Volume 11
-
No. 12 December 2010
Caspase-1-mediated pyroptosis can occur in vitro. Aderem and colleagues now establish caspase-1-induced pyroptosis as an innate immune effector mechanism against intracellular bacteria in vivo (p 1136). Original image by Adrian Ozinsky and Alan Aderem shows a macrophage interacting with a flagellated bacterium. Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 11 November 2010
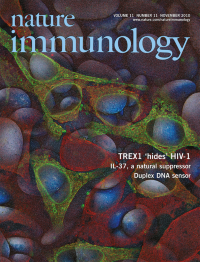
Intracellular recognition receptors are rarely triggered after infection with human immunodeficiency virus. Lieberman and colleagues show that the host endonuclease TREX1 helps this virus avoid detection (p 1005 and News & Views by Geijtenbeek p 979). The original epifluorescent microscopy image shows hemagglutinin-tagged TREX1 (green) and endoplasmic reticulum (red) in HeLa cells.Original image by Nan Yan.
Collection
-
No. 10 October 2010
The DNA-binding factor TO X is required for the development of CD4+, natural killer and regulatory T cells. Kaye and colleagues now show that TO X is also required for development of the natural killer and lymphoid tissue-inducer lymphoid lineages (p 945 and News and Views by Di Santo, p 885). Original immunofluorescence staining of a TO X-deficient Peyer's patch shows the presence of B cells (green) and paucity of T cells (red). Original image by Parinaz Aliahmad and Kolja Wawrowsky. Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 9 September 2010
Whether fish have specialized mucosal antibodies was unknown. Sunyer and colleagues show that secreted immunoglobulin T fulfills this function in trout (p 827 and News & Views by Flajnik, p 777). Original differential interference contrast image shows a trout gut cryosection with immunoglobulin T-positive B cells (green) in the epithelium (nuclei are stained with the DNA-intercalating dye DAPI); the parasite Ceratomyxa shasta (magneta) is located in the luminal area. Original image by Irene Salinas. Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 8 August 2010
Winning a game of chess requires complex decision making. Similar to chess, the immune system must make strategic 'decisions' to produce an efficient immune response. This month we focus on decision making in the immune system in a series of specially commissioned articles looking at how immune cell development, lineage decisions and effector functions are mediated during an immune response (http://www.nature.com/ni/focus/decisionmaking/). Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 7 July 2010
Nature Immunology was launched 10 years ago this month. To commemorate our 10th anniversary, we asked several prominent scientists to imagine what the next decade of research might bring in particular areas of immunology (http://www.nature.com/ni/focus/tenthbirthday/index.html). Artwork by Lewis Long.
Focus
-
No. 6 June 2010
The relationship between hematopoietic stem cells and progenitor populations during acute infection remains to be defined. Potocnik and colleagues identify a unique IL-7Rα+c-Kithi progenitor subset that arises during acute malaria infection and gives rise to predominantly myeloid cells. Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 5 May 2010
Influenza virus M2, a pH-gated H+ channel that neutralizes the pH of the trans-Golgi network, activates the NLR P3 inflammasome (p 404). The original confocal image shows colocalization (yellow) of M2 (red) and the trans-Golgi network (green) in influenza virus-infected cells. Original image by Takeshi Ichinohe. Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 4 April 2010
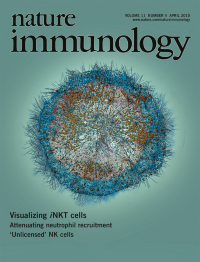
How and where invariant natural killer T cells encounter glycolipids in vivo remains unclear. Batista and colleagues show that CD169+ macrophages present lipid antigens to iNKT cells in lymph nodes (p 303). Original multiphoton microscopy image shows B cells (blue) and CD4+ T cells (red) that define the follicular and paracortical regions of a popliteal lymph node. Original image by Patricia Barral. Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 3 March 2010
Hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) selfrenewal and differentiation are tightly regulated. Aifantis and colleagues (p 207; see also News and Views by Garrison and Rossi, p 193) show that HSC differentiation can be modulated by the E3 ligase Fbw7 and its target substrate c-Myc. Original image shows a mouse embryonic stem cell line expressing an Fbw7-lacZ reporter. Original image by Kelly Crusio. Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 2 February 2010
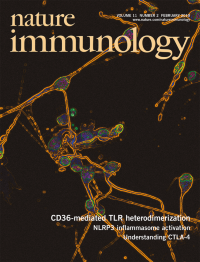
Neurons in in vitro culture are exposed to inflammatory mediators released by β-amyloid-activated microglial cells. Moore and colleagues (p 155) show that a CD36-TLR4-TLR6 heterotrimer mediates β-amyloid recognition and microglial cell activation in the brain. The original confocal image shows CAD mouse neuronal cells cultured together with microglial cells stimulated with Aβ1–42 and stained with antibody to neuronal class III β-tubulin (green). DAPI nuclear staining is blue. Original image by Janine M van Gils and Laurent Boyer. Artwork by Lewis Long.
-
No. 1 January 2010
Just as removing one or two poorly chosen blocks can reduce a neat but precariously balanced stack to a pile of rubble, mutating or impairing one or a few mechanisms responsible for maintaining immune tolerance can precipitate an autoimmune attack. The series of articles in this Focus issue cover what is known about the biological processes that underpin immune tolerance and highlight the possibility that the limited understanding of the etitology and pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases may indicate that additional important immune tolerance mechanisms still await identification. Artwork by Lewis Long.
Focus