Collection |
Collections
Filters
-
Collection Type
-
-
Collection |
Microorganism cell death – a new era
The ability of cells to self-destruct appears to be essential for cellular life. However, the existence of genetically programmed death pathways in single-cell organisms has been long debated. Thus, cell death research on microorganisms was sparse while the field focused on human tumor cells, animal models and some plants. In addition, microbial death is most commonly viewed as a consequence of being killed by host immune tactics and antibiotics, rather than intrinsic microorganism cell suicide. However, a new perspective has recently emerged, stemming from elegant delineation of cell suicide mechanisms in diverse prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbes. The molecular details often resemble components of human innate immunity, further suggesting that some early forms of cell death arose in microorganisms as defense mechanisms against their own pathogens.
Open for submissions -
Collection |
 Cell Death & Differentiation Readers' Choice: 2020-2022
Cell Death & Differentiation Readers' Choice: 2020-2022
In this Collection we have collated the top read and cited articles from Cell Death & Differentiation from the past three years. This focus includes a spectrum of articles covering the cellular and molecular biology of disease and features original articles, as well as thought-provoking reviews and comment. Read on to see what our readers worldwide have been citing and reading.
-
Special |
 p53: Recent Facts and New Questions
p53: Recent Facts and New Questions
This Special Issue of Cell Death & Differentiation brings together a set of articles focused on p53. Almost four decades of research and thousands of publications have firmly established p53 as one of the most frequently altered genes in cancer and the hub of the cell response to stress. Yet, new functions continue to emerge adding further complexity but also providing new translational avenues. Read through to explore recent findings on p53 mutants, family members, mechanisms of tumor suppression, regulation of ferroptosis and response to DNA replication and ribosome biogenesis stress, while challenged by the thought-provoking questions posed by leading scientists in the field.
Image: Liu and Gu, 2022: 10.1038/s41418-022-00943-y -
Special |
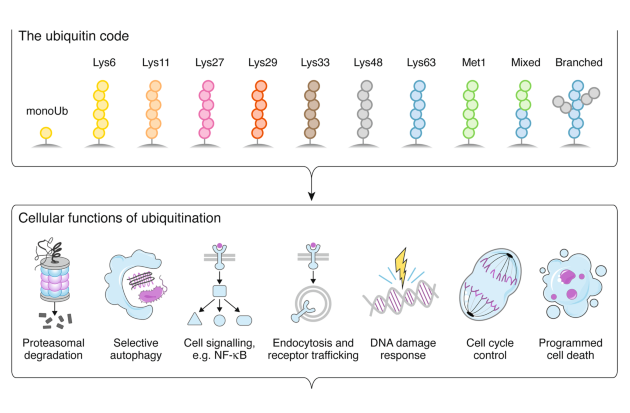 Ubiquitin Signaling in Health and Disease
Ubiquitin Signaling in Health and Disease
This Special Issue of Cell Death & Differentiation is dedicated to ubiquitination, one of the most complex and pervasive post-translational protein modifications that affects thousands of targets and all aspects of eukaryotic biology. In this set of commissioned articles, the authors discuss new players of the complex ubiquitin system, the role of new 'ciphers' of the ubiquitin code, and emerging concepts of ubiquitin-mediated processes in cell physiology and disease development. Read through to learn how targeting components of the ubiquitin machinery could translate into new therapeutic opportunities.
Image: Rune Damgaard, Cell Death & Differentiation (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41418-020-00703-w -
Special |
Human Organoids: Filling the Gap Between Basic and Translational Research
This Special Issue of Cell Death & Differentiation brings together a set of reviews focused on human organoids. Pioneers of the field discuss strategies to develop 3D cultures that faithfully recapitulate key features of human organs such as brain, inner ear, female reproductive or gastrointestinal tract, which can be used to study not only tissue physiology but also the pathogenic mechanisms of multiple diseases, ranging from infections to cancer. The authors discuss current challenges as well as strategies to harness the tremendous potential of organoids to fill the gap between basic and translational research.
Image: Alzamil et al, Cell Death & Differentiation, 2020 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41418-020-0565-5 -
Special |
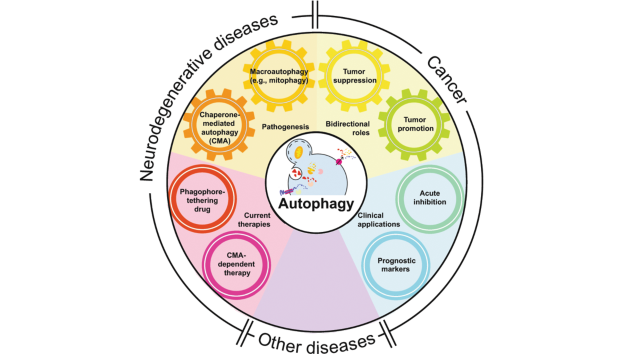 Special Issue: Autophagy in Physiology and Disease
Special Issue: Autophagy in Physiology and Disease
This Cell Death & Differentiation special issue on Autophagy brings together a series of commissioned reviews dedicated to the rapidly expanding autophagy field. Outstanding experts discuss how autophagy emerged as a key process in most organismal developmental stages, from fertilization throughout adult life and regeneration; how the removal of cellular organelles and infectious agents needs to be carefully controlled, impacting on the immune response and on an expanding list of diseases; what are the best strategies to modulate autophagy for the treatment of cancer and other pathologies? The readers will be challenged by this and other thought-provoking questions which we hope will help them charting innovative paths toward our thorough understanding of this fundamental process and its therapeutic applications.
Image: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-019-0480-9 -
Collection |
 The Best of Cell Death & Differentiation 2018-2019
The Best of Cell Death & Differentiation 2018-2019
In this Web Focus we have showcased the top read, shared and cited articles from Cell Death & Differentiation from 2018 and 2019. This collection includes a spectrum of articles covering the cellular and molecular biology of disease and features both original articles and thought-provoking reviews. We hope you enjoy reading this collection.
Image: National Institutes of Health/Stocktrek Images -
Collection |
 Best of CDDpress 2018 on p53
Best of CDDpress 2018 on p53
CDDpress, with its three journals (Cell Death & Differentiation, Cell Death & Disease, Cell Death Discovery), has just finished the publication for the year 2018, publishing insightful and high-impact articles on the frontlines of cell biology and biochemistry research. In 2018, the journals received nearly 5000 submissions and published around 1400 selected papers. Of particular interest were several pivotal and influential papers highlighting the role of p53 in cancer and other diseases. Here, with the "Best of CDDpress 2018 on p53" collection, we offer a selection of 2017-2018’s most impactful papers on p53. We hope that you will enjoy reading this special collection.
-
Special |
 Special issue on Necroinflammation
Special issue on Necroinflammation
This Special Issue of Cell Death & Differentiation focuses on necroinflammation, the inflammatory response to necrotic cell death. Leading experts in the field discuss the remarkable advances made in both basic and translational research, dissecting the highly interconnected pathways underlying various programmed necrosis forms, understanding how these pathways differently engage the immune system, how they impact on health and disease, and how they can be monitored and targeted in the clinical practice.
-
Collection |
 CDD 25th anniversary collection: seminal papers from the past 25 years
CDD 25th anniversary collection: seminal papers from the past 25 years
To celebrate 25 years of CDD, our Co-Editors-in-Chief have selected some of the journal's most seminal papers to highlight the impact of the journal over the past 25 years.
-
Collection |
 Cell Death, Small Molecules, and Translational Medicine
Cell Death, Small Molecules, and Translational Medicine
The recent 26th ECDO conference ‘From small molecules to translational medicine’ in Saint-Petersburg (locally organized by Professors Zhivotovsky, Barlev and Lavrik) highlighted the recent developments in the field of cell death with a focus on the small molecules discovery and development. Pharmacological targeting via small molecule-based chemical probes has recently emerged as a valuable tool to delineate molecular mechanisms of various cell death pathways and pave the way towards novel therapeutic approaches in cancer, neurodegenerative and autoimmune diseases. We suggest the selection of articles from the CDD press that will lead through a breathtaking journey from the target –oriented drug development to translational applications.
Image: National Institutes of Health/Stocktrek Images

 CDDpress: Monthly Readers' Choice
CDDpress: Monthly Readers' Choice