Abstract
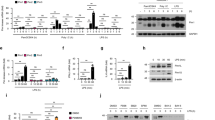
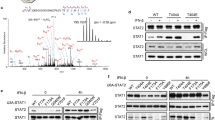
Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1)-associated death domain protein (TRADD) is essential in recruiting signaling molecules to the TNFR1 receptor complex. Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) is a potent activator of macrophages and uses signal transducer and activator of transcription 1-α (STAT1-α) for signal transduction. Here we demonstrate that IFN-γ induces the formation of a nuclear-localized TRADD–STAT1-α complex. IFN-γ-mediated STAT1-α phosphorylation was prolonged in cells with reduced TRADD expression. Moreover, we noted an increase in IFN-γ-mediated STAT1-α DNA-binding activity, nuclear presence and transcriptional potential in the TRADD knockdown cells. These data indicate that TRADD may be involved in IFN-γ signaling by forming a complex with STAT1-α within the nucleus and regulating IFN-γ-mediated STAT1-α activation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Locksley, R.M., Killeen, N. & Lenardo, M.J. The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: integrating mammalian biology. Cell 104, 487–501 (2001).
Boehm, U., Klamp, T., Groot, M. & Howard, J.D. Cellular responses to interferon-γ. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 15, 749–795 (1997).
Stark, G.R., Kerr, I.M., Williams, B.R., Silverman, R.H. & Schreiber, R.D. How cells respond to interferons. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67, 227–264 (1998).
Kisseleva, T., Bhattacharya, S., Braunstein, J. & Schindler, C.W. Signaling through the JAK/STAT pathway, recent advances and future challenges. Gene 285, 1–24 (2002).
Decker, T. & Kovarik, P. Serine phosphorylation of STATs. Oncogene 19, 2628–2637 (2000).
Wang, Y., Wu, T.R., Cai, S., Welte, T. & Chin, Y.E. Stat1 as a component of tumor necrosis factor α receptor 1-TRADD signaling complex to inhibit NF-κB activation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 4505–4512 (2000).
Nguyen, V.T. & Benveniste, E.N. Critical role of TNF-α and NF-κB in IFN-γ-induced CD40 expression in microglia/macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 13796–13803 (2002).
Wesemann, D., Dong, Y., O'Keefe, G.M., Nguyen, V.T. & Benveniste, E.N. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 inhibits cytokine induction of CD40 expression in macrophages. J. Immunol. 169, 2354–2360 (2002).
Ramana, C.V. et al. Stat1-independent regulation of gene expression in response to IFN-γ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 6674–6679 (2001).
Ramana, C.V., Gil, M.P., Schreiber, R.D. & Stark, G.R. Stat1-dependent and -independent pathways in IFN-γ-dependent signaling. Trends Immunol. 23, 96–101 (2002).
Yasukawa, H. et al. The JAK-binding protein JAB inhibits Janus tyrosine kinase activity through binding in the activation loop. EMBO J. 18, 1309–1320 (1999).
Park, Y.C. et al. A novel mechanism of TRAF signaling revealed by structural and functional analyses of the TRADD-TRAF2 interaction. Cell 101, 777–787 (2000).
Meyer, T., Marg, A., Lemke, P., Wiesner, B. & Vinkemeier, U. DNA binding controls inactivation and nuclear accumulation of the transcription factor Stat1. Genes Dev. 17, 1992–2005 (2003).
Morgan, M., Thorburn, J., Pandolfi, P.P. & Thorburn, A. Nuclear and cytoplasmic shuttling of TRADD induces apoptosis via different mechanisms. J. Cell Biol. 157, 975–984 (2002).
Screaton, R.A. et al. Fas-associated death domain protein interacts with methyl-CpG binding domain protein 4: a potential link between genome surveillance and apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 5211–5216 (2003).
Anest, V. et al. A nucleosomal function for IκB kinase-α in NF-κB-dependent gene expression. Nature 423, 659–663 (2003).
Yamamoto, Y., Verma, U.N., Prajapati, S., Kwak, Y.-T. & Gaynor, R.B. Histone H3 phosphorylation by IKK-α is critical for cytokine-induced gene expression. Nature 423, 655–659 (2003).
ten Hoeve, J. et al. Identification of a nuclear Stat1 protein tyrosine phosphatase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 5662–5668 (2002).
Wu, T.R. et al. SHP-2 is a dual-specificity phosphatase involved in Stat1 dephosphorylation at both tyrosine and serine residues in nuclei. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 47572–47580 (2002).
Zhu, W., Mustelin, T. & David, M. Arginine methylation of STAT1 regulates its dephosphorylation by T cell protein tyrosine phosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 35787–35790 (2002).
Micheau, O. & Tschopp, J. Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell 114, 181–190 (2003).
Inada, H. et al. Keratin attenuates tumor necrosis factor-induced cytotoxicity through association with TRADD. J. Cell Biol. 155, 415–426 (2001).
Paludan, S.R. Synergistic action of pro-inflammatory agents: cellular and molecular aspects. J. Leukoc. Biol. 67, 18–25 (2000).
Nguyen, V.T. & Benveniste, E.N. Involvement of STAT-1α and ets family members in interferon-γ induction of CD40 transcription in macrophages/microglia. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 23674–23684 (2000).
O'Keefe, G.M., Nguyen, V.T., Tang, L.P. & Benveniste, E.N. IFN-γ regulation of class II transactivator promoter IV in macrophages and microglia: involvement of the suppressors of cytokine signaling-1 protein. J. Immunol. 166, 2260–2269 (2001).
O'Keefe, G.M., Nguyen, V.T. & Benveniste, E.N. Class II transactivator and class II MHC gene expression in microglia: modulation by the cytokines TGF-β, IL-4, IL-13, and IL-10. Eur. J. Immunol. 29, 1275–1285 (1999).
Elbashir, S.M., Harborth, J., Weber, K. & Tuschl, T. Analysis of gene function in somatic mammalian cells using small interfering RNAs. Methods 26, 199–213 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank Z.D. Ma and R. Shah for assistance with the ChIP assay; C. Wilson for assistance with RPA analysis; and S. Frank for comments on the manuscript. The TRADD expression construct was a gift from H. Wu. Supported in part by National Institutes of Health grants NS-36765 and NS-39954 (E.N.B.), and the Medical Scientist Training Program at The University of Alabama at Birmingham and National Institutes of Health Predoctoral Fellowships T32 AI-07051-26 and F30 NS-47051 (D.R.W.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wesemann, D., Qin, H., Kokorina, N. et al. TRADD interacts with STAT1-α and influences interferon-γ signaling. Nat Immunol 5, 199–207 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1025
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1025
This article is cited by
-
TNF-α synergises with IFN-γ to induce caspase-8-JAK1/2-STAT1-dependent death of intestinal epithelial cells
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
cFLIP is critical for oligodendrocyte protection from inflammation
Cell Death & Differentiation (2015)
-
TRADD contributes to tumour suppression by regulating ULF-dependent p19Arf ubiquitylation
Nature Cell Biology (2012)
-
Non‐apoptotic functions of apoptosis‐regulatory proteins
EMBO reports (2012)
-
Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 inhibits caspase activation and protects from cytokine-induced beta cell death
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2009)