Abstract
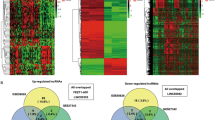
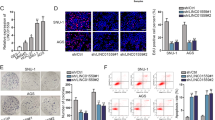
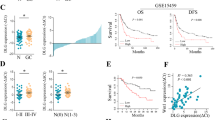
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) play a key role in human cancer development; nevertheless, the effect of lncRNA LINC00665 on the progression of gastric cancer (GC) still unclear. In this study, we found that LINC00665 expression is upregulated in GC than normal gastric mucosa tissues and higher LINC00665 expression is associated with a poor prognosis in GC patients. Downregulated LINC00665 inhibited GC cells proliferation, invasion, and migration in vitro. Pulmonary metastasis animal models showed that downregulated LINC00665 could reduce the lung metastasis of GC in vivo. Tumor organoids were generated from human malignant GC tissues, downregulated LINC00665 could inhibit the growth of the organoids of GC tissues. Mechanistically, downregulated LINC00665 could inhibit GC cells EMT. RNA pulldown, RIP, and RIP-seq studies found that LINC00665 can bind to the transcription factor YBX1 and form a positive feed-forward loop. The luciferase reporter and CHIP results showed that YBX1 could regulate the transcriptional activity of Wnt3a, and downregulation of LINC00665 could block the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. In conclusion, our results identified a feedback loop between LINC00665 and YBX1 that activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling, and it may be a potential therapeutic approach to suppress GC progression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files. The datasets are also available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49.
Kim H, Hwang Y, Sung H, Jang J, Ahn C, Kim SG, et al. Effectiveness of gastric cancer screening on gastric cancer incidence and mortality in a community-based prospective cohort. Cancer Res Treat. 2018;50:582–9.
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–32.
Zhang T, Chen H, Yin X, He Q, Man J, Yang X, et al. Changing trends of disease burden of gastric cancer in China from 1990 to 2019 and its predictions: Findings from Global Burden of Disease Study. Chin J Cancer Res. 2021;33:11–26.
Machlowska J, Baj J, Sitarz M, Maciejewski R, Sitarz R. Gastric cancer: epidemiology, risk factors, classification, genomic characteristics and treatment strategies. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:4012.
Cabianca DS, Casa V, Bodega B, Xynos A, Ginelli E, Tanaka Y, et al. A long ncRNA links copy number variation to a polycomb/trithorax epigenetic switch in FSHD muscular dystrophy. Cell. 2012;149:819–31.
Wu P, Mo Y, Peng M, Tang T, Zhong Y, Deng X, et al. Emerging role of tumor-related functional peptides encoded by lncRNA and circRNA. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:22.
Liang ZX, Liu HS, Wang FW, Xiong L, Zhou C, Hu T, et al. LncRNA RPPH1 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by interacting with TUBB3 and by promoting exosomes-mediated macrophage M2 polarization. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:829.
Wu H, Yang L, Chen LL. The diversity of long noncoding RNAs and their generation. Trends Genet. 2017;33:540–52.
Ding J, Zhao J, Huan L, Liu Y, Qiao Y, Wang Z, et al. Inflammation-induced LINC00665 increases the malignancy through activating PKR/NF-kappaB pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2020;72:1666–81.
Liang Y, Song X, Li Y, Chen B, Zhao W, Wang L, et al. LncRNA BCRT1 promotes breast cancer progression by targeting miR-1303/PTBP3 axis. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:85.
Chang KC, Diermeier SD, Yu AT, Brine LD, Russo S, Bhatia S, et al. MaTAR25 lncRNA regulates the Tensin1 gene to impact breast cancer progression. Nat Commun. 2020;11:6438.
Huang C, Leng D, Lei KC, Sun S, Zhang XD. Transcriptome analysis reveals lncRNA-mediated complex regulatory network response to DNA damage in the liver tissue of Rattus norvegicus. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:23216–31.
Ransohoff JD, Wei Y, Khavari PA. The functions and unique features of long intergenic non-coding RNA. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19:143–57.
Zhang E, He X, Zhang C, Su J, Lu X, Si X, et al. A novel long noncoding RNA HOXC-AS3 mediates tumorigenesis of gastric cancer by binding to YBX1. Genome Biol. 2018;19:154.
Zhuo W, Liu Y, Li S, Guo D, Sun Q, Jin J, et al. Long noncoding RNA GMAN, up-regulated in gastric cancer tissues, is associated with metastasis in patients and promotes translation of ephrin A1 by competitively binding GMAN-AS. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:676–691.e11.
Chen Y, Li Z, Chen X, Zhang S. Long non-coding RNAs: from disease code to drug role. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11:340–54.
Li H, Ma X, Yang D, Suo Z, Dai R, Liu C. PCAT-1 contributes to cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer through epigenetically silencing PTEN via recruiting EZH2. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121:1353–61.
Ji W, Diao Y-L, Qiu Y-R, Ge J, Cao X-C, Yu Y. LINC00665 promotes breast cancer progression through regulation of the miR-379-5p/LIN28B axis. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:16.
Cong Z, Diao Y, Xu Y, Li X, Jiang Z, Shao C, et al. Long non-coding RNA linc00665 promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression and functions as ceRNA to regulate AKR1B10-ERK signaling by sponging miR-98. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:84.
Guo B, Wu S, Zhu X, Zhang L, Deng J, Li F, et al. Micropeptide CIP2A-BP encoded by LINC00665 inhibits triple-negative breast cancer progression. EMBO J. 2020;39:e102190.
Qi H, Xiao Z, Wang Y. Long non-coding RNA LINC00665 gastric cancer tumorigenesis by regulation miR-149-3p/RNF2 axis. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:6981–90.
Conlon T, John-Schuster G, Heide D, Pfister D, Lehmann M, Hu Y, et al. Inhibition of LTβR signalling activates WNT-induced regeneration in lung. Nature. 2020;588:151–6.
Zhang Y, Wang X. Targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13:165.
Abitbol S, Dahmani R, Coulouarn C, Ragazzon B, Mlecnik B, Senni N, et al. AXIN deficiency in human and mouse hepatocytes induces hepatocellular carcinoma in the absence of β-catenin activation. J Hepatol. 2018;68:1203–13.
Yu S, Li L, Cai H, He B, Gao Y, Li Y. Overexpression of NELFE contributes to gastric cancer progression via Wnt/β-catenin signaling-mediated activation of CSNK2B expression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021;40:1–16.
Wang Z, Li Z, Ji H. Direct targeting of β-catenin in the Wnt signaling pathway: current progress and perspectives. Med Res Rev. 2021;41:2109–29.
Zhai W, Sun Y, Guo C, Hu G, Wang M, Zheng J, et al. LncRNA-SARCC suppresses renal cell carcinoma (RCC) progression via altering the androgen receptor(AR)/miRNA-143-3p signals. Cell Death Differentiation. 2017;24:1502–17.
Wang J, Chen C, Wang S, Zhang Y, Yin P, Gao Z, et al. Bufalin inhibits HCT116 colon cancer cells and its orthotopic xenograft tumor in mice model through genes related to apoptotic and PTEN/AKT pathways. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2015;2015:1–11.
Wang J, Cai H, Xia Y, Wang S, Xing L, Chen C, et al. Bufalin inhibits gastric cancer invasion and metastasis by down-regulating Wnt/ASCL2 expression. Oncotarget. 2018;9:23320–33.
Li W, Wong CC, Zhang X, Kang W, Nakatsu G, Zhao Q, et al. CAB39L elicited an anti-Warburg effect via a LKB1-AMPK-PGC1alpha axis to inhibit gastric tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2018;37:6383–98.
Simion V, Zhou H, Haemmig S, Pierce JB, Mendes S, Tesmenitsky Y, et al. A macrophage-specific lncRNA regulates apoptosis and atherosclerosis by tethering HuR in the nucleus. Nat Commun. 2020;11:6135.
Wang X, Li L, Zhao K, Lin Q, Li H, Xue X, et al. A novel LncRNA HITT forms a regulatory loop with HIF-1alpha to modulate angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell Death Differ. 2020;27:1431–46.
Seidlitz T, Merker SR, Rothe A, Zakrzewski F, von Neubeck C, Grützmann K, et al. Human gastric cancer modelling using organoids. Gut. 2019;68:207–17.
Wang CY, Colognori D, Sunwoo H, Wang D, Lee JT. PRC1 collaborates with SMCHD1 to fold the X-chromosome and spread Xist RNA between chromosome compartments. Nat Commun. 2019;10:2950.
Yuan L, Xu ZY, Ruan SM, Mo S, Qin JJ, Cheng XD. Long non-coding RNAs towards precision medicine in gastric cancer: early diagnosis, treatment, and drug resistance. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:96.
Xu J, Ji L, Liang Y, Wan Z, Zheng W, Song X, et al. CircRNA-SORE mediates sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by stabilizing YBX1. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5:298.
Feng M, Xie X, Han G, Zhang T, Li Y, Li Y, et al. YBX1 is required for maintaining myeloid leukemia cell survival by regulating BCL2 stability in an m6A-dependent manner. Blood. 2021;138:71–85.
Lin Y, Zhang J, Li Y, Guo W, Chen L, Chen M, et al. CTPS1 promotes malignant progression of triple-negative breast cancer with transcriptional activation by YBX1. J Transl Med. 2022;20:17.
Shi C, Yang Y, Yu J, Meng F, Zhang T, Gao Y. The long noncoding RNA LINC00473, a target of microRNA 34a, promotes tumorigenesis by inhibiting ILF2 degradation in cervical cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2017;7:2157–68.
Zhang X, Wu J. LINC00665 promotes cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis by activating the TGF-beta pathway in gastric cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 2021;224:153492.
Yang B, Bai Q, Chen H, Su K, Gao C. LINC00665 induces gastric cancer progression through activating Wnt signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121:2268–76.
Conlon GA, Murray GI. Recent advances in understanding the roles of matrix metalloproteinases in tumour invasion and metastasis. J Pathol. 2019;247:629–40.
Mittal V. Epithelial mesenchymal transition in tumor metastasis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2018;13:395–412.
Zhan T, Rindtorff N, Boutros M. Wnt signaling in cancer. Oncogene. 2017;36:1461–73.
Ma Y, Yang Y, Wang F, Moyer M, Wei Q, Zhang P, et al. Long non-coding RNA CCAL regulates colorectal cancer progression by activating Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway via suppression of activator protein 2α. Gut. 2016;65:1494–504.
Wang H, Wu M, Lu Y, He K, Cai X, Yu X, et al. LncRNA MIR4435-2HG targets desmoplakin and promotes growth and metastasis of gastric cancer by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Aging. 2019;11:6657–73.
MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell. 2009;17:9–26.
Mo D, Fang H, Niu K, Liu J, Wu M, Li S, et al. Human helicase RECQL4 drives cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer by activating an AKT-YB1-MDR1 signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 2016;76:3057–66.
Wu Y, Yamada S, Izumi H, Li Z, Shimajiri S, Wang KY, et al. Strong YB-1 expression is associated with liver metastasis progression and predicts shorter disease-free survival in advanced gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2012;105:724–30.
Byrne AT, Alferez DG, Amant F, Annibali D, Arribas J, Biankin AV, et al. Interrogating open issues in cancer precision medicine with patient-derived xenografts. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17:254–68.
Steele NG, Chakrabarti J, Wang J, Biesiada J, Holokai L, Chang J, et al. An organoid-based preclinical model of human gastric cancer. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;7:161–84.
Sato T, Stange DE, Ferrante M, Vries RG, Van Es JH, Van den Brink S, et al. Long-term expansion of epithelial organoids from human colon, adenoma, adenocarcinoma, and Barrett’s epithelium. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:1762–72.
Dekkers JF, van Vliet EJ, Sachs N, Rosenbluth JM, Kopper O, Rebel HG, et al. Long-term culture, genetic manipulation and xenotransplantation of human normal and breast cancer organoids. Nat Protoc. 2021;16:1936–65.
Bleijs M, van de Wetering M, Clevers H, Drost J. Xenograft and organoid model systems in cancer research. EMBO J. 2019;38:e101654.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the GEO and TCGA databases, Kaplan–Meier Plotter database for providing their platforms and contributors for uploading their meaningful datasets.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (81973625), the foundation of National Key Research and Development Program of China (2019YFC1316000), the foundation of Shanghai key medical specialty construction project (ZK2019B18), the foundation of within the budget of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2019LK037), and the foundation of clinical specialized disease Construction Project of Shanghai Putuo District Municipal Health Comission (2019tszb01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TC and CC conceived or designed the experiments; JW, DXS, and CSL performed the experiments and write the manuscript; QYL performed part of the animal experiments; JHL, DHT, and YJF performed part of the cell and molecular and biology experiments; QSZ and PHY performed part of the clinical patients collect and data analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Human samples used in this study was obtained with informed consent and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Putuo Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (PTEC-A-2020-5(S)-1). All the animal studies were performed strictly in accordance with the Animal Care Guidelines approved by the Animal Care Committee of East China Normal University.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Shen, D., Li, S. et al. LINC00665 activating Wnt3a/β-catenin signaling by bond with YBX1 promotes gastric cancer proliferation and metastasis. Cancer Gene Ther 30, 1530–1542 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-023-00657-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-023-00657-4