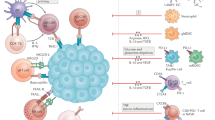
Abstract
We have recently witnessed substantial progress with immunotherapy for selected diseases. Checkpoint inhibitors and chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cells are among the most promising agents. Whereas much of the early success with CAR-T cells has been demonstrated with hematological malignancies, important barriers remain for the application of CAR-T cell therapies for the management of metastatic solid tumors. The challenges are particularly apparent when considering primary and metastatic tumors in the liver. At baseline, the intrahepatic space is immunosuppressive and this feature is exploited by malignant cells. Fortunately, our evolving understanding of liver immune cell biology is allowing the development of novel immunotherapeutic strategies for the treatment of liver tumors. Furthermore, the unique anatomic features of the liver make possible highly selective immunotherapeutic delivery approaches that may maximize antitumor efficacy while limiting off-target damage to healthy tissues. This review summarizes the immunobiology of the intrahepatic space and how this knowledge enables identification of hurdles and potential solutions to the barriers facing immunotherapy for liver tumors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knolle PA, Gerken G . Local control of the immune response in the liver. Immunol Rev 2000; 174: 21–34.
Bamboat ZM, Stableford JA, Plitas G, Burt BM, Nguyen HM, Welles AP et al. Human liver dendritic cells promote T cell hyporesponsiveness. J Immunol 2009; 182: 1901–1911.
Jewell AP . Is the liver an important site for the development of immune tolerance to tumours? Med Hypotheses 2005; 64: 751–754.
Katz SC, Pillarisetty VG, Bleier JI, Shah AB, DeMatteo RP . Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells are insufficient to activate T cells. J Immunol 2004; 173: 230–235.
Katz SC, Pillarisetty VG, Bleier JI, Kingham TP, Chaudhry UI, Shah AB et al. Conventional liver CD4 T cells are functionally distinct and suppressed by environmental factors. Hepatology 2005; 42: 293–300.
Thorn M, Point GR, Burga RA, Nguyen CT, Joseph Espat N, Katz SC . Liver metastases induce reversible hepatic B cell dysfunction mediated by Gr-1+CD11b+ myeloid cells. J Leukoc Biol 2014; 96: 883–894.
Rosenberg SA, Spiess P, Lafreniere R . A new approach to the adoptive immunotherapy of cancer with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Science 1986; 233: 1318–1321.
Katz SC, Bamboat ZM, Maker AV, Shia J, Pillarisetty VG, Yopp AC et al. Regulatory T cell infiltration predicts outcome following resection of colorectal cancer liver metastases. Ann Surg Oncol 2013; 20: 946–955.
Khan H, Pillarisetty VG, Katz SC . The prognostic value of liver tumor T cell infiltrates. J Surg Res 2014; 191: 189–195.
Mathai AM, Kapadia MJ, Alexander J, Kernochan LE, Swanson PE, Yeh MM . Role of Foxp3-positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in the histologic features and clinical outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 2012; 36: 980–986.
Li YW, Qiu SJ, Fan J, Gao Q, Zhou J, Xiao YS et al. Tumor-infiltrating macrophages can predict favorable prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2009; 135: 439–449.
Huang Y, Wang F, Wang Y, Zhu Z, Gao Y, Ma Z et al. Intrahepatic interleukin-17+ T cells and FoxP3+ regulatory T cells cooperate to promote development and affect the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014; 29: 851–859.
Huang Y, Wang FM, Wang T, Wang YJ, Zhu ZY, Gao YT et al. Tumor-infiltrating FoxP3+ Tregs and CD8+ T cells affect the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Digestion 2012; 86: 329–337.
Takagi S, Miyagawa S, Ichikawa E, Soeda J, Miwa S, Miyagawa Y et al. Dendritic cells, T-cell infiltration, and Grp94 expression in cholangiocellular carcinoma. Hum Pathol 2004; 35: 881–886.
Tomlinson JS, Jarnagin WR, DeMatteo RP, Fong Y, Kornprat P, Gonen M et al. Actual 10-year survival after resection of colorectal liver metastases defines cure. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 4575–4580.
Galon J, Costes A, Sanchez-Cabo F, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Lagorce-Pages C et al. Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome. Science 2006; 313: 1960–1964.
Katz SC, Pillarisetty V, Bamboat ZM, Shia J, Hedvat C, Gonen M et al. T cell infiltrate predicts long-term survival following resection of colorectal cancer liver metastases. Ann Surg Oncol 2009; 16: 2524–2530.
Turcotte S, Katz SC, Shia J, Jarnagin WR, Kingham TP, Allen PJ et al. Tumor MHC class I expression improves the prognostic value of T-cell density in resected colorectal liver metastases. Cancer Immunol Res 2014; 2: 530–537.
Katz SC, Donkor C, Glasgow K, Pillarisetty VG, Gonen M, Espat NJ et al. T cell infiltrate and outcome following resection of intermediate-grade primary neuroendocrine tumours and liver metastases. HPB (Oxford) 2010; 12: 674–683.
Calne RY, Sells RA, Pena JR, Davis DR, Millard PR, Herbertson BM et al. Induction of immunological tolerance by porcine liver allografts. Nature 1969; 223: 472–476.
Emtage PC, Lo AS, Gomes EM, Liu DL, Gonzalo-Daganzo RM, Junghans RP . Second-generation anti-carcinoembryonic antigen designer T cells resist activation-induced cell death, proliferate on tumor contact, secrete cytokines, and exhibit superior antitumor activity in vivo: a preclinical evaluation. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 8112–8122.
Burga RA, Thorn M, Point GR, Guha P, Nguyen CT, Licata LA et al. Liver myeloid-derived suppressor cells expand in response to liver metastases in mice and inhibit the anti-tumor efficacy of anti-CEA CAR-T. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2015; 64: 817–829.
Norris S, Collins C, Doherty DG, Smith F, McEntee G, Traynor O et al. Resident human hepatic lymphocytes are phenotypically different from circulating lymphocytes. J Hepatol 1998; 28: 84–90.
Crispe IN, Mehal WZ . Strange brew: T cells in the liver. Immunol Today 1996; 17: 522–525.
Crispe IN . Hepatic T cells and liver tolerance. Nat Rev Immunol 2003; 3: 51–62.
Pruvot FR, Navarro F, Janin A, Labalette M, Masy E, Lecomte-Houcke M et al. Characterization, quantification, and localization of passenger T lymphocytes and NK cells in human liver before transplantation. Transpl Int 1995; 8: 273–279.
Klugewitz K, Topp SA, Dahmen U, Kaiser T, Sommer S, Kury E et al. Differentiation-dependent and subset-specific recruitment of T-helper cells into murine liver. Hepatology 2002; 35: 568–578.
Klugewitz K, Blumenthal-Barby F, Schrage A, Knolle PA, Hamann A, Crispe IN . Immunomodulatory effects of the liver: deletion of activated CD4+ effector cells and suppression of IFN-gamma-producing cells after intravenous protein immunization. J Immunol 2002; 169: 2407–2413.
Katz SC, Ryan K, Ahmed N, Plitas G, Chaudhry UI, Kingham TP et al. Obstructive jaundice expands intrahepatic regulatory T cells, which impair liver T lymphocyte function but modulate liver cholestasis and fibrosis. J Immunol 2011; 187: 1150–1156.
Stross L, Gunther J, Gasteiger G, Asen T, Graf S, Aichler M et al. Foxp3+ regulatory T cells protect the liver from immune damage and compromise virus control during acute experimental hepatitis B virus infection in mice. Hepatology 2012; 56: 873–883.
Chen X, Du Y, Huang Z . CD4+CD25+ Treg derived from hepatocellular carcinoma mice inhibits tumor immunity. Immunol Lett 2012; 148: 83–89.
Licata LA, Nguyen CT, Burga RA, Falanga V, Espat NJ, Ayala A et al. Biliary obstruction results in PD-1-dependent liver T cell dysfunction and acute inflammation mediated by Th17 cells and neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol 2013; 94: 813–823.
Jinushi M, Takehara T, Tatsumi T, Kanto T, Miyagi T, Suzuki T et al. Negative regulation of NK cell activities by inhibitory receptor CD94/NKG2A leads to altered NK cell-induced modulation of dendritic cell functions in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J Immunol 2004; 173: 6072–6081.
Jinushi M, Takehara T, Tatsumi T, Yamaguchi S, Sakamori R, Hiramatsu N et al. Natural killer cell and hepatic cell interaction via NKG2A leads to dendritic cell-mediated induction of CD4 CD25 T cells with PD-1-dependent regulatory activities. Immunology 2007; 120: 73–82.
Tyznik AJ, Verma S, Wang Q, Kronenberg M, Benedict CA . Distinct requirements for activation of NKT and NK cells during viral infection. J Immunol 2014; 192: 3676–3685.
Sun R, Gao B . Negative regulation of liver regeneration by innate immunity (natural killer cells/interferon-gamma). Gastroenterology 2004; 127: 1525–1539.
Horst AK, Neumann K, Diehl L, Tiegs G . Modulation of liver tolerance by conventional and nonconventional antigen-presenting cells and regulatory immune cells. Cell Mol Immunol 2016; 13: 277–292.
Schurich A, Berg M, Stabenow D, Bottcher J, Kern M, Schild HJ et al. Dynamic regulation of CD8 T cell tolerance induction by liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. J Immunol 2010; 184: 4107–4114.
Knolle PA, Limmer A . Control of immune responses by savenger liver endothelial cells. Swiss Med Wkly 2003; 133: 501–506.
Wong J, Johnston B, Lee SS, Bullard DC, Smith CW, Beaudet AL et al. A minimal role for selectins in the recruitment of leukocytes into the inflamed liver microvasculature. J Clin Invest 1997; 99: 2782–2790.
Knolle PA, Uhrig A, Hegenbarth S, Loser E, Schmitt E, Gerken G et al. IL-10 down-regulates T cell activation by antigen-presenting liver sinusoidal endothelial cells through decreased antigen uptake via the mannose receptor and lowered surface expression of accessory molecules. Clin Exp Immunol 1998; 114: 427–433.
Knolle PA, Germann T, Treichel U, Uhrig A, Schmitt E, Hegenbarth S et al. Endotoxin down-regulates T cell activation by antigen-presenting liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. J Immunol 1999; 162: 1401–1407.
Carambia A, Frenzel C, Bruns OT, Schwinge D, Reimer R, Hohenberg H et al. Inhibition of inflammatory CD4 T cell activity by murine liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. J Hepatol 2013; 58: 112–118.
Lau AH, Thomson AW . Dendritic cells and immune regulation in the liver. Gut 2003; 52: 307–314.
Pillarisetty VG, Shah AB, Miller G, Bleier JI, DeMatteo RP . Liver dendritic cells are less immunogenic than spleen dendritic cells because of differences in subtype composition. J Immunol 2004; 172: 1009–1017.
Onishi Y, Fehervari Z, Yamaguchi T, Sakaguchi S . Foxp3+ natural regulatory T cells preferentially form aggregates on dendritic cells in vitro and actively inhibit their maturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 10113–10118.
Bilzer M, Roggel F, Gerbes AL . Role of Kupffer cells in host defense and liver disease. Liver Int 2006; 26: 1175–1186.
Bingisser RM, Tilbrook PA, Holt PG, Kees UR . Macrophage-derived nitric oxide regulates T cell activation via reversible disruption of the Jak3/STAT5 signaling pathway. J Immunol 1998; 160: 5729–5734.
Chensue SW, Terebuh PD, Remick DG, Scales WE, Kunkel SL . In vivo biologic and immunohistochemical analysis of interleukin-1 alpha, beta and tumor necrosis factor during experimental endotoxemia. Kinetics, Kupffer cell expression, and glucocorticoid effects. Am J Pathol 1991; 138: 395–402.
Knolle P, Schlaak J, Uhrig A, Kempf P, Meyer zum Buschenfelde KH, Gerken G . Human Kupffer cells secrete IL-10 in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge. J Hepatol 1995; 22: 226–229.
You Q, Cheng L, Kedl RM, Ju C . Mechanism of T cell tolerance induction by murine hepatic Kupffer cells. Hepatology 2008; 48: 978–990.
Heymann F, Peusquens J, Ludwig-Portugall I, Kohlhepp M, Ergen C, Niemietz P et al. Liver inflammation abrogates immunological tolerance induced by Kupffer cells. Hepatology 2015; 62: 279–291.
Xie Z, Chen Y, Zhao S, Yang Z, Yao X, Guo S et al. Intrahepatic PD-1/PD-L1 up-regulation closely correlates with inflammation and virus replication in patients with chronic HBV infection. Immunol Invest 2009; 38: 624–638.
Youn JI, Gabrilovich DI . The biology of myeloid-derived suppressor cells: the blessing and the curse of morphological and functional heterogeneity. Eur J Immunol 2010; 40: 2969–2975.
Thorn M, Guha P, Cunetta M, Espat NJ, Miller G, Junghans RP et al. Tumor-associated GM-CSF overexpression induces immunoinhibitory molecules via STAT3 in myeloid-suppressor cells infiltrating liver metastases. Cancer Gene Ther 2016; 23: 188–198.
Thorn M, Guha P, Cunetta M, Espat NJ, Miller G, Junghans RP et al. Tumor-associated GM-CSF overexpression induces immunoinhibitory molecules via STAT3 in myeloid-suppressor cells infiltrating liver metastases. Cancer Gene Ther 2016; 23: 188–198.
Weiskirchen R, Tacke F . Cellular and molecular functions of hepatic stellate cells in inflammatory responses and liver immunology. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr 2014; 3: 344–363.
Trautwein C, Friedman SL, Schuppan D, Pinzani M . Hepatic fibrosis: concept to treatment. J Hepatol 2015; 62 (1 Suppl): S15–S24.
Lee YA, Wallace MC, Friedman SL . Pathobiology of liver fibrosis: a translational success story. Gut 2015; 64: 830–841.
Dunham RM, Thapa M, Velazquez VM, Elrod EJ, Denning TL, Pulendran B et al. Hepatic stellate cells preferentially induce Foxp3+ regulatory T cells by production of retinoic acid. J Immunol 2013; 190: 2009–2016.
Yu MC, Chen CH, Liang X, Wang L, Gandhi CR, Fung JJ et al. Inhibition of T-cell responses by hepatic stellate cells via B7-H1-mediated T-cell apoptosis in mice. Hepatology 2004; 40: 1312–1321.
Fourcade J, Sun Z, Pagliano O, Chauvin JM, Sander C, Janjic B et al. PD-1 and Tim-3 regulate the expansion of tumor antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells induced by melanoma vaccines. Cancer Res 2014; 74: 1045–1055.
Lines JL, Pantazi E, Mak J, Sempere LF, Wang L, O'Connell S et al. VISTA is an immune checkpoint molecule for human T cells. Cancer Res 2014; 74: 1924–1932.
Okazaki T, Okazaki IM, Wang J, Sugiura D, Nakaki F, Yoshida T et al. PD-1 and LAG-3 inhibitory co-receptors act synergistically to prevent autoimmunity in mice. J Exp Med 2011; 208: 395–407.
Egen JG, Allison JP . Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 accumulation in the immunological synapse is regulated by TCR signal strength. Immunity 2002; 16: 23–35.
Linsley PS, Greene JL, Brady W, Bajorath J, Ledbetter JA, Peach R . Human B7-1 (CD80) and B7-2 (CD86) bind with similar avidities but distinct kinetics to CD28 and CTLA-4 receptors. Immunity 1994; 1: 793–801.
Riley JL, Mao M, Kobayashi S, Biery M, Burchard J, Cavet G et al. Modulation of TCR-induced transcriptional profiles by ligation of CD28, ICOS, and CTLA-4 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 11790–11795.
Schneider H, Downey J, Smith A, Zinselmeyer BH, Rush C, Brewer JM et al. Reversal of the TCR stop signal by CTLA-4. Science 2006; 313: 1972–1975.
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, Bourque K, Chernova T, Nishimura H et al. Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med 2000; 192: 1027–1034.
Ishida Y, Agata Y, Shibahara K, Honjo T . Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J 1992; 11: 3887–3895.
Keir ME, Liang SC, Guleria I, Latchman YE, Qipo A, Albacker LA et al. Tissue expression of PD-L1 mediates peripheral T cell tolerance. J Exp Med 2006; 203: 883–895.
Nishimura H, Okazaki T, Tanaka Y, Nakatani K, Hara M, Matsumori A et al. Autoimmune dilated cardiomyopathy in PD-1 receptor-deficient mice. Science 2001; 291: 319–322.
Park JJ, Omiya R, Matsumura Y, Sakoda Y, Kuramasu A, Augustine MM et al. B7-H1/CD80 interaction is required for the induction and maintenance of peripheral T-cell tolerance. Blood 2010; 116: 1291–1298.
Paterson AM, Brown KE, Keir ME, Vanguri VK, Riella LV, Chandraker A et al. The programmed death-1 ligand 1:B7-1 pathway restrains diabetogenic effector T cells in vivo. J Immunol 2011; 187: 1097–1105.
Fanoni D, Tavecchio S, Recalcati S, Balice Y, Venegoni L, Fiorani R et al. New monoclonal antibodies against B-cell antigens: possible new strategies for diagnosis of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas. Immunol Lett 2011; 134: 157–160.
Terme M, Ullrich E, Aymeric L, Meinhardt K, Desbois M, Delahaye N et al. IL-18 induces PD-1-dependent immunosuppression in cancer. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 5393–5399.
Goldberg MV, Drake CG . LAG-3 in cancer immunotherapy. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2011; 344: 269–278.
Huang CT, Workman CJ, Flies D, Pan X, Marson AL, Zhou G et al. Role of LAG-3 in regulatory T cells. Immunity 2004; 21: 503–513.
Blackburn SD, Shin H, Haining WN, Zou T, Workman CJ, Polley A et al. Coregulation of CD8+ T cell exhaustion by multiple inhibitory receptors during chronic viral infection. Nat Immunol 2009; 10: 29–37.
Grosso JF, Goldberg MV, Getnet D, Bruno TC, Yen HR, Pyle KJ et al. Functionally distinct LAG-3 and PD-1 subsets on activated and chronically stimulated CD8 T cells. J Immunol 2009; 182: 6659–6669.
Baitsch L, Legat A, Barba L, Fuertes Marraco SA, Rivals JP, Baumgaertner P et al. Extended co-expression of inhibitory receptors by human CD8 T-cells depending on differentiation, antigen-specificity and anatomical localization. PLoS One 2012; 7: e30852.
Fourcade J, Sun Z, Benallaoua M, Guillaume P, Luescher IF, Sander C et al. Upregulation of Tim-3 and PD-1 expression is associated with tumor antigen-specific CD8+ T cell dysfunction in melanoma patients. J Exp Med 2010; 207: 2175–2186.
Sakuishi K, Apetoh L, Sullivan JM, Blazar BR, Kuchroo VK, Anderson AC . Targeting Tim-3 and PD-1 pathways to reverse T cell exhaustion and restore anti-tumor immunity. J Exp Med 2010; 207: 2187–2194.
Katz SC, Burga RA, McCormack E, Wang LJ, Mooring W, Point GR et al. Phase I hepatic immunotherapy for metastases study of intra-arterial chimeric antigen receptor-modified T-cell therapy for CEA+ liver metastases. Clin Cancer Res 2015; 21: 3149–3159.
Saied A, Licata L, Burga RA, Thorn M, McCormack E, Stainken BF et al. Neutrophil:lymphocyte ratios and serum cytokine changes after hepatic artery chimeric antigen receptor-modified T-cell infusions for liver metastases. Cancer Gene Ther 2014; 21: 457–462.
Kemeny NE, Melendez FD, Capanu M, Paty PB, Fong Y, Schwartz LH et al. Conversion to resectability using hepatic artery infusion plus systemic chemotherapy for the treatment of unresectable liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 3465–3471.
Keilholz U, Scheibenbogen C, Brado M, Georgi P, Maclachlan D, Brado B et al. Regional adoptive immunotherapy with interleukin-2 and lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cells for liver metastases. Eur J Cancer 1994; 30A: 103–105.
Junghans RP, Manning W, Safar M, Quist W . Biventricular cardiac thrombosis during interleukin-2 infusion. N Engl J Med 2001; 344: 859–860.
Thorn M, Guha P, Cunetta M, Espat NJ, Miller G, Junghans RP et al. Tumor-associated GM-CSF overexpression induces immunoinhibitory molecules via STAT3 in myeloid-suppressor cells infiltrating liver metastases. Cancer Gene Ther 2016; 23: 188–198.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guha, P., Reha, J. & Katz, S. Immunosuppression in liver tumors: opening the portal to effective immunotherapy. Cancer Gene Ther 24, 114–120 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2016.54
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2016.54
This article is cited by
-
Novel treatment paradigms for metastatic uveal melanoma
Cancer Gene Therapy (2022)
-
Regional infusion of a class C TLR9 agonist enhances liver tumor microenvironment reprogramming and MDSC reduction to improve responsiveness to systemic checkpoint inhibition
Cancer Gene Therapy (2022)
-
Monocytic and granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cell plasticity and differentiation are organ-specific
Oncogene (2021)
-
Comparative analysis of assays to measure CAR T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity
Nature Protocols (2021)
-
Comparison of immune profiles between hepatocellular carcinoma subtypes
Biophysics Reports (2020)