Abstract
Glucose electrolysis offers a prospect of value-added glucaric acid synthesis and energy-saving hydrogen production from the biomass-based platform molecules. Here we report that nanostructured NiFe oxide (NiFeOx) and nitride (NiFeNx) catalysts, synthesized from NiFe layered double hydroxide nanosheet arrays on three-dimensional Ni foams, demonstrate a high activity and selectivity towards anodic glucose oxidation. The electrolytic cell assembled with these two catalysts can deliver 100 mA cm−2 at 1.39 V. A faradaic efficiency of 87% and glucaric acid yield of 83% are obtained from the glucose electrolysis, which takes place via a guluronic acid pathway evidenced by in-situ infrared spectroscopy. A rigorous process model combined with a techno-economic analysis shows that the electrochemical reduction of glucose produces glucaric acid at a 54% lower cost than the current chemical approach. This work suggests that glucose electrolysis is an energy-saving and cost-effective approach for H2 production and biomass valorization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Biomass conversion into commodity chemicals is a promising strategy to reduce society’s dependence on fossil fuel resource1,2,3,4,5,6. Glucose, one of the most abundant biomass-based compounds, can be converted into various commodity chemicals like 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, sorbitol, gluconic acid (GNA), and glucaric acid (GRA)2,7,8. GRA is recognized as a “top value added compound” produced from biomass9, because it is a key intermediate for the production of biodegradable polymers, biodegradable detergents, and metal complexation agents10,11. Moreover, GRA and its derivatives (e.g., GRA-Ca, GRA-1,4-lactone) can also be used for healthcare purposes such as cancer chemotherapy and cholesterol reduction12,13,14. According to a market report by Grand View Research, Inc.15, the global GRA market size in 2016 was about USD 550.4 million and is expected to reach USD 1.30 billion by 2025.
GRA is currently produced from either chemical oxidation16,17,18 or microbial fermentation, and the former is the main industrial process for GRA production19,20,21. For example, Rivertop Renewables Inc. (Montana, USA) has developed a catalytic oxidation process to produce GRA from glucose with an annual output of 25k tons22. Chemical oxidation is performed either by stoichiometric oxidation of glucose with HNO3 in the absence of catalysts23,24, or by catalytic oxidation of glucose with O2 (air) in the presence of noble metal (e.g., Au, Pt, Pd, and Ru)-based catalysts at 45−120 °C25,26,27,28. In chemical oxidation, various byproducts such as GNA, glucuronic acid, and other organic acids are formed. For example, Qi et al.29 investigated glucose oxidation over an Au-based catalyst with O2 (0.3 MPa) at 120 °C, with a GNA yield of 92% and a GRA yield of less than 5%. Jin et al.30 reported oxidation of glucose to GRA with a yield of 45% over bimetallic Pt-Cu catalysts at 45 °C and 0.1 MPa O2. Conventional catalytic oxidation of glucose to GRA has several shortcomings: (1) a large amount of toxic oxidant is required (more than double the stoichiometric ratio); (2) a low selectivity to GRA (the GRA selectivity is reported to be less than 60%); and (3) generation of various byproducts (e.g., 2,3-dihydroxysuccinic acid, 2,3-dihydroxy-4-oxobutanoic acid, and oxalic acid) with similar chemical properties; and (4) use of high pressure O2 (or air and HNO3). Avoiding the use of high pressure O2 (or air) reduces the use of high pressure vessels and safety risks. Microbial fermentation does not consume as many raw materials and operates at less severe operating conditions compared to chemical oxidation. However, fermentation also suffers from various disadvantages such as long fermentation time (more than 2 days), low selectivity (GRA yield < 20%), and difficulty in product separation (large amounts of microbial biomass and hundreds of byproducts with similar properties are co-produced)31.
Electrochemical oxidation involves electron transfer in the reactions (Scheme 2) and eliminates the use of high pressure O2 or hazardous chemical oxidants. The electrochemical oxidation process can be operated under mild conditions, and production of other byproducts can be easily suppressed via tuning the electrode potential, leading to a high GRA selectivity. Electrochemical oxidation could be practiced commercially at small scales in distributed areas and becomes cheaper as the price of renewable electricity produced continues to decline32. The electrochemical oxidation process is particularly suitable for GRA production, as GRA is produced on a smaller scale, and therefore cannot take advantage of improved economics due to large economies of scale that larger bulk chemicals have. Glucose electrolysis to GRA provides H2 gas as a product stream as hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) occurs at the cathode and the oxidation of glucose occurs at the anode. This reaction also has a lower standard redox potential (0.05 V) than conventional water electrolysis (1.23 V)33,34.
Although the anodic oxidation of glucose can be achieved efficiently with the noble metal (e.g., Pt, Ru, Rh, and Pd)-based catalysts35,36, their scarcity and high costs motivate researchers to seek abundant and inexpensive alternative catalysts. Recent research on electrochemical oxidation has developed a series of earth-abundant transition metal-based catalysts with high catalytic activity and stability towards the electro-oxidation of various organic compounds, such as Co3O4 nanosheets for ethanol electro-oxidation37, Ni–Mo-based nanostructures for urea electro-oxidation38, Co-Cu-based nanostructures for benzyl alcohol electro-oxidation39, and Ni-Fe LDH nanosheets for 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural electro-oxidation40.
In previous studies of electrochemical oxidation of glucose, GRA yields were reported to be less than 40%41, although Ibert et al.42 reported that 2, 2, 6, 6-tetramethyl-1-piperidinyloxy (TEMPO)-mediated electro-oxidation of glucose could obtain GRA with a yield of 85%. However, the high-cost and difficulty in TEMPO separation and recycle may hinder this technology’s industrial application. It has been a challenge to produce GRA with a high yield in a cost-effective way.
In this work, we synthesize the NiFe oxides (NiFeOx) and NiFe nitrides (NiFeNx) using the NiFe LDH nanosheet arrays as a precursor material, and investigate their electrocatalytic performance toward anodic glucose oxidation and cathodic HER using various electrochemical approaches. These catalysts show a high activity and selectivity towards anodic glucose oxidation and cathodic hydrogen evolution respectively.
Results
Synthesis and characteristics of the catalyst materials
The structural and composition characterizations of the as-synthesized catalysts are presented in Supplementary Method 1. Figure 1a is a schematic for the synthesis of Ni-Fe-OH catalyst. A commercially available nickel foam (NF) with open fibrous structure was used to confer the 3D structure of the electrode and provide the Ni source for the NiFe(OH)x. The NiFe(OH)x precursor grew on the NF through a hydrothermal reaction of FeCl3 and CO(NH2)2 (urea) in a mixed solution. Urea was added to the solution to increase the pH, which resulted in the controlled hydrolysis of the Ni and Fe metal ions40,43. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern (Supplementary Fig. 1) of the resulting solid indicates the formation of hydrotalcite-like NiFe layer double hydroxides, Ni(OH)2, and FeOOH crystalline phases.
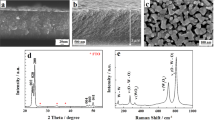
The NiFe(OH)x precursor was then heated at 300 °C for 3 h under air flow to form Ni-Fe oxides (NiFeOx). The XRD pattern (Fig. 1b) shows that the diffraction peaks matched those of NiFe2O4 (PDF: 00-044-1485). The NiFe(OH)x precursor was also heated in an NH3 flow to obtain NiFe nitrides (NiFeNx), and the diffraction peaks of this product matched those of Ni3FeN (PDF: 00-050-1434). Three large diffraction peaks of Ni metal are in both XRD patterns, which are the Ni foam.
The surface chemistry and composition of the catalysts were probed with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The Fe 2p spectra of NiFeOx and NiFeNx are shown in Fig. 1c. Two peaks located at binding energy of 725.2 and 711.7 eV of NiFeOx spectrum are assigned to the Fe 2p1/2 and Fe 2p3/2, respectively, with a difference of 13.5 eV, implying that the Fe in the NiFeOx was in its tri-valent oxidation state (Fe(III))44. The Fe 2p3/2 peak in the NiFeNx was deconvoluted into two peaks, which are assigned to Fe-O species (711.9 eV) and Fe-N species (710.5 eV), respectively45,46. The Ni 2p spectra of NiFeOx and NiFeNx are presented in Fig. 1d. Two prominent peaks located at 856 and 874 eV of NiFeOx spectrum were attributed to the 2p3/2 peaks from Ni and 2p1/2 peaks in Ni-O species, respectively. The Ni 2p3/2 in the NiFeNx was deconvoluted into two peaks attributed to the Ni-O (856.1 eV) and Ni-N (854.7 eV) species, respectively. For comparison, the Fe 2p and Ni 2p XPS spectra of the NiFe(OH)x precursor in Supplementary Fig. 2 show that the Ni 2p spectrum of NiFe(OH)x was almost the same as that of NiFeOx, suggesting that the chemical state of Ni was unchanged during the heat treatment in air. The Fe 2p 3/2 branch in NiFe(OH)x could be deconvoluted into two peaks, which are attributed to the Fe(II) (710.4 eV) and Fe(III) (712.8 eV) species, respectively. The Fe(II) species cannot be found in the NiFeOx sample, confirming that heat treatment transformed Fe(II) into Fe(III). In comparison with NiFe(OH)x, the oxidation states of Ni and Fe in the NiFeNx sample were reduced to lower valence.
The morphology of the NiFe(OH)x, NiFeOx, and NiFeNx samples were examined with scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Typical SEM images of NiFe(OH)x (Supplementary Fig. 3) show that the as-synthesized hydroxides consisted of nanosheets aligned vertically on the NF covering the entire substrate. Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) elemental mapping results (Supplementary Fig. 4) indicate that the Ni, Fe, and O elements were distributed evenly on the NF. After calcination, the obtained NiFeOx product retained the nanosheet morphology of the hydroxide precursor (Fig. 2a, b). The EDS results also confirm that the Ni, Fe, and O elements were distributed homogenously (Fig. 2c). However, after the heat treatment in NH3, the produced NiFeNx material did not maintain the morphology of the hydroxide precursor, but consisted of irregularly shaped interconnected particles with micropores and mesopores (Fig. 2d, e). The EDS elemental mapping (Fig. 2f) confirms the homogenous distribution of the Fe, Ni, and N in the NiFeNx sample, and some O element was also found, which might be due to the incomplete nitridation of the NiFe(OH)x.
Electrocatalytic glucose oxidation
The glucose oxidation involves two steps: (1) the oxidation of glucose into GNA, which involves two electrons, and (2) the oxidation of GNA to GRA, which involves four electrons (Fig. 3). Oxygen evolution reaction (OER) is the main undesired competing reaction47,48. The linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) profiles and the corresponding parameters for the glucose (100 mM) oxidation and OER with the NiFeOx-NF and NiFeNx-NF electrodes in 1 M KOH solution (pH = 13.9) are presented in Fig. 4a, Table 1, and Supplementary Table 5. NiFeOx-NF presented a current density of 87.6 mA cm−2 at a potential of 1.30 V (vs. reversible hydrogen electrode, RHE) for glucose oxidation with a TOF value of 0.16 s−1 (entry 5, Table 1). The NiFeNx-NF electrode displayed a lower current density (22.1 mA cm−2) and with a TOF value of only 0.04 s−1 (entry 6, Table 1), confirming that NiFeOx was a more active catalyst for glucose oxidation than NiFeNx. However, for the OER, NiFeNx (entry 2, Table 1) was more efficient than NiFeOx (entry 1, Table 1). Both the current densities and TOF values for glucose oxidation were much lower than the current densities and TOF for OER. NiFeNx oxidized into high surface-area metal oxides/hydroxides in the oxidative environment of OER reaction (Supplementary Fig. 5) and also likely in the glucose oxidation reactions49. The Tafel slopes (Fig. 4b) for glucose oxidation with NiFeOx-NF and NiFeNx-NF electrodes were calculated as 19 and 23 mV dec−1, respectively, which were much lower than the Tafel slopes for OER with those two electrodes. The Tafel slope is closely related to the electron transfer rate, and a smaller Tafel slope means a more rapid electron transfer rate and more favorable catalytic reaction kinetics50. The lower Tafel slope of the anodic glucose oxidation confirms that more rapid electron transfer occurs in the oxidation of CHO group to COOH in C1 position (two-electron transfer) and the oxidation of CH2OH group to COOH in C6 position (four-electron transfer) than the cleavage of O−H bonds in H2O molecule to produce O2. The low value of the Tafel slope also implies a lower adsorption potential of glucose to the electrode51 and the intimate contact between the electrode catalysts and electrolyte52.
a LSV profiles of the NiFeOx-NF and NiFeNx-NF catalysts for glucose oxidation and OER (scan rate of 5 mV s−1; electrolyte: 1 M KOH; glucose concentration 100 mM). b Corresponding Tafel plots. c Capacitive current densities of different electrodes for glucose oxidation as a function of scan rate. d Nyquist plots (taken at 1.3 V vs. RHE) of different electrodes for glucose oxidation. e Concentration of glucose and oxidation products as a function of time for chronoamperometric tests at 1.30 V vs. RHE. f Glucose concentration changes in five successive cycles.
It should be noted that unlike many previous reports, in which the electrode materials with high OER performance usually have high catalytic performance for oxidation of organic compounds37,38,40, the NiFeOx-NF electrode had a lower OER performance compared to NiFeNx-NF, but possessed a higher glucose oxidation performance in a low potential region. To probe why this phenomenon occurred, the relative electrochemically active surface areas (ECSA) in glucose oxidation with the electrodes were compared by extracting their double-layer capacitances using cyclic voltammetry (CV). The CV profiles (Supplementary Fig. 6) were collected in the non-Faradaic potential region (0.925−1.0 V), in which only double-layer capacitance is accounted for the current response. The capacitance for NiFeOx-NF was calculated to be 53.3 mF cm−2 based on the CV results, higher than those of NiFeNx-NF (42.1 mF cm−2) and only NF (11.1 mF cm−2) (Fig. 4c). Thus, the NiFeOx-NF electrode had a larger ECSA than the NiFeNx-NF electrode. This indicates that the higher catalytic activity of NiFeOx-NF was likely due to the higher number of catalytic active sites, and the in situ generated surface Ni-Fe oxyhydroxides (FeOOH and NiOOH) could be the catalytic active sites of NiFeOx-NF electrode for both glucose oxidation and OER53,54. For example, the formation of Ni oxyhydroxides was confirmed by their polarization curves of OER (Fig. 4a), in which a small peak located at E = 1.36 V could be attributed to the oxidation of Ni(II) into NiOOH: (NiO + OH− → NiOOH + e−). The formation of FeOOH could not be confirmed by the polarization curves as it does not experience a valence variation in the electrochemical process, but the XPS spectra of NiFeOx-NF after glucose oxidation (Supplementary Fig. 5) confirm the formation of NiOOH and FeOOH species. We have also carried out control experiments to verify that the Ni-Fe oxyhydroxides are the catalytic active sites. The NiFeOx-NF and NiFeNx-NF catalysts were treated with H2O2 in 1 M of KOH solution to produce more NiOOH and FeOOH species. These treated catalysts were then used as anodic catalysts for both glucose oxidation and OER. The LSV profiles of these materials shown in Supplementary Fig. 7 indicate that after the H2O2 treatments, both NiFeOx-NF and NiFeNx-NF catalysts exhibited higher catalytic activities for OER (Supplementary Fig. 7a) and glucose oxidation (Supplementary Fig. 7b). Such improvements in the catalytic activities should be attributed to the higher activity of the Ni-Fe oxyhydroxides sites.
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was used to investigate the kinetics of the electrode materials. An equivalent circuit consisting of a series resistance (Rs), a charge-transfer resistance (Rct), and a constant phase element (CPE) was constructed. As shown in Fig. 4d, the NiFeOx-NF electrode displayed a smaller charge-transfer resistance (Rct) of about 1.7 Ohm, in contrast to the NiFeOx-NF (3.8 Ohm) and raw nickel foam electrodes (9.5 Ohm). The small Rct means favorable electron transport rate and catalytic kinetics, resulting in a small Tafel slope55. Meanwhile, the EIS profiles also show that the NiFeOx-NF and NiFeNx-NF electrodes had small Rs values (1.21 and 1.26 Ohm, respectively), revealing good electrical contacts between the catalysts and the nickel foam substrate. This was attributed to the formation of NiFeOx and NiFeNx catalysts via direct reactions of Ni foam, leading to strong adhesion to the Ni foam substrate.
We also investigated the catalytic performance of other catalysts, including NiFe(OH)x-NF, NF, as well as the benchmark Pt/C and RuO2 catalysts, for glucose oxidation (Supplementary Fig. 8; also see entries 7−10, Table 1). Among all the examined catalysts, the NiFeOx-NF electrode demonstrated the highest catalytic activity, with the lowest Eonset and Ej = 100 mA cm−2 values. The highest catalytic activity of the NiFeOx-NF electrode could be attributed to the following two reasons: (1) it possessed the highest number of catalytic active sites as indicated from the ECSA (Supplementary Fig. 9); and (2) it had the lowest charge-transfer resistance (Supplementary Fig. 10), which means a high electron transport rate and rapid catalytic kinetics. The rapid catalytic kinetics of the NiFeOx-NF electrode can also be revealed by its lowest Tafel slope (Fig. 4b).
The effect of glucose concentration on glucose oxidation was studied with the NiFeOx-NF electrode (Table 1). Supplementary Fig. 11a shows the LSV profiles of the NiFeOx-NF for glucose oxidation at various concentrations. The current density at E = 1.25 V had a linear relationship with the glucose concentration for 0−150 mM glucose concentration (Supplementary Fig. 11b). The current density did not change with a further increase in glucose concentration (150−500 mM). The electrochemical glucose oxidation followed the first-order reaction kinetics at low glucose concentrations, but changed into the zero-order reaction kinetics after the glucose concentration exceeding 150 mM. A similar result was reported for the glucose oxidation on RuO2 electrodes in 1 M of NaOH solution56.
The chronoamperometric measurements of glucose oxidation were conducted at a constant potential of 1.30 V, and the concentrations of glucose and its oxidation products (GNA and GRA) in chronoamperometric tests were monitored with HPLC as detailed in Supplementary Method 2 and Supplementary Fig. 12. The concentrations of the products and reactant as a function of reaction time are shown in Fig. 4e (initial concentration: 10 mM). These results indicate that GNA was the initial product, which was then converted into GRA. The glucose conversion after 120-min reaction was 98.3%, with a yield of GNA plus GRA of 91.9%, and a Faradaic efficiency (FE) for GNA plus GRA production of 87% (entry 3, Table 1). We also studied the potential glucose decomposition in an alkaline aqueous solution on open circuit with 1H, 13C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and 2D-HSQC NMR (Supplementary Fig. 13). Glucose (10 mmol/L) was not degraded after 24 h in the alkaline solution, suggesting that no significant self-decomposition of glucose occurred under the reaction conditions. This result is consistent with other glucose oxidation studies in alkaline solutions57,58.
Five successive cycles of chronoamperometric measurements were conducted to evaluate the stability and durability of the NiFeOx-NF electrode for glucose oxidation. The conversion of glucose slightly decreased from 98.3 to 91.2% after five cycles (Fig. 4f), and the reaction rates slightly decreased from 1.36 × 10−4 to 1.27 × 10−4 mmol glucose s−1 in these five successive cycles, but the FE values (Supplementary Fig. 14) of each cycle remained almost unchanged. The XRD patterns (Supplementary Fig. 15) of the catalyst after five cycles show that NiFe2O4 was the main crystalline phase. The XPS spectra of the reused NiFeOx-NF catalyst (Supplementary Fig. 16) show a new peak at 857.4 eV in the Ni 3d spectrum, which could be attributed to the Ni(III) species, suggesting that some Ni(III) species were formed in the anodic oxidation process. It is reported that the formation of Ni(III) is important for the anodic organic compound oxidation because the higher-valence state of Ni facilitates the adsorption of OH− ions and reduces the energy barrier for the transition of Ni species from lower- to higher-valence states in promoting anodic oxidation reactions59. The SEM image (Supplementary Fig. 17) shows that after reuse, the nanosheet structure of the NiFeOx kept almost unchanged. The EDS mapping results (Supplementary Fig. 18) of the reused catalyst demonstrate that the Fe and Ni elements were evenly distributed on the NF.
To gain some insights into the mechanism of the anodic glucose oxidation over the NiFeOx-NF catalyst (Fig. 5), in situ ATR-FTIR, 2D-HSQC NMR and LC-MS analysis was performed. The IR spectra collected in the potential step experiments ranging from 1.0 to 1.6 V provides useful information on the glucose oxidation pathways (Fig. 6a). The cleavage of C−C bond did not occur because of the mild conditions of the electrochemical oxidation process. Thus, the possible intermediates and products of glucose oxidation were proposed as follows: GNA and gluconolactone (oxidation of H−C=O group to COOH in C1 position, two-electron transfer), glucuronic acid (oxidation of CH2OH group to H−C=O in C6 position, two-electron transfer), and GRA (further oxidation of H−C=O group in C6 position, two-electron transfer). The assignments of IR bands as well as the identification of the reaction intermediates were conducted by comparing with the reference spectra (Supplementary Fig. 19 and Supplementary Table 1). The bands appearing synchronously at wavenumbers of 1573−1506 cm−1 and 1483−1431 cm−1 were attributed to the asymmetric stretching and symmetric vibrations of O−C−O, respectively, confirming the formation of glucuronic acid (Pyranuronic form). No C−C bond breaking occurred in the electrochemical glucose oxidation process, as no C−C bond cleavage compounds (CO: 1900−2100 cm−1 and CO32−: 1390−1400 cm−1) were observed in the IR spectra. However, the complete oxidation of glucose into GNA and GRA cannot be achieved in the in situ ATR-FTIR reactor due to insufficient reaction time. Another note is that the formation of GNA and GRA could not be differentiated with the FTIR spectra only, as these two compounds have very similar functional group compositions. In addition to the IR spectra, the 1H, 13C and 2D HSQC NMR as well as LC-MS analyses were also performed. The 1H and 13C NMR spectra of the reactant and 6-h products from glucose electrolysis are presented in Supplementary Fig. 20. The signals in the chemical shift of 0 and 2.50 ppm could be attributed to the reference TMS (tetramethylsilane) and DMSO-H6 (a main impurity of the deuterated DMSO solvent for NMR), while the signals in the chemical shift of 3−6 ppm could be ascribed to glucose and its oxidation products. A very small signal could be found in the chemical shift of 11.1 ppm, which could be attributed to the H atom in the COOH groups. This small signal does not mean that the COOH content in the product was of a very low level because the intensity of the 1 H NMR signal for COOH is not proportional to the concentration of COOH in the samples. Such a weak H signal is likely to be attributed to the mobility of H in the COOH group60,61. Nevertheless, the presence of COOH in the reacted sample was confirmed by the 13C NMR spectra. The C1, C6 (COOH) regions in the 2D HSQC NMR spectrum (Fig. 6b) could be attributed to the GNA, GRA and guluronic acid. To further identify these compounds, we examined the 13C NMR of the standard glucose and its main oxidation products (e.g., GNA, GRA, and guluronic acid). As shown in Supplementary Fig. 21, the presence of glucose was confirmed by the characteristic peaks at chemical shifts of 60.9 and 92.4 ppm, while the presence of GNA could be observed via the characteristic peak at chemical shift of 64.4 ppm and the signal of COOH (δ = 175.4 ppm). The presence of GRA could be observed via the characteristic peak at chemical shift of 69.7 ppm and the signal of COOH (δ = 175.5 ppm), while the presence of guluronic acid could be observed via the characteristic peak at chemical shift of 97.2 ppm and the signal of COOH (δ = 175.7 ppm). The presence of 1,5-gluconolactone could be inferred from the C1, C6 (R−O−C=O) regions in Fig. 6b. The LC-MS analytic results of the reaction solution after 6-h electrolysis (Supplementary Fig. 22) further confirm the presence of GNA, GRA and some intermediates like 1,5-gluconolactone and guluronic acid.
Cathodic HER
The cathodic HER under alkaline conditions was also investigated using the Ni-Fe-OH-based electrodes together with other electrodes, as shown in the LSV profiles in Fig. 7a. Unlike the glucose oxidation, the NiFeNx-NF electrode showed a higher HER activity in 1 M KOH solution than the NiFeOx-NF and NiFe(OH)x-NF electrodes. The overpotentials for reaching current densities of 10 and 100 mA cm−2 by the NiFeNx-NF electrode were 40.6 and 104 mV, respectively, higher than those of 20% Pt/C catalyst (Supplementary Fig. 23). The Tafel slope of the NiFeNx-NF electrode for HER was calculated as 39 mV dec−1, much lower than those of the NiFe(OH)x-NF (142 mV dec−1) and NiFeOx-NF (97 mV dec−1) electrodes (Fig. 7b), further confirming that NiFeNx-NF was an efficient cathodic HER catalyst. For comparison, an in situ grown iron−nickel nitride nanostructure (Ni3FeN-NF) was reported to deliver 10 mA cm−2 of current at an overpotential of 75 mV with a Tafel slope of 98 mV dec−1 62. The data in Supplementary Table 2 further confirm that, with the low overpotential (40.6 mV for 10 mA cm−2) and Tafel slope (39 mV dec−1) values, the NiFeNx-NF electrode is among the best performing noble-metal-free HER catalysts in alkaline solution. The EIS spectra (Supplementary Fig. 24) indicate a much lower charge-transfer resistance of the NiFeNx-NF electrode than those of the NiFeOx-NF and NF electrodes.
a LSV profiles of the different electrodes for HER in 1 M KOH electrolyte (scan rate of 5 mV s−1). b Corresponding Tafel plots. c Comparison of LSV profiles of the NiFeNx-NF catalyst for HER with and without 100 mM of glucose. d Chronoamperometric test of the NiFeNx-NF catalysts for HER with 100 mM of glucose, left inset: LSV profiles of the NiFeNx-NF catalysts before and after 24-h chronoamperometric test, right inset: amplified region of the chronoamperometric curve.
In order to integrate the anodic glucose oxidation with cathodic HER, the cathodic electrode must have stable catalytic activity for HER in the presence of glucose, as the glucose in the anode compartment of the electrolyzer can cross over the anion-exchange membrane into the cathode compartment. Thus, the glucose tolerance of the NiFeNx-NF electrode for HER was evaluated with the same glucose concentration found in the anode compartment. Figure 7c shows that the LSV profiles of the NiFeNx-NF electrode with and without 100 mM of glucose were very similar—only about 20 mV higher overpotential was required to reach the same current density when 100 mM of glucose was in the cathode compartment. A 24-h chronoamperometry test of HER was also conducted in the presence of 100 mM glucose at a potential of −0.135 V (Fig. 7d and right inset), which shows that the electrocatalytic current density of the NiFeNx-NF electrode remained almost unchanged, confirming its strong glucose tolerance. The LSV profiles of the fresh and 24-h-used NiFeNx-NF electrodes exhibited no difference (left inset of Fig. 5d), demonstrating the stability of the electrode.
Discussion
A glucose electrolyzer was constructed using NiFeOx-NF as the anodic electrode and NiFeNx-NF as the cathodic electrode, separated by a anion-exchange membrane, in an H-cell with 1 M KOH and 0.5 M glucose + 1 M KOH as the anodic and cathodic electrolytes, respectively (Supplementary Fig. 25). A water electrolyzer with the same configuration was also constructed in the absence of glucose. The LSV profiles (Fig. 8a) show that the glucose oxidation electrolysis exhibited a higher current density than the water electrolysis with the same cell potential. Such low cell voltages required for glucose electrolyzer also compare favorably to the values reported for electrolyzers for the oxidation of many other organic compounds (e.g., urea, ethanol, benzyl alcohol, etc.) (Supplementary Table 3), demonstrating the higher energy efficiency of glucose electrolyzers using NiFeOx-NF and NiFeNx-NF electrodes. After 24-h at cell voltage of 1.4 V, 21.3% of the glucose was converted with the GRA and GNA yields or 11.6% and 4.7%, respectively. A high glucose concentration of 0.5 M was used to ensure that the current density did not fade in the entire electrolysis process, because the electrolysis current density would decrease with a low glucose concentration (less than 0.15 M) (Supplementary Fig. 11).
a Comparison of glucose electrolysis and water electrolysis with the same anodic NiFeOx-NF and cathodic NiFeNx-NF catalysts (scan rate: 5 mV s−1, glucose concentration: 100 mM, 1 M KOH). b Long-term stability of the glucose electrolysis at a cell voltage of 1.4 V. c Comparison of the revenues and costs for electrocatalytic glucose oxidation and nonelectrocatalytic oxidation processes (HNO3 oxidation) for GRA production (1000 tons GRA per year).
The H2 production in the glucose electrolyzer was observed by the evolution of bubbles at the cathode, and further confirmed by gas chromatography analysis. The long-term stability of the glucose electrolyzer was evaluated via chronoamperometry, which shows that the electrolyzer delivered a current density of 101.2 mA cm−2 at a voltage of 1.4 V and exhibited less than 4% decrease in this value (97.8 mA cm−2 remaining) after 24-h operation (Fig. 8b). It should be mentioned that in the chronoamperometry test, no bubbles were observed at the anode, confirming that the competing OER process did not occur in the glucose electrolysis process.
The economic feasibility for the electrocatalytic and nonelectrocatalytic glucose oxidation strategies was estimated assuming a production scale of 1000 tons GRA per year63. The minimum selling price (MSP) of GRA was calculated via a discounted cash flow analysis and setting the NPV (net present value) to 0 using the economic and technological assumptions and parameters shown in Supplementary Methods 3 and 4 and simulated with ASPEN Plus (Aspen Engineering V8.4, AspenTech, USA) (Supplementary Figs. 26–29 and Supplementary Tables 6−15). As shown in Supplementary Table 12, the electrochemical glucose oxidation has a lower capital costs ($10.5 vs. $19.3 million), lower raw material cost ($1.2 vs. $1.9 million yr−1), lower operating cost ($5.9 vs. 7.6 million yr−1) and higher revenues ($17.2 vs. 15.1 million yr−1) than the chemical glucose oxidation. The MSP for GRA for the electrocatalytic glucose oxidation approach is calculated to be $9.32 kg−1 (Fig. 8c). For comparison, the MSP of GRA for the nonelectrocatalytic oxidation process is $17.04 per kg.
In Supplementary Table 4, the electrocatalytic glucose oxidation process proposed in this work is compared with conventional chemical oxidation23,24 and microbial fermentation19,20 processes for GRA production to highlight the sustainability of glucose electrolysis. The electrocatalytic glucose oxidation process has several advantages over the other two processes because of its higher GRA yield, shorter reaction time and lower E-factor (the mass ratio of the generated waste to target products). The electrocatalytic glucose oxidation process has lower operation and downstream separation costs and a much smaller environmental impact. One main challenge for the electrocatalytic glucose oxidation process is that it will require large amounts of KOH (370 tons KOH for production of 1000 tons GRA) and the associated equipment. Fortunately, KOH is not directly discharged into the environment after the reaction, but converted into K2SO4 (650 tons per year), which can be sold as a byproduct to produce fertilizers.
In conclusion, an electrolysis method was developed to convert glucose into GRA and H2. The NiFeOx-NF and NiFeNx-NF electrodes derived from NiFe LDH nanosheet arrays demonstrate high yields toward anodic glucose oxidation and cathodic HER respectively. The low onset potentials (1.13 V) and Tafel slopes (19 mV dec−1) confirm that glucose oxidation is much more favorable than OER, leading to a high Faradaic efficiency (87%) toward GNA and GRA production. A two-electrode glucose electrolyzer constructed with NiFeOx-NF as the anode for glucose oxidation and NiFeNx-NF as the cathode for HER can deliver a current density of 200 mA cm−2 with a voltage of only 1.48 V, and run stably for 24 h, placing such a glucose electrolyzer among the best organic compound electrolyzers with noble-metal-free electrodes reported so far. Because of the abundant nature of these catalyst materials and the cost-effective and energy-saving production of value-added chemicals like GRA and H2, this organic compound electrolysis strategy is expected to be promising and sustainable for valorization of biomass feedstocks.
Methods
Synthesis of NiFe-OH nanosheets-based electrocatalysts
The chemicals and materials used in this work are listed in Supplementary Note 1. The NiFe hydroxides nanosheets were grown on the NF via a facile hydrothermal approach described as follows: FeCl3•6H2O (540.6 mg, 2 mmol) was dissolved in 10 mL of H2O, which was then transferred to a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave of 50 mL. A piece of NF was immersed into the Fe(III) solution and reacted under ultrasonic for 30 min. Urea (900 mg, 15 mmol) was dissolved in 10 mL H2O and mixed with the Fe(III) solution, and then 20 mL of ethanol was added into the solution. The autoclave was subsequently sealed and heated to 160 °C for 24 h. Afterwards, the NF was washed with H2O and ethanol several times to obtain the NiFe hydroxide nanosheets (denoted as NiFe(OH)x-NF). The NiFe(OH)x-NF was then heated in air or NH3-Ar gas mixture (20:80) at 300 °C (heating rate 2 °C per min) for 3 h to obtain Ni-Fe oxides (denoted as NiFeOx-NF) or nitrides (denoted as NiFeNx-NF), respectively.
Electrochemical measurements
The glucose electrochemical oxidation was conducted with a CHI 760D electrochemical workstation (ChenHua Instrument Inc., China), in which the Ag/AgCl electrode was used as reference electrode, the as-synthesized catalysts on NF electrodes (NiFeOx-NF, NiFeNx-NF, and NiFe(OH)x-NF) were used directly as working electrodes, and a Pt wire was used as counter electrode (unless otherwise stated). The tested potential vs. Ag/AgCl can be converted into potential vs. RHE via the Nernst equation listed as follows:
The water electrolysis experiments were conducted in an H-type electrochemical cell, in which the anode and cathode electrolyte were both 1 M KOH (100 mL), and an anion-exchange membrane (AMI-7001, Membranes International Inc., USA) was used to separate the cathode and anode compartments. The glucose electrolysis experiments were conducted in the same manner as water electrolysis except that the anode electrolyte was 1 M of KOH solution dissolved with glucose (0−100 mM). The polarization curves were collected with LSV at 5 mV s−1. The stability of the catalysts for glucose electrolysis was evaluated through chronoamperometry at 1.30 V in 100 mL of glucose solution (10 mM in 1 M of KOH) for five successive cycles. EIS were recorded at 1.3 V and −0.3 V for glucose electrolysis and HER, respectively, with a frequency range from 1 Hz to 100 kHz. The concentration profiles of glucose and its oxidation products in the electrolysis process were analyzed with an HPLC equipped with a refractive index detector.
Data availability
All data are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
Besson, M., Gallezot, P. & Pinel, C. Conversion of biomass into chemicals over metal catalysts. Chem. Rev. 114, 1827–1870 (2014).
Mika, L. T., Cséfalvay, E. & Németh, Á. Catalytic conversion of carbohydrates to initial platform chemicals: chemistry and sustainability. Chem. Rev. 118, 505–613 (2017).
Liu, C., Wang, H., Karim, A. M., Sun, J. & Wang, Y. Catalytic fast pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 7594–7623 (2014).
Zakzeski, J., Bruijnincx, P. C. A., Jongerius, A. L. & Weckhuysen, B. M. The catalytic valorization of lignin for the production of renewable chemicals. Chem. Rev. 110, 3552–3599 (2010).
Huber, G. W., Iborra, S. & Corma, A. Synthesis of transportation fuels from biomass: chemistry, catalysts, and engineering. Chem. Rev. 106, 4044–4098 (2006).
Bozell, J. J. Connecting biomass and petroleum processing with a chemical bridge. Science 329, 522–523 (2010).
Zhang, Z. & Huber, G. W. Catalytic oxidation of carbohydrates into organic acids and furan chemicals. Chem. Soc. Rev. 47, 1351–1390 (2018).
van Putten, R.-J. et al. Hydroxymethylfurfural, a versatile platform chemical made from renewable resources. Chem. Rev. 113, 1499–1597 (2013).
Ragauskas, A. J. The path forward for biofuels and biomaterials. Science 311, 484–489 (2006).
Mangiameli, M. F., González, J. C., Bellú, S., Bertoni, F. & Sala, L. F. Redox and complexation chemistry of the Cr VI/Cr V-d-glucaric acid system. Dalton Trans. 43, 9242–9254 (2014).
Mehtiö, T. et al. Production and applications of carbohydrate-derived sugar acids as generic biobased chemicals. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 36, 904–916 (2016).
Khaw, B.-A., Narula, J. & Hartner, W. Attenuation of microvascular injury in preconditioned ischemic myocardium: imaging with Tc-99m glucaric acid and In-111 human fibrinogen. Curr. Mol. Imag. 4, 20–28 (2015).
Houson, H. A., Nkepang, G. N., Hedrick, A. F. & Awasthi, V. Imaging of isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury with 18F labeled fluoroglucaric acid in a rat model. Nucl. Med. Biol. 59, 9–15 (2018).
Sinch, J. & Gupta, K. P. Calcium glucarate prevents tumor formation in mouse skin. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 16, 9–16 (2003).
Grand-View-Research. Glucaric Acid Market Size & Share. Global Industry Report (2017).
Derrien, E., Marion, P., Pinel, C. & Besson, M. Influence of residues contained in softwood hemicellulose hydrolysates on the catalytic oxidation of glucose to glucarate in alkaline aqueous solution. Org. Process Res. Dev. 20, 1265–1275 (2016).
Boussie, T. R., Dias, E. L., Fresco, Z. M. & Murphy, V. J. Production of glutaric acid and derivatives from carbohydrate-containing materials. US Patent 8,785,683 (2014).
Kunz, M., Schwarz, A. & Kowalczyk, J. Method and apparatus for producing di-and more highly oxidized carboxylic acids. US Patent 5,772,013 (1998).
Moon, T. S., Yoon, S.-H., Lanza, A. M., Roy-Mayhew, J. D. & Prather, K. L. J. Production of glucaric acid from a synthetic pathway in recombinant Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75, 589–595 (2009).
Moon, T. S., Dueber, J. E., Shiue, E. & Prather, K. L. J. Use of modular, synthetic scaffolds for improved production of glucaric acid in engineered E. coli. Metab. Eng. 12, 298–305 (2010).
Liu, Y. et al. Production of glucaric acid from myo-inositol in engineered Pichia pastoris. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 91, 8–16 (2016).
Rivertop Renewables begins commercial production of glucaric acid. http://www.rivertop.com/products/glucarates.php (2015).
Mehltretter, C. & Rist, C. Sugar oxidation, saccharic and oxalic acids by the nitric acid oxidation of dextrose. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1, 779–783 (1953).
Mustakas, G., Slotter, R. & Zipf, R. Pilot plant potassium acid saccharate by nitric acid oxidation of dextrose. Ind. Eng. Chem. 46, 427–434 (1954).
Lee, J., Saha, B. & Vlachos, D. G. Pt catalysts for efficient aerobic oxidation of glucose to glucaric acid in water. Green Chem. 18, 3815–3822 (2016).
Solmi, S., Morreale, C., Ospitali, F., Agnoli, S. & Cavani, F. Oxidation of d-glucose to glucaric acid using Au/C catalysts. ChemCatChem 9, 2797–2806 (2017).
Derrien, E. et al. Aerobic oxidation of glucose to glucaric acid under alkaline-free conditions: Au-based bimetallic catalysts and the effect of residues in a hemicellulose hydrolysate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 56, 13175–13189 (2017).
Jin, X. et al. Synergistic effects of bimetallic PtPd/TiO2 nanocatalysts in oxidation of glucose to glucaric acid: structure dependent activity and selectivity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55, 2932–2945 (2016).
Qi, P. et al. Catalysis and reactivation of ordered mesoporous carbon-supported gold nanoparticles for the base-free oxidation of glucose to gluconic acid. ACS Catal. 5, 2659–2670 (2015).
Jin, X. et al. Exceptional performance of bimetallic Pt1Cu3/TiO2 nanocatalysts for oxidation of gluconic acid and glucose with O2 to glucaric acid. J. Catal. 330, 323–329 (2015).
Jiang, Y. et al. Gluconic acid production from potato waste by gluconobacter oxidans using sequential hydrolysis and fermentation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 5, 6116–6123 (2017).
Weber, R. S. Effective use of renewable electricity for making renewable fuels and chemicals. ACS Catal. 9, 946–950 (2019).
Vogt, S. & Schneider, M. Schäfer-Eberwein, H. & Nöll, G. Determination of the pH dependent redox potential of glucose oxidase by spectroelectrochemistry. Anal. Chem. 86, 7530–7535 (2014).
Komori, H. et al. An extended-gate CMOS sensor array with enzyme-immobilized microbeads for redox-potential glucose detection. In Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), 2014 IEEE 464−467 (IEEE, 2014).
Pasta, M., La Mantia, F. & Cui, Y. Mechanism of glucose electrochemical oxidation on gold surface. Electrochim. Acta 55, 5561–5568 (2010).
Cui, H.-F., Ye, J.-S., Liu, X., Zhang, W.-D. & Sheu, F.-S. Pt–Pb alloy nanoparticle/carbon nanotube nanocomposite: a strong electrocatalyst for glucose oxidation. Nanotechnology 17, 2334 (2006).
Dai, L. et al. Electrochemical partial reforming of ethanol into ethyl acetate using ultrathin Co3O4 nanosheets as a highly selective anode catalyst. ACS Cent. Sci. 2, 538–544 (2016).
Yu, Z.-Y. et al. Ni-Mo-O nanorod-derived composite catalysts for efficient alkaline water-to-hydrogen conversion via urea electrolysis. Energy Environ. Sci. 11, 1890–1897 (2018).
Jian, Z. et al. Hierarchical porous NC@CuCo nitride nanosheet networks: Highly efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting and selective electrooxidation of benzyl alcohol. Adv. Func. Mater. 27, 1704169 (2017).
Liu, W.-J. et al. Electrochemical oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural with NiFe layered double hydroxide (LDH) nanosheet Catalysts. ACS Catal. 8, 5533–5541 (2018).
Bin, D. et al. Controllable oxidation of glucose to gluconic acid and glucaric acid using an electrocatalytic reactor. Electrochim. Acta 130, 170–178 (2014).
Ibert, M. et al. Improved preparative electrochemical oxidation of d-glucose to d-glucaric acid. Electrochim. Acta 55, 3589–3594 (2010).
Dang, L. et al. Direct synthesis and anion exchange of noncarbonate-intercalated NiFe-layered double hydroxides and the influence on electrocatalysis. Chem. Mater. 30, 4321–4330 (2018).
Zboril, R., Mashlan, M. & Petridis, D. Iron (III) oxides from thermal processes synthesis, structural and magnetic properties, Mössbauer spectroscopy characterization, and applications. Chem. Mater. 14, 969–982 (2002).
Grosvenor, A., Kobe, B., Biesinger, M. & McIntyre, N. Investigation of multiplet splitting of Fe 2p XPS spectra and bonding in iron compounds. Surf. Interf. Anal. 36, 1564–1574 (2004).
Yamashita, T. & Hayes, P. Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 2441–2449 (2008).
Xie, S. et al. Hydrogen production from solar driven glucose oxidation over Ni (OH)2 functionalized electroreduced-TiO2 nanowire arrays. Green Chem. 15, 2434–2440 (2013).
Martínez-Huitle, C. A. & Ferro, S. Electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants for the wastewater treatment: direct and indirect processes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 35, 1324–1340 (2006).
Jin, S. Are Metal chalcogenides, nitrides, and phosphides oxygen evolution catalysts or bifunctional catalysts? ACS Energy Lett. 2, 1937–1938 (2017).
Lv, L., Yang, Z., Chen, K., Wang, C. & Xiong, Y. 2D layered double hydroxides for oxygen evolution reaction: from fundamental design to application. Adv. Energy Mater. 9, 1803358 (2019).
Exner, K. S. Is thermodynamics a good descriptor for the activity? Re-investigation of dabatier’s principle by the free energy diagram in electrocatalysis. ACS Catal. 9, 5320–5329 (2019).
Yu, L. et al. Cu nanowires shelled with NiFe layered double hydroxide nanosheets as bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Energy Environ. Sci. 10, 1820–1827 (2017).
Zhang, J. et al. Single-atom Au/NiFe layered double hydroxide electrocatalyst: probing the origin of activity for oxygen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 3876–3879 (2018).
Wang, T. et al. NiFe (Oxy) Hydroxides derived from NiFe disulfides as an efficient oxygen evolution catalyst for rechargeable Zn–Air batteries: the effect of surface S residues. Adv. Mater. 30, 1800757 (2018).
Zhou, H. et al. Highly efficient hydrogen evolution from edge-oriented WS2(1–x)Se2x particles on three-dimensional porous NiSe2 foam. Nano Lett. 16, 7604–7609 (2016).
Lyons, M. E., Fitzgerald, C. A. & Smyth, M. R. Glucose oxidation at ruthenium dioxide based electrodes. Analyst 119, 855–861 (1994).
Pasta, M., Ruffo, R., Falletta, E., Mari, C. & Della Pina, C. Alkaline glucose oxidation on nanostructured gold electrodes. Gold. Bull. 43, 57–64 (2010).
Aoun, S. B. et al. Effect of metal ad-layers on Au (1 1 1) electrodes on electrocatalytic oxidation of glucose in an alkaline solution. J. Electroanal. Chem. 567, 175–183 (2004).
Barwe, S. et al. Electrocatalytic oxidation of 5-(Hydroxymethyl)furfural using high-durface-area nickel boride. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 11460–11464 (2018).
Iida, T. et al. 1H and 13C NMR signal assignments of carboxyl-linked glucosides of bile acids. Magn. Reson. Chem. 41, 260–264 (2003).
Dong, W., Zhou, Y., Yan, D., Li, H. & Liu, Y. pH-responsive self-assembly of carboxyl-terminated hyperbranched polymers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 9, 1255–1262 (2007).
Zhang, B. et al. Iron–nickel nitride nanostructures in situ grown on surface-redox-etching nickel foam: efficient and ultrasustainable electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Chem. Mater. 28, 6934–6941 (2016).
Kim, H. J. et al. Coproducing value-added chemicals and hydrogen with electrocatalytic glycerol oxidation technology: experimental and techno-economic investigations. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 5, 6626–6634 (2017).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21590812, 51538011, 21607147 and 51821006), and the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University of the Ministry of Education of China for supporting this work. S.J. thanks the support by National Science Foundation Grant (1508558).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.W.H., S.J., H.-Q.Y. and W.-J.L. devised the concept. H.-Q.Y., supervised the project. W.-J.L. performed the experiments of materials synthesis and glucose electrolysis. Z.X. and X.-Q.P. helped for the materials characterizations and products analysis. D.Z., X.H. and H.-C.L. helped for the materials synthesis. Z.-Y.F., W.-K.W., G.-H.Z., helped for the in situ FTIR analysis. W.-J.L. wrote the manuscript. G.W.H., S.J., H.-Q.Y. and W.-J.L. revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests
Additional information
Peer review information Nature Communications thanks Mike Lyons, Basudeb Saha, and other, anonymous, reviewers for their contributions to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, WJ., Xu, Z., Zhao, D. et al. Efficient electrochemical production of glucaric acid and H2 via glucose electrolysis. Nat Commun 11, 265 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-14157-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-14157-3
This article is cited by
-
Surface engineering of 1-D nanocatalysts for value-added selective electrooxidation of organic chemicals
Nano Research (2024)
-
Unraveling the role of iron on Ni-Fe alloy nanoparticles during the electrocatalytic ethanol-to-acetate process
Nano Research (2024)
-
Hydrogen production via steam reforming of small organic compounds present in the aqueous fraction of bio-oil over Ni-La-Me catalysts (Me = Ce, Ti, Zr)
Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery (2024)
-
Highly selective electrosynthesis of 3,4-dihydroisoquinoline accompanied with hydrogen production over three-dimensional hollow CoNi-based microarray electrocatalysts
Nano Research (2024)
-
Acidic enol electrooxidation-coupled hydrogen production with ampere-level current density
Nature Communications (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.