Abstract
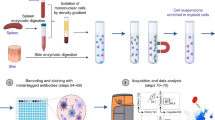
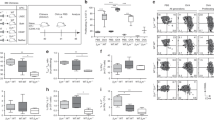
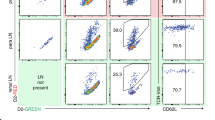
Dendritic cells (DCs) are crucial in immune induction. Not only do they collect antigens in peripheral tissues, and transport and process them for presentation to lymphocytes in draining lymph nodes, but they also regulate the immune response by modulating T-cell differentiation. Intestinal and hepatic DCs migrating in lymph can be collected from rats under near-physiological conditions. Initially, the mesenteric or celiac lymph nodes are removed from young rats (30 min). The afferent and efferent lymph vessels subsequently heal, permitting DCs to enter the thoracic duct. After at least 6 wk, the duct is cannulated (40 min). Lymph can be collected for up to 48 h. DCs can subsequently be identified, enriched and sorted to high degrees of purity. This two-stage technique generates large numbers of immunologically relevant DCs under near-physiological conditions. Lymph collection requires 2–3 h per animal over 6 wk.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banchereau, J. & Steinman, R.M. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature 392, 245–252 (1998).
Banchereau, J. et al. Immunobiology of dendritic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18, 767–811 (2000).
Turnbull, E. & MacPherson, G. Immunobiology of dendritic cells in the rat. Immunol. Rev. 184, 58–68 (2001).
MacPherson, G., Kushnir, N. & Wykes, M. Dendritic cells, B cells and the regulation of antibody synthesis. Immunol. Rev. 172, 325–334 (1999).
Merad, M. et al. Langerhans cells renew in the skin throughout life under steady-state conditions. Nat. Immunol. 3, 1135–1141 (2002).
Randolph, G.J., Inaba, K., Robbiani, D.F., Steinman, R.M. & Muller, W.A. Differentiation of phagocytic monocytes into lymph node dendritic cells in vivo. Immunity 11, 753–761 (1999).
Randolph, G.J., Sanchez Schmitz, G., Liebman, R.M. & Schakel, K. The CD16(+) (FcgammaRIII(+)) subset of human monocytes preferentially becomes migratory dendritic cells in a model tissue setting. J. Exp. Med. 196, 517–527 (2002).
Yrlid, U., Jenkins, C.D. & MacPherson, G.G. Relationships between distinct blood monocyte subsets and migrating intestinal lymph dendritic cells in vivo under steady-state conditions. J. Immunol. 176, 4155–4162 (2006).
Yoffey, J.M. & Courtice, C. Lymphatics, Lymph and the Lymphomyeloid Complex, 548 (Academic Press, London, New York, 1970).
Pugh, C.W., MacPherson, G.G. & Steer, H.W. Characterization of nonlymphoid cells derived from rat peripheral lymph. J. Exp. Med. 157, 1758–1779 (1983).
Smith, I.B., McIntosh, G.H. & Morris, B. The traffic of cells through tissues: a study of peripheral lymph in sheep. J. Anat. 107, 87–100 (1970).
Bollman, J.L., Cain, J.C. & Grindley, J.H. Techniques for the collection of lymph from the liver, small intestine or thoracic duct of the rat. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 33, 1349 (1948).
Gowans, J.L. The recirculation of lymphocytes from blood to lymph in the rat. J. Physiol. 146, 54 (1959).
Sanders, A.G. & Florey, H.W. The effects of the removal of lymphoid tissue. Brit. J. Exp. Pathol. 21, 275 (1940).
MacPherson, G.G. Properties of lymph-borne (veiled) dendritic cells in culture. I. Modulation of phenotype, survival and function: partial dependence on GM-CSF. Immunology 68, 102–107 (1989).
Liu, L.M. & MacPherson, G.G. Antigen acquisition by dendritic cells: intestinal dendritic cells acquire antigen administered orally and can prime naive T cells in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 177, 1299–1307 (1993).
Liu, L.M. & MacPherson, G.G. Antigen processing: cultured lymph-borne dendritic cells can process and present native protein antigens. Immunology 84, 241–246 (1995).
Liu, L.M., Zhang, M., Jenkins, C. & MacPherson, G.G. Dendritic cell heterogeneity in vivo: two functionally different dendritic cell populations in rat intestinal lymph can be distinguished by CD4 expression. J. Immunol. 161, 1146–1155 (1998).
Huang, F.P. et al. A discrete subpopulation of dendritic cells transports apoptotic intestinal epithelial cells to T cell areas of mesenteric lymph nodes. J. Exp. Med. 191, 435–444 (2000).
Wykes, M. & MacPherson, G. Dendritic cell-B-cell interaction: dendritic cells provide B cells with CD40-independent proliferation signals and CD40-dependent survival signals. Immunology 100, 1–3 (2000).
Huang, F.P., Farquhar, C.F., Mabbott, N.A., Bruce, M.E. & MacPherson, G.G. Migrating intestinal dendritic cells transport PrP(Sc) from the gut. J. Gen. Virol. 83, 267–71 (2002).
Turnbull, E.L., Yrlid, U., Jenkins, C.D. & Macpherson, G.G. Intestinal dendritic cell subsets: differential effects of systemic TLR4 stimulation on migratory fate and activation in vivo. J. Immunol. 174, 1374–1384 (2005).
Yrlid, U. et al. Regulation of intestinal dendritic cell migration and activation by plasmacytoid dendritic cells, TNF-alpha and type 1 IFNs after feeding a TLR7/8 ligand. J. Immunol. 176, 5205–5212 (2006).
Matsuno, K., Kudo, S., Ezaki, T. & Miyakawa, K. Isolation of dendritic cells in the rat liver lymph. Transplantation 60, 765–768 (1995).
Matsuno, K., Ezaki, T., Kudo, S. & Uehara, Y. A life stage of particle-laden rat dendritic cells in vivo: their terminal division, active phagocytosis, and translocation from the liver to the draining lymph. J. Exp. Med. 183, 1865–1878 (1996).
Kudo, S., Matsuno, K., Ezaki, T. & Ogawa, M. A novel migration pathway for rat dendritic cells from the blood: hepatic sinusoids-lymph translocation. J. Exp. Med. 185, 777–784 (1997).
Matsuno, K. & Ezaki, T. Dendritic cell dynamics in the liver and hepatic lymph. Int. Rev. Cytol. 197, 83–136 (2000).
Matsuno, K., Nomiyama, H., Yoneyama, H. & Uwatoku, R. Kupffer cell-mediated recruitment of dendritic cells to the liver crucial for a host defense. Dev. Immunol. 9, 143–149 (2002).
Hopkins, J. & Hall, J.G. Selective entry of immunoblasts into gut from intestinal lymph. Nature 259, 308 (1976).
Bujdoso, R., Hopkins, J., Dutia, B.M., Young, P. & McConnell, I. Characterisation of sheep afferent lymph dendritic cells and their role in antigen carriage. J. Exp. Med. 170, 1285–1302 (1989).
Bujdoso, R., Hopkins, J., Dutia, B.M., Young, P. & McConnell, I. Characterization of sheep afferent lymph dendritic cells and their role in antigen carriage. J. Exp. Med. 170, 1285–1301 (1989).
Hopkins, J., Dutia, B.M., Bujdoso, R. & McConnell, I. In vivo modulation of CD1 and MHC class II expression by sheep afferent lymph dendritic cells. Comparison of primary and secondary immune responses. J. Exp. Med. 170, 1303–1318 (1989).
Bujdoso, R., Harkiss, G., Hopkins, J. & McConnell, I. Afferent lymph dendritic cells: a model for antigen capture and presentation in vivo. Int. Rev. Immunol. 6, 177–186 (1990).
Harkiss, G., Hopkins, J. & McConnell, I. Uptake of antigen by afferent lymph dendritic cells mediated by antibody. Eur. J. Immunol. 20, 2367–2373 (1990).
Hope, J.C. et al. Identification of dendritic cells as a major source of interleukin-6 in draining lymph nodes following skin sensitization of mice. Immunology 86, 441–447 (1995).
Coughlan, S.N., Harkiss, G.D., Dickson, L. & Hopkins, J. Fc gamma receptor expression on sheep afferent lymph dendritic cells and rapid modulation of cell surface phenotype following Fc gamma receptor engagement in vitro and in vivo. Scand. J. Immunol. 43, 31–38 (1996).
Haig, D.M., Hopkins, J. & Miller, H.R. Local immune responses in afferent and efferent lymph. Immunology 96, 155–163 (1999).
Howard, C.J. et al. Dendritic cells in cattle: phenotype and function. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 72, 119–124 (1999).
Hope, J.C., Sopp, P., Collins, R.A. & Howard, C.J. Differences in the induction of CD8+ T cell responses by subpopulations of dendritic cells from afferent lymph are related to IL-1 alpha secretion. J. Leukoc. Biol. 69, 271–279 (2001).
Howard, C.J. & Hope, J.C. Dendritic cells, implications on function from studies of the afferent lymph veiled cell. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 77, 1–13 (2000).
Stephens, S.A., Brownlie, J., Charleston, B. & Howard, C.J. Differences in cytokine synthesis by the sub-populations of dendritic cells from afferent lymph. Immunology 110, 48–57 (2003).
Gliddon, D.R., Hope, J.C., Brooke, G.P. & Howard, C.J. DEC-205 expression on migrating dendritic cells in afferent lymph. Immunology 111, 262–272 (2004).
Paulin, S.M. et al. Analysis of Salmonella enterica serotype-host specificity in calves: avirulence of S. enterica serotype gallinarum correlates with bacterial dissemination from mesenteric lymph nodes and persistence in vivo. Infect. Immun. 70, 6788–6797 (2002).
Barratt-Boyes, S.M., Rossitto, P.V., Taylor, B.C., Ellis, J.A. & MacLachlan, N.J. Response of the regional lymph node to bluetongue virus infection in calves. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 45, 73–84 (1995).
Hope, J.C., Howard, C.J., Prentice, H. & Charleston, B. Isolation and purification of afferent lymph dendritic cells that drain the skin of cattle. Nat. Protocols 1, 982–987 (2006).
Moslen, M.T., Kanz, M.F., Bhatia, J. & Catarau, E.M. Two cannula method for parenteral infusion and serial blood sampling in the freely moving rat. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 12, 633–637 (1988).
Hauss, D., Fogal, S. & Ficorilli, J. Chronic collection of mesenteric lymph from conscious, tethered rats. Contemp. Top. Lab. Anim. Sci. 37, 56–58 (1998).
Mandel, M.A. Isolation of mouse lymphocytes for immunologic studies by thoracic duct cannulation. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 126, 521–524 (1967).
Lewis, H., Mitchell, J. & Nossal, G.J. Subpopulations of rat and mouse thoracic duct small lymphocytes in the Salmonella flagellar antigen system. Immunology 17, 955–967 (1969).
Miller, J.F. & Sprent, J. Thymus-derived cells in mouse thoracic duct lymph. Nat. New Biol. 230, 267–270 (1971).
Bankhurst, A.D. & Warner, N.L. Surface immunoglobulins on the thoracic duct lymphocytes of the congenitally athymic (nude) mouse. Aust. J. Exp. Biol. Med. Sci. 50, 661–664 (1972).
Deaton, J.G. Thoracic duct lymph drainage in the mouse: a technique for producing lymphocyte-depleted animals. Lymphology 5, 115–120 (1972).
Sprent, J. & Basten, A. Circulating T and B lymphocytes of the mouse. II. Lifespan. Cell. Immunol. 7, 40–59 (1973).
Sprent, J. Circulating T and B lymphocytes of the mouse. I. Migratory properties. Cell Immunol. 7, 10–39 (1973).
Kearney, J.F. & Reade, P.C. The kinetics of mouse thoracic duct lymphocyte activation by mitogens in vitro. Aust. J. Exp. Biol. Med. Sci. 52, 21–31 (1974).
Ropke, C., Hougen, H.P. & Everett, N.B. Long-lived T and B lymphocytes in the bone marrow and thoracic duct lymph of the mouse. Cell Immunol. 15, 82–93 (1975).
Bainbridge, D.R. The mouse circus: a simple apparatus for thoracic duct cannulation and continuous intravenous infusion. J. Immunol. Methods 17, 63–72 (1977).
Freitas, A.A. & Coutinho, A.A. Characterization of mouse thoracic duct B lymphocytes. I. Evidence of functional heterogeneity. Eur. J. Immunol. 10, 772–776 (1980).
Freitas, A.A., Rose, M. & Rocha, B. Random recirculation of small T lymphocytes from thoracic duct lymph in the mouse. Cell Immunol. 56, 29–39 (1980).
Korngold, R. & Bennink, J.R. Collection of mouse thoracic duct lymphocytes. Methods Enzymol. 108, 270–274 (1984).
Ionac, M., Laskay, T., Labahn, D., Geisslinger, G. & Solbach, W. Improved technique for cannulation of the murine thoracic duct: a valuable tool for the dissection of immune responses. J. Immunol. Methods 202, 35–40 (1997).
Rhodes, J.M. Isolation of large mononuclear Ia-positive veiled cells from the mouse thoracic duct. J. Immunol. Methods 85, 383–392 (1985).
Rhodes, J.M. & Agger, R. Comparison of membrane antigens of mouse dendritic cell types. Immunol. Lett. 16, 107–112 (1987).
Rhodes, J.M., Balfour, B.M., Blom, J. & Agger, R. Comparison of antigen uptake by peritoneal macrophages and veiled cells from the thoracic duct using isotope-, FITC-, or gold-labelled antigen. Immunology 68, 403–409 (1989).
Tilney, N.L. Patterns of lymphatic drainage in the adult laboratory rat. J. Anat. 109, 3 (1971).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the staff of the animal facility for care of the animals. We gratefully acknowledge A. Milling and M. Nassar for critical reading of the manuscript. The work was funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, UK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milling, S., Jenkins, C. & MacPherson, G. Collection of lymph-borne dendritic cells in the rat. Nat Protoc 1, 2263–2270 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.315
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.315
This article is cited by
-
Lymphatic Distribution of Etanercept Following Intravenous and Subcutaneous Delivery to Rats
Pharmaceutical Research (2020)
-
Interleukin-22 binding protein (IL-22BP) is constitutively expressed by a subset of conventional dendritic cells and is strongly induced by retinoic acid
Mucosal Immunology (2014)
-
Intestinal CD103− dendritic cells migrate in lymph and prime effector T cells
Mucosal Immunology (2013)
-
CD8+ T lymphocytes protective against malaria liver stages are primed in skin-draining lymph nodes
Nature Medicine (2007)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.