Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and biochemical analysis of family 92 carbohydrate-binding modules uncovers multivalent binding to β-glucans
Structural and biochemical analysis of family 92 carbohydrate-binding modules uncovers multivalent binding to β-glucans
Carbohydrate binding modules (CBMs) are non-catalytic domains found within multi-modular carbohydrate-active enzymes like glycoside hydrolases. Here, the authors show the crystal structures of two CBM family 92 members, which use three different surface binding sites to bind to β-glucans.
- Meng-Shu Hao
- , Scott Mazurkewich
- & Lauren S. McKee
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-function analysis of the cyclic β-1,2-glucan synthase from Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Structure-function analysis of the cyclic β-1,2-glucan synthase from Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Here, the authors present the structure of cyclic β-1,2-glucan synthase from Agrobacterium tumefaciens, revealing a distinct mechanism that uses a tyrosine-linked oligosaccharide intermediate in cycles of polymerization and processing of the glucan chain.
- Jaroslaw Sedzicki
- , Dongchun Ni
- & Christoph Dehio
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and mechanistic characterization of bifunctional heparan sulfate N-deacetylase-N-sulfotransferase 1
Structural and mechanistic characterization of bifunctional heparan sulfate N-deacetylase-N-sulfotransferase 1
Heparan sulfate biosynthesis is a complex process involving multiple reactions that extend and modify the polysaccharide. Here, the authors resolve structures of NDST1, responsible for the critical N-sulfoglucosamine modification of heparan sulfate.
- Courtney J. Mycroft-West
- , Sahar Abdelkarim
- & Liang Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Longitudinal quantification of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis reveals late colonization in the infant gut independent of maternal milk HMO composition
Longitudinal quantification of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis reveals late colonization in the infant gut independent of maternal milk HMO composition
Here, the authors develop a high-throughput method to quantify Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis (BL. infantis), a proficient HMO-utilizer, from metagenomic sequencing, and applied it to a longitudinal cohort consisting of 21 mother-infant dyads, suggesting BL. infantis colonization to start late in the breast-feeding period.
- Dena Ennis
- , Shimrit Shmorak
- & Moran Yassour
-
Article
| Open Access Enzymatic β-elimination in natural product O- and C-glycoside deglycosylation
Enzymatic β-elimination in natural product O- and C-glycoside deglycosylation
Biological degradation of glycosides involves, alongside hydrolysis, β-elimination for glycosidic bond cleavage. Here, the authors report an O-glycoside β-eliminase from Agrobacterium tumefaciens that converts the C3-oxidized O-β-d-glucoside of phloretin into the aglycone and the 2-hydroxy-3-keto-d-glycal elimination product, and suggest convergent evolution of β-eliminase active sites for the cleavage of natural product 3-keto-O-glycosides.
- Johannes Bitter
- , Martin Pfeiffer
- & Bernd Nidetzky
-
Article
| Open Access Structural adaptation of fungal cell wall in hypersaline environment
Structural adaptation of fungal cell wall in hypersaline environment
Solid-state NMR snapshots of Aspergillus sydowii and other halophilic fungal species reveal the structural rearrangement of polysaccharides and proteins, which create a thick, stiff and hydrophobic cell wall to withstand external stress and thrive in hypersaline environment
- Liyanage D. Fernando
- , Yordanis Pérez-Llano
- & Tuo Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Sialic acid O-acetylation patterns and glycosidic linkage type determination by ion mobility-mass spectrometry
Sialic acid O-acetylation patterns and glycosidic linkage type determination by ion mobility-mass spectrometry
O-acetylation is a common modification of sialic acids. Here, a library of synthetic O-acetylated sialosides made it possible to develop an ion mobility mass spectrometry (IM-MS) approach that can elucidate exact O-acetylation patterns and glycosidic linkage types of sialosides isolated from biological samples.
- Gaёl M. Vos
- , Kevin C. Hooijschuur
- & Geert-Jan Boons
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular mechanism of decision-making in glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis
Molecular mechanism of decision-making in glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis
Heparan sulfate (HS) and chondroitin sulfate (CS) are different glycosaminoglycan chains that are attached to core proteins via the same linker tetrasaccharide, and it was unclear how core proteins are specifically modified with HS or CS. Here, the authors determine that the CS-initiating glycosyltransferase CSGALNACT2 is promiscuous, whereas the HS-initiating glycosyltransferase EXTL3 selects only certain core proteins for modification.
- Douglas Sammon
- , Anja Krueger
- & Erhard Hohenester
-
Article
| Open Access Host heparan sulfate promotes ACE2 super-cluster assembly and enhances SARS-CoV-2-associated syncytium formation
Host heparan sulfate promotes ACE2 super-cluster assembly and enhances SARS-CoV-2-associated syncytium formation
The molecular mechanism of syncytium formation during SARS-CoV-2 infection is not fully understood. Zhang et al. now show that cell surface heparan sulfate enhances spike-induced ACE2 clustering and cell-cell fusion, which depends on a conserved ACE2 linker and is blocked by a heparan sulfate binding drug.
- Qi Zhang
- , Weichun Tang
- & Yihong Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Chemoenzymatic synthesis of genetically-encoded multivalent liquid N-glycan arrays
Chemoenzymatic synthesis of genetically-encoded multivalent liquid N-glycan arrays
Cellular glycosylation is complex and heterogeneous, which is challenging to reproduce synthetically. Here, the authors report on enzymatic remodelling of multivalent glycosylated bacteriophages to produce genetically encoded library of N-glycans which can be used to measure glycan-protein interactions with lectins on the surface of live cells and organs.
- Chih-Lan Lin
- , Mirat Sojitra
- & Ratmir Derda
-
Article
| Open Access The Gram-positive bacterium Romboutsia ilealis harbors a polysaccharide synthase that can produce (1,3;1,4)-β-d-glucans
The Gram-positive bacterium Romboutsia ilealis harbors a polysaccharide synthase that can produce (1,3;1,4)-β-d-glucans
(1,3;1,4)-β-d-Glucans are widely distributed in many organisms, but little is known about the enzymes responsible for their synthesis outside the grasses. Here, the authors report on the presence of (1,3;1,4)-β-d-glucans in the exopolysaccharides of the Gram-positive bacterium Romboutsia ilealis and identify and characterize the (1,3;1,4)-β-d-glucan synthase RiGT2.
- Shu-Chieh Chang
- , Mu-Rong Kao
- & Yves S. Y. Hsieh
-
Article
| Open Access Determining the metabolic effects of dietary fat, sugars and fat-sugar interaction using nutritional geometry in a dietary challenge study with male mice
Determining the metabolic effects of dietary fat, sugars and fat-sugar interaction using nutritional geometry in a dietary challenge study with male mice
The role of dietary fat vs sugar in the global obesity epidemic remains controversial. Using Nutritional Geometry methodology, the authors show that, in mice, both fats and sugars could lead to adverse metabolic outcomes, depending on the dietary context.
- Jibran A. Wali
- , Duan Ni
- & Stephen J. Simpson
-
Article
| Open Access Establishing mammalian GLUT kinetics and lipid composition influences in a reconstituted-liposome system
Establishing mammalian GLUT kinetics and lipid composition influences in a reconstituted-liposome system
Transport assays using purified glucose transporters (GLUTs) have proven to be difficult to implement, hampering deeper mechanistic insights. Here the authors have optimized a transport assay in liposomes that will provide insight to study other membrane transport proteins.
- Albert Suades
- , Aziz Qureshi
- & David Drew
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of human SGLT in the occluded state reveal conformational changes during sugar transport
Structures of human SGLT in the occluded state reveal conformational changes during sugar transport
SGLT plays key roles in sugar uptake and reabsorption. Here the authors provided the cryo-EM structures of human SGLT1 and SGLT2 in the substrate-bound occluded state, uncovering the conformational changes of SGLT during sugar transport.
- Wenhao Cui
- , Yange Niu
- & Lei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial metabolomics reveals glycogen as an actionable target for pulmonary fibrosis
Spatial metabolomics reveals glycogen as an actionable target for pulmonary fibrosis
Spatial metabolomics are used to describe the location and chemistry of small molecules involved in metabolic phenotypes. Here, Conroy et al. present a bioinformatic pipeline to analyze MALDI data and show that it can be used to identify actionable targets such as glycogen in fibrotic lungs of both human and mice.
- Lindsey R. Conroy
- , Harrison A. Clarke
- & Ramon C. Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Siglec-6 mediates the uptake of extracellular vesicles through a noncanonical glycolipid binding pocket
Siglec-6 mediates the uptake of extracellular vesicles through a noncanonical glycolipid binding pocket
Siglec-glycolipid interactions are often studied outside the context of a lipid bilayer. Here, the authors combine a variety of chemical biology techniques to demonstrate a unique and physiologically relevant ability of Siglec-6 to recognize glycolipids in a membrane.
- Edward N. Schmidt
- , Dimitra Lamprinaki
- & Matthew S. Macauley
-
Article
| Open Access A selective and atom-economic rearrangement of uridine by cascade biocatalysis for production of pseudouridine
A selective and atom-economic rearrangement of uridine by cascade biocatalysis for production of pseudouridine
Pseudouridine (Ψ), the C-nucleoside isomer of uridine, and its 1-N-methyl derivative, are incorporated in mRNA vaccines and essential for their efficiency, but difficult to synthetically access. Here, the authors report on selective and atom-economic 1N-5C rearrangement of β-d-ribosyl on uracil to obtain Ψ from unprotected U in quantitative yield
- Martin Pfeiffer
- , Andrej Ribar
- & Bernd Nidetzky
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of d-arabinan-degrading enzymes in mycobacteria
Identification of d-arabinan-degrading enzymes in mycobacteria
Bacterial cell growth and division require the coordinated action of enzymes that synthesize and degrade cell wall polymers. Here, the authors identify enzymes that cleave the D-arabinan core of arabinogalactan, an unusual component of the cell wall of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other mycobacteria.
- Omar Al-Jourani
- , Samuel T. Benedict
- & Patrick J. Moynihan
-
Article
| Open Access High-resolution separation of bioisomers using ion cloud profiling
High-resolution separation of bioisomers using ion cloud profiling
Ion mobility is used in mass spectrometers for structure analysis of biomolecules. Here, the authors show that ion mobility analysis in an ion trap under ultra-high fields enables isomer separation at resolutions over 10,000, wich they demonstrate for isomers of disaccharides, phospholipids, and peptides.
- Xiaoyu Zhou
- , Zhuofan Wang
- & Zheng Ouyang
-
Article
| Open Access Visible light-exposed lignin facilitates cellulose solubilization by lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases
Visible light-exposed lignin facilitates cellulose solubilization by lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases
Degradation of plant biomass, comprised of cellulose and polyaromatic lignin, is promoted by light. Here, the authors show that light promotes lignin-catalyzed generation of hydrogen peroxide, which is used by redox enzymes to degrade cellulose.
- Eirik G. Kommedal
- , Camilla F. Angeltveit
- & Vincent G. H. Eijsink
-
Article
| Open Access Hedgehog is relayed through dynamic heparan sulfate interactions to shape its gradient
Hedgehog is relayed through dynamic heparan sulfate interactions to shape its gradient
The Hedgehog morphogen creates gradients during development, but diffusion alone cannot explain its spatiotemporal dynamics. Hedgehog transport requires binding heparan sulfate sugar chains, and the authors now show that Hedgehogs can spread by interacting with sequential heparan molecules.
- Fabian Gude
- , Jurij Froese
- & Kay Grobe
-
Article
| Open Access A Mycobacterium tuberculosis fingerprint in human breath allows tuberculosis detection
A Mycobacterium tuberculosis fingerprint in human breath allows tuberculosis detection
Most conventional tuberculosis diagnostic tests rely on difficult to obtain sputum samples. In this proof-of-concept study, authors analyse whether pulmonary tuberculosis can be detected using exhaled breath condensate samples.
- Sergio Fabián Mosquera-Restrepo
- , Sophie Zuberogoïtia
- & Jérôme Nigou
-
Article
| Open Access Chemoenzymatic synthesis of sulfur-linked sugar polymers as heparanase inhibitors
Chemoenzymatic synthesis of sulfur-linked sugar polymers as heparanase inhibitors
Heparin is a family of complex carbohydrates binding to proteins to modulate cell activities. Here the authors report the synthesis, and conformations simulations of S-linked hemi-A heparosan [GlcA-S-GlcNAc]n, a thio-glycosidic uncleavable polysaccharide, and test it as human heparanase inhibitor.
- Peng He
- , Xing Zhang
- & Paul L. DeAngelis
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis for glycan recognition and reaction priming of eukaryotic oligosaccharyltransferase
Molecular basis for glycan recognition and reaction priming of eukaryotic oligosaccharyltransferase
Oligosaccharyltransferase (OST), the central enzyme in N-glycosylation, modifies acceptor proteins by attaching a complex glycan. Cryo-EM structures of OST in distinct states, reveal the molecular basis of substrate recognition and catalysis.
- Ana S. Ramírez
- , Mario de Capitani
- & Kaspar P. Locher
-
Article
| Open Access Biotechnologically produced chitosans with nonrandom acetylation patterns differ from conventional chitosans in properties and activities
Biotechnologically produced chitosans with nonrandom acetylation patterns differ from conventional chitosans in properties and activities
Degree of polymerisation, fraction and pattern of acetylation change the material and biological properties of chitosan. Here, the authors show that enzymes can N-acetylate fully deacetylated chitosan to replicate the natural control over acetylation pattern not found in chemically produced chitosan allowing more control over properties.
- Sruthi Sreekumar
- , Jasper Wattjes
- & Bruno M. Moerschbacher
-
Article
| Open Access N6-methyladenosine modification governs liver glycogenesis by stabilizing the glycogen synthase 2 mRNA
N6-methyladenosine modification governs liver glycogenesis by stabilizing the glycogen synthase 2 mRNA
Here the authors find that the mRNA of GYS2, the liver-specific glycogen synthase, is a substrate of METTL3 and IGF2BP2 and that m6A-mediated regulation of Gys2 mRNA is critical for the maintenance of liver glycogenesis in mammals during growth, such as mice and rats.
- Xiang Zhang
- , Huilong Yin
- & Rui Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A universal glycoenzyme biosynthesis pipeline that enables efficient cell-free remodeling of glycans
A universal glycoenzyme biosynthesis pipeline that enables efficient cell-free remodeling of glycans
Access to glycoenzymes for basic and applied research is limited by difficulties with their recombinant expression. Here, the authors describe a universal strategy for converting membrane-bound glycosyltransferases into water-soluble biocatalysts, which are expressed at high levels with retention of activity.
- Thapakorn Jaroentomeechai
- , Yong Hyun Kwon
- & Matthew P. DeLisa
-
Article
| Open Access A pathway for chitin oxidation in marine bacteria
A pathway for chitin oxidation in marine bacteria
Lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases contribute to microbial degradation of chitin, but how the resulting oxidized chitooligosaccharides are utilized by microbes is unclear. Here, the authors describe a complete pathway for oxidative chitin utilization in marine bacteria.
- Wen-Xin Jiang
- , Ping-Yi Li
- & Yu-Zhong Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access The evolutionary advantage of an aromatic clamp in plant family 3 glycoside exo-hydrolases
The evolutionary advantage of an aromatic clamp in plant family 3 glycoside exo-hydrolases
Barley β-d-glucan glucohydrolase is a glycoside hydrolase family 3 (GH3) enzyme critical for growth and development. Here the authors carryout mutagenesis, structural analyses and multi-scale molecular dynamics to examine the binding and conformational behaviour of several β-d-glucosides during the substrate-product assisted catalysis that operates in GH3 hydrolases.
- Sukanya Luang
- , Xavier Fernández-Luengo
- & Maria Hrmova
-
Article
| Open Access Maladaptive positive feedback production of ChREBPβ underlies glucotoxic β-cell failure
Maladaptive positive feedback production of ChREBPβ underlies glucotoxic β-cell failure
ChREBP is a glucose-responsive transcription factor, which regulates glucose-mediated proliferation and cell death in pancreatic β-cells. Here the authors show that the acute feed forward induction of ChREBPβ is required for adaptive β-cell expansion, that chronic overexpression of ChREBPβ is toxic to β-cells, and offer mitigation strategies
- Liora S. Katz
- , Gabriel Brill
- & Donald K. Scott
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and mechanistic insights into the cleavage of clustered O-glycan patches-containing glycoproteins by mucinases of the human gut
Structural and mechanistic insights into the cleavage of clustered O-glycan patches-containing glycoproteins by mucinases of the human gut
AM0627 is a bis-O-glycan mucinase that might work in the final steps of mucus degradation, thereby providing a carbon and nitrogen source for Akkermansia muciniphila. Here, the authors provide molecular insights into AM0627 function from X-ray crystallography and computer simulations.
- Víctor Taleb
- , Qinghua Liao
- & Ramon Hurtado-Guerrero
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic phosphoethanolamine-modified oligosaccharides reveal the importance of glycan length and substitution in biofilm-inspired assemblies
Synthetic phosphoethanolamine-modified oligosaccharides reveal the importance of glycan length and substitution in biofilm-inspired assemblies
The phosphoethanolamine modified cellulose in E. colibiofilms has revealed that polysaccharide functionalization alters the biofilm properties. Here, the authors show a model system to explore the role of phosphoethanolamine and other unnatural modifications on the properties of the biofilm-inspired assemblies.
- Theodore Tyrikos-Ergas
- , Soeun Gim
- & Martina Delbianco
-
Article
| Open Access Cell surface glycan engineering reveals that matriglycan alone can recapitulate dystroglycan binding and function
Cell surface glycan engineering reveals that matriglycan alone can recapitulate dystroglycan binding and function
Matriglycan, a repeating disaccharide on α-dystroglycan, is the receptor for Lassa virus and specific extracellular matrix proteins. Here, the authors demonstrate that matriglycan, in a length-dependent tunable manner, is both necessary and sufficient for protein binding and viral infection.
- M. Osman Sheikh
- , Chantelle J. Capicciotti
- & Geert-Jan Boons
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering substrate specificity of HAD phosphatases and multienzyme systems development for the thermodynamic-driven manufacturing sugars
Engineering substrate specificity of HAD phosphatases and multienzyme systems development for the thermodynamic-driven manufacturing sugars
Haloacid dehalogenase-like phosphatases are widespread across all domains of life and play a crucial role in the regulation of levels of sugar phosphate metabolites in cells. The authors report on the structure-guided engineering of phosphatases for dedicated substrate specificity for the conversion of sucrose and starch into fructose and mannose.
- Chaoyu Tian
- , Jiangang Yang
- & Yanhe Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Complete biosynthetic pathway to the antidiabetic drug acarbose
Complete biosynthetic pathway to the antidiabetic drug acarbose
The market demand for acarbose, a drug used for treatment of patients affected by type-2 diabetes, has increased. In this article, the authors report the acarbose complete biosynthetic pathway, clarifying previously unknown steps and identifying a pseudoglycosyltransferase enzyme, AcbS, a homologue of AcbI that catalyzes the formation of a non-glycosidic C-N bond.
- Takeshi Tsunoda
- , Arash Samadi
- & Taifo Mahmud
-
Article
| Open Access Elucidating Human Milk Oligosaccharide biosynthetic genes through network-based multi-omics integration
Elucidating Human Milk Oligosaccharide biosynthetic genes through network-based multi-omics integration
Human milk oligosaccharides are fundamental to infant health. Here the authors deploy a multi-omics systems biology approach to elucidate their biosynthetic network, including the associated enzymes and likely structures of ambiguous oligosaccharides.
- Benjamin P. Kellman
- , Anne Richelle
- & Nathan E. Lewis
-
Article
| Open Access PplD is a de-N-acetylase of the cell wall linkage unit of streptococcal rhamnopolysaccharides
PplD is a de-N-acetylase of the cell wall linkage unit of streptococcal rhamnopolysaccharides
The cell wall of the bacterial pathogen Group A Streptococcus is decorated with a polysaccharide termed GAC, which is a target for vaccine development. Here, Rush et al. characterize the linkage between GAC and peptidoglycan, and identify a protein that deacetylates the linkage and thus protects the pathogen against host cationic antimicrobial proteins.
- Jeffrey S. Rush
- , Prakash Parajuli
- & Natalia Korotkova
-
Article
| Open Access Carbohydrate-aromatic interface and molecular architecture of lignocellulose
Carbohydrate-aromatic interface and molecular architecture of lignocellulose
The plant biomass is a composite formed by a variety of polysaccharides and an aromatic polymer named lignin. Here, the authors use solid-state NMR spectroscopy to unveil the carbohydrate-aromatic interface that leads to the variable architecture of lignocellulose biomaterials.
- Alex Kirui
- , Wancheng Zhao
- & Tuo Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Stereoselective gold(I)-catalyzed approach to the synthesis of complex α-glycosyl phosphosaccharides
Stereoselective gold(I)-catalyzed approach to the synthesis of complex α-glycosyl phosphosaccharides
Glycosyl phosphosaccharides represent a large and important family of complex glycans, but are difficult to synthesize efficiently. Here, the authors disclose a stereoselective methodology to make α-glycosyl phosphosaccharides, via gold(I)-catalyzed glycosylation of phosphoric acid acceptors.
- Xiaojuan Zhang
- , Yutong Yang
- & Yugen Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Neutron crystallography reveals mechanisms used by Pseudomonas aeruginosa for host-cell binding
Neutron crystallography reveals mechanisms used by Pseudomonas aeruginosa for host-cell binding
Pseudomonas aeruginosa employs lectins to bind to its host cells, and is known to be the major cause of lung infections. Lectin B (LecB) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa binds specifically to galactose and fucose and is important for pathogenicity, adhesion and biofilm formation. In this work, the neutron crystal structure (1.9 Å) of the deuterated LecB/Ca/fucose complex is reported. The structure, in combination with perdeuteration of the ligand and the receptor allowed the observation of hydrogen atoms, protonation states and hydrogen bonds involved in the interaction between pathogenic bacteria and host cells. Thus the study provides structural insights into the mechanism of high affinity binding of LecB to its targets.
- Lukas Gajdos
- , Matthew P. Blakeley
- & Anne Imberty
-
Article
| Open Access Fluorinated rhamnosides inhibit cellular fucosylation
Fluorinated rhamnosides inhibit cellular fucosylation
Aberrant expression of fucosylated glycans has been linked to several disease states. Control of fucose expression on live cells is needed to aid research and therapy development. Here the authors report on the development of a class of fucosylation metabolic prodrug inhibitors and demonstrated inhibition of cellular fucosylation.
- Johan F. A. Pijnenborg
- , Emiel Rossing
- & Thomas J. Boltje
-
Article
| Open Access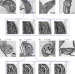 Coalescence and directed anisotropic growth of starch granule initials in subdomains of Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplasts
Coalescence and directed anisotropic growth of starch granule initials in subdomains of Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplasts
Starch is the major form of energy storage in plant cells and forms discrete, semi-crystalline granules within plastids. Here the authors use electron tomography and nanoSIMS to show that Arabidopsis starch granules initiate in stromal pockets between thylakoid membranes that coalesce before growing anisotropically.
- Léo Bürgy
- , Simona Eicke
- & Samuel C. Zeeman
-
Article
| Open Access A molecular vision of fungal cell wall organization by functional genomics and solid-state NMR
A molecular vision of fungal cell wall organization by functional genomics and solid-state NMR
The fungal cell wall is a complex structure composed mainly of glucans, chitin and glycoproteins. Here, the authors use solid-state NMR spectroscopy to assess the cell wall architecture of Aspergillus fumigatus, comparing wild-type cells and mutants lacking major structural polysaccharides, with insights into the distinct functions of these components.
- Arnab Chakraborty
- , Liyanage D. Fernando
- & Tuo Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Glycan remodeled erythrocytes facilitate antigenic characterization of recent A/H3N2 influenza viruses
Glycan remodeled erythrocytes facilitate antigenic characterization of recent A/H3N2 influenza viruses
Here, Broszeit et al. show that circulating A/H3N2 viruses have evolved binding specificity to α2,6-sialosides on extended LacNAc moieties and therefore cannot agglutinate erythrocytes. Applying glycan remodeling allows to install functional receptors on erythrocytes and promotes identification of newly circulating variants to facilitate vaccine design.
- Frederik Broszeit
- , Rosanne J. van Beek
- & Geert-Jan Boons
-
Article
| Open Access Chemoenzymatic modular assembly of O-GalNAc glycans for functional glycomics
Chemoenzymatic modular assembly of O-GalNAc glycans for functional glycomics
O-GalNAc glycans are essential in many biological and pathological processes, but difficult to access due to their structural complexity and synthetic challenges. Here, the authors report an efficient chemoenzymatic modular assembly strategy to construct structurally diverse O-GalNAc glycans, use the synthesised glycans to generate a synthetic mucin O-glycan microarray and profile binding specificities of glycan-binding proteins.
- Shuaishuai Wang
- , Congcong Chen
- & Lei Li
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of fungal oligosaccharide-oxidising flavo-enzymes with previously unknown substrates, redox-activity profiles and interplay with LPMOs
Discovery of fungal oligosaccharide-oxidising flavo-enzymes with previously unknown substrates, redox-activity profiles and interplay with LPMOs
Microbial oxidoreductases are key in biomass breakdown. Here, the authors expand the specificity and redox scope within fungal auxiliary activity 7 family (AA7) enzymes and show that AA7 oligosaccharide dehydrogenases can directly fuel cellulose degradation by lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases.
- Majid Haddad Momeni
- , Folmer Fredslund
- & Maher Abou Hachem
-
Article
| Open Access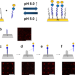 Glycan chip based on structure-switchable DNA linker for on-chip biosynthesis of cancer-associated complex glycans
Glycan chip based on structure-switchable DNA linker for on-chip biosynthesis of cancer-associated complex glycans
Current methods for on-chip glycan biosynthesis suffer from analysing products, often resulting in poor purity and yield. Here the authors report a glycan chip developed by introducing a pH-responsive i-motif DNA linker to control the immobilization and isolation of glycans on chips.
- Hye Ryoung Heo
- , Kye Il Joo
- & Hyung Joon Cha
-
Article
| Open Access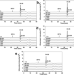 Discovery of exolytic heparinases and their catalytic mechanism and potential application
Discovery of exolytic heparinases and their catalytic mechanism and potential application
Exolytic heparinases are needed for sequencing of heparin and heparan sulfate (HP), but have not yet been reported. Here, the authors identify exolytic heparinases from different bacteria and show that the heparinases preferentially digest HP, determine the crystal structure of the exoheparinase BlexoHep and perform sequencing of HP octasaccharides using the enzyme.
- Qingdong Zhang
- , Hai-Yan Cao
- & Fuchuan Li
-
Article
| Open Access Diatom fucan polysaccharide precipitates carbon during algal blooms
Diatom fucan polysaccharide precipitates carbon during algal blooms
The fate of ocean carbon is determined by the balance between primary productivity and heterotrophic breakdown of that photosynthate. Here the authors show that diatoms produce a polysaccharide that resists bacterial degradation, accumulates, aggregates and stores carbon during spring blooms.
- Silvia Vidal-Melgosa
- , Andreas Sichert
- & Jan-Hendrik Hehemann

 A comprehensive synthetic library of poly-N-acetyl glucosamines enabled vaccine against lethal challenges of Staphylococcus aureus
A comprehensive synthetic library of poly-N-acetyl glucosamines enabled vaccine against lethal challenges of Staphylococcus aureus