Abstract
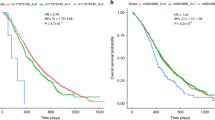
The development of genotyping technologies has allowed for wider screening for inherited causes of variable outcomes following drug administration. We have performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS) on 221 colorectal cancer (CRC) patients that had been treated with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), either alone or in combination with oxaliplatin (FOLFOX). A validation set of 791 patients was also studied. Seven SNPs (rs16857540, rs2465403, rs10876844, rs10784749, rs17626122, rs7325568 and rs4243761) showed evidence of association (pooled P-values 0.020, 9.426E-03, 0.010, 0.017, 0.042, 2.302E-04, 2.803E-03) with adverse drug reactions (ADRs). This is the first study to explore the genetic basis of inter-individual variation in toxicity responses to the administration of 5-FU or FOLFOX in CRC patients on a genome-wide scale.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beutler E, Dern RJ, Flanagan CL, Alving AS . The hemolytic effect of primaquine. VII. Biochemical studies of drug-sensitive erythrocytes. J Lab Clin Med 1955; 45: 286–295.
Wilke RA, Lin DW, Roden DM, Watkins PB, Flockhart D, Zineh I et al. Identifying genetic risk factors for serious adverse drug reactions: current progress and challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2007; 6: 904–916.
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM . Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer 2010; 127: 2893–2917.
Quasar Collaborative G, Gray R, Barnwell J, McConkey C, Hills RK, Williams NS et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy versus observation in patients with colorectal cancer: a randomised study. Lancet 2007; 370: 2020–2029.
Meyerhardt JA, Mayer RJ . Systemic therapy for colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 476–487.
de Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, Homerin M, Hmissi A, Cassidy J et al. Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 2938.
Eng C . Toxic effects and their management: daily clinical challenges in the treatment of colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2009; 6: 207–218.
Van Kuilenburg ABP, Meinsma R, Zoetekouw L, Van Gennip AH . High prevalence of the IVS14 1G> A mutation in the dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase gene of patients with severe 5-fluorouracil-associated toxicity. Pharmacogenet Genom 2002; 12: 555.
Ichikawa W, Takahashi T, Suto K, Sasaki Y, Hirayama R . Orotate phosphoribosyltransferase gene polymorphism predicts toxicity in patients treated with bolus 5-fluorouracil regimen. Clin Cancer Res 2006; 12: 3928.
Iyer L, King CD, Whitington PF, Wen M, Ramirez J, Karrison T et al. Genetic predisposition to the metabolism of irinotecan (CPT-11). Role of uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase isoform 1A1 in the glucuronidation of its active metabolite (SN-38) in human liver microsomes. J Clin Invest 1998; 101: 847.
Meyer UA . Pharmacogenetics and adverse drug reactions. Lancet 2000; 356: 1667–1671.
Yin M, Yan J, Martinez-Balibrea E, Graziano F, Lenz HJ, Kim HJ et al. ERCC1 and ERCC2 polymorphisms predict clinical outcomes of oxaliplatin-based chemotherapies in gastric and colorectal cancer: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 1632–1640.
Azfal S, Gusella M, Vainer B, Vogel UB, Andersen JT, Broedbaek K et al. Combinations of polymorphisms in genes involved in the 5-Fluorouracil metabolism pathway are associated with gastrointestinal toxicity in chemotherapy-treated colorectal cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 3822–3829.
Crowley JJ, Sullivan PF, McLeod HL . Pharmacogenomic genome-wide association studies: lessons learned thus far. Pharmacogenomics 2009; 10: 161–163.
Pinol V, Castells A, Andreu M, Castellvi-Bel S, Alenda C, Llor X et al. Accuracy of revised Bethesda guidelines, microsatellite instability, and immunohistochemistry for the identification of patients with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. JAMA 2005; 293: 1986–1994.
Paré L, Marcuello E, Altés A, del Rio E, Sedano L, Salazar J et al. Pharmacogenetic prediction of clinical outcome in advanced colorectal cancer patients receiving oxaliplatin/5-fluorouracil as first-line chemotherapy. Br J Cancer 2008; 99: 1050–1055.
Chua W, Goldstein D, Lee CK, Dhillon H, Michael M, Mitchell P et al. Molecular markers of response and toxicity to FOLFOX chemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 2009; 101: 998–1004.
Martinez-Balibrea E, Abad A, Martinez-Cardus A, Ginés A, Valladares M, Navarro M et al. UGT1A and TYMS genetic variants predict toxicity and response of colorectal cancer patients treated with first line irinotecan and fluorouracil combination therapy. Br J Cancer 2010; 103: 581–589.
Korn JM, Kuruvilla FG, McCarroll SA, Wysoker A, Nemesh J, Caqley S et al. Integrated genotype calling and association analysis of SNPs, common copy number polymorphisms and rare CNVs. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 1253–1260.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Patterson N, Price AL, Reich D . Population structure and eigenanalysis. PLoS Genet 2006; 2: e190.
Price AL, Weale ME, Patterson N, Myers SR, Need AC, Shianna KV et al. Long-range LD can confound genome scans in admixed populations. Am J Hum Genet 2008; 83: 132–135.
Ihaka R, Gentleman R . R: A language for data analysis and graphics. J Comput Graph Stat 1996; 5: 299–314.
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ . Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005; 21: 263–265.
Colella S, Yau C, Taylor JM, Mirza G, Butler H, Clouston P et al. QuantiSNP: an Objective Bayes Hidden-Markov Model to detect and accurately map copy number variation using SNP genotyping data. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 35: 2013–2025.
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Genome-wide association study of CNVs in 16,000 cases of eight common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 2010; 464: 713–720.
Zhang H, Li YM, Jin X . DPYD* 5 gene mutation contributes to the reduced DPYD enzyme activity and chemotherapeutic toxicity of 5-FU: results from genotyping study on 75 gastric carcinoma and colon carcinoma patients. Med Oncol 2007; 24: 251.
Sohn KJ, Corxford R, Yates Z, Lucock M, Kim YI . Effect of the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677 T polymorphism on chemosensitivity of colon and breast cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil and methotrexate. J Natl Cancer Inst 2004; 96: 134.
Lecomte T, Landi B, Beaune P, Laurent-Puig P, Loriot MA . Glutathione S-transferase P1 polymorphism (Ile105Val) predicts cumulative neuropathy in patients receiving oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 2006; 12: 3050.
Daly AK . Genome-wide association studies in pharmacogenomics. Nat Rev Genet 2010; 11: 241–246.
Weinshilboum R, Wang L . Pharmacogenomics: bench to bedside. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2004; 3: 739–748.
Conrad DF, Pinto D, Redon R, Feuk L, Gokcumen O, Zhang Y et al. Origins and functional impact of copy number variation in the human genome. Nature 2009; 464: 704–712.
Skol AD, Scott LJ, Abecasis GR, Boehnke M . Joint analysis is more efficient than replication-based analysis for two-stage genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 209–213.
Zhu Y, Richardson JA, Parada LF, Graff JM . Smad3 mutant mice develop metastatic colorectal cancer. Cell 1998; 94: 703–714.
Ashcroft GS, Yang X, Glick AB, Weinstein M, Letterio JJ, Mizel DE et al. Mice lacking Smad3 show accelerated wound healing and an impaired local inflammatory response. Nat Cell Biol 1999; 1: 260–266.
Cirulli ET, Goldstein DB . Uncovering the roles of rare variants in common disease through whole-genome sequencing. Nat Rev Genet 2010; 11: 415–425.
Acknowledgements
We are sincerely grateful to all patients participating in this study, who were recruited as part of the EPICOLON project. This work was supported by Grants from Fondo de Investigación Sanitatia/FEDER (06/1384, CP06/0267, 06/1712, 08/0024, 08/1276, PI08-1359, PI08-1635, PS09/02368), Instituto de Salud Carlos III (Acción Transversal de Cáncer), Xunta de Galicia (PGIDT08CSA005208PR, PGIDIT07PXIB9101209PR), Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación SAF 07-64873 and SAF 2010-19273), Fundación Privada Olga Torres (CRP), Fundación Barrie de la Maza (Programa DIANA), Asociación Española contra el Cáncer (Fundación Científica y Junta de Barcelona), Fundación Mutua Madrileña (LFLA), Fundación Ramón Areces (LFLA), Grant 209/12/2009 Agencia d'Informació Avaluació i Qualitat en Salut, and FP7 CHIBCHA Consortium (SCB and ACar). CIBERehd and CIBERER are funded by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III. SCB and CFR are supported by contracts from the Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria (CP 03-0070 to SCB and PS09/02368 to CFR). JBCs work was supported by the Wellcome Trust core award Grant number 075491/Z/04. We acknowledge the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium for making available data about SNP tagging of common CNVs (http://www.wtccc.org.uk/wtcccplus_cnv/supplemental.shtml).'
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the The Pharmacogenomics Journal website
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernandez-Rozadilla, C., Cazier, J., Moreno, V. et al. Pharmacogenomics in colorectal cancer: a genome-wide association study to predict toxicity after 5-fluorouracil or FOLFOX administration. Pharmacogenomics J 13, 209–217 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2012.2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2012.2
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The science of mucositis
Supportive Care in Cancer (2022)
-
Precision medicine: from pharmacogenomics to pharmacoproteomics
Clinical Proteomics (2016)
-
Clinical Association Between Pharmacogenomics and Adverse Drug Reactions
Drugs (2015)
-
'Toxgnostics': an unmet need in cancer medicine
Nature Reviews Cancer (2014)