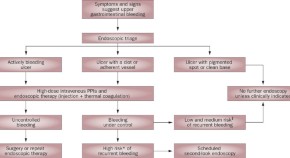
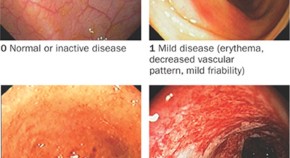
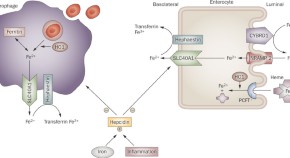
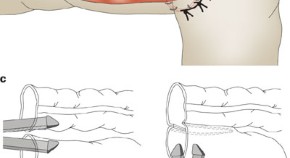
Review Articles, News & Views, Perspectives, Hypotheses, Analyses and Review in 2009
Filter By:
Article Type
Year