Abstract
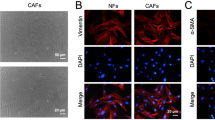
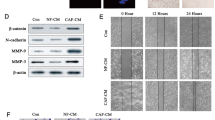
This study was designed to investigate the role and mechanism of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs)-derived exosomes (CAFs-exo) in metastatic and chemoresistant colorectal cancer (CRC). First, CAFs and normal fibroblasts (NFs) were isolated from CRC tissues and histologically normal adjacent tissues. Then, CAFs-exo and NFs-exo were separated with the help of ultracentrifugation. Next, the morphology, diameter and marker expression of exos were evaluated by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) and western blot, respectively. Besides, real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was used to detect the expression levels of LINC00355, miR-34b-5p, and CRKL in clinical tissue samples, CRC cells, fibroblasts and exos; MTT assay and cell colony formation assay to assess the chemoresistance and colony formation ability of CRC cells, respectively. Subsequently, the targeting relationship among LINC00355, miR-34b-5p, and CRKL (a target gene of miR-34b-5p) was verified by Luciferase reporter assay; and the binding relationship between LINC00355 and miR-34b-5p was assessed by a pull-down assay. Finally, the expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related proteins, and CRKL in cells or exos were detected using western blot. After a series of treatments, CAFs and NFs, CAFs-exo and NFs-exo were successfully isolated and identified. It could be observed that CAFs-exo promoted EMT, colony formation and multidrug resistance in CRC cells by secreting LINC00355. Further studies demonstrated that CAFs-exo-secreted LINC00355 increased the expression of CRKL via inhibiting the expression of miR-34b-5p, thereby enhancing chemoresistance and promoting EMT progression in CRC cells. Collectively, CAFs-exo-derived LINC00355 promotes EMT and chemoresistance in CRC by regulating the miR-34b-5p/CRKL axis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49.
Xi Y, Xu P. Global colorectal cancer burden in 2020 and projections to 2040. Transl Oncol. 2021;14:101174.
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108.
Marquardt JU, Fischer K, Baus K, Kashyap A, Ma S, Krupp M, et al. Sirtuin-6-dependent genetic and epigenetic alterations are associated with poor clinical outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Hepatology. 2013;58:1054–64.
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:10513–8.
McQuade RM, Stojanovska V, Bornstein JC, Nurgali K. Colorectal cancer chemotherapy: the evolution of treatment and new approaches. Curr Med Chem. 2017;24:1537–57.
Meads MB, Gatenby RA, Dalton WS. Environment-mediated drug resistance: a major contributor to minimal residual disease. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:665–74.
Kalluri R. The biology and function of exosomes in cancer. J Clin Invest. 2016;126:1208–15.
Mittelbrunn M, Sanchez-Madrid F. Intercellular communication: diverse structures for exchange of genetic information. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:328–35.
Asif PJ, Longobardi C, Hahne M, Medema JP. The role of cancer-associated fibroblasts in cancer invasion and metastasis. Cancers. 2021;13:4720.
Gong J, Lin Y, Zhang H, Liu C, Cheng Z, Yang X, et al. Reprogramming of lipid metabolism in cancer-associated fibroblasts potentiates migration of colorectal cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:267.
Chevillet JR, Kang Q, Ruf IK, Briggs HA, Vojtech LN, Hughes SM, et al. Quantitative and stoichiometric analysis of the microRNA content of exosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:14888–93.
Yuan D, Xu J, Wang J, Pan Y, Fu J, Bai Y, et al. Extracellular miR-1246 promotes lung cancer cell proliferation and enhances radioresistance by directly targeting DR5. Oncotarget. 2016;7:32707–22.
Richards KE, Zeleniak AE, Fishel ML, Wu J, Littlepage LE, Hill R. Cancer-associated fibroblast exosomes regulate survival and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene. 2017;36:1770–8.
Ren J, Ding L, Zhang D, Shi G, Xu Q, Shen S, et al. Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts promote the stemness and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer by transferring exosomal lncRNA H19. Theranostics. 2018;8:3932–48.
Chen X, Liu Y, Zhang Q, Liu B, Cheng Y, Zhang Y, et al. Exosomal miR-590-3p derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts confers radioresistance in colorectal cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;24:113–26.
Yang K, Zhang J, Bao C. Exosomal circEIF3K from cancer-associated fibroblast promotes colorectal cancer (CRC) progression via miR-214/PD-L1 axis. BMC Cancer. 2021;21:933.
Shurtleff MJ, Yao J, Qin Y, Nottingham RM, Temoche-Diaz MM, Schekman R, et al. Broad role for YBX1 in defining the small noncoding RNA composition of exosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114:E8987–95.
Kopp F, Mendell JT. Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2018;172:393–407.
Dong Z, Yang P, Qiu X, Liang S, Guan B, Yang H, et al. KCNQ1OT1 facilitates progression of non-small-cell lung carcinoma via modulating miRNA-27b-3p/HSP90AA1 axis. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:11304–14.
Yang F, Ning Z, Ma L, Liu W, Shao C, Shu Y, et al. Exosomal miRNAs and miRNA dysregulation in cancer-associated fibroblasts. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:148.
Li WJ, Li G, Liu ZW, Chen ZY, Pu R. LncRNA LINC00355 promotes EMT and metastasis of bladder cancer cells through the miR-424-5p/HMGA2 axis. Neoplasma. 2021;68:1225–35.
Luo X, ABudureyimu M, Yang G, Yan Z, Fu X, Lu P, et al. LINC00355 triggers malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via the sponge effect on miR-217-5p with the involvement of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. J BUON. 2021;26:1964–9.
Lu S, Sun Z, Tang L, Chen L. LINC00355 promotes tumor progression in HNSCC by hindering microrna-195-mediated suppression of HOXA10 expression. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;19:61–71.
Zhao W, Jin Y, Wu P, Yang J, Chen Y, Yang Q, et al. LINC00355 induces gastric cancer proliferation and invasion through promoting ubiquitination of P53. Cell Death Discov. 2020;6:99.
Wang Y, Zhang B, Gao G, Zhang Y, Xia Q. Long non-coding RNA LINC00355 promotes the development and progression of colorectal cancer by elevating guanine nucleotide exchange factor t expression via RNA binding protein lin-28 homolog A. Front Oncol. 2020;10:582669.
Luo G, Zhang Y, Wu Z, Zhang L, Liang C, Chen X. Exosomal LINC00355 derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes bladder cancer cell resistance to cisplatin by regulating miR-34b-5p/ABCB1 axis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 2021;53:558–66.
Zhang Y, Luo G, You S, Zhang L, Liang C, Chen X. Exosomal LINC00355 derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes bladder cancer cell proliferation and invasion by regulating miR-15a-5p/HMGA2 axis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 2021;53:673–82.
Wang S, Cui J, Zhang K, Gu J, Zheng Y, Zhang B, et al. SP13786 inhibits the migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cell A549 by supressing Stat3-EMT via CAFs exosomes. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2021;24:384–93.
Zhang H, Deng T, Liu R, Ning T, Yang H, Liu D, et al. CAF secreted miR-522 suppresses ferroptosis and promotes acquired chemo-resistance in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:43.
Zheng T, Pu J, Chen Y, Mao Y, Guo Z, Pan H, et al. Plasma exosomes spread and cluster around beta-amyloid plaques in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017;9:12.
Zhu B, Liu W, Liu H, Xu Q, Xu W. LINC01094 down-regulates miR-330-3p and enhances the expression of MSI1 to promote the progression of glioma. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:6511–21.
Wang Y, Liu Q, Wang F. Potential roles of exosome non‑coding RNAs in cancer chemoresistance (Review). Oncol Rep. 2021;45:439–47.
McGeary SE, Lin KS, Shi CY, Pham TM, Bisaria N, Kelley GM, et al. The biochemical basis of microRNA targeting efficacy. Science. 2019;366:eaav1741.
Cazzoli R, Buttitta F, Di Nicola M, Malatesta S, Marchetti A, Rom WN, et al. microRNAs derived from circulating exosomes as noninvasive biomarkers for screening and diagnosing lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2013;8:1156–62.
Dijkstra S, Birker IL, Smit FP, Leyten GH, de Reijke TM, van Oort IM, et al. Prostate cancer biomarker profiles in urinary sediments and exosomes. J Urol. 2014;191:1132–8.
Chen Y, McAndrews KM, Kalluri R. Clinical and therapeutic relevance of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18:792–804.
Peng L, Wang D, Han Y, Huang T, He X, Wang J, et al. Emerging role of cancer-associated fibroblasts-derived exosomes in tumorigenesis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:795372.
Mao YC. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote radioresistance of lung cancer by transferring exosomal IncRNA KCNQ1OT1: the mechanisms. Kunming Medical University; 2019.
Hu Y, Yan C, Mu L, Huang K, Li X, Tao D, et al. Fibroblast-derived exosomes contribute to chemoresistance through priming cancer stem cells in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0125625.
Hu JL, Wang W, Lan XL, Zeng ZC, Liang YS, Yan YR, et al. CAFs secreted exosomes promote metastasis and chemotherapy resistance by enhancing cell stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:91.
Esteller M. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12:861–74.
Han D, Gao X, Wang M, Qiao Y, Xu Y, Yang J, et al. Long noncoding RNA H19 indicates a poor prognosis of colorectal cancer and promotes tumor growth by recruiting and binding to eIF4A3. Oncotarget. 2016;7:22159–73.
Yan L, Wang P, Fang W, Liang C. Cancer-associated fibroblasts-derived exosomes-mediated transfer of LINC00355 regulates bladder cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Cell Biochem Funct. 2020;38:257–65.
Misso G, Di Martino MT, De Rosa G, Farooqi AA, Lombardi A, Campani V, et al. Mir-34: a new weapon against cancer? Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2014;3:e194.
Dong L, Chen F, Fan Y, Long J. MiR-34b-5p inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion through targeting ARHGAP1 in breast cancer. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12:269–80.
Cordova-Rivas S, Fraire-Soto I, Mercado-Casas Torres A, Servin-Gonzalez LS, Granados-Lopez AJ, Lopez-Hernandez Y, et al. 5p and 3p strands of miR-34 family members have differential effects in cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in cervical cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:545.
Zhang S, Cui Z. MicroRNA-34b-5p inhibits proliferation, stemness, migration and invasion of retinoblastoma cells via Notch signaling. Exp Ther Med. 2021;21:255.
Zhao J, Lin H, Huang K, Li S. Cancer-associated fibroblasts-derived extracellular vesicles carrying lncRNA SNHG3 facilitate colorectal cancer cell proliferation via the miR-34b-5p/HuR/HOXC6 axis. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8:346.
Tian J, Cui P, Li Y, Yao X, Wu X, Wang Z, et al. LINC02418 promotes colon cancer progression by suppressing apoptosis via interaction with miR-34b-5p/BCL2 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:460.
Feller SM. Crk family adaptors-signalling complex formation and biological roles. Oncogene. 2001;20:6348–71.
Birge RB, Kalodimos C, Inagaki F, Tanaka S. Crk and CrkL adaptor proteins: networks for physiological and pathological signaling. Cell Commun Signal. 2009;7:13.
Natsume H, Shinmura K, Tao H, Igarashi H, Suzuki M, Nagura K, et al. The CRKL gene encoding an adaptor protein is amplified, overexpressed, and a possible therapeutic target in gastric cancer. J Transl Med. 2012;10:97.
Fu L, Dong Q, Xie C, Wang Y, Li Q. CRKL protein overexpression enhances cell proliferation and invasion in pancreatic cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:1015–22.
Guo C, Gao C, Lv X, Zhao D, Greenaway FT, Hao L, et al. CRKL promotes hepatocarcinoma through enhancing glucose metabolism of cancer cells via activating PI3K/Akt. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25:2714–24.
Jiang Y, Liu G, Ye W, Xie J, Shao C, Wang X, et al. ZEB2-AS1 accelerates epithelial/mesenchymal transition through miR-1205/CRKL pathway in colorectal cancer. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020;35:153–62.
Funding
This research was supported by the Henan Medical Science and Technology Public Relations Project (SBGJ202102121).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J-HH conceptualized and designed the study and drafted the initial manuscript. H-NT and Y-HW collected the data and carried out the initial analyses. J-HH critically reviewed the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, JH., Tang, HN. & Wang, YH. Cancer-associated fibroblast exosome LINC00355 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer through the miR-34b-5p/CRKL axis. Cancer Gene Ther 31, 259–272 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-023-00700-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-023-00700-4
This article is cited by
-
MicroRNA-34b-5p increases chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Molecular & Cellular Toxicology (2024)