Abstract
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a serious condition, and a myocardial injury or dysfunction could contribute to the outcome. We assessed the prevalence and prognostic impact of cardiac involvement in a cohort with SAH. This is a prospective observational multicenter study. We included 192 patients treated for non-traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage. We performed ECG recordings, echocardiographic examinations, and blood sampling within 24 h of admission and on days 3 and 7 and at 90 days. The primary endpoint was the evidence of cardiac involvement at 90 days, and the secondary endpoint was to examine the prevalence of a myocardial injury or dysfunction. The median age was 54.5 (interquartile range [IQR] 48.0–64.0) years, 44.3% were male and the median World Federation of Neurological Surgeons (WFNS) score was 2 (IQR 1–4). At day 90, 22/125 patients (17.6%) had left ventricular ejection fractions ≤ 50%, and 2/121 patients (1.7%) had evidence of a diastolic dysfunction as defined by mitral peak E-wave velocity by peak eʹ velocity (E/eʹ) > 14. There was no prognostic impact from echocardiographic evidence of cardiac complications on neurological outcomes. The overall prevalence of cardiac dysfunction was modest. We found no demographic or SAH-related factors associated with 90 days cardiac dysfunction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
A subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a serious condition with high mortality and morbidity. Patients with SAH may develop several complications, including acute myocardial injury and cardiac dysfunction1. Accordingly, there is a need for updated evidence and information on the prevalence of cardiac injury, myocardial dysfunction, and cardiac arrhythmias in a contemporary cohort of SAH patients. More information is also needed regarding the relationship between cardiac involvement and clinical outcomes in SAH patients.
A left ventricle (LV) dysfunction occurs most often in SAH patients with elevated cardiac enzymes and B-type natriuretic peptides (BNP)2, electrocardiogram changes (ECG) and severe grades of SAH3. The triad of elevated cardiac biomarkers, ventricular arrhythmias4 and eventually overt cardiac dysfunction5,6,7 has been observed for decades in SAH patients6, but whether they represent risks in addition to established risk models is currently not known. Moreover, to detect cardiac involvement in patients with SAH, there is a need to integrate information from ECG, cardiac biomarkers, and echocardiography4. Accordingly, in this multicenter epidemiological study, we aimed to provide updated information related to evidence of cardiac involvement in non-traumatic SAH patients and to examine the prognostic impact of myocardial injury or dysfunction added to established risk scoring systems.
The study is registered in Clinical Trials (NCT01670838) 22/08/2012.
Methods
Participants
We included 197 consecutive patients treated in Kuopio University Hospital, Finland, Turku University Hospital, Finland, and Bern University Hospital, Switzerland, from March 2014 to February 2016. Five patients were excluded due to the missing World Federation of Neurological Surgeons (WFNS) score. The inclusion criteria were patients with acute non-traumatic SAH, age ≥ 18 years and written consent. The exclusion criteria were anticipated brain death < 24 h or an otherwise moribund patient (expected to die < 24 h or treated only as a donor candidate). Screening log is presented below.

Written informed consent was requested from the patients by the intensive care unit (ICU) study personnel. If the patient was not capable of acting, consent was requested from next-of-kin or the patient’s legal representative. This manuscript reports results that were acquired according to the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) guidelines. Five patients with missing data for World Federation of Neurological Surgeons (WFNS) scores were excluded, leaving 192 patients available for analyses.
All measurements were made during ICU and hospital stays, and the 90-day measurements were performed at the outpatient visit. Systolic cardiac dysfunction was defined as a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ≤ 50%, and diastolic dysfunction was defined as a ratio of early mitral inflow velocity, and mitral annular early diastolic velocity (E/eʹ) > 14 by echocardiography. The severity of SAH was classified using the WFNS score as follows: grade I Glasgow coma scale (GCS) 15, no motor deficit, grade II GCS 13–14, no motor deficit, grade III GCS 13–14 and motor deficit, grade IV GCS 7–12 and grade V GCS 3–6. The Hunt and Hess clinical grading system was also used to classify the severity of SAH, and we used the Fisher scale to grade the computer tomography appearance of bleeding8 (Table 1).
The intensive care treatment protocol of the SAH patients is presented in Table 2.
Data collection
Patient demographics were collected prospectively from electronic patient data management systems, including the admission WFNS score9. Routine laboratory markers were collected daily at 8 a.m. from admission to day 7 and at 90 days at the outpatient clinic. We collected the following routine laboratory markers: blood gases, blood hemoglobin, thrombocytes, leukocytes, international normalized ratio (INR), bilirubin, creatinine, C-reactive protein (CRP), creatinine kinase (CK), creatinine kinase myocardial band (CK-MB), cardiac troponin T (cTnT), N‐terminal pro‐B‐type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), sodium, potassium, and magnesium. All routine laboratory samples were analyzed by accredited laboratories at the study hospitals. Both cTnT and NT-proBNP were measured by the electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLIA) assays (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany). We calculated the estimated glomerular filtration (eGFR) using the CKD-EPI formula10.
We also measured plasma norepinephrine and epinephrine concentrations during the first 24 h after admission (day 1) and later at days 3 and 7 and after 3 months. For these measurements, plasma samples were collected in 10 ml plastic tubes in ice containing EGTA (Ethylene glycolbis (2-aminoethylether)-N, N, Nʹ, Nʹ-tetra acetic acid) and reduced glutathione as a preservative. The samples were centrifuged immediately, and the plasma was stored frozen at − 70 °C until analyzed. For the chromatographic analysis of catecholamines, a Chromsystems reagent kit (Chromsystems Instruments and Chemicals GmbH, Munich, Germany) was used. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated by weight (Kg)/ [height (m)] 2.
Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) was performed during the first 24 h after admission (day 1), at days 3 and 7 and at 3 months outpatient clinic visit. A limited number of experienced cardiologists or intensivists performed cardiac ultrasound examinations according to the specific study protocol. LV end-diastolic diameter (LVEDD), end-systolic diameter (LVESD), interventricular wall thickness (IVS), posterior wall thickness (PW), aortic root diameter (Ao) and left atrium diameter (LA) were recorded from the parasternal long-axis view. LVEF was measured using the parasternal M-mode view and apical 4-chamber projection and was calculated using the Simpson method. We assessed motion abnormalities in the anterior, lateral, inferior and septal walls using the long-axis parasternal view, and the findings were reported as normal wall motion/hypokinesia/akinesia/dyskinesia. LV diastolic function was assessed based on the mitral inflow pattern, E-wave and A-wave velocities, E/A ratio and deceleration time (DT). Diastolic tissue motion velocity in the lateral mitral annulus (lat eʹ) and septal annulus (sept eʹ) was recorded using pulsed wave tissue Doppler and was averaged (eʹ). Diastolic function and left ventricular filling pressure were assessed by calculating the E/eʹ ratio. Right ventricular function was assessed by a tricuspid annulus plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) and by measuring systolic tissue velocity in the tricuspid annulus (tricuspid Sʹ). The right ventricular end-diastolic diameter was measured from the apical 4-chamber view. Pulmonary artery pressure was estimated based on tricuspid regurgitation. Other significant abnormalities of the heart (e.g., valves, pericardial effusion, atrial septal defect, intracardial thrombosis) were also recorded.
We performed a 24-h Holter®-monitoring at day 1 and at day 7, concurrent with the cardiac echocardiography examination, and we performed Holter-monitoring at the 3-month outpatient visit. The Holter-registrations were performed using a Medilog AR4-recorder. Data were automatically analyzed by a software engine (Darwin, ScanMed AS) with manual corrections for artefacts. The mean heart rate and any arrhythmias were registered as well as measures of heart rate variability (standard deviation of RR-interval (SDNN), power in the high-frequency spectrum, power in the low-frequency spectrum and their ratios.
Clinical outcomes
All patients were scheduled for a routine 90-day neurosurgical follow-up, and the neurologic outcome was assessed using the Modified Rankin Scale (mRS)11 or the Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOSE)11. We did not have three-month follow-ups for patients with non-aneurysmal bleeding (n = 22) or patients with no need for clinical control due to a vegetative state. For the prognostic analyses, we dichotomized the outcome as a good clinical outcome, which we defined as mRS 0–2 or GOSE 6–8, or a poor clinical outcome for patients that died or were dependent on help after SAH (mRS > 2 or GOSE < 6). The definitions of cardiac complications during admission and follow-up are detailed in Table 3.
Statistical analysis
This was a prospective observational study investigating the incidence of cardiac involvement with the aim to document possible predisposing factors during ICU stays for cardiac dysfunction at 90 days in patients with acute non-traumatic SAH. Power calculations before study commencement demonstrated that a sample size of 200 patients would be sufficient to detect a weak correlation (r = 0.20) with alpha 0.05 and power 80%, and we based patient inclusion on this calculation. This sample size would enable group comparisons with an adequate power and with this cohort size also the regression analysis could be performed reliably. Sample size calculations were executed by R statistical software with library ‘pwr’. Categorical data are presented as absolute numbers (proportions) and continuous data as the median (interquartile range [IQR]). For categorical variables, the two-sided χ2 test or Fischer’s exact test were used. Continuous data were compared with the Mann–Whitney U-test or the Kruskal–Wallis test of variance.
First, we aimed to assess the prevalence and predictive factors of cardiac complications in patients with non-traumatic SAH. As a secondary outcome measure, we assessed mortality and morbidity caused by cardiac complications. We assessed clinical variables associated with outcomes, and variables with a p-value < 0.10 were included in a multivariable logistical regression model. To determine the association between cardiac involvement and neurological outcomes, we further established a prognostic model with patients stratified into categories based on WFNS grading scores and concentrations of cTnT or NT-proBNP (category 1: WFNS < 3, cTnT < 8 ng/L/NT-proBNP < 380 ng/L [cohort medians], category 2: WFNS < 3, cTnT ≥ 8 ng/L/NT-proBNP ≥ 380 ng/L, category 3: WFNS ≥ 3, cTnT < 8 ng/L/NT-proBNP < 380 ng/L, category 4: WFNS ≥ 3, cTnT ≥ 8 ng/L/NT-proBNP ≥ 380 ng/L). The prognostic models were adjusted for age and sex as well as for a priori selected variables associated with cardiovascular prognosis (systolic blood pressure, BMI, coronary artery disease, diabetes mellitus, current smoking, eGFR and concentrations of norepinephrine). Participants with missing covariate data were excluded from the multivariable regression analyses. The incremental prognostic value of cTnT and NT-proBNP to the WFNS grading score was assessed using C statistics derived from logistic regression models as well as the continuous net reclassification index (cNRI) and integrated discrimination improvement (IDI).
P-values ≤ 0.05 were set to indicate statistically significant results. We used SPSS Statistics for Windows (version 22, IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA) and STATA 16.1 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX) for the statistical analyses.
Ethical approval
The ethics committees of Northern Savo, Finland (record no 78/2011), Hospital District of Southwest Finland, Turku (T4/2014) and Inselspital Bern, Switzerland (record no 239/12), approved the study. Informed consent was obtained. The study has been performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendment and is registered in clinical trials 22/08/2012, NCT01670838.
Results
Baseline characteristics
The baseline characteristics of the patients according to the WFNS grading scores are presented in Supplement Table S1.
The median age was 54.5 (48.0–64.0) years, 44.3% % were male and the median WFNS was 2 (1–4). In general, the prevalence of premorbid conditions was low. Concentrations of cTnT and norepinephrine as well as QTc increased in parallel with the WFNS score.
Cardiac complications at admission and at the 90-day follow-up
The details regarding cardiac involvement and other complications during admission and after discharge are outlined in Table 4.
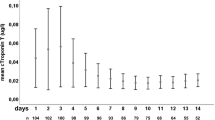
At day 90, 22/125 patients (17.6%) had LVEF ≤ 50%, and 2/121 patients (1.7%) had E/eʹ > 14. None of the patient population or SAH related investigated factors was predictive of cardiac dysfunction at day 90 (Supplement Table S2). The proportion of patients with elevated cTnT was significantly lower at day 90 (7.7%) compared to day 1 (29.4%; p < 0.001). The proportion of patients with elevated NT-proBNP was significantly lower at day 7 (15.8%) and day 90 (3.1%) compared to day 1 (25.6%; p < 0.001).
The most common ECG finding was QTc prolongation, with an incidence of 56.1% at day 1, 35.0% at day 3, 29.9% at day 7 and 33.1% at day 90 (all p < 0.001 compared to day 1). At day 90, there was a higher proportion of patients with reduced LVEF (< 50%) and a lower proportion of patients with regional wall motion abnormalities compared to the baseline.
Concentrations of cTnT at day 1 according to different categories of clinical status, severity of bleeding and categories of cardiopulmonary events and outcome measures are presented in Table 5.
Patients with a worse clinical status and more severe bleeding exhibited higher concentrations of cTnT, which was also the case for patients with worse neurological outcomes at the three-month follow-up. The corresponding analyses for NT-proBNP and endogenous catecholamines are presented in Tables 6 and 7.
Concentrations of NT-proBNP were associated with the Glasgow Coma Scale, QTc prolongation and regional wall disturbances on the echocardiography. Concentrations of endogenous catecholamines were similar across all analyzed subgroups, apart from different concentrations of endogenous epinephrine according to the Fisher grading score (lower in more severe grades) and different concentrations of endogenous norepinephrine according to Hunt and Hess and the World Federation of Neurological Surgeons grading score (higher in more severe grades).
Predictors of neurological outcomes
Table 8 outlines variables indicated by the univariate analysis to be associated with poor neurological outcomes, i.e., dependence (mRS > 2 or GOSE < 6) after SAH.
Variables significantly associated with the poor outcome were analyzed further in a multivariable logistic regression model. In this analysis, age (OR 1.04 [95% CI 1.01–1.08]) and the presence of an intracerebral hemorrhage (OR 4.96 [95% CI 1.96–12.60]) and an intraventricular hemorrhage (OR 3.14 [95% CI 1.39–7.11]) were independently associated with poor neurological outcomes. Our model showed an explanatory rate (Nagelkerke) of R2 0.30.
There was a significant association in the logistic regression model between the WFNS grading score, cTnT and poor neurological outcomes at the three-month follow-up (Supplement Table S3). Patients with high WFNS grading scores and cTnT above the median had more than a fourfold increased risk of poor neurological outcomes (adjusted odds ratio 4.45 [95% CI 1.5–13.4]). The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC-AUC) of the WFNS grading score in predicting poor neurological outcomes was 0.677 (95% CI 0.595–0.759). The addition of cTnT improved the prognostic model of ROC-AUC to 0.719 (95% CI 0.638–0.801), p for comparison = 0.05, Fig. 1). We observed no improvement in cNRI (0.113 [95% CI − 0.188 to 0.473]) or IDI (0.034 [95% CI − 0.005 to 0.107]) when adding cTnT to the WFNS grading score.
Supplement Table S4 shows the associations between the WFNS grading score, NT-proBNP and poor neurological outcomes at the three-month follow-up. Compared to cTnT, the results for NT-proBNP were less consistent, and an association of a high WFNS grading score and a NT-proBNP above the median with poor neurological outcomes was attenuated in the adjusted models. The addition of NT-proBNP to the WFNS grading score did not improve the ROC-AUC for the prognostic model (ROC-AUC 0.68 [95% CI 0.59–0.76], p for comparison = 0.53, Fig. 1). We observed no improvement in cNRI (0.05 [95% CI − 0.40 to 0.40]) or IDI (− 0.004 [95% CI − 0.01 to 0.05]) when adding NT-proBNP to the WFNS grading score.
Discussion
In a large cohort of patients with non-traumatic SAH, we found no demographic or SAH-related factors associated with cardiac dysfunction at 90 days. The most frequent cardiac findings were increased concentrations of cTnT and NT-proBNP as well as QTc prolongation; however, the overall incidence of cardiac dysfunction was modest. SAH patients with the most severe disease, as quantified by the WFNS grading score and elevated concentrations of cTnT, had an especially poor prognosis at follow-up 90 days after hospital admission.
Cardiac dysfunction appears early and is most often reversible. The left ventricular systolic dysfunction was modest in our study cohort; this finding is in concordance with the findings of the M Tanabe group12,13. Diastolic dysfunction is associated with increased troponin12, but in our population, diastolic dysfunction was extremely rare. Elevated concentrations of cardiac troponin I are associated with regional wall motion abnormalities in patients with SAH14, which is in line with the results from the current investigation, where patients with regional wall motion disturbances exhibited highly elevated concentrations of cTnT. This was also the case for patients with decreased LVEF and QTc prolongation. Furthermore, concentrations of cTnT increased with increasing disease severity quantified by the WFNS grading score. These findings highlight that there is a subpopulation of patients with potential for an early detrimental cardiac impact of SAH, resulting in both overt and subclinical myocardial injury as well as arrhythmia.
Cardiac troponin concentrations are elevated in patients with SAH14 and correlate positively with the severity of bleeding4, delayed cerebral ischemia, poor outcomes, and mortality15. Concentrations of cTnT in our study were uniformly increased according to disease severity in the SAH patients with poor neurological outcomes after 90 days as well. Our results are in concordance with prior studies14,16, although elevated cardiac troponin concentrations were less common than in the study by Nastasovic et al.17; however, in previous investigations, patients with a known history of cardiac and neurologic diseases have been excluded18, making the results less comparable.
Cardiac troponins and natriuretic peptides are the established biomarkers of contemporary cardiology, reflecting myocardial injury and stress. Of the two, cTnT is more strongly associated with disease severity and neurological outcomes. In the absence of an overt myocardial infarction, cardiac troponins are hypothesized to reflect subclinical myocardial injury. The causes of a cardiac troponin increase are multifactorial, possibly including both myocardial ischemia and strain. In our patients with acute non-traumatic SAH, the activation of the renin–angiotensin, sympathetic and inflammatory systems may have mediated the cardiac troponin release. In comparison, NT-proBNP and catecholamines are less frequently associated with cardiac complications, disease severity and poor neurological outcomes.
Elevated catecholamine concentrations are used as surrogate markers for increased sympathetic activity19. Our study results are in concordance with results from the Moussoutas group20, where norepinephrine levels but not epinephrine levels were associated with clinical status. Salem et al.21 showed that myocardial alterations and catecholamine concentrations are regressive during the first week, which is comparable to the findings of our study. We measured catecholamine concentrations at the same time points as the cardiac echocardiography and ECGs were performed but found no association of cardiac function and arrhythmia with endogenous catecholamine concentrations.
Our study has its strengths and limitations. We included study patients from three different hospitals in two European countries with a high quality of neuro-intensive care. A major strength is the repeated multimodal cardiac assessment with a long-term follow-up. The incidence of morbidity and cardiac complications was modest compared to previous studies. One explanation is that our population reflects a whole spectrum of non-traumatic SAH, not only selected poor-grade patients.
Conclusion
Patients with non-traumatic SAH are at risk for cardiac complications, especially with regard to a subclinical myocardial injury and arrhythmia. Along with clinical risk scoring systems, measurements of cardiac troponin may improve risk assessments for long-term prognosis. There could be a subgroup of patients, who should be multidisciplinary evaluated at day 90, to identify those in need of cardiac care.
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due the Finnish legislation. The applicable Finnish legislations does not allow sharing and/or submitting datasets from the study. Applicable legislation states that 1) any health data should only be processed if there is a valid legal basis. Even then, any transfer to a country outside EU/EEA requires specific basis and protective measures. (General Data Protection Regulation, GDPR) 2) patient data is strictly confidential and cannot be revealed to third parties (Act on the Status and Rights of Patients) 3) secondary use of health data (e.g., for scientific research) must comply with the Act on Secondary use of Data. This legislation prohibits us from allowing data transfers/ access to datasets that would include patient/health data. Therefore, raw data or even de-identified (pseudonymized) data cannot be shared publicly. The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Ao:
-
Aortic root diameter
- AV:
-
Atrioventricular
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- BNP:
-
B-type natriuretic peptide
- CI:
-
Confidence Interval
- CK:
-
Creatinine kinase
- CK-MB:
-
Creatinine kinase myocardial band
- cNRI:
-
Continuous net reclassification index
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- DT:
-
Deceleration time
- cTnT:
-
Cardiac troponine T
- E/Eʹ:
-
By mitral peak E-wave velocity by peak Eʹ velocity
- ECG:
-
Electrocardiogram
- eGFR:
-
Estimated glomerular filtration
- EGTA:
-
Ethylene glycolbis (2-aminoethylether)-N, N, Nʹ, Nʹ-tetra acetic acid
- GCS:
-
Glasgow coma scale
- GOSE:
-
Glasgow outcome scale extended
- E/A:
-
E-wave and A-wave velocities
- ECLIA:
-
Electrochemiluminescence immunoassay
- IDI:
-
Integrated discrimination improvement
- INR:
-
International normalized ratio
- ICH:
-
Intracerebral hemorrhage
- IVH:
-
Intraventricular hemorrhage
- ICU:
-
Intensive care unit
- IVS:
-
Interventricular wall thickness
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- Lat Eʹ:
-
Lateral mitral annulus
- LA:
-
Left atrium diameter
- LV:
-
Left ventricle
- LVEDD:
-
LV end-diastolic diameter
- LVESD:
-
LV end-systolic diameter
- LVEF:
-
Left ventricular ejection fraction
- MRs:
-
Modified Rankin scale
- NT-ProBNP:
-
N‐terminal Pro‐B‐type natriuretic peptide
- PW:
-
Posterior wall thickness
- QTc:
-
Corrected QT interval
- SAH:
-
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- SDH:
-
Subdural hemorrhage
- Sept Eʹ:
-
Septal annulus
- SDNN:
-
Standard deviation of RR-interval
- TAPSE:
-
Tricuspid annulus plane systolic excursion
- TTE:
-
Transthoracic echocardiography
- WFNS:
-
World federation of neurological surgeons
References
Chen, S. et al. The harmful effects of subarachnoid hemorrhage on extracerebral organs. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 858496 (2014).
Lee, V. H., Oh, J. K., Mulvagh, S. L. & Wijdicks, E. F. Mechanisms in neurogenic stress cardiomyopathy after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care. 5, 243–249 (2006).
Mayer, S. A. et al. Myocardial injury and left ventricular performance after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 30, 780–786 (1999).
Tung, P. et al. Predictors of neurocardiogenic injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 35, 548–551 (2004).
Sakr, Y. L., Ghosn, I. & Vincent, J. L. Cardiac manifestations after subarachnoid hemorrhage: A systematic review of the literature. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 45, 67–80 (2002).
Parekh, N. et al. Cardiac troponin I predicts myocardial dysfunction in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 36, 1328–1335 (2000).
Schuiling, W. J. et al. Troponin I in predicting cardiac or pulmonary complications and outcome in subarachnoid haemorrhage. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 76, 1565–1569 (2005).
Aisiku, I., Edlow, J. A., Goldstein, J. & Thomas, L. E. An evidence-based approach to diagnosis and management of subarachnoid hemorrhage in the emergency department. Emerg. Med. Pract. 16, 1–29 (2014).
van Heuven, A. W., Dorhout Mees, S. M., Algra, A. & Rinkel, G. J. Validation of a prognostic subarachnoid hemorrhage grading scale derived directly from the Glasgow Coma Scale. Stroke 39, 1347–1348 (2008).
Levey, A. S. et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 150, 604–612 (2009).
Geraghty, J. R., Lara-Angulo, M. N., Spegar, M., Reeh, J. & Testai, F. D. Severe cognitive impairment in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: Predictors and relationship to functional outcome. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 29, 105027 (2020).
Tanabe, M. et al. Relation of elevation in cardiac troponin I to clinical severity, cardiac dysfunction, and pulmonary congestion in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Am. J. Cardiol. 102, 1545–1550 (2008).
Kagiyama, N. et al. Neurocardiac injury assessed by strain imaging is associated with in-hospital mortality in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 13, 535–546 (2020).
Naidech, A. M. et al. Cardiac troponin elevation, cardiovascular morbidity, and outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Circulation 112, 2851–2856 (2005).
Zhang, L., Zhang, B. & Qi, S. Impact of echocardiographic wall motion abnormality and cardiac biomarker elevation on outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a meta-analysis. Neurosurg. Rev. 43, 59–68 (2020).
Oras, J. et al. Elevated high-sensitive troponin T on admission is an indicator of poor long-term outcome in patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage: A prospective observational study. Crit. Care 20, 11–015 (2016).
Nastasovic, T., Milakovic, B., Marinkovic, J. E., Grujicic, D. & Stosic, M. Could cardiac biomarkers predict neurogenic pulmonary edema in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage?. Acta Neurochir. (Wien) 159, 705–712 (2017).
Ichinomiya, T. et al. QTc interval and neurological outcomes in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care. 13, 347–354 (2010).
Sugimoto, K. et al. Association between elevated plasma norepinephrine levels and cardiac wall motion abnormality in poor-grade subarachnoid hemorrhage patients. Neurosurg. Rev. 36, 259–266 (2013).
Moussouttas, M., Mearns, E., Walters, A. & DeCaro, M. Plasma catecholamine profile of subarachnoid hemorrhage patients with neurogenic cardiomyopathy. Cerebrovasc. Dis. Extra. 5, 57–67 (2015).
Salem, R. et al. Subarachnoid hemorrhage induces an early and reversible cardiac injury associated with catecholamine release: one-week follow-up study. Crit. Care 18, 558–614 (2014).
Acknowledgements
Cardiologist Heikki Miettinen, Study nurses Elina Halonen, Sari Rahikainen and Saija Rissanen from Kuopio University Hospital Intensivist Ari Katila, Neurosurgeons Ilkka Saarenpää, Anna Kotkansalo and Jussi Posti from Turku University Hospital.
Funding
State research funding, Åkershus University Hospital and Finnish Intensive Care Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conception and methodology: all authors. Data collection and cleaning: M.L., T.K., R.T., M.R., J.W. Cardiac ultrasound examinations: A.T., M.V., J.G., T.M.M. Statistical analysis: M.N.L., M.L. Drafting of the manuscript: M.L., S.B., M.N.L., H.R. Critical revision of the manuscript and approval of the final manuscript: all authors. Study supervision: S.M.J., R.T., T.O., H.R., S.B. This manuscript complies with all instructions to authors. All authors have a substantial contribution to conception, design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data. All authors have participated in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content. All authors have approved the final version of this manuscript. All authors have an agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Lång, M., Jakob, S.M., Takala, R. et al. The prevalence of cardiac complications and their impact on outcomes in patients with non-traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage. Sci Rep 12, 20109 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-24675-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-24675-8
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.