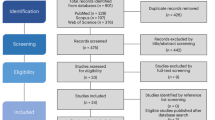
Abstract
The zebrafish (Danio rerio) is a model animal that is being increasingly used in neuroscience research. A decade ago, the first study on unpredictable chronic stress (UCS) in zebrafish was published, inspired by protocols established for rodents in the early 1980s. Since then, several studies have been published by different groups, in some cases with conflicting results. Here we conducted a systematic review to identify studies evaluating the effects of UCS in zebrafish and meta-analytically synthetized the data of neurobehavioral outcomes and relevant biomarkers. Literature searches were performed in three databases (PubMed, Scopus and Web of Science) with a two-step screening process based on inclusion/exclusion criteria. The included studies underwent extraction of qualitative and quantitative data, as well as risk-of-bias assessment. Outcomes of included studies (n = 38) were grouped into anxiety/fear-related behavior, locomotor function, social behavior or cortisol level domains. UCS increased anxiety/fear-related behavior and cortisol levels while decreasing locomotor function, but a significant summary effect was not observed for social behavior. Despite including a substantial number of studies, the high heterogeneity and the methodological and reporting problems evidenced in the risk-of-bias analysis made it difficult to assess the internal validity of most studies and the overall validity of the model. Our review thus evidences the need to conduct well-designed experiments to better evaluate the effects of UCS on diverse behavioral patterns displayed by zebrafish.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
We are sorry, but there is no personal subscription option available for your country.
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available in Open Science Framework (https://osf.io/j2zva/).
References
Katz, R. J. & Hersh, S. Amitriptyline and scopolamine in an animal model of depression. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 5, 265–271 (1981).
Katz, R. J., Roth, K. A. & Carroll, B. J. Acute and chronic stress effects on open field activity in the rat: implications for a model of depression. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 5, 247–251 (1981).
Katz, R. J. Animal model of depression: pharmacological sensitivity of a hedonic deficit. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 16, 965–968 (1982).
Willner, P., Towell, A., Sampson, D., Sophokleous, S. & Muscat, R. Reduction of sucrose preference by chronic unpredictable mild stress, and its restoration by a tricyclic antidepressant. Psychopharmacology 93, 358–364 (1987).
Willner, P. Validity, reliability and utility of the chronic mild stress model of depression: a 10-year review and evaluation. Psychopharmacology 134, 319–329 (1997).
Willner, P. The chronic mild stress (CMS) model of depression: history, evaluation and usage. Neurobiol. Stress 6, 78–93 (2017).
Nollet, M. Models of depression: unpredictable chronic mild stress in mice. Curr. Protoc. 1, e208 (2021).
Strekalova, T. & Steinbusch, H. in Mood and Anxiety Related Phenotypes in Mice: Characterization Using Behavioral Tests (ed. Gould, T. D.) 153–176 (Humana Press, 2009).
Willner, P. Reliability of the chronic mild stress model of depression: a user survey. Neurobiol. Stress 6, 68–77 (2017).
Antoniuk, S., Bijata, M., Ponimaskin, E. & Wlodarczyk, J. Chronic unpredictable mild stress for modeling depression in rodents: meta-analysis of model reliability. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 99, 101–116 (2019).
Piato, Â. L. et al. Unpredictable chronic stress model in zebrafish (Danio rerio): behavioral and physiological responses. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 35, 561–567 (2011).
Maximino, C. et al. Non-mammalian models in behavioral neuroscience: consequences for biological psychiatry. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 9, 233 (2015).
Weber-Stadlbauer, U. & Meyer, U. Challenges and opportunities of a-priori and a-posteriori variability in maternal immune activation models. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 28, 119–128 (2019).
Marcon, M. et al. Prevention of unpredictable chronic stress-related phenomena in zebrafish exposed to bromazepam, fluoxetine and nortriptyline. Psychopharmacology 233, 3815–3824 (2016).
Bertelli, P. R. et al. Anti-stress effects of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist liraglutide in zebrafish. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 111, 110388 (2021).
Golla, A., Østby, H. & Kermen, F. Chronic unpredictable stress induces anxiety-like behaviors in young zebrafish. Sci Rep. 10, 10339 (2020).
Zimmermann, F. F. et al. Unpredictable chronic stress alters adenosine metabolism in zebrafish brain. Mol. Neurobiol. 53, 2518–2528 (2016).
Jayamurali, D. & Govindarajulu, S. N. Impact of chronic unpredictable stress on the expression of apoptotic genes in zebrafish brain. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 8, 4363–4370 (2017).
Marcon, M. et al. Enriched environment prevents oxidative stress in zebrafish submitted to unpredictable chronic stress. PeerJ 6, e5136 (2018).
Huang, V., Butler, A. A. & Lubin, F. D. Telencephalon transcriptome analysis of chronically stressed adult zebrafish. Sci Rep. 9, 1379 (2019).
Zhang, R. et al. A reliable high-throughput screening model for antidepressant. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 9505 (2021).
Kirsten, K. et al. Acute and chronic stress differently alter the expression of cytokine and neuronal markers genes in zebrafish brain. Stress 24, 107–112 (2021).
Demin, K. A. et al. Modulation of behavioral and neurochemical responses of adult zebrafish by fluoxetine, eicosapentaenoic acid and lipopolysaccharide in the prolonged chronic unpredictable stress model. Sci Rep. 11, 14289 (2021).
Extracted data + meta-analysis templates. Open Science Framework https://osf.io/pbhy4 (2023).
Individualized scores for risk of bias and reporting quality - updated version. Open Science Framework https://osf.io/gav7p (2023).
Kompagne, H. et al. Chronic mild stress generates clear depressive but ambiguous anxiety-like behavior in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 193, 311–314 (2008).
Cox, B. M., Alsawah, F., McNeill, P. C., Galloway, M. P. & Perrine, S. A. Neurochemical, hormonal, and behavioral effects of chronic unpredictable stress in the rat. Behav. Brain Res. 220, 106–111 (2011).
Zhu, S., Shi, R., Wang, J., Wang, J.-F. & Li, X.-M. Unpredictable chronic mild stress not chronic restraint stress induces depressive behaviors in mice. NeuroReport 25, 1151–1155 (2014).
Kumar, B., Kuhad, A. & Chopra, K. Neuropsychopharmacological effect of sesamol in unpredictable chronic mild stress model of depression: behavioral and biochemical evidences. Psychopharmacology 214, 819–828 (2011).
Sequeira-Cordero, A., Salas-Bastos, A., Fornaguera, J. & Brenes, J. C. Behavioral characterisation of chronic unpredictable stress based on ethologically relevant paradigms in rats. Sci. Rep. 9, 17403 (2019).
Boxelaere van, M., Clements, J., Callaerts, P., D’Hooge, R. & Callaerts-Vegh, Z. Unpredictable chronic mild stress differentially impairs social and contextual discrimination learning in two inbred mouse strains. PLoS ONE 12, e0188537 (2017).
Lages, Y. V. M., Rossi, A. D., Krahe, T. E. & Landeira-Fernandez, J. Effect of chronic unpredictable mild stress on the expression profile of serotonin receptors in rats and mice: a meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 124, 78–88 (2021).
Rambo, C. L. et al. Gender differences in aggression and cortisol levels in zebrafish subjected to unpredictable chronic stress. Physiol. Behav. 171, 50–54 (2017).
Palucha-Poniewiera, A., Podkowa, K., Rafalo-Ulinska, A., Branski, P. & Burnat, G. The influence of the duration of chronic unpredictable mild stress on the behavioral responses of C57BL/6J mice. Behav. Pharmacol. 31, 574–582 (2020).
Fontana, B. D., Gibbon, A. J., Cleal, M., Norton, W. H. J. & Parker, M. O. Chronic unpredictable early-life stress (CUELS) protocol: early-life stress changes anxiety levels of adult zebrafish. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 108, 110087 (2021).
Bosch, K. et al. Repeated testing modulates chronic unpredictable mild stress effects in male rats. Behav. Brain Res. 432, 113960 (2022).
Jankord, R. et al. Stress vulnerability during adolescent development in rats. Endocrinology 152, 629–638 (2011).
Sert Du, N. P. et al. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: updated guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 18, e3000410 (2020).
Baker, D., Lidster, K., Sottomayor, A. & Amor, S. Two years later: journals are not yet enforcing the ARRIVE guidelines on reporting standards for pre-clinical animal studies. PLoS Biol. 12, e1001756 (2014).
Macleod, M. R. et al. Risk of bias in reports of in vivo research: a focus for improvement. PLoS Biol. 13, e1002273 (2015).
Samsa, G. & Samsa, L. A guide to reproducibility in preclinical research. Acad. Med. 94, 47–52 (2019).
Gerlai, R. Reproducibility and replicability in zebrafish behavioral neuroscience research. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 178, 30–38 (2019).
Worp van der, H. B. et al. Can animal models of disease reliably inform human studies? PLoS Med. 7, e1000245 (2010).
Chakravarty, S. et al. Chronic unpredictable stress (CUS)-induced anxiety and related mood disorders in a zebrafish model: altered brain proteome profile implicates mitochondrial dysfunction. PLoS ONE 8, e63302 (2013).
Manuel, R. et al. Unpredictable chronic stress decreases inhibitory avoidance learning in Tuebingen long-fin zebrafish: stronger effects in the resting phase than in the active phase. J. Exp. Biol. 217, 3919–3928 (2014).
Pavlidis, M., Theodoridi, A. & Tsalafouta, A. Neuroendocrine regulation of the stress response in adult zebrafish, Danio rerio. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 60, 121–131 (2015).
Davis, D. J. et al. Lactobacillus plantarum attenuates anxiety-related behavior and protects against stress-induced dysbiosis in adult zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 6, 33726 (2016).
Benneh, C. K. et al. Maerua angolensis stem bark extract reverses anxiety and related behaviors in zebrafish—involvement of GABAergic and 5-HT systems. J. Ethnopharmacol. 207, 129–145 (2017).
Fulcher, N., Tran, S., Shams, S., Chatterjee, D. & Gerlai, R. Neurochemical and behavioral responses to unpredictable chronic mild stress following developmental isolation: the zebrafish as a model for major depression. Zebrafish 14, 23–34 (2017).
Grzelak, A. K. et al. Stress leukogram induced by acute and chronic stress in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp. Med. 67, 263–269 (2017).
dos Santos Sampaio, T. I. et al. Leaves of Spondias mombin L. a traditional anxiolytic and antidepressant: pharmacological evaluation on zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Ethnopharmacol. 224, 563–578 (2018).
Marcon, M. et al. Environmental enrichment modulates the response to chronic stress in zebrafish. J. Exp. Biol. 221, jeb176735 (2018).
Reddy, R. G. et al. Fellutamide B synthetic path intermediates with in vitro neuroactive function shows mood-elevating effect in stress-induced zebrafish model. ACS Omega 3, 10534–10544 (2018).
Song, C. et al. Modeling consequences of prolonged strong unpredictable stress in zebrafish: complex effects on behavior and physiology. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 81, 384–394 (2018).
Costa de Melo, N. et al. Anxiolytic and antidepressant effects of the hydroethanolic extract from the leaves of Aloysia polystachya (Griseb.) Moldenke: a study on zebrafish (Danio rerio). Pharmaceuticals 12, 106 (2019).
Marcon, M. et al. Acetyl-l-carnitine as a putative candidate for the treatment of stress-related psychiatric disorders: novel evidence from a zebrafish model. Neuropharmacology 150, 145–152 (2019).
Mocelin, R. et al. N-acetylcysteine reverses anxiety and oxidative damage induced by unpredictable chronic stress in zebrafish. Mol. Neurobiol. 56, 1188–1195 (2019).
Reddy, R. G. et al. Crafting carbazole-based vorinostat and tubastatin-A-like histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors with potent in vitro and in vivo neuroactive functions. ACS Omega 4, 17295–17300 (2019).
Demin, K. A. et al. Understanding complex dynamics of behavioral, neurochemical and transcriptomic changes induced by prolonged chronic unpredictable stress in zebrafish. Sci Rep. 10, 19981 (2020).
O'Daniel, M. P. & Petrunich-Rutherford, M. L. Effects of chronic prazosin, an α-1 adrenergic antagonist, on anxiety-like behavior and cortisol levels in a chronic unpredictable stress model in zebrafish (Danio rerio). PeerJ 8, e8472 (2020).
Thomson, J. S. et al. Acute and chronic stress prevents responses to pain in zebrafish: evidence for stress-induced analgesia. J. Exp. Biol. 223, jeb224527 (2020).
Biney, R. P., Benneh, C. K., Adongo, D. W., Ameyaw, E. O. & Woode, E. Evidence of an antidepressant-like effect of xylopic acid mediated by serotonergic mechanisms. Psychopharmacology 238, 2105–2120 (2021).
Chen, B. et al. Study on improving effect of oyster hydrolysate on depressive behavior of zebrafish under chronic unpredictable mild stress. Shipin Kexue Jishu Xuebao 39, 55–63 (2021).
Fontana, B. D., Cleal, M., Norton, W. H. J. & Parker, M. O. The impact of chronic unpredictable early-life stress (CUELS) on boldness and stress-reactivity: differential effects of stress duration and context of testing. Physiol. Behav. 240, 113526 (2021).
Fontana, B. D. et al. Moderate early life stress improves adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) working memory but does not affect social and anxiety-like responses. Dev. Psychobiol. 63, 54–64 (2021).
Reddy, B. R. et al. Proteome profile of telencephalon associates attenuated neurogenesis with chronic stress induced mood disorder phenotypes in zebrafish model. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 204, 173170 (2021).
Rosdy, M. S., Rofiee, M. S., Samsulrizal, N., Salleh, M. Z. & Teh, L. K. Understanding the effects of Moringa oleifera in chronic unpredictable stressed zebrafish using metabolomics analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 278, 114290 (2021).
Shams, S., Khan, A. & Gerlai, R. Early social deprivation does not affect cortisol response to acute and chronic stress in zebrafish. Stress 24, 273–281 (2021).
Gallas-Lopes, M. et al. Unpredictable chronic stress in zebrafish: a systematic review. Open Science Framework https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/9RVYN (2021).
Page, M. J. et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Brit. Med. J. 372, n71 (2021).
Ouzzani, M., Hammady, H., Fedorowicz, Z. & Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 5, 210 (2016).
Unpredictable chronic stress in zebrafish: a systematic review. Open Science Framework https://osf.io/j2zva/ (2023).
Rohatgi, A. WebPlotDigitizer. Automeris version 4.5 https://automeris.io/WebPlotDigitizer (2021).
van Eck, N. J. & Waltman, L. in Advances in Data Analysis (eds Decker, R. & Lenz, H.-J.) 299–306 (Springer, 2007).
van Eck, N. J. & Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 84, 523–538 (2010).
Hooijmans, C. R. et al. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 14, 43 (2014).
Landis, S. C. et al. A call for transparent reporting to optimize the predictive value of preclinical research. Nature 490, 187–191 (2012).
Risk of bias assessment guide for reviewers. Open Science Framework https://osf.io/sdpwb (2023).
McGuinness, L. A. & Higgins, J. P. T. Risk-of-bias VISualization (robvis): an R package and Shiny web app for visualizing risk-of-bias assessments. Res. Synth. Methods 12, 55–61 (2021).
Ranking of tests and outcomes. Open Science Framework https://osf.io/rvn8b (2023).
Vesterinen, H. M. et al. Meta-analysis of data from animal studies: a practical guide. J. Neurosci. Methods 221, 92–102 (2014).
Balduzzi, S., Rücker, G. & Schwarzer, G. How to perform a meta-analysis with R: a practical tutorial. Evid. Based Ment. Health 22, 153–160 (2019).
meta. R Project version 6.0-0 https://cran.r-project.org/package=meta (2022).
Wilkinson, L. ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis by WICKHAM, H. Biometrics 67, 678–679 (2011).
Higgins, J. P. T. & Thompson, S. G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 21, 1539–1558 (2002).
Cochran, W. G. Some methods for strengthening the common χ2 tests. Biometrics 10, 417–451 (1954).
Viechtbauer, W. Bias and efficiency of meta-analytic variance estimators in the random-effects model. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 30, 261–293 (2005).
Veroniki, A. A. et al. Methods to estimate the between‐study variance and its uncertainty in meta‐analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 7, 55–79 (2016).
Knapp, G. & Hartung, J. Improved tests for a random effects meta-regression with a single covariate. Stat. Med. 22, 2693–2710 (2003).
Higgins, J. P. et al. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (John Wiley & Sons, 2019).
Richardson, M., Garner, P. & Donegan, S. Interpretation of subgroup analyses in systematic reviews: a tutorial. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 7, 192–198 (2019).
Duval, S. & Tweedie, R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot–based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 56, 455–463 (2000).
Egger, M., Smith, G. D., Schneider, M. & Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Brit. Med. J. 315, 629–634 (1997).
Miller, R. G. The jackknife—a review. Biometrika 61, 1–15 (1974).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq, proc. 303343/2020-6), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES), and Pró-Reitoria de Pesquisa (PROPESQ) at Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul (UFRGS) for funding and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.G.-L., A.P. and A.P.H. conceived and designed the project. M.G.-L. and A.P.H. curated acquired data and administrated the project. A.P.H. supervised the project. M.G.-L., A.C.P. and A.P.H. collaborated on the formal analysis and data visualization. M.G.-L., L.M.B., R.B., A.P. and A.P.H. contributed to the investigation and methodology. M.G.-L. drafted the article. L.M.B., R.B., A.C.P., A.P. and A.P.H. provided critical revisions of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Lab Animal thanks Sumana Chakravarty, Torsten Rackoll and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Fig. 1.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gallas-Lopes, M., Bastos, L.M., Benvenutti, R. et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of 10 years of unpredictable chronic stress in zebrafish. Lab Anim 52, 229–246 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41684-023-01239-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41684-023-01239-5