Abstract
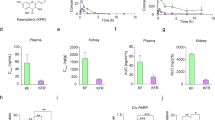
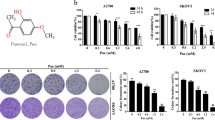
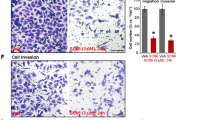
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) has been reported to kill a wide variety of tumor cells with minimal effects on normal cell. However, renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cells 786-0 and OS-RC-2 were resistant to TRAIL. The present study examines the potential of combining polyphenolic compound resveratrol (RES) with TRAIL. We found that RES can sensitize RCC cells to TRAIL-induced death. Electron microscopy analyses showed that RES plus TRAIL can induce both autophagy and apoptosis in RCC cells. It was proved that the apoptosis is caspase-dependent and the activation of caspase-8, caspase-9, and caspase-3 was involved in this process. Besides, we also found that XIAP expression was significantly inhibited after RES plus TRAIL treatment in RCC cells. Furthermore, a fiber-modified replication-deficient adenovirus Ad5/35-TRAIL was generated to test the synergistic effect of RES and TRAIL in vivo. Our data demonstrated that RES plus Ad5/35-TRAIL significantly inhibited RCC xenograft growth in nude mice. These results suggest the possibility of a new combination therapeutic leading to the improvement of RCC treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK, et al. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 1995;3:673–82.
Bouralexis S, Findlay DM, Evdokiou A. Death to the bad guys: targeting cancer via Apo2L/TRAIL. Apoptosis. 2005;10:35–51.
Gillissen B, Richter A, Richter A, Preissner R, Schulze-Osthoff K, Essmann F, et al. Bax/Bak-independent mitochondrial depolarization and reactive oxygen species induction by sorafenib overcome resistance to apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma. J Biol Chem. 2017;292:6478–92.
Ou YC, Li JR, Kuan YH, Raung SL, Wang CC, Hung YY, et al. Luteolin sensitizes human 786-O renal cell carcinoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Life Sci. 2014;100:110–7.
Brooks AD, Jacobsen KM, Li W, Shanker A, Sayers TJ. Bortezomib sensitizes human renal cell carcinomas to TRAIL apoptosis through increased activation of caspase-8 in the death-inducing signaling complex. Mol Cancer Res. 2010;8:729–38.
VanOosten RL, Earel JK Jr, Griffith TS. Enhancement of Ad5-TRAIL cytotoxicity against renal cell carcinoma with histone deacetylase inhibitors. Cancer Gene Ther. 2006;13:628–32.
Jiang Z, Chen K, Cheng L, Yan B, Qian W, Cao J, et al. Resveratrol and cancer treatment: updates. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017;1403:59–69.
Tameda M, Sugimoto K, Shiraki K, Inagaki Y, Ogura S, Kasai C, et al. Resveratrol sensitizes HepG2 cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Anticancer Drugs. 2014;25:1028–34.
Haviv YS, Blackwell JL, Kanerva A, Nagi P, Krasnykh V, Dmitriev I, et al. Adenoviral gene therapy for renal cancer requires retargeting to alternative cellular receptors. Cancer Res. 2002;62:4273–81.
Coyne CB, Bergelson JM. CAR: a virus receptor within the tight junction. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005;57:869–82.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of the People’s Republic of China (grant nos. 81760287, 31700763), Longyuan Youth Fund for Innovation and Entrepreneurship, Major Cultivation Projects in Central Colleges and Universities (31920190045) and Cultivation Project of Innovation Team in Central Colleges and Universities (31920190027) of Northwest Minzu University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Y., Li, Fd., Shi, Cw. et al. Mechanism and therapeutic prospect of resveratrol combined with TRAIL in the treatment of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther 27, 619–623 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-019-0150-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-019-0150-6