Abstract
Polymer matrix nanocomposites with nanosized fillers are becoming an inseparable part of various industries owing to their unique properties. Among the nanosized fillers, layered double hydroxides are a good candidate due to their fantastic properties such as the ability to ion exchange and adsorption capacity. In the present work, a simple and green synthesis procedure was applied for the preparation of novel modified Cu–Ca–Al-based layered double hydroxide/polymer matrix nanocomposites. Notably, the synthesis was performed in a water medium as solvent. The layered double hydroxide was synthesized and itaconic acid was used for the surface functionalization of the prepared material. The modified material was then incorporated into the natural polymer of gellan gum to produce polymer matrix nanocomposites with different filler contents. The prepared materials were characterized using infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction analysis, scanning and transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction analysis, thermogravimetric analysis, and N2 adsorption/desorption technique. After characterization, the prepared materials were used for the adsorption of Congo red. After investigation of the important experimental parameters, the isotherm and kinetic studies were also performed. Among the studied kinetic models, the pseudo-second-order model and intra-particle diffusion model were obtained the best in the case of Congo red adsorption. The Freundlich isotherm model showed the best results. Finally, maximum adsorption capacities of 80.9, 90.1, and 99.9 mg g−1 were obtained for nanocomposites containing 1%, 3%, and 5 wt% of filler, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Nowadays, water pollution, as an unpleasant result of the industrialization process is a serious international problem. The disposal of toxic substances into the environmental water sources caused severe concerns about the health of creatures1,2,3. Scientists are working to find a solution to this global problem. Several decontamination strategies have been reported to remove toxic substances from environmental media. They are generally included physical, chemical, and biological treatments4. Adsorption, coagulation, oxidation, membrane separation, biological degradation, etc. are important methodologies that have been reported5,6. As a conventional strategy, the adsorption technique provided several benefits to be used for water treatment. This method is easy to handle, low-cost, and flexible. No harmful by-products are produced during the removal process5,7. In the case of organic dyes, various natural and synthetic adsorbents have been reported to be used as adsorbents8,9,10.
Layered double hydroxides (LDHs) consisted of layers with a positive charge and an interlayer region with the ability of anion exchange11,12,13. The stoichiometry of LDHs is demonstrated \(\left[ {{\text{M}}_{{1 - {\text{x}}}}^{2 + } {\text{M}}_{{\text{x}}}^{3 + } \left( {{\text{OH}}} \right)_{2} } \right]^{{{\text{x}} + }} \left( {{\text{A}}^{{{\text{n}} - }} } \right)_{{{\text{x}}/{\text{n}}}} \cdot {\text{mH}}_{2} {\text{O}}\)14,15 in which the \({\text{M}}^{2 + }\), \({\text{M}}^{3 + }\), and \({\text{A}}^{{{\text{n}} - }}\), are metals and charge balancing anion, respectively. These groups of inorganic layered nanomaterials have received scientists' attention because of their fantastic properties such as the ability to ion exchange and adsorption capacity. They can be easily designed to be used in the fields of catalysis16, environmental remediation17,18, sample preparation19,20, drug delivery21, and energy conversion and storage22. Agglomeration of nanosized materials such as LDHs is a well-known phenomenon as a result of their surface energy and characteristics. Their high surface area and polar or ionic surface make them thermodynamically unstable with respect to agglomerated species. These cause low efficiency for specific applications. To increase the performance and application field of LDHs, several modification strategies have been reported. Hybrid assembly, surface modification, intercalation, defect introduction, and layer composition tuning are some common functionalization strategies that can be found in detail in a review in 202023.
Polymer matrix nanocomposites as a class of nanosized materials are becoming an inseparable part of various industries owing to their unique properties. Polymer matrix nanocomposites consist of a polymer or copolymer in which a nanosized filler is dispersed in the matrix of the polymer. The properties of a polymer matrix nanocomposite are related to the size scale of its components and the degree of mixing24. In this context, the use of nanosized filler in polymeric nanocomposites gathering the special advantages of nanosized filler including high surface area, and high thermal and mechanical stability, and the flexibility of organic polymers. Generally, the properties of nanocomposites are enhanced because of the ability of nanosized materials to affect the properties of the polymer matrix. The incorporation of layered nanosized fillers into the polymer matrices has attracted great attention because of their distinctive properties25. As a subclass of polymer/layered inorganic nanocomposites, LDHs-based polymer matrix nanocomposites have shown significant improvement in the composites’ overall physical and chemical properties. In the case of LDHs, various polymer matrix nanocomposites with organic polymers such as polyaniline, polypropylene, polyurethane, poly (vinylchloride), polyacrylonitrile, poly(methylmethacrylate), poly (ethylene terephthalate), etc. have been reported26. The use of natural polymers for the synthesis of polymer matrix nanocomposites has gained considerable interest to researchers in recent years. They are renewable, eco-friendly, biodegradable, and easily available. Among them, gellan gum polysaccharide produced by Sphingomonas elodea consists of glucose units, glucuronic acid, and rhamnose with a ratio of 2:1:127.
In this work, a novel nanocomposite based on modified Cu-Ca-Al-LDH and gellan gum was synthesized for adsorption purposes. The LDH was synthesized with a simple and green route and then modified to improve compatibility with polymer matrix, surface area, adsorption properties, and other surface characteristics. The prepared material was then composited with Gellan gum as a natural polymer to obtain a novel polymer matrix nanocomposite-based adsorbent. To study the adsorption capability of the prepared polymer matrix nanocomposite, Congo red dye was chosen as a model analyte.
Experimental section
Materials and methods
In this study, copper(II) nitrate trihydrate (≥ 99.0%), calcium nitrate tetrahydrate (≥ 99.0%), aluminum nitrate nonahydrate (≥ 98.0%), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), sodium carbonate, ammonium persulfate, and itaconic acid were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Gellan gum, Congo red (CR), glacial acetic acid (99.5%), and phosphoric acid (85%) were purchased from Merck Co. A stock solution of Congo red was prepared in water at the concentration level of 2000 mg L−1.
Apparatus and instruments
A Jasco-FT-IR-350 (Tokyo, Japan) instrument was applied (4400–400 cm−1, KBr pellets). Scanning and transmission electron microscopy (SEM, TEM) were done on a JSM-6510 (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) and CM120 (Philips Electronics, Eindhoven, Netherlands) instruments, respectively. A Rigaku-DMax 2500 diffractometer (Japanese science and science Co., Tokyo, Japan) was used to record XRD patterns. N2 adsorption/desorption experiments were done on a Belsorp-mini II (BEL Japan Inc., Osaka, Japan) instrument. An STA 503 (Bahr GmbH, Hullhorst, Germany) instrument was used for thermogravimetric analysis (10 °C min−1, up to 800 °C). To determine dye concentration in sample solutions, a UV-1601 spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Japan) was used (499 nm).
Synthesis of the materials
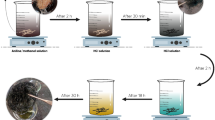
This section aims to introduce a synthesis procedure to prepare itaconic acid-modified Cu–Ca–Al–LDH/gellan gum nanocomposites containing 1%, 3%, and 5% of filler. In a container, 8 mmol of Ca(NO3)2·4H2O (1908 mg), 8 mmol of Cu(NO3)2·3H2O (1952 mg), and 4 mmol Al(NO3)3·9H2O (1532 mg) were dissolved in 200 mL of pure water. After that, 200 mL of alkaline solution (50 mmol L−1 of Na2CO3 and 150 mmol L−1 of NaOH) was prepared in another container. The two solutions were mixed in an 800 mL glass flask (pH = 10–11 during the addition). After 60 min stirring at room temperature, the temperature of the mixture was increased to 60 °C and 100 mL of water with 5.0 g of itaconic acid was added to the mixture and maintained for 1 h. Then, 1 g of gellan gum to prepare nanocomposites containing 1%, 3%, and 5% of filler was dissolved in water (5.0 mL). This solution together with 1.0 mL of aqueous ammonium persulfate (0.065 mmol) was added to the LDH solution and stirred for 12 h. Then, the mixture was maintained for 20 h (without stirring). The obtained slurry was cooled, filtered, and washed with pure water and dried (85 °C).
Batch adsorption experiments
For the experiments, 5.0 mL of an aqueous standard solution of CR was used. The adsorbent was added and the experiment was performed in a shaker (298 K, 220 rpm) for a period of time. To calculate the removal efficiency (RE, %), the following equation (Eq. 1) was used in which, Ci and Ce are the initial and equilibrium concentration of CR (mg L−1), respectively. To compute the adsorption capacity (qe, mg g−1), (Eq. 2) was applied in which, m is the amount of adsorbent (mg) and V is the volume of solution (mL).
Results and discussion
Synthesis and characterization of the materials
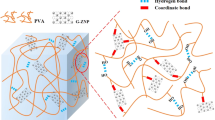
In this work, a simple and green synthesis procedure was used for the preparation of novel modified Cu–Ca–Al–LDH/polymer matrix nanocomposites. At first, the LDH was simply prepared and then functionalized with itaconic acid. In this work, itaconic acid was applied as a surface modifier to decrease agglomeration and improve the surface area, compatibility with polymer matrix, and adsorption properties. The modified material was then incorporated into the natural polymer of gellan gum to produce polymer matrix nanocomposites with different filler contents. Water as a green and non-toxic solvent was used in the synthesis procedure (no use of hazardous solvents). The nanocomposites were used for the adsorption of Congo red from aqueous solutions due to their capability in hydrogen bond establishing between hydroxyl groups and functional groups of Congo red, as well as their ion-exchange ability. Figure 1 reveals the structure of the prepared materials and possible interactions during dye adsorption from an aqueous solution. As can be seen in Fig. 1, the itaconic acid as a modifier can establish a strong hydrogen bond with the surface of LDH. The hydrogen bond between hydroxyl groups and functional groups of Congo red and polymer matrix nanocomposite and also the anion-exchange mechanism are responsible for the adsorption process.
The FT-IR spectra of Cu-Ca-Al-LDH, LDH-ITA, and nanocomposite containing 1% of filler (NC-1%) are shown in Fig. 2. The pristine Cu–Ca–Al–LDH provided broadband centered at 3435 cm−1 related to the O–H groups. On the other hand, the band at 1633 cm−1 is assigned to the water molecules bending vibration28. The band related to NO3− anions of the interlayer can be seen at 1421 cm−1. Other bands including 876, 712, 604, 515, 445, etc., (vibrational modes of the LDH lattice) result from M–O–M, O–M–O, and M–O bonds (M = metal) 29. In the modified sample, the broadband centered at 3473 cm−1 is related to the hydroxyl groups. On the other hand, the bands at 1646 cm−1 and 1431 cm−1 are assigned to the carboxylic ions absorption bands30,31. The C=C stretching vibration can be observed at 1565 cm−1. The band located at 1421 cm−1 disappeared in LDH-ITA, indicating the replacement of NO3− ions by itaconic acid anions. The band located at 1384 cm−1 is related to the carboxylate ions. In the case of NC-1%, in addition to the peaks related to the filler, the characteristic peaks of gellan gum also appear which is reported in previous work27,32. The broadband centered at 3417 cm−1 is related to the stretching vibrations of O–H (both gellan gum and filler). The C=C stretching vibration at 1565 cm−1 is weakened in NC-1% due to the reaction of radical of gellan gum with C=C bond of itaconic acid.
The XRD results of the materials are illustrated in Fig. 3a. The characteristic peaks of pristine Cu-Ca-Al-LDH are in accordance with previous reports33. For LDH-ITA, two peaks centered at 35.6° and 38.6° correspond to the CuO structure. The characteristic peaks of 23.4°, 29.5°, 36.9°, 39.5°, 43.1°, 47.5°, and 48.5° are related to CaCO333,34,35. The disappearance of some diffraction peaks as well as appearing some new peaks in the LDH-ITA XRD pattern indicated incorporating the itaconic acid modifier into the LDH structure. In the case of gellan gum, broadband centered at 2θ values of 20 indicate its amorphous nature27. The NC-5% XRD pattern provided characteristic peaks related to LDH and amorphous gellan gum. The crystallinity and the amorphous characteristics of the prepared nanocomposites can be predicted from the sharp peaks and broad peak in the diffractogram.
The TGA curves of the prepared materials are illustrated in Fig. 3b. In the thermogram of the LDH, a mass loss (2.7%) was observed between 30 and 235 °C because of the removal of water30. Also, a mass loss of about 3.7% occurred between 235 and 580 °C due to decomposition of –OH groups and degradation of the layered structure. The final mass loss (580–800 °C, 22.6%) was occurred because of dehydroxylation of the LDH and the formation of metal oxides of calcium, copper, and aluminum. In the case of LDH-ITA, decomposition of itaconic acid began near 200 °C. The pure gellan gum showed degradation steps in its TGA curve. In the first step (below 150 °C), the moisture content of the sample is lost. In the second step (between 240 and 280 °C), a major weight loss of about 40% was occurred due to the breaking of the glycosidic linkage and decomposition of the polysaccharide backbone. Finally, decomposition of gellan gum occurred and only 28% of the sample remains as residual matter at 800 °C. The NC-5% showed several steps like LDH-ITA and provided better thermal stability in comparison to the pure polymer. More than 48% of the sample remains as residual matter at 800 °C.
The scanning and transmission electron microscopy images of the prepared materials are shown in Fig. 4a–f. The prepared LDH (Fig. 4a) and LDH-ITA (Fig. 4b) showed a plate-like morphology33. The pristine LDH represents a higher degree of aggregation in comparison with the modified LDH, because of hydrogen bond formation. In the case of pure gellan gum (Fig. 4c), a relatively homogeneous and smooth surface is observed32. As can be seen in Fig. 4d and e, the prepared NC-1% showed both homogeneous gellan gum particles and plate-like LDH-ITA filler. A relatively homogeneous dispersion of LDH-ITA in the polymer matrix appeared. The SEM and TEM images revealed a porous structure of the prepared materials to be used for adsorption purposes.
The N2 adsorption/desorption isotherms of the materials are illustrated in Fig. 5. The pristine LDH provided a combination of isotherms of type III and IV (H3-type hysteresis loops). Also, the synthesized LDH-ITA exhibited IV-type isotherm (H3-type hysteresis loops). The prepared LDH and LDH-ITA showed BET surface areas of 15.6 and 24.8 m2 g−1 with pore volumes of 0.142 and 0.080 cm3 g−1, respectively (Table 1). Both pure gellan gum and NC-1% exhibited a combination of type III and IV isotherms and H2 and H3-type hysteresis loops. The flattened isotherms indicate less accessible pores in comparison with the prepared LDHs which are common in neat organic polymers. BET surface areas of 7.6 and 8.7 m2 g−1 with pore volumes of 0.0093 and 0.0223 cm3 g−1 were obtained for gellan gum and NC-1%, respectively (Table 1).
Adsorption studies
Sample solution pH
The effect of sample solution pH was investigated between 5.0 and 9.0. Lower pHs were not studied because of the instability of the dye36. 5.0 mL of the standard solution of CR (50 mg L−1) and an adsorbent amount of 10.0 mg were used (298 K, 2 h, 1500 rpm). As Fig. 6a shows, the removal efficiency was firstly decreased with increasing the solution pH and then slightly increased. The decrease in the removal efficiency is may be related to this phenomenon that the surface of the material becomes less positive when pH enhanced from 5.0 to 7.0. Based on the results, pH = 5.0 was chosen.
Adsorbent amount
Various adsorbent amounts between 1.0 and 20.0 mg were tested. A dye concentration of 50 mg L−1 (pH = 5.0) was adopted (298 K, 2 h, 1500 rpm). The removal efficiency was first increased by enhancing the adsorbent dosage, and then no significant increase was observed in the case of all nanocomposites (Fig. 6b). Finally, 10.0 mg of each adsorbent was chosen.
Contact time
Contact times in the range of 10 and 240 min were tested to investigate the effect of time on the adsorption process. Standard solutions of CR (50 mg L−1, pH = 5.0) with an adsorbent amount of 10.0 mg were used (298 K). As Fig. 6c shows, an increase in removal efficiency occurred for all three nanocomposites when the stirring time was enhanced from 10 to 180 min. A time of 180 min was chosen for further experiments.
The kinetic studies
In this step, four kinetic models including pseudo-first-order (PFO, Eq. 3), pseudo-second-order (PSO, Eqs. 4, 5), Elovich (Eq. 6), and intra-particle diffusion (IPD, Eq. 7) were used to study the mechanism of adsorption. In the following equations, qe and qt (mg g−1) are the capacity of adsorption at equilibrium condition and at time t, k1 (min−1) is PFO rate constant, h (mg g−1 min−1) is the initial sorption rate in PSO, k2 (g mg-1 min−1) is PSO rate constant, α (mg g−1 min−1) & β (g mg−1) are Elovich constants, kdif (mg g−1 min−0.5) is the IPD rate constant. Also, C (mg g−1) is a constant. The obtained results are shown in Fig. 7 and Table 2. For all three nanocomposites, the PSO and IPD kinetic models provided the best results regarding the R2 value (a physiochemical process) with an intraparticle diffusion mechanism. The obtained R2 values for the PSO model were 0.9909, 0.9926, and 0.9906 for NC-1%, NC-3%, and NC-5%, respectively. Also, the obtained R2 values for IPD model were 0.9863, 0.9939, and 0.9918 for NC-1%, NC-3%, and NC-5%, respectively.
Initial CR concentration and adsorption isotherm
In this step, various concentrations of CR (10–300 mg L−1, pH = 5.0) were tested (10 mg of adsorbent, 180 min contact time). Based on Fig. 8a, maximum adsorption capacities of 80.8, 90.1, and 99.9 mg g−1 were obtained for NC-1%, NC-3%, and NC-5%, respectively, for CR adsorption. Then, the Langmuir, Freundlich, and Dubinin–Radushkevich (D–R) isotherm models were studied. The used equations for Langmuir, Freundlich, and (D–R) isotherms are shown in Eqs. (8–10), respectively.
In the above-mentioned equations, Ce (mg L−1) is the CR concentration at equilibrium, qe (mg g−1) is the adsorption capacity at equilibrium, qmax (mg g−1) is the maximum adsorption capacity of the adsorbent, kL (L mg−1) is the Langmuir model constant, n & kF ((mg g−1) (L mg−1)1/n) are the Freundlich isotherm model constants, B (mol2 kJ−2) is the Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherm model constant, R (j mol−1 K−1) is the universal gas constant, and T (K) is temperature. The adsorption isotherms are illustrated in Fig. 8b–d. Also, the calculated parameters from the used isotherm models are illustrated in Table 3. Based on the obtained results and considering the R2 values, the Freundlich isotherm model showed the best fit for all three nanocomposites. The obtained R2 values were 0.9835, 0.9810, and 0.9868 for NC-1%, NC-3%, and NC-5%, respectively.
To study the reusability of the prepared material, the spent polymer matrix nanocomposites were washed with pure water while shaking for 5 min. After that, the adsorbent was separated from the solution by centrifugation and dried for further experiments. The regenerated adsorbent was subjected to repeated adsorption/desorption cycles. All the experiments were performed at optimum conditions. Data showed that the adsorbent can be reused 5 times with a 10% decrease in adsorption efficiency.
Comparison with other studies
To compare the present method with other methods, contact time, pH, and adsorption capacity of the methods are provided in Table 4. The present method provided good adsorption capacity. Also, a shorter equilibrium time was obtained by the present method indicating the better performance of the prepared nanocomposites for CR removal due to the occurrence of adsorption through both anion exchange and surface adsorption by H-bonding mechanisms.
Conclusions
In the present work, we synthesized novel modified Cu–Ca–Al–LDH/polymer matrix nanocomposites using a simple and environmentally friendly approach. The Cu–Ca–Al–LDH was synthesized at first and then functionalized with itaconic acid. The modified material was then incorporated into the natural polymer of gellan gum to produce polymer matrix nanocomposites with different filler contents. The FT-IR spectra, as well as TGA curves of the prepared materials, indicate the successful synthesis of the desired products. The XRD results showed characteristic peaks of the materials in accordance with previous reports. Also, the SEM and TEM images revealed the porous structure of the prepared materials. After the characterization of the synthesized nanocomposites, the prepared materials were used for the adsorption of CR from aqueous samples. The effect of pH, adsorbent dosage, stirring time, and dye concentration on adsorption was investigated. A sample pH = 5.0 with the adsorbent dosage of 10.0 mg and 180 min contact time were selected for isotherm and kinetic studies. The novel prepared materials provided notable adsorption performance toward CR. The PSO kinetic model obtained the best model for the adsorption of dye (R2 values of 0.9909, 0.9926, and 0.9906 for NC-1%, NC-3%, and NC-5%, respectively). In the case of isotherm models, the Freundlich model provided the best fit (R2 values of 0.9835, 0.9810, and 0.9868 for NC-1%, NC-3%, and NC-5%, respectively). Maximum adsorption capacities of 74, 80, and 100 mg g-1 were obtained for NC-1%, NC-3%, and NC-5%, respectively, for CR adsorption. Prospects related to this class of adsorbent include the synthesis of polymer matrix nanocomposites utilizing other high-performance nanosized materials to improve adsorption capability and also tuning the sorbent structure for selective adsorption.
References
Achour, Y. et al. Insight into adsorption mechanism of Congo red dye onto Bombax Buonopozense bark Activated-carbon using Central composite design and DFT studies. Surfaces and Interfaces 23, 100977 (2021).
Zhu, S. et al. Adsorption and desorption of Pb (II) on l-lysine modified montmorillonite and the simulation of interlayer structure. Appl. Clay Sci. 169, 40–47 (2019).
Zhu, S., Khan, M. A., Wang, F., Bano, Z. & Xia, M. Exploration of adsorption mechanism of 2-phosphonobutane-1, 2, 4-tricarboxylic acid onto kaolinite and montmorillonite via batch experiment and theoretical studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 403, 123810 (2021).
Tkaczyk, A., Mitrowska, K. & Posyniak, A. Synthetic organic dyes as contaminants of the aquatic environment and their implications for ecosystems: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 717, 137222 (2020).
Soltani, R., Shahvar, A., Gordan, H., Dinari, M. & Saraji, M. Covalent triazine framework-decorated phenyl-functionalised SBA-15: its synthesis and application as a novel nanoporous adsorbent. New J. Chem. 43, 13058–13067 (2019).
Peng, N. et al. Superabsorbent cellulose–clay nanocomposite hydrogels for highly efficient removal of dye in water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 4, 7217–7224 (2016).
Ghorai, S. et al. Enhanced removal of methylene blue and methyl violet dyes from aqueous solution using a nanocomposite of hydrolyzed polyacrylamide grafted xanthan gum and incorporated nanosilica. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 6, 4766–4777 (2014).
Zhou, Y., Lu, J., Zhou, Y. & Liu, Y. Recent advances for dyes removal using novel adsorbents: A review. Environ. Pollut. 252, 352–365 (2019).
Dinari, M., Soltani, R. & Mohammadnezhad, G. Kinetics and thermodynamic study on novel modified–mesoporous silica MCM-41/polymer matrix nanocomposites: Effective adsorbents for trace CrVI removal. J. Chem. Eng. Data 62, 2316–2329 (2017).
Gupta, V. Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: A review. J. Environ. Manage. 90, 2313–2342 (2009).
Dinari, M., Haghighi, A. & Asadi, O. Facile synthesis of ZnAl-EDTA layered double hydroxide/poly (vinyl alcohol) nanocomposites as an efficient adsorbent of Cd (II) ions from the aqueous solution. Appl. Clay Sci. 170, 21–28 (2019).
Nalawade P, Aware B, Kadam V, Hirlekar R, Layered double hydroxides: A review, (2009).
Dinari, M. & Tabatabaeian, R. Ultra-fast and highly efficient removal of cadmium ions by magnetic layered double hydroxide/guargum bionanocomposites. Carbohyd. Polym. 192, 317–326 (2018).
He, J. et al. Preparation of Layered Double Hydroxides 89–119 (Springer, 2006).
Duan, X. & Evans, D. G. Layered Double Hydroxides (Springer, 2006).
Fan, G., Li, F., Evans, D. G. & Duan, X. Catalytic applications of layered double hydroxides: Recent advances and perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 7040–7066 (2014).
Shabani, S. & Dinari, M. Cu-Ca-Al-layered double hydroxide modified by itaconic acid as an adsorbent for anionic dye removal: Kinetic and isotherm study. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 133, 108914 (2021).
Zubair, M., Daud, M., McKay, G., Shehzad, F. & Al-Harthi, M. A. Recent progress in layered double hydroxides (LDH)-containing hybrids as adsorbents for water remediation. Appl. Clay Sci. 143, 279–292 (2017).
Shao, M. et al. Preparation of Fe3O4@ SiO2@ layered double hydroxide core–shell microspheres for magnetic separation of proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 1071–1077 (2012).
Soltani, R., Shahvar, A., Dinari, M. & Saraji, M. Environmentally-friendly and ultrasonic-assisted preparation of two-dimensional ultrathin Ni/Co-NO3 layered double hydroxide nanosheet for micro solid-phase extraction of phenolic acids from fruit juices. Ultrason. Sonochem. 40, 395–401 (2018).
Rives, V., del Arco, M. & Martín, C. Layered double hydroxides as drug carriers and for controlled release of non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): A review. J. Control. Release 169, 28–39 (2013).
Long, X., Wang, Z., Xiao, S., An, Y. & Yang, S. Transition metal based layered double hydroxides tailored for energy conversion and storage. Mater. Today 19, 213–226 (2016).
Laipan, M. et al. Functionalized layered double hydroxides for innovative applications. Mater. Horiz. 7, 715–745 (2020).
Shabani, S. & Dinari, M. Ag/LDH-itaconic acid-gellan gam nanocomposites: Facile and green synthesis, characterization, and excellent catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 193, 1645–1652 (2021).
Huang, G., Zhuo, A., Wang, L. & Wang, X. Preparation and flammability properties of intumescent flame retardant-functionalized layered double hydroxides/polymethyl methacrylate nanocomposites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 130, 714–720 (2011).
Mochane, M. J., Magagula, S. I., Sefadi, J. S., Sadiku, E. R. & Mokhena, T. C. Morphology, thermal stability, and flammability properties of polymer-layered double hydroxide (LDH) nanocomposites: A review. Curr. Comput.-Aided Drug Des. 10, 612 (2020).
Arun Krishna, K. & Vishalakshi, B. Gellan gum-based novel composite hydrogel: Evaluation as adsorbent for cationic dyes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 134, 45527 (2017).
Yi, H. et al. Influence of calcination temperature on the hydrolysis of carbonyl sulfide over hydrotalcite-derived Zn–Ni–Al catalyst. Catal. Commun. 12, 1492–1495 (2011).
Lafi, R., Charradi, K., Djebbi, M. A., Amara, A. B. H. & Hafiane, A. Adsorption study of Congo red dye from aqueous solution to Mg–Al–layered double hydroxide. Adv. Powder Technol. 27, 232–237 (2016).
Wang, S. et al. Effect of modified hydrotalcites on flame retardancy and physical properties of paper. BioResources 14, 3991–4005 (2019).
Shi, Y., Chen, F., Yang, J. & Zhong, M. Crystallinity and thermal stability of LDH/polypropylene nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 50, 87–91 (2010).
Zauro, S. A. & Vishalakshi, B. Amphoteric gellan gum-based terpolymer–montmorillonite composite: Synthesis, swelling, and dye adsorption studies, International Journal of Industrial. Chemistry 8, 345–362 (2017).
Geng, G., Wei, R., Liang, T., Zhou, M. & Xiao, G. Hydrogenolysis of glycerol to propanediols on Cu–Ca–Al hydrotalcites derived catalysts. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 117, 239–251 (2016).
Ashok, J., Kathiraser, Y., Ang, M. & Kawi, S. Bi-functional hydrotalcite-derived NiO–CaO–Al2O3 catalysts for steam reforming of biomass and/or tar model compound at low steam-to-carbon conditions. Appl. Catal. B 172, 116–128 (2015).
Chang, P. H., Chang, Y. P., Chen, S. Y., Yu, C. T. & Chyou, Y. P. Ca-rich Ca–Al-oxide, high-temperature-stable sorbents prepared from hydrotalcite precursors: Synthesis, characterization, and CO2 capture capacity. Chemsuschem 4, 1844–1851 (2011).
Sriram, G. et al. Mg–Al-layered double hydroxide (LDH) modified diatoms for highly efficient removal of congo red from aqueous solution. Appl. Sci. 10, 2285 (2020).
Pal, J. & Deb, M. K. Efficient adsorption of congo red dye from aqueous solution using green synthesized coinage nanoparticles coated activated carbon beads. Appl. Nanosci. 4, 967–978 (2014).
Ansari, M. O. et al. Anion selective pTSA doped polyaniline@ graphene oxide-multiwalled carbon nanotube composite for Cr (VI) and Congo red adsorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 496, 407–415 (2017).
Bhattacharyya, K. G. & Sharma, A. Azadirachta indica leaf powder as an effective biosorbent for dyes: A case study with aqueous Congo Red solutions. J. Environ. Manage. 71, 217–229 (2004).
Rahimi, R., Kerdari, H., Rabbani, M. & Shafiee, M. Synthesis, characterization and adsorbing properties of hollow Zn-Fe2O4 nanospheres on removal of Congo red from aqueous solution. Desalination 280, 412–418 (2011).
Fu, Y. & Viraraghavan, T. Removal of congo red from an aqueous solution by fungus Aspergillus niger. Adv. Environ. Res. 7, 239–247 (2002).
Khalaf, I. H., Al-Sudani, F. T., AbdulRazak, A. A., Aldahri, T. & Rohani, S. Optimization of Congo red dye adsorption from wastewater by a modified commercial zeolite catalyst using response surface modeling approach. Water Sci. Technol. 83, 1369–1383 (2021).
Khaniabadi, Y. O. et al. Adsorption of congo red dye from aqueous solutions by montmorillonite as a low-cost adsorbent. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng https://doi.org/10.1515/ijcre-2016-0203 (2018).
Vimonses, V., Lei, S., Jin, B., Chow, C. W. & Saint, C. Kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analysis of Congo Red adsorption by clay materials. Chem. Eng. J. 148, 354–364 (2009).
Dinari, M. & Neamati, S. Surface modified layered double hydroxide/polyaniline nanocomposites: Synthesis, characterization and Pb2+ removal. Colloids Surfaces A 598, 124438 (2020).
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the research council of the Isfahan University of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S. S.: Software, visualization, writing—original draft preparation, conceptualization, validation, formal analysis, and investigation. M. D.: Supervision, project administration, conceptualization, validation, investigation, resources, and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Shabani, S., Dinari, M. Itaconic acid-modified layered double hydroxide/gellan gum nanocomposites for Congo red adsorption. Sci Rep 12, 4356 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-08414-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-08414-7
This article is cited by
-
Potassium citrate-derived porous carbon with high CO2 capture and Congo red adsorption performance
Environmental Sciences Europe (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.