Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Gravitational caustics in an atom laser
Gravitational caustics in an atom laser
Previously, the study of caustics has mostly focused on experiments with light. Here, the authors demonstrate gravitational caustics and investigate catastrophe atom optics using the matter waves of an atom laser generated from a Bose-Einstein condensate.
- M. E. Mossman
- , T. M. Bersano
- & P. Engels
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneous bicolor interrogation in thulium optical clock providing very low systematic frequency shifts
Simultaneous bicolor interrogation in thulium optical clock providing very low systematic frequency shifts
There are continuous efforts in improving the stability and systematic shifts of optical clocks. Here the authors demonstrate thulium optical clock utilizing bicolor scheme involving interrogation of both hyperfine levels and they are able to cancel the quadratic Zeeman shift.
- Artem A. Golovizin
- , Dmitry O. Tregubov
- & Nikolai N. Kolachevsky
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Reply to ‘Comment on “Coherent control in the extreme ultraviolet and attosecond regime by synchrotron radiation”’
Reply to ‘Comment on “Coherent control in the extreme ultraviolet and attosecond regime by synchrotron radiation”’
- Y. Hikosaka
- , T. Kaneyasu
- & M. Katoh
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access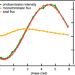 On “Coherent control in the extreme ultraviolet and attosecond regime by synchrotron radiation” by Hikosaka et al, Nat. Comm. 10, 4988 (2019)
On “Coherent control in the extreme ultraviolet and attosecond regime by synchrotron radiation” by Hikosaka et al, Nat. Comm. 10, 4988 (2019)
- Kevin C. Prince
- & Bruno Diviacco
-
Article
| Open Access Ultracold atom interferometry in space
Ultracold atom interferometry in space
Conducting atom-optical experiments in space is interesting for fundamental physics and challenging due to different environment compared to ground. Here the authors report matter-wave interferometry in space using atomic BECs in a sounding rocket.
- Maike D. Lachmann
- , Holger Ahlers
- & Ernst M. Rasel
-
Article
| Open Access Charged particle guiding and beam splitting with auto-ponderomotive potentials on a chip
Charged particle guiding and beam splitting with auto-ponderomotive potentials on a chip
There is interest in controlling particle beams using electric fields and using them in compact devices. Here the authors demonstrate guiding and splitting of charged particle (electron and ion) beams on a chip designed with special structures.
- Robert Zimmermann
- , Michael Seidling
- & Peter Hommelhoff
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of edge solitons in photonic graphene
Observation of edge solitons in photonic graphene
Edge states are excitations existing at the boundary of truncated periodic materials with specific spectral degeneracies, and their properties are enriched when materials possess a nonlinear response. Here, the authors provide experimental evidence of edge soliton formation in a nonlinear photonic graphene lattice induced in an atomic vapour cell.
- Zhaoyang Zhang
- , Rong Wang
- & Min Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Chip-scale atomic diffractive optical elements
Chip-scale atomic diffractive optical elements
Quantum coherence and the nonlinear properties of atoms are highly useful in optical devices. Here the authors show quantum-optic hybrid platforms in fully integrated chip-scale atomic diffractive optical elements by embedding hot atomic Rb vapor in microfabricated structures in silicon.
- Liron Stern
- , Douglas G. Bopp
- & John E. Kitching
-
Article
| Open Access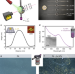 Atomic dispensers for thermoplasmonic control of alkali vapor pressure in quantum optical applications
Atomic dispensers for thermoplasmonic control of alkali vapor pressure in quantum optical applications
Robust and fast control of the atomic vapor pressure in alkali vapor cells would greatly extend their use for many quantum technologies. Here, the authors exploit plasmonic absorption in a cell coating containing gold nanoparticles to control the vapor pressure with milliseconds response time.
- Kristina R. Rusimova
- , Dimitar Slavov
- & Ventsislav K. Valev
-
Article
| Open Access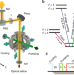 Inner-shell clock transition in atomic thulium with a small blackbody radiation shift
Inner-shell clock transition in atomic thulium with a small blackbody radiation shift
Precise and stable optical clocks are important for fundamental science and applications. Here the authors demonstrate a clock transitions in thulium (Tm), which has a small black body radiation frequency shift and is suitable for transportable atomic clocks.
- A. Golovizin
- , E. Fedorova
- & N. Kolachevsky
-
Article
| Open Access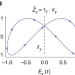 Floquet group theory and its application to selection rules in harmonic generation
Floquet group theory and its application to selection rules in harmonic generation
It is commonly assumed that a complete theory for selection rules in optical nonlinear harmonic generation was developed previously. Here, the authors present more general group theory based formalism for harmonic generation from dilute and dense media, yielding new symmetries and selection rules.
- Ofer Neufeld
- , Daniel Podolsky
- & Oren Cohen
-
Article
| Open Access 39Ar dating with small samples provides new key constraints on ocean ventilation
39Ar dating with small samples provides new key constraints on ocean ventilation
The rare noble gas isotope 39Ar is the ideal tracer to investigate the ventilation of the deep ocean in the time range of 50 to 1000 years. Here the authors constrain transit time distributions in the eastern Tropical Atlantic with 39Ar-measurements done on a sample size of 5 L of water utilising modern atom-optical techniques.
- Sven Ebser
- , Arne Kersting
- & Markus K. Oberthaler
-
Article
| Open Access Multiparameter optimisation of a magneto-optical trap using deep learning
Multiparameter optimisation of a magneto-optical trap using deep learning
Dynamics in cold atomic ensembles involve complex many-body interactions that are hard to treat analytically. Here, the authors use machine learning to optimise the cooling and trapping of neutral atoms, showing an improvement in the resulting resonant optical depth compared to more traditional solutions.
- A. D. Tranter
- , H. J. Slatyer
- & G. T. Campbell
-
Article
| Open Access Attosecond time-resolved photoelectron holography
Attosecond time-resolved photoelectron holography
Field induced tunneling is one of the fundamental processes of light-matter interaction. Here the authors reconstruct the temporal properties of tunneling using two-color electron holography with attosecond time resolution using argon atoms.
- G. Porat
- , G. Alon
- & N. Dudovich
-
Article
| Open Access Establishing and storing of deterministic quantum entanglement among three distant atomic ensembles
Establishing and storing of deterministic quantum entanglement among three distant atomic ensembles
Continuous-variable encoding is a promising approach for quantum information and communication networks. Here, the authors show how to map entanglement from three spatial optical modes to three separated atomic samples via electromagnetically induced transparency, releasing it later on demand.
- Zhihui Yan
- , Liang Wu
- & Kunchi Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring finite-range phase coherence in an optical lattice using Talbot interferometry
Measuring finite-range phase coherence in an optical lattice using Talbot interferometry
Quantum gas experiments are useful to study non-equilibrium many-body dynamics. Here, the authors demonstrate how the Talbot effect can be used to measure the spreading of phase coherence of ultracold atoms in an optical lattice.
- Bodhaditya Santra
- , Christian Baals
- & Herwig Ott
-
Article
| Open Access Strong coupling and high-contrast all-optical modulation in atomic cladding waveguides
Strong coupling and high-contrast all-optical modulation in atomic cladding waveguides
Studying the effects of quantum coherence and shifts in nanoscale atomic cladding waveguides is challenging. Here, Sternet al. construct a highly compact serpentine silicon-nitride atomic vapour cladding waveguide and observe phenomena such as van-der-Waals shifts, dynamical stark shifts and strong coupling.
- Liron Stern
- , Boris Desiatov
- & Uriel Levy
-
Article
| Open Access Dual matter-wave inertial sensors in weightlessness
Dual matter-wave inertial sensors in weightlessness
Atom interferometers in microgravity environments can reach precisions unattainable on Earth. Here the authors report the operation of a dual species interferometer onboard a zero-G aircraft, testing universality of free fall in microgravity and providing a test bed for future moving inertial sensors.
- Brynle Barrett
- , Laura Antoni-Micollier
- & Philippe Bouyer
-
Article
| Open Access Time-resolved scattering of a single photon by a single atom
Time-resolved scattering of a single photon by a single atom
The efficient excitation of atoms using photons is a fundamental step in the control of photon-atom interaction and quantum information protocols. Here the authors show that photons with an exponentially rising envelope excite a single atom efficiently compared to a decaying temporal shape.
- Victor Leong
- , Mathias Alexander Seidler
- & Christian Kurtsiefer
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent manipulation of a solid-state artificial atom with few photons
Coherent manipulation of a solid-state artificial atom with few photons
Quantum information processing requires a system in which a single photon controls a single atom and vice versa. Here, the authors demonstrate such reciprocal operation and achieve coherent manipulation of a quantum dot by a few photons sent on an optical cavity.
- V. Giesz
- , N. Somaschi
- & P. Senellart
-
Article
| Open Access Diffractive imaging of a rotational wavepacket in nitrogen molecules with femtosecond megaelectronvolt electron pulses
Diffractive imaging of a rotational wavepacket in nitrogen molecules with femtosecond megaelectronvolt electron pulses
Imaging changes in molecular geometries with sufficient temporal and spatial resolution to image nuclei is a critical challenge in the chemical sciences. Here the authors report gasphase Megaelectronvolt electron diffraction with 100 fs temporal resolution and subAngstrom spatial resolution.
- Jie Yang
- , Markus Guehr
- & Xijie Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Collective atomic scattering and motional effects in a dense coherent medium
Collective atomic scattering and motional effects in a dense coherent medium
Light scattering from a dense coherent medium is determined by the interplay of dispersive and radiative dipole–dipole interactions. Here, the authors control the motional effects that obscure the coherence of scattered light and study collective emission in a driven gas of cold strontium-88 atoms.
- S. L. Bromley
- , B. Zhu
- & J. Ye
-
Article |
 Requirements for fault-tolerant factoring on an atom-optics quantum computer
Requirements for fault-tolerant factoring on an atom-optics quantum computer
As quantum information technologies develop into practical computational engines, many technical issues must be considered. Devittet al.estimate the resources needed to perform prime factorization with Shor’s algorithm on an atom-optics quantum computer and show how to optimize the computer's performance.
- Simon J. Devitt
- , Ashley M. Stephens
- & Kae Nemoto
-
Article
| Open Access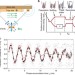 Integrated Mach–Zehnder interferometer for Bose–Einstein condensates
Integrated Mach–Zehnder interferometer for Bose–Einstein condensates
Atom interferometers exploit wave-particle duality and can be used as sensitive measurement devices. Berrada et al.present a Mach–Zehnder interferometer for Bose–Einstein condensates trapped on an atom chip and demonstrate enhanced performance using non-classical states.
- T. Berrada
- , S. van Frank
- & J Schmiedmayer

 A compact cold-atom interferometer with a high data-rate grating magneto-optical trap and a photonic-integrated-circuit-compatible laser system
A compact cold-atom interferometer with a high data-rate grating magneto-optical trap and a photonic-integrated-circuit-compatible laser system