article |
 Fast GCaMPs for improved tracking of neuronal activity
Fast GCaMPs for improved tracking of neuronal activity
Genetically encoded calcium indicators are commonly used to study cellular activity, but their usefulness is limited by their response kinetics. Here the authors generate indicators with faster responses to calcium events in both Drosophila melanogasterand mammalian neurons.
- Xiaonan R. Sun
- , Aleksandra Badura
- & Samuel S. -H. Wang
-
Article |
 Visualization of caspase-3-like activity in cells using a genetically encoded fluorescent biosensor activated by protein cleavage
Visualization of caspase-3-like activity in cells using a genetically encoded fluorescent biosensor activated by protein cleavage
Proteases of the caspase family are important regulators of apoptosis. Here, Zhang et al. present a genetically encoded protein biosensor that fluoresces if cleaved by caspase-3-like proteases, allowing real-time measurements of apoptosis in cells.
- Jiao Zhang
- , Xin Wang
- & Binghui Li
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Analytical biochemistry
- Behavioural methods
- Bioinformatics
- Biological models
- Biophysical methods
- Cytological techniques
- Electrophysiology
- Epigenetics analysis
- Experimental organisms
- Gene delivery
- Gene expression analysis
- Genetic engineering
- Genetic techniques
- Genomic analysis
- High-throughput screening
- Imaging
- Immunological techniques
- Isolation, separation and purification
- Lab-on-a-chip
- Mass spectrometry
- Metabolomics
- Microbiology techniques
- Microscopy
- Molecular engineering
- Nanobiotechnology
- Optogenetics
- Proteomic analysis
- Sensors and probes
- Sequencing
- Software
- Optical spectroscopy
- Structure determination

 Macromolecular structures probed by combining single-shot free-electron laser diffraction with synchrotron coherent X-ray imaging
Macromolecular structures probed by combining single-shot free-electron laser diffraction with synchrotron coherent X-ray imaging