Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access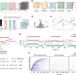 An automated Bayesian pipeline for rapid analysis of single-molecule binding data
An automated Bayesian pipeline for rapid analysis of single-molecule binding data
Analysis of single-molecule binding assays still requires substantial manual user intervention. Here, the authors present a pipeline for rapid, automated analysis of co-localization single-molecule spectroscopy images, with a modular user interface that can be adjusted to a range of experimental conditions.
- Carlas S. Smith
- , Karina Jouravleva
- & David Grunwald
-
Article
| Open Access Characterization of the Src-regulated kinome identifies SGK1 as a key mediator of Src-induced transformation
Characterization of the Src-regulated kinome identifies SGK1 as a key mediator of Src-induced transformation
The systemic understanding of oncogenic kinase signalling is still limited. Here, the authors combine chemical proteomics with functional screens to assess the impact of oncogenic Src on the expressed kinome and identify SGK1 as a critical mediator of Src-induced cell transformation.
- Xiuquan Ma
- , Luxi Zhang
- & Roger J. Daly
-
Article
| Open Access Domain insertion permissibility-guided engineering of allostery in ion channels
Domain insertion permissibility-guided engineering of allostery in ion channels
Allostery is a fundamental principle of protein regulation that remains challenging to engineer. Here authors screen human Inward Rectifier K + Channel Kir2.1 for permissibility to domain insertions and propose that differential permissibility is a metric of latent allosteric capacity in Kir2.1.
- Willow Coyote-Maestas
- , Yungui He
- & Daniel Schmidt
-
Article
| Open Access Kinetic analysis of multistep USP7 mechanism shows critical role for target protein in activity
Kinetic analysis of multistep USP7 mechanism shows critical role for target protein in activity
Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) are critical regulators of cellular processes by removing ubiquitin from specific targets. Here global kinetic modelling reveals the mechanism by which the low intrinsic activity of USP7 is substantially enhanced on a specific physiological target.
- Robbert Q. Kim
- , Paul P. Geurink
- & Titia K. Sixma
-
Article
| Open Access Recurrent activating mutations of PPARγ associated with luminal bladder tumors
Recurrent activating mutations of PPARγ associated with luminal bladder tumors
Activation of the PPARγ/RXRα pathway in luminal bladder cancers has mainly been linked to PPARG gene amplifications and activating point mutations in RXRα. Here, the authors identify recurrent PPARγ mutations with similar effects and elucidate the structural basis for this mutational PPARγ activation.
- Natacha Rochel
- , Clémentine Krucker
- & Isabelle Bernard-Pierrot
-
Article
| Open Access A conserved dimer interface connects ERH and YTH family proteins to promote gene silencing
A conserved dimer interface connects ERH and YTH family proteins to promote gene silencing
In fission yeast, Erh1, ortholog of human ERH, interacts with the YTH family RNA binding protein Mmi1 to form the Erh1-Mmi1 complex (EMC), which has been implicated in gene silencing. Here, the authors present the cocrystal structure of Erh1 homodimers interacting with Mmi1 and further characterise the role of EMC in facultative heterochromatin assembly and gene silencing.
- Guodong Xie
- , Tommy V. Vo
- & Shiv I. S. Grewal
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of tRNA splicing enzyme Tpt1 illuminates the mechanism of RNA 2′-PO4 recognition and ADP-ribosylation
Structure of tRNA splicing enzyme Tpt1 illuminates the mechanism of RNA 2′-PO4 recognition and ADP-ribosylation
Tpt1 catalyzes the final essential step in yeast tRNA splicing and is a potential antifungal target. Here the authors provide structural insights into how Tpt1 recognizes a 2’-PO4 RNA splice junction and the mechanism of RNA phospho-ADP-ribosylation.
- Ankan Banerjee
- , Annum Munir
- & Stewart Shuman
-
Article
| Open Access Aminoacyl sulfonamide assembly in SB-203208 biosynthesis
Aminoacyl sulfonamide assembly in SB-203208 biosynthesis
Sulfonamide is in many important drugs yet is rare in nature and little is known about the synthesis of sulfonamide containing antibiotics. Here, the authors report on a detailed analysis of the biosynthesis machineries of the aminoacyl sulfonamide antibiotics.
- Zhijuan Hu
- , Takayoshi Awakawa
- & Ikuro Abe
-
Article
| Open Access Coordinative metabolism of glutamine carbon and nitrogen in proliferating cancer cells under hypoxia
Coordinative metabolism of glutamine carbon and nitrogen in proliferating cancer cells under hypoxia
Glutamine metabolism is increased in proliferating cells under hypoxia potentially generating exceeding nitrogen. Here the authors show that under hypoxia a specific metabolic pathway is activated to push glutamine carbons and excess nitrogen via the reductive pathway to dihyroorotate which is then secreted by the cells and that such pathway is necessary for tumor growth.
- Yuanyuan Wang
- , Changsen Bai
- & Binghui Li
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid determination of quaternary protein structures in complex biological samples
Rapid determination of quaternary protein structures in complex biological samples
Protein structure determination in complex biological samples is still challenging. Here, the authors develop a computational modeling-guided cross-linking mass spectrometry method, obtaining a high-resolution model of a 1.8 MDa protein assembly from cross-links detected in a mixture of human plasma and bacteria.
- Simon Hauri
- , Hamed Khakzad
- & Lars Malmström
-
Article
| Open Access Tetrathiomolybdate induces dimerization of the metal-binding domain of ATPase and inhibits platination of the protein
Tetrathiomolybdate induces dimerization of the metal-binding domain of ATPase and inhibits platination of the protein
Tetrathiomolybdate (TM) and Cu-ATPases, e.g. Wilson (WLN) protein, affect the efficacy of common anticancer drug cisplatin. Here, the authors show that TM generates a protein dimer with a WLN domain by expelling copper and provide insight into the synergy of TM and cisplatin in cancer chemotherapy.
- Tiantian Fang
- , Wanbiao Chen
- & Yangzhong Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Expression of novel long noncoding RNAs defines virus-specific effector and memory CD8+ T cells
Expression of novel long noncoding RNAs defines virus-specific effector and memory CD8+ T cells
Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) genes do not encode protein products yet are emerging as key regulators of cellular processes such as transcription and translation. Here, by examining lncRNA profiles from human and mouse CD8 T cells, the authors show that stages of CD8+ T cell differentiation are defined by expression of lncRNA genes.
- William H. Hudson
- , Nataliya Prokhnevska
- & Haydn T. Kissick
-
Article
| Open Access Pentatricopeptide repeat poly(A) binding protein KPAF4 stabilizes mitochondrial mRNAs in Trypanosoma brucei
Pentatricopeptide repeat poly(A) binding protein KPAF4 stabilizes mitochondrial mRNAs in Trypanosoma brucei
Polyadenylation stabilizes edited mitochondrial mRNAs in Trypanosoma brucei, but the involved poly(A) binding protein is unknown. Here, Mesitov et al. show that a pentatricopeptide repeat factor KPAF4 binds to A-tail and prevents exonucleolytic degradation as well as translation of incompletely edited mRNAs.
- Mikhail V. Mesitov
- , Tian Yu
- & Inna Aphasizheva
-
Article
| Open Access Dinitroimidazoles as bifunctional bioconjugation reagents for protein functionalization and peptide macrocyclization
Dinitroimidazoles as bifunctional bioconjugation reagents for protein functionalization and peptide macrocyclization
The selective formation of protein bioconjugates under physiological conditions is a challenging task. Here, the authors report that 1,4-dinitroimidazoles are reagents of choice for protein bioconjugation at either cysteine or lysine sites within short times and provide facile access to peptide macrocycles.
- Qunfeng Luo
- , Youqi Tao
- & Huan Wang
-
Article
| Open Access SREBP-dependent lipidomic reprogramming as a broad-spectrum antiviral target
SREBP-dependent lipidomic reprogramming as a broad-spectrum antiviral target
Viruses rely on host cell metabolism for replication, making these pathways potential therapeutic targets. Here, the authors show that AM580, a retinoid derivative and RAR-α agonist, affects replication of several RNA viruses by interfering with the activity of SREBP.
- Shuofeng Yuan
- , Hin Chu
- & Kwok-Yung Yuen
-
Article
| Open Access A tRNA half modulates translation as stress response in Trypanosoma brucei
A tRNA half modulates translation as stress response in Trypanosoma brucei
Trypanosoma brucei mainly relies on translational regulation to adjust gene expression, but details are unclear. Here the authors show that, under stress conditions, tRNAThr half level increases, associates with ribosomes and polysomes, and stimulates protein synthesis by facilitating mRNA loading.
- Roger Fricker
- , Rebecca Brogli
- & Norbert Polacek
-
Article
| Open Access Shifts in the selectivity filter dynamics cause modal gating in K+ channels
Shifts in the selectivity filter dynamics cause modal gating in K+ channels
Spontaneous activity shifts at constant experimental conditions are widespread among ion channels but the molecular origins are poorly understood. Here, using solid-state NMR and MD simulations, the authors reveal that modal gating shifts in K + channels are caused by large shifts in the channel dynamics which perturb the selectivity filter.
- Shehrazade Jekhmane
- , João Medeiros-Silva
- & Markus Weingarth
-
Article
| Open Access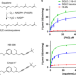 Structure and inhibition mechanism of the catalytic domain of human squalene epoxidase
Structure and inhibition mechanism of the catalytic domain of human squalene epoxidase
Squalene epoxidase (SQLE) is a key enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis and is a target for hypercholesteremia and cancer drug development. Here the authors present the crystal structures of the human SQLE catalytic domain alone and bound with small molecule inhibitors, which will facilitate the development of next-generation SQLE inhibitors.
- Anil K. Padyana
- , Stefan Gross
- & Gromoslaw A. Smolen
-
Article
| Open Access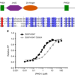 Histone H3 binding to the PHD1 domain of histone demethylase KDM5A enables active site remodeling
Histone H3 binding to the PHD1 domain of histone demethylase KDM5A enables active site remodeling
The demethylase activity of KDM5A is allosterically enhanced by binding of histone H3 to its PHD1 reader domain, through an unknown mechanism. Here the authors show that the PHD1 domain drives ligand-induced allosteric stimulation by stabilizing the binding of substrate to the catalytic domain.
- James E. Longbotham
- , Cynthia M. Chio
- & Danica Galonić Fujimori
-
Article
| Open Access Highly modified and immunoactive N-glycans of the canine heartworm
Highly modified and immunoactive N-glycans of the canine heartworm
The glycome of parasites can have immunomodulatory properties or help to avoid immune surveillance, but details are unknown. Here, Martini et al. characterize the N-glycome of the canine heartworm, reveal an unprecedented complexity, particularly in anionic N-glycans, and determine recognition by components of the immune system.
- Francesca Martini
- , Barbara Eckmair
- & Katharina Paschinger
-
Article
| Open Access Online photochemical derivatization enables comprehensive mass spectrometric analysis of unsaturated phospholipid isomers
Online photochemical derivatization enables comprehensive mass spectrometric analysis of unsaturated phospholipid isomers
Mass spectrometry is widely used for large-scale lipid profiling but distinguishing unsaturated lipid isomers is still challenging. Here, the authors present an analytical platform for high-throughput identification of lipid C=C location isomers in clinical samples, showing that isomer ratios may guide biomarker discovery.
- Wenpeng Zhang
- , Donghui Zhang
- & Yu Xia
-
Article
| Open Access Promotion of homology-directed DNA repair by polyamines
Promotion of homology-directed DNA repair by polyamines
The maintenance polyamines homeostasis is important for cell growth, and several cancers harbor elevated levels of polyamines that may contribute to sustained proliferative potential. Here the authors demonstrate that polyamines participate in DNA double-strand break repair through the stimulation of RAD51-mediated homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange.
- Chih-Ying Lee
- , Guan-Chin Su
- & Peter Chi
-
Article
| Open Access The transcription factor STAT5 catalyzes Mannich ligation reactions yielding inhibitors of leukemic cell proliferation
The transcription factor STAT5 catalyzes Mannich ligation reactions yielding inhibitors of leukemic cell proliferation
The oncogene STAT5 is involved in cancer cell proliferation. Here, the authors use STAT5 protein to assemble its own small molecule inhibitors via Mannich ligation (three-component-reactions) and show that the resultant ligands can inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells in a mouse model.
- Ee Lin Wong
- , Eric Nawrotzky
- & Jörg Rademann
-
Article
| Open Access Fibril formation and therapeutic targeting of amyloid-like structures in a yeast model of adenine accumulation
Fibril formation and therapeutic targeting of amyloid-like structures in a yeast model of adenine accumulation
Small molecule metabolites like phenylalanine can form amyloid-like structures but so far this has only been demonstrated in vitro. Here the authors generate a yeast in vivo model of adenine self-assembly and characterize the adenine assemblies in cells by indicative amyloid dye and anti-adenine assemblies antibodies.
- Dana Laor
- , Dorin Sade
- & Ehud Gazit
-
Article
| Open Access Inward- and outward-facing X-ray crystal structures of homodimeric P-glycoprotein CmABCB1
Inward- and outward-facing X-ray crystal structures of homodimeric P-glycoprotein CmABCB1
P-glycoprotein, an ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter, extrudes a large variety of xenobiotics from the cell which protects tissues from toxins. Here authors solve a pair of X-ray structures of homodimeric P-glycoprotein and resolve structural elements proposed to participate in the mechanism of the transporter.
- Atsushi Kodan
- , Tomohiro Yamaguchi
- & Hiroaki Kato
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental evidence of symmetry breaking of transition-path times
Experimental evidence of symmetry breaking of transition-path times
Microscopic transition mechanisms impact many biophysical systems. In this work, the authors explore transition path times between thermodynamic states experimentally, and show symmetry breaking in the transition times under an external force that drives the system out of equilibrium.
- J. Gladrow
- , M. Ribezzi-Crivellari
- & U. F. Keyser
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into trans-histone regulation of H3K4 methylation by unique histone H4 binding of MLL3/4
Structural insights into trans-histone regulation of H3K4 methylation by unique histone H4 binding of MLL3/4
MLL3 and MLL4 are members of the SET1/MLL family of histone H3K4 methyltransferases, which are responsible for monomethylating histone H3K4 on enhancers. Here the authors show that an extended PHD domain (ePHD6) in MLL3 and MLL4 specifically recognizes an H4H18-containing fragment of histone H4, and that modifications of residues surrounding H4H18 modulate H4 binding to MLL3/4.
- Yanli Liu
- , Su Qin
- & Jinrong Min
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structures of the human neurokinin 1 receptor in complex with clinically used antagonists
Crystal structures of the human neurokinin 1 receptor in complex with clinically used antagonists
Neurokinin receptors are G protein-coupled receptors. Here the authors present three crystal structures of the neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R) in complex with small-molecule antagonists including aprepitant and netupitant and observe that these clinically approved compounds induce a conformational change in the receptor.
- Jendrik Schöppe
- , Janosch Ehrenmann
- & Andreas Plückthun
-
Article
| Open Access Completion of the cytosolic post-chorismate phenylalanine biosynthetic pathway in plants
Completion of the cytosolic post-chorismate phenylalanine biosynthetic pathway in plants
Phenylalanine is mostly synthesized in plant plastids, but cytosolic transamination of phenylpyruvate also contributes. Here the authors show that a cytosolic chorismate mutase and a prephenate dehydratase encoded by an isoform of the plastidial ADT3 enzyme, produce phenylpyruvate in the cytosol.
- Yichun Qian
- , Joseph H. Lynch
- & Natalia Dudareva
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of BAI1/ELMO2 complex reveals an action mechanism of adhesion GPCRs via ELMO family scaffolds
Structure of BAI1/ELMO2 complex reveals an action mechanism of adhesion GPCRs via ELMO family scaffolds
Brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor (BAI) is an adhesion G protein-coupled receptor that acts through the ELMO/DOCK/Rac signaling pathway. Here the authors provide molecular insights into BAI/ELMO interactions by solving the crystal structure of the C-terminal cytoplasmic tail of BAI bound to the RAE tandem domains of ELMO2.
- Zhuangfeng Weng
- , Chenghao Situ
- & Rongguang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access The mTORC1/4E-BP1 axis represents a critical signaling node during fibrogenesis
The mTORC1/4E-BP1 axis represents a critical signaling node during fibrogenesis
The PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway has been previously implicated in fibrosis and a pan-PI3K/mTOR inhibitor is currently under clinical evaluation for the treatment of IPF. Here the authors show that the mTORC1/4E-BP1 axis is critical for TGF-β1-induced fibrogenesis in in vitro and ex vivo models and that canonical PI3K/Akt signalling is dispensable.
- Hannah V. Woodcock
- , Jessica D. Eley
- & Rachel C. Chambers
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of a human intramembrane ceramidase explains enzymatic dysfunction found in leukodystrophy
Structure of a human intramembrane ceramidase explains enzymatic dysfunction found in leukodystrophy
Alkaline ceramidases (ACERs) are a class of poorly understood transmembrane enzymes controlling the homeostasis of ceramides. Here authors solve the Xray structure of human ACER3 and uncover a Ca2+ binding site providing an explanation for the known regulatory role of Ca2+ on ACER3 activity.
- Ieva Vasiliauskaité-Brooks
- , Robert D. Healey
- & Sébastien Granier
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of transcribing RNA polymerase II-nucleosome complex
Structure of transcribing RNA polymerase II-nucleosome complex
Eukaryotic transcription requires passage of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) through chromatin, which is impaired by nucleosomes. Here the authors report the cryo-EM structure of transcribing Pol II engaged with a downstream nucleosome core particle at an overall resolution of 4.4 Å, providing insights into the mechanism of chromatin transcription.
- Lucas Farnung
- , Seychelle M. Vos
- & Patrick Cramer
-
Article
| Open Access Nucleotide-dependent DNA gripping and an end-clamp mechanism regulate the bacteriophage T4 viral packaging motor
Nucleotide-dependent DNA gripping and an end-clamp mechanism regulate the bacteriophage T4 viral packaging motor
Packaging of viral DNA depends on strong molecular motors that are powered by ATP hydrolysis. Here, the authors develop a single-molecule assay to monitor how nucleotide binding regulates motor-DNA interactions and reveal a generic mechanism that prevents exit of the whole DNA from the viral capsid during packaging.
- Mariam Ordyan
- , Istiaq Alam
- & Douglas E. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Serine synthesis through PHGDH coordinates nucleotide levels by maintaining central carbon metabolism
Serine synthesis through PHGDH coordinates nucleotide levels by maintaining central carbon metabolism
Serine synthesis from glucose is required even when serine is available from the environment. Here, the authors explain this paradox by showing that the enzyme PHGDH enables nucleotide synthesis by coordinating anabolic fluxes related to central carbon metabolism, independent of its role in serine production.
- Michael A. Reid
- , Annamarie E. Allen
- & Jason W. Locasale
-
Article
| Open Access A structural and dynamic model for the assembly of Replication Protein A on single-stranded DNA
A structural and dynamic model for the assembly of Replication Protein A on single-stranded DNA
Replication Protein A (RPA) coats single stranded DNA (ssDNA) generated during DNA recombination, replication and repair. Here the authors present a structural model suggesting how RPA’s DNA-binding domains promote cooperative assembly of multiple RPAs on long ssDNA.
- Luke A. Yates
- , Ricardo J. Aramayo
- & Xiaodong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access An electrogenic redox loop in sulfate reduction reveals a likely widespread mechanism of energy conservation
An electrogenic redox loop in sulfate reduction reveals a likely widespread mechanism of energy conservation
The bacterial complex QrcABCD plays a key role in the bioenergetics of sulfate respiration. Here, Duarte et al. show that this complex is electrogenic, with protons and electrons required for quinone reduction being extracted from opposite sides of the membrane.
- Américo G. Duarte
- , Teresa Catarino
- & Inês A. C. Pereira
-
Article
| Open Access The H/ACA complex disrupts triplex in hTR precursor to permit processing by RRP6 and PARN
The H/ACA complex disrupts triplex in hTR precursor to permit processing by RRP6 and PARN
Telomerase RNA (hTR) is transcribed as a 3′-extended precursor. Here the authors examine the processing of hTR precursors of various lengths and show that processing occurs in distinct steps involving different nucleases PARN and RRP6.
- Chi-Kang Tseng
- , Hui-Fang Wang
- & Peter Baumann
-
Article
| Open Access RNA helicases mediate structural transitions and compositional changes in pre-ribosomal complexes
RNA helicases mediate structural transitions and compositional changes in pre-ribosomal complexes
Pre-ribosomes undergo numerous structural rearrangements during their assembly. Here the authors identify the binding sites of three essential RNA helicases on pre-ribosomal particles, enabling them to provide insights into the structural and compositional changes that occur during biogenesis of the large ribosomal subunit.
- Lukas Brüning
- , Philipp Hackert
- & Markus T. Bohnsack
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the type VI secretion system TssK–TssF–TssG baseplate subcomplex revealed by cryo-electron microscopy
Structure of the type VI secretion system TssK–TssF–TssG baseplate subcomplex revealed by cryo-electron microscopy
Type VI secretion systems (T6SSs) translocate effector proteins into eukaryotic and bacterial recipient cells and are present in many Gram-negative bacteria. Here the authors present the 3.7 Å cryoEM structure of the E.coli T6SS baseplate wedge comprising TssK–TssF–TssG and propose a model for the T6SS baseplate and needle complex.
- Young-Jun Park
- , Kaitlyn D. Lacourse
- & David Veesler
-
Article
| Open Access HDX-MS reveals dysregulated checkpoints that compromise discrimination against self RNA during RIG-I mediated autoimmunity
HDX-MS reveals dysregulated checkpoints that compromise discrimination against self RNA during RIG-I mediated autoimmunity
RIG-I is a critical receptor in the induction of innate immune responses, but mutations in RIG-I can be associated with hyperactive signalling and autoimmune disease. Here Zheng et al. apply HDX-MS approaches to reveal dysregulated checkpoints that result in recognition of self-derived RNA during RIG-I mediated autoimmunity.
- Jie Zheng
- , Chen Wang
- & Patrick R. Griffin
-
Article
| Open Access A viral-fusion-peptide-like molecular switch drives membrane insertion of botulinum neurotoxin A1
A viral-fusion-peptide-like molecular switch drives membrane insertion of botulinum neurotoxin A1
The translocation domain (HN) of Botulinum neurotoxins (BoNTs) mediates the delivery of the BoNT light chain (LC) into neuronal cytosol. Here the authors provide insights into HN membrane insertion by determining the crystal structure of BoNT/A1 HN at acidic pH, which reveals a molecular switch in HN, where buried α-helices are transformed into surface-exposed hydrophobic β-hairpins.
- Kwok-ho Lam
- , Zhuojun Guo
- & Rongsheng Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Muc5b overexpression causes mucociliary dysfunction and enhances lung fibrosis in mice
Muc5b overexpression causes mucociliary dysfunction and enhances lung fibrosis in mice
The promoter variant rs35705950 confers a gain of function to the MUC5B gene and is the dominant risk factor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Here the authors show that mice overexpressing Muc5b in distal airspaces show impaired mucociliary clearance and increased susceptibility to bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis, and that both characteristics are reduced by treatment with a mucolytic agent.
- Laura A. Hancock
- , Corinne E. Hennessy
- & David A. Schwartz
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of meiotic telomere attachment to the nuclear envelope by MAJIN-TERB2-TERB1
Structural basis of meiotic telomere attachment to the nuclear envelope by MAJIN-TERB2-TERB1
The meiotic telomere complex (MAJIN, TERB1, TERB2) tethers telomere ends to the nuclear envelope. Here the authors present the crystal structure of human MAJIN-TERB2 and combine biophysical approaches and structured illumination microscopy analysis of mouse meiotic chromosomes to characterize the molecular architecture of the wider MAJIN-TERB2-TERB1 complex and its interactions with TRF1.
- James M. Dunce
- , Amy E. Milburn
- & Owen R. Davies
-
Article
| Open Access Lysosomal protease deficiency or substrate overload induces an oxidative-stress mediated STAT3-dependent pathway of lysosomal homeostasis
Lysosomal protease deficiency or substrate overload induces an oxidative-stress mediated STAT3-dependent pathway of lysosomal homeostasis
How cells regulate their lysosomal proteolytic capacity is only partly understood. Here, the authors show that lysosomal protease deficiency or substrate overload induces lysosomal stress leading to activation of a STAT3-dependent, TFEB-independent pathway of lysosomal hydrolase expression.
- Jonathan Martínez-Fábregas
- , Alan Prescott
- & Colin Watts
-
Article
| Open Access Myopathy associated BAG3 mutations lead to protein aggregation by stalling Hsp70 networks
Myopathy associated BAG3 mutations lead to protein aggregation by stalling Hsp70 networks
BAG3 is a Hsp70 co-chaperone that is highly expressed in muscles. Here the authors show that several myofibrillar myopathy causing BAG3 mutations are not impaired in Hsp70 binding, but rather impair the ADP-ATP exchange step of the Hsp70 cycle, causing the aggregation of BAG3, Hsp70 and Hsp70 clients and leading to a collapse of protein homeostasis.
- Melanie Meister-Broekema
- , Rebecca Freilich
- & Harm H. Kampinga
-
Article
| Open Access CryoEM reveals how the complement membrane attack complex ruptures lipid bilayers
CryoEM reveals how the complement membrane attack complex ruptures lipid bilayers
The complement membrane attack complex (MAC) is a lytic immune pore that kills pathogens. Here the authors use cryoEM to provide a structural and biophysical mechanism for how β-pore forming proteins breach the lipid bilayer, providing pathways to explore pore-formation in molecular detail.
- Anaïs Menny
- , Marina Serna
- & Doryen Bubeck
-
Article
| Open Access Tropinone synthesis via an atypical polyketide synthase and P450-mediated cyclization
Tropinone synthesis via an atypical polyketide synthase and P450-mediated cyclization
Tropinone is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of tropane alkaloids. Here, the authors discovered the enzymes AbPYKS and AbCYP82M3, a non-canonical polyketide synthase and a cytochrome P450, that work sequentially to form tropinone from N-methyl-Δ1-pyrrolinium cation.
- Matthew A. Bedewitz
- , A. Daniel Jones
- & Cornelius S. Barry
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrahigh specificity in a network of computationally designed protein-interaction pairs
Ultrahigh specificity in a network of computationally designed protein-interaction pairs
The molecular basis of ultrahigh specificity in protein-protein interactions remains obscure. The authors present a computational method to design atomically accurate new pairs exhibiting >100,000-fold specificity switches, generating a large and complex interaction network.
- Ravit Netzer
- , Dina Listov
- & Sarel J. Fleishman
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Biocatalysis
- Biogeochemistry
- Bioinorganic chemistry
- Biophysical chemistry
- Carbohydrates
- Chemical modification
- Cytokines
- DNA
- Enzyme mechanisms
- Enzymes
- Glycobiology
- Glycomics
- Histocytochemistry
- Hormones
- Immunochemistry
- Ion channels
- Isoenzymes
- Kinases
- Lipidomics
- Lipids
- Metabolomics
- Metals
- Neurochemistry
- Peptides
- Prions
- Proteases
- Protein folding
- Proteins
- Proteolysis
- Proteomics
- RNA
- Structural biology

 WDR76 is a RAS binding protein that functions as a tumor suppressor via RAS degradation
WDR76 is a RAS binding protein that functions as a tumor suppressor via RAS degradation