Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Lineage tracing of acute myeloid leukemia reveals the impact of hypomethylating agents on chemoresistance selection
Lineage tracing of acute myeloid leukemia reveals the impact of hypomethylating agents on chemoresistance selection
The development of post-chemotherapy resistance is a significant issue in the management of AML. Here, Caiado et al. suggest that the issue might be circumvented via upfront combination with hypomethylating agents that shape the clonal dynamics and transcriptional landscape of relapsing AML
- Francisco Caiado
- , Diogo Maia-Silva
- & Bruno Silva-Santos
-
Article
| Open Access An anionic, endosome-escaping polymer to potentiate intracellular delivery of cationic peptides, biomacromolecules, and nanoparticles
An anionic, endosome-escaping polymer to potentiate intracellular delivery of cationic peptides, biomacromolecules, and nanoparticles
Most reagents designed to deliver cargo into cells are cationic and so cannot deliver cationic cargo. Here the authors show that pretreating cells with the anionic polymer poly(propylacrylic acid) facilitates the uptake and endosomal escape of a wide variety of cationic cargo in numerous cell types.
- Brian C. Evans
- , R. Brock Fletcher
- & Craig L. Duvall
-
Article
| Open Access Full-length transcriptome reconstruction reveals a large diversity of RNA and protein isoforms in rat hippocampus
Full-length transcriptome reconstruction reveals a large diversity of RNA and protein isoforms in rat hippocampus
It is challenging to characterize diverse transcript isoforms by short-read sequencing. Here the authors report full-length transcriptomes in rat hippocampus by hybrid-sequencing, predict isoform-specific translational status, and reconstruct open reading frames validated by mass spectrometry.
- Xi Wang
- , Xintian You
- & Wei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Clathrin light chain A drives selective myosin VI recruitment to clathrin-coated pits under membrane tension
Clathrin light chain A drives selective myosin VI recruitment to clathrin-coated pits under membrane tension
Clathrin light chains (CLCa and CLCb) are major constituents of clathrin-coated vesicles. Here authors find and structurally characterize the selective interaction between CLCa and the actin motor protein myosin VI which act together to generate the force that leads to invagination and fission at the apical surface.
- Matteo Biancospino
- , Gwen R. Buel
- & Simona Polo
-
Article
| Open Access Split selectable markers
Split selectable markers
Selectable markers are widely used in cell engineering but there is only a limited variety to choose from. Here the authors split markers using inteins, allowing up to six transgene integration events to be selected for with one marker.
- Nathaniel Jillette
- , Menghan Du
- & Albert Wu Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Symmetry group factorization reveals the structure-function relation in the neural connectome of Caenorhabditis elegans
Symmetry group factorization reveals the structure-function relation in the neural connectome of Caenorhabditis elegans
The 302-neuron connectome of the nematode C. elegans has been completely mapped, yet the design principles that explain how the connectome structure determines its function are unknown. Here, the authors show that physical principles of symmetry and mathematical tools of symmetry groups can be used to understand C. elegans neural locomotion circuits.
- Flaviano Morone
- & Hernán A. Makse
-
Article
| Open Access Split intein-mediated selection of cells containing two plasmids using a single antibiotic
Split intein-mediated selection of cells containing two plasmids using a single antibiotic
Engineering cell lines often requires multiple plasmids with different selection markers. Here the authors present SiMPl, a method based on rationally engineered split enzymes which get reconstituted via intein-mediated protein splicing to maintain two plasmids using a single antibiotic.
- Navaneethan Palanisamy
- , Anna Degen
- & Barbara Di Ventura
-
Article
| Open Access Network curvature as a hallmark of brain structural connectivity
Network curvature as a hallmark of brain structural connectivity
The brain can often continue to function despite lesions in many areas, but damage to particular locations may have serious effects. Here, the authors use the concept of Ollivier-Ricci curvature to investigate the robustness of brain networks.
- Hamza Farooq
- , Yongxin Chen
- & Christophe Lenglet
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule sensing of peptides and nucleic acids by engineered aerolysin nanopores
Single-molecule sensing of peptides and nucleic acids by engineered aerolysin nanopores
Aerolysin pores have potential to improve the accuracy of DNA sequencing and single-molecule proteomics. Here, the authors rationally design a set of mutated pores to achieve a more accurate detection of peptides and nucleic acids.
- Chan Cao
- , Nuria Cirauqui
- & Matteo Dal Peraro
-
Article
| Open Access Goal congruency dominates reward value in accounting for behavioral and neural correlates of value-based decision-making
Goal congruency dominates reward value in accounting for behavioral and neural correlates of value-based decision-making
Decision-making research has confounded the reward value of options with their goal-congruency, as the task goal was always to pick the most rewarding option. Here, authors separately asked participants to select the least rewarding of a set of options, revealing a dominant role for goal congruency.
- Romy Frömer
- , Carolyn K. Dean Wolf
- & Amitai Shenhav
-
Article
| Open Access Early detection and staging of chronic liver diseases with a protein MRI contrast agent
Early detection and staging of chronic liver diseases with a protein MRI contrast agent
Non-invasive early diagnosis of liver fibrosis is important to prevent disease progression and direct treatment strategies. Here the authors developed a collagen-targeting contrast agent for the detection of early stage fibrosis and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by magnetic resonance and tested it in animal models.
- Mani Salarian
- , Ravi Chakra Turaga
- & Jenny J. Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide microhomologies enable precise template-free editing of biologically relevant deletion mutations
Genome-wide microhomologies enable precise template-free editing of biologically relevant deletion mutations
DNA repair by microhomology-mediated end joining creates precise deletions based on flanking microhomologies. Here the authors use CRISPR-Cas9 to recreate pathogenic deletion mutations using existing microhomologies in the human genome identified by their program MHcut.
- Janin Grajcarek
- , Jean Monlong
- & Knut Woltjen
-
Article
| Open Access Large scale and integrated platform for digital mass culture of anchorage dependent cells
Large scale and integrated platform for digital mass culture of anchorage dependent cells
Large scale culture of adherent cells would benefit from a platform for continuous monitoring and control of cell growth and culture conditions. Here the authors develop an integrated, smart cell culture platform where cells are grown on multiple layers of thin sensors that can be wirelessly integrated across several incubators.
- Kyoung Won Cho
- , Seok Joo Kim
- & Dae-Hyeong Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-nanomolar sensitive GZnP3 reveals TRPML1-mediated neuronal Zn2+ signals
Sub-nanomolar sensitive GZnP3 reveals TRPML1-mediated neuronal Zn2+ signals
Numerous fluorescent Zn2+ sensors are available but most are unsuitable to detect physiological dynamics of cytosolic Zn2+. In this study, the authors present a genetically encoded sensor with sub-nanomolar sensitivity and show that Zn2 + is released from endolysosomal vesicles via TRPML1 in neurons.
- Taylor F. Minckley
- , Chen Zhang
- & Yan Qin
-
Article
| Open Access Oncolytic adenovirus programmed by synthetic gene circuit for cancer immunotherapy
Oncolytic adenovirus programmed by synthetic gene circuit for cancer immunotherapy
It is difficult to improve the efficacy of oncolytic virotherapy due to immune system responses and limited understanding of population dynamics. Here the authors use synthetic biology gene circuits to control adenoviral replication and release of immunomodulators in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
- Huiya Huang
- , Yiqi Liu
- & Zhen Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Transcriptional programming using engineered systems of transcription factors and genetic architectures
Transcriptional programming using engineered systems of transcription factors and genetic architectures
Successful approaches for controlling gene expression modulate mRNA synthesis by coupling it to inducible transcription effectors. Here the authors design 27 non-natural and non-synonymous transcription factors.
- Ronald E. Rondon
- , Thomas M. Groseclose
- & Corey J. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access CUTseq is a versatile method for preparing multiplexed DNA sequencing libraries from low-input samples
CUTseq is a versatile method for preparing multiplexed DNA sequencing libraries from low-input samples
Genomics DNA library preparation from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues is challenging. Here the authors describe CUTseq that uses restriction enzymes and in vitro amplification to barcode samples for reduced representation genome sequencing.
- Xiaolu Zhang
- , Silvano Garnerone
- & Nicola Crosetto
-
Article
| Open Access Functional profiling of single CRISPR/Cas9-edited human long-term hematopoietic stem cells
Functional profiling of single CRISPR/Cas9-edited human long-term hematopoietic stem cells
Previous gene editing in haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) has focussed on a heterogeneous CD34+ population. Here, the authors demonstrate high efficiency CRISPR/Cas9-based editing of purified long-term HSCs using non-homologous end joining and homology-directed repair, by directing isoform-specific expression of GATA1.
- Elvin Wagenblast
- , Maria Azkanaz
- & Eric R. Lechman
-
Article
| Open Access Optical mapping of biological water in single live cells by stimulated Raman excited fluorescence microscopy
Optical mapping of biological water in single live cells by stimulated Raman excited fluorescence microscopy
Recent studies have proposed that intracellular water is different from bulk water at the molecular level. Here the authors introduce a Raman microscopy-based method to image the distribution of water states in living cells, and report intracellular water heterogeneity between nucleus and cytoplasm.
- Lixue Shi
- , Fanghao Hu
- & Wei Min
-
Article
| Open Access DNA mechanotechnology reveals that integrin receptors apply pN forces in podosomes on fluid substrates
DNA mechanotechnology reveals that integrin receptors apply pN forces in podosomes on fluid substrates
Podosomes are protrusive structures that coordinate diverse functions related to cell invasion, migration, bone resorption and immune surveillance. Here the authors integrate DNA nanotechnology with FLIM-FRET to demonstrate that podosomes apply pN integrin tensile forces to sense and respond to substrate mechanics.
- Roxanne Glazier
- , Joshua M. Brockman
- & Khalid Salaita
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid single-wavelength lightsheet localization microscopy for clarified tissue
Rapid single-wavelength lightsheet localization microscopy for clarified tissue
It has been challenging to perform super-resolution imaging in large volumes due to aberrations encountered. Here, the authors combine single-wavelength Bessel lightsheet localization microscopy with tissue clearing techniques and image neurons across the whole brain of adult fruit flies.
- Li-An Chu
- , Chieh-Han Lu
- & Bi-Chang Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Microbe-host interplay in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis
Microbe-host interplay in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis
Atopic dermatitis (AD) and psoriasis (PSO) are associated with dysbiosis. Here, by analyses of skin microbiome and host transcriptome of AD and PSO patients, the authors find distinct microbial and disease-related gene transcriptomic signatures that differentiate both diseases.
- Nanna Fyhrquist
- , Gareth Muirhead
- & Harri Alenius
-
Article
| Open Access Epi-illumination gradient light interference microscopy for imaging opaque structures
Epi-illumination gradient light interference microscopy for imaging opaque structures
Quantitative phase imaging techniques have been limited by multiple scattering of light or its use in transmission mode. Here, the authors show a gradient light interference microscopy method in a reflection geometry which allows for label-free phase imaging of bulk and opaque samples.
- Mikhail E. Kandel
- , Chenfei Hu
- & Gabriel Popescu
-
Article
| Open Access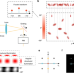 Super-resolution imaging of fluorescent dipoles via polarized structured illumination microscopy
Super-resolution imaging of fluorescent dipoles via polarized structured illumination microscopy
Polarization microscopy has been combined with single-molecule localization, but it’s often limited in either speed or resolution. Here the authors present polarized Structured Illumination Microscopy (pSIM), a method that uses polarized laser excitation to measure dye orientation during fast super-resolution live cell imaging.
- Karl Zhanghao
- , Xingye Chen
- & Peng Xi
-
Article
| Open Access Nanosecond photochemically promoted click chemistry for enhanced neuropeptide visualization and rapid protein labeling
Nanosecond photochemically promoted click chemistry for enhanced neuropeptide visualization and rapid protein labeling
Mass spectrometry-based quantitative proteomics aim to identify and quantify proteins from complex biological samples. Here, the authors developed a method for simultaneous high-throughput protein labelling and on-demand matrix removal within nanoseconds.
- Gongyu Li
- , Fengfei Ma
- & Lingjun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Thermodynamics and kinetics guided probe design for uniformly sensitive and specific DNA hybridization without optimization
Thermodynamics and kinetics guided probe design for uniformly sensitive and specific DNA hybridization without optimization
Optimisation of nucleic acid probes and blocker strands can be laborious. Here the authors construct a theoretical model of competitive DNA hybridisation to design DNA probes for optimisation-free mutation detection.
- Xin Chen
- , Na Liu
- & Xianjin Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access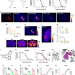 High-potency ligands for DREADD imaging and activation in rodents and monkeys
High-potency ligands for DREADD imaging and activation in rodents and monkeys
Designer Receptors Exclusively Activated by Designer Drugs (DREADDs) are a powerful tool for neuroscience, but the standard DREADD ligand, CNO, has significant drawbacks. Here the authors report two novel high-potency DREADD ligands and a novel DREADD radiotracer for imaging purposes.
- Jordi Bonaventura
- , Mark A. G. Eldridge
- & Michael Michaelides
-
Article
| Open Access Proteomic atlas of organ vasculopathies triggered by Staphylococcus aureus sepsis
Proteomic atlas of organ vasculopathies triggered by Staphylococcus aureus sepsis
Vascular surfaces are rapidly remodeled during systemic inflammatory responses and sepsis. Here, the authors combine in vivo biotinylation and high-resolution mass spectrometry to characterize organ-level changes of the murine vascular cell surface proteome induced by MRSA sepsis.
- Alejandro Gómez Toledo
- , Gregory Golden
- & Jeffrey D. Esko
-
Article
| Open Access Meiotic crossovers characterized by haplotype-specific chromosome painting in maize
Meiotic crossovers characterized by haplotype-specific chromosome painting in maize
Meiotic crossovers (COs) are essential for proper chromosome segregation and generating novel combinations of alleles. Here, the authors develop haplotype-specific oligos on maize chromosome 10 for fluorescence in situ hybridization and analyze CO patterns in an intermated recombinant population derived from B73 and Mo17.
- Lívia do Vale Martins
- , Fan Yu
- & Jiming Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access N6-methyladenosine mRNA marking promotes selective translation of regulons required for human erythropoiesis
N6-methyladenosine mRNA marking promotes selective translation of regulons required for human erythropoiesis
Erythropoiesis can be regulated by transcriptional, epigenetic, and post-transcriptional mechanisms. Here the authors report that N6-methyladenosine mRNA methyltransferase complex stimulates erythropoiesis by promoting translation of specific mRNAs.
- Daniel A. Kuppers
- , Sonali Arora
- & Patrick J. Paddison
-
Article
| Open Access Consciousness-specific dynamic interactions of brain integration and functional diversity
Consciousness-specific dynamic interactions of brain integration and functional diversity
How do diversity (entropy) and integration of activity across brain regions interact to support consciousness? Here the authors show that anaesthetised individuals and patients with disorders of consciousness exhibit overlapping reductions in both diversity and integration in the brain’s default mode network.
- Andrea I. Luppi
- , Michael M. Craig
- & Emmanuel A. Stamatakis
-
Article
| Open Access Anatomy and function of the vertebral column lymphatic network in mice
Anatomy and function of the vertebral column lymphatic network in mice
The lymphatic vasculature is essential to maintain fluid homeostasis and immune surveillance, including in the brain where lymphatic vessels were only recently identified. Here, Jacob et al. provide an anatomical map of lymphatic vessels in the vertebral column, where they find these contribute to fluid drainage and immune responses.
- Laurent Jacob
- , Ligia Simoes Braga Boisserand
- & Jean-Leon Thomas
-
Article
| Open Access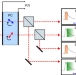 Electro-optic imaging enables efficient wide-field fluorescence lifetime microscopy
Electro-optic imaging enables efficient wide-field fluorescence lifetime microscopy
Nanosecond imaging techniques, such as fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM), are limited by low efficiency of current detectors. Here, the authors implement an electro-optic approach using Pockels cells for wide-field image gating and demonstrate high throughput FLIM on standard camera sensors.
- Adam J. Bowman
- , Brannon B. Klopfer
- & Mark A. Kasevich
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid selection and identification of functional CD8+ T cell epitopes from large peptide-coding libraries
Rapid selection and identification of functional CD8+ T cell epitopes from large peptide-coding libraries
High-throughput assays for TCR specificity are a bottleneck in understanding T cell immunity and harnessing it for medicine. Here the authors develop a functional screening method to identify T cell specificity in the natural context of peptide-MHC presentation, enabling detection of physiologically relevant T cell antigens from large libraries of peptide-coding sequences.
- Govinda Sharma
- , Craig M. Rive
- & Robert A. Holt
-
Article
| Open Access Dendronized fluorosurfactant for highly stable water-in-fluorinated oil emulsions with minimal inter-droplet transfer of small molecules
Dendronized fluorosurfactant for highly stable water-in-fluorinated oil emulsions with minimal inter-droplet transfer of small molecules
Microdroplets are used as chemical and biological reactors; however, stability and inter-droplet transfer are major issues. Here, the authors report on the development of dendritic glycerol-based surfactants for the creation of stable microdroplets and demonstrate application for PCR, minimal emulsion, and cell encapsulation.
- Mohammad Suman Chowdhury
- , Wenshan Zheng
- & Rainer Haag
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo non-invasive monitoring of dystrophin correction in a new Duchenne muscular dystrophy reporter mouse
In vivo non-invasive monitoring of dystrophin correction in a new Duchenne muscular dystrophy reporter mouse
Dystrophin-deficient mice are used to test corrective strategies for Duchenne muscular dystrophy, but evaluation of dystrophin expression requires collection of tissue samples from specific muscles and time points. Here, the authors generate mice in which dystrophin expression is coupled to luciferase, and show that bioluminescence allows non-invasive monitoring of dystrophin expression following genome editing.
- Leonela Amoasii
- , Hui Li
- & Eric N. Olson
-
Article
| Open Access Reduced mu opioid receptor availability in schizophrenia revealed with [11C]-carfentanil positron emission tomographic Imaging
Reduced mu opioid receptor availability in schizophrenia revealed with [11C]-carfentanil positron emission tomographic Imaging
Post-mortem studies have suggested a possible reduction in mu-opioid receptor (MOR) density in people with schizophrenia. Here, the authors examined MOR in living patients with schizophrenia using PET imaging, and found local reductions of MOR compared to controls.
- Abhishekh H. Ashok
- , Jim Myers
- & Oliver D. Howes
-
Article
| Open Access Fast objective coupled planar illumination microscopy
Fast objective coupled planar illumination microscopy
Light sheet microscopy holds potential for imaging dynamics in 3D biological specimens, but is limited by scan speed and camera acquisition rate. Here the authors address both issues by developing speed-optimized Objective Coupled Planar Illumination and parallelizing image acquisition across cameras to achieve 40 Hz imaging over thick samples.
- Cody J. Greer
- & Timothy E. Holy
-
Article
| Open Access A tunable dual-input system for on-demand dynamic gene expression regulation
A tunable dual-input system for on-demand dynamic gene expression regulation
Cellular systems have numerous mechanisms to control gene expression. Here the authors build a Tet-On system with conditional destablising elements to regulate gene expression and protein stability, allowing fine modulation of mESC signalling pathways.
- Elisa Pedone
- , Lorena Postiglione
- & Lucia Marucci
-
Article
| Open Access CENP-A nucleosome clusters form rosette-like structures around HJURP during G1
CENP-A nucleosome clusters form rosette-like structures around HJURP during G1
Human centromeric nucleosomes contain the specific CENP-A histone variant, which replaces canonical histone H3 and epigenetically marks the centromeres. Here the authors show that CENP-A nucleosomes form large supramolecular clusters during the G1 phase of the cell cycle which are arranged as rosette-like structures.
- Leonid Andronov
- , Khalid Ouararhni
- & Ali Hamiche
-
Article
| Open Access The ALFA-tag is a highly versatile tool for nanobody-based bioscience applications
The ALFA-tag is a highly versatile tool for nanobody-based bioscience applications
Epitope tags are widely used in various applications, but often lack versatility. Here, the authors introduce a small, alpha helical tag, which is recognized by a high affinity nanobody and can be used in a range of different applications, from protein purification to super-resolution imaging and in vivo detection of proteins.
- Hansjörg Götzke
- , Markus Kilisch
- & Steffen Frey
-
Article
| Open Access Zika virus enhances monocyte adhesion and transmigration favoring viral dissemination to neural cells
Zika virus enhances monocyte adhesion and transmigration favoring viral dissemination to neural cells
Zika virus (ZIKV) can infect the central nervous system, but it is not clear how it reaches the brain. Here, Ayala-Nunez et al. show in ex vivo and in vivo models that ZIKV can hitch a ride in monocytes in a Trojan Horse manner to cross the endothelium and disseminate the virus.
- Nilda Vanesa Ayala-Nunez
- , Gautier Follain
- & Raphael Gaudin
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic changes in epithelial cell morphology control thymic organ size during atrophy and regeneration
Dynamic changes in epithelial cell morphology control thymic organ size during atrophy and regeneration
One aspect of ageing on immunity is attributed to accelerated thymic atrophy, but the underlying mechanism is still lacking. Here the authors show, using conditional reporter mouse models, that both atrophy and regeneration of the thymus are regulated by rate-limiting morphological changes in epithelial stroma, independent of cell death or proliferation.
- Thomas Venables
- , Ann V. Griffith
- & Howard T. Petrie
-
Article
| Open Access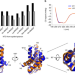 Methionine in a protein hydrophobic core drives tight interactions required for assembly of spider silk
Methionine in a protein hydrophobic core drives tight interactions required for assembly of spider silk
Spider silk is of interest in material science research. Here the authors show that the tight binding of a spider silk protein domain relies on the amino acid methionine, which is abundant in the domain core where it facilitates dynamic shape adaption of the binding interface.
- Julia C. Heiby
- , Benedikt Goretzki
- & Hannes Neuweiler
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplexed and high-throughput neuronal fluorescence imaging with diffusible probes
Multiplexed and high-throughput neuronal fluorescence imaging with diffusible probes
Multiplexed imaging of synaptic proteins can provide useful information on the heterogeneity of synaptic architecture and plasticity. Here the authors use high affinity locked nucleic acid probes and low affinity DNA imaging probes to achieve multiplexed confocal and super-resolution imaging of synaptic and cytoskeletal proteins.
- Syuan-Ming Guo
- , Remi Veneziano
- & Mark Bathe
-
Article
| Open Access Optical control of protein phosphatase function
Optical control of protein phosphatase function
Protein phosphatases play an essential role in signal transduction, but are understudied due to the difficulties in detecting phosphate removal and the lack of good inhibitors. Here the authors develop a light-activated protein phosphatase using photocaged, unnatural amino acids and use it to study ERK nuclear translocation.
- Taylor M. Courtney
- & Alexander Deiters
-
Article
| Open Access A fiber-deprived diet disturbs the fine-scale spatial architecture of the murine colon microbiome
A fiber-deprived diet disturbs the fine-scale spatial architecture of the murine colon microbiome
Here, employing laser capture microdissection and omics, the authors determine the effects of fiber-deprived diet on the spatial structure of the murine colon microbiome, finding that the absence of dietary fiber and polysaccharides leads to local changes along the colon and deterioration of the mucus layer.
- Alessandra Riva
- , Orest Kuzyk
- & David Berry
-
Article
| Open Access Massively parallel RNA device engineering in mammalian cells with RNA-Seq
Massively parallel RNA device engineering in mammalian cells with RNA-Seq
Synthetic RNA-based devices can dynamically control a wide range of processes. Here the authors develop a quantitative and high-throughput mammalian cell-based RNA-seq assay to efficiently engineer ribozyme switches.
- Joy S. Xiang
- , Matias Kaplan
- & Christina D. Smolke
-
Article
| Open Access Linked-read sequencing of gametes allows efficient genome-wide analysis of meiotic recombination
Linked-read sequencing of gametes allows efficient genome-wide analysis of meiotic recombination
Meiotic crossovers (COs) generate genetic variation and ensure proper chromosome segregation. Here, the authors develop a method for identifying COs at kilobase resolution in pooled recombinants using linked-read sequencing data, and apply it to investigate genome-wide CO landscapes of Arabidopsis thaliana.
- Hequan Sun
- , Beth A. Rowan
- & Korbinian Schneeberger
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Analytical biochemistry
- Behavioural methods
- Bioinformatics
- Biological models
- Biophysical methods
- Cytological techniques
- Electrophysiology
- Epigenetics analysis
- Experimental organisms
- Gene delivery
- Gene expression analysis
- Genetic engineering
- Genetic techniques
- Genomic analysis
- High-throughput screening
- Imaging
- Immunological techniques
- Isolation, separation and purification
- Lab-on-a-chip
- Mass spectrometry
- Metabolomics
- Microbiology techniques
- Microscopy
- Molecular engineering
- Nanobiotechnology
- Optogenetics
- Proteomic analysis
- Sensors and probes
- Sequencing
- Software
- Optical spectroscopy
- Structure determination

 A tool for functional brain imaging with lifespan compliance
A tool for functional brain imaging with lifespan compliance