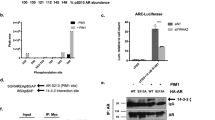
Abstract
The promotion and progression of prostate cancer (PCa) are associated with androgen receptor (AR) signalling. AR functions are modulated by a variety of co-factors amongst which we identified the nucleophosmin (NPM/B23), a member of the histone chaperone family. Here, we show that NPM is overexpressed in PCa compared to normal adjacent tissues. AR and NPM interact in vitro and in vivo, and NPM is critical for androgen-dependent transcriptional activation in LNCaP cells as an anti-NPM siRNA downregulates transcription of a transfected androgen response element (ARE)-containing reporter promoter as well as expression of the endogenous androgen responsive prostate-specific antigen (PSA) gene. By investigating the effect of NPM on AR, we have also observed that NPM enhances AR binding to an ARE in vitro in electrophoretic gel mobility-shift assay experiments. Chromatin immunoprecipitation studies further demonstrated that both AR and NPM associate with AREs of the PSA gene in vivo. Altogether, our data suggest that the molecular histone chaperone NPM could regulate AR functions by promoting assembly of AR-containing regulatory complexes and that high levels of NPM might alter AR functions in PCa.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baron S, Manin M, Beaudoin C, Léotoing L, Communal Y, Veyssiere G et al. (2004). Androgen receptor mediates non-genomic activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-OH kinase in androgen-sensitive epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 279: 14579–14586.
Bertwistle D, Sugimoto M, Sherr CJ . (2004). Physical and functional interactions of the Arf tumor suppressor protein with nucleophosmin/B23. Mol Cell Biol 24: 985–996.
Bocker T, Bittinger A, Wieland W, Buettner R, Fauser G, Hofstaedter F et al. (1995). In vitro and ex vivo expression of nucleolar proteins B23 and p120 in benign and malignant epithelial lesions of the prostate. Mod Pathol 8: 226–231.
Boonyaratanakornkit V, Melvin V, Prendergast P, Altmann M, Ronfani L, Bianchi ME et al. (1998). High-mobility group chromatin proteins 1 and 2 functionally interact with steroid hormone receptors to enhance their DNA binding in vitro and transcriptional activity in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol 18: 4471–4487.
Colombo E, Marine JC, Danovi D, Falini B, Pelicci PG . (2002). Nucleophosmin regulates the stability and transcriptional activity of p53. Nat Cell Biol 4: 529–533.
Darne CH, Morel L, Claessens F, Manin M, Fabre S, Veyssiere G et al. (1997). Ubiquitous transcription factors NF1 and Sp1 are involved in the androgen activation of the mouse vas deferens protein promoter. Mol Cell Endocrinol 132: 13–23.
Dhar SK, Lynn BC, Daosukho C, St Clair DK . (2004). Identification of nucleophosmin as an NF-kappaB co-activator for the induction of the human SOD2 gene. J Biol Chem 279: 28209–28219.
Fabre S, Manin M, Pailhoux E, Veyssiere G, Jean C . (1994). Identification of a functional androgen response element in the promoter of the gene for the androgen-regulated aldose reductase-like protein specific to the mouse vas deferens. J Biol Chem 269: 5857–5864.
Fu M, Wang C, Reutens AT, Wang J, Angeletti RH, Siconolfi-Baez L et al. (2000). p300 and p300/cAMP-response element-binding protein-associated factor acetylate the androgen receptor at sites governing hormone-dependent transactivation. J Biol Chem 275: 20853–20860.
Haelens A, Tanner T, Denayer S, Callewaert L, Claessens F . (2007). The hinge region regulates DNA binding, nuclear translocation, and transactivation of the androgen receptor. Cancer Res 67: 4514–4523.
Heinlein CA, Chang C . (2002). Androgen receptor (AR) coregulators: an overview. Endocr Rev 23: 175–200.
Hingorani K, Szebeni A, Olson MO . (2000). Mapping the functional domains of nucleolar protein B23. J Biol Chem 275: 24451–24457.
Hsing AW, Tsao L, Devesa SS . (2000). International trends and patterns of prostate cancer incidence and mortality. Int J Cancer 85: 60–67.
Hu YC, Yeh S, Yeh SD, Sampson ER, Huang J, Li P et al. (2004). Functional domain and motif analyses of androgen receptor coregulator ARA70 and its differential expression in prostate cancer. J Biol Chem 279: 33438–33446.
Inouye CJ, Seto E . (1994). Relief of YY1-induced transcriptional repression by protein-protein interaction with the nucleolar phosphoprotein B23. J Biol Chem 269: 6506–6510.
Kang Z, Janne OA, Palvimo JJ . (2004). Coregulator recruitment and histone modifications in transcriptional regulation by the androgen receptor. Mol Endocrinol 18: 2633–2648.
Kim J, Jia L, Tilley WD, Coetzee GA . (2003). Dynamic methylation of histone H3 at lysine 4 in transcriptional regulation by the androgen receptor. Nucleic Acids Res 31: 6741–6747.
Lemon B, Tjian R . (2000). Orchestrated response: a symphony of transcription factors for gene control. Genes Dev 14: 2551–2569.
Léotoing L, Manin M, Monte D, Baron S, Communal Y, Lours C et al. (2007). Crosstalk between androgen receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor-signalling pathways: a molecular switch for epithelial cell differentiation. J Mol Endocrinol 39: 151–162.
Liu H, Tan BC, Tseng KH, Chuang CP, Yeh CW, Chen KD et al. (2007). Nucleophosmin acts as a novel AP2alpha-binding transcriptional corepressor during cell differentiation. EMBO Rep 8: 394–400.
Maiguel DA, Jones L, Chakravarty D, Yang C, Carrier F . (2004). Nucleophosmin sets a threshold for p53 response to UV radiation. Mol Cell Biol 24: 3703–3711.
Melvin VS, Edwards DP . (1999). Coregulatory proteins in steroid hormone receptor action: the role of chromatin high mobility group proteins HMG-1 and -2. Steroids 64: 576–586.
Morimoto RI . (2002). Dynamic remodeling of transcription complexes by molecular chaperones. Cell 110: 281–284.
Okuwaki M, Matsumoto K, Tsujimoto M, Nagata K . (2001). Function of nucleophosmin/B23, a nucleolar acidic protein, as a histone chaperone. FEBS Lett 506: 272–276.
Ranganathan S, Salazar H, Benetatos CA, Hudes GR . (1997). Immunohistochemical analysis of beta-tubulin isotypes in human prostate carcinoma and benign prostatic hypertrophy. Prostate 30: 263–268.
Savkur RS, Olson MO . (1998). Preferential cleavage in pre-ribosomal RNA byprotein B23 endoribonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res 26: 4508–4515.
Shatkina L, Mink S, Rogatsch H, Klocker H, Langer G, Nestl A et al. (2003). The cochaperone Bag-1L enhances androgen receptor action via interaction with the NH2-terminal region of the receptor. Mol Cell Biol 23: 7189–7197.
Subong EN, Shue MJ, Epstein JI, Briggman JV, Chan PK, Partin AW . (1999). Monoclonal antibody to prostate cancer nuclear matrix protein (PRO:4-216) recognizes nucleophosmin/B23. Prostate 39: 298–304.
Swaminathan V, Kishore AH, Febitha KK, Kundu TK . (2005). Human histone chaperone nucleophosmin enhances acetylation-dependent chromatin transcription. Mol Cell Biol 25: 7534–7545.
Szebeni A, Herrera JE, Olson MO . (1995). Interaction of nucleolar protein B23 with peptides related to nuclear localization signals. Biochemistry 34: 8037–8042.
Takemura M, Sato K, Nishio M, Akiyama T, Umekawa H, Yoshida S . (1999). Nucleolar protein B23.1 binds to retinoblastoma protein and synergistically stimulates DNA polymerase alpha activity. J Biochem (Tokyo) 125: 904–909.
Verrijdt G, Haelens A, Schoenmakers E, Rombauts W, Claessens F . (2002). Comparative analysis of the influence of the high-mobility group box 1 protein on DNA binding and transcriptional activation by the androgen, glucocorticoid, progesterone and mineralocorticoid receptors. Biochem J 361: 97–103.
Volle DH, Repa JJ, Mazur A, Cummins CL, Val P, Henry-Berger J et al. (2004). Regulation of the aldo-keto reductase gene akr1b7 by the nuclear oxysterol receptor LXRalpha (liver X receptor-alpha) in the mouse intestine: putative role of LXRs in lipid detoxification processes. Mol Endocrinol 18: 888–898.
Wang L, Hsu CL, Chang C . (2005). Androgen receptor corepressors: an overview. Prostate 63: 117–130.
Weng JJ, Yung BY . (2005). Nucleophosmin/B23 regulates PCNA promoter through YY1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 335: 826–831.
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to J-P Saru, A de Haze for their technical assistance, A Bruhat for his pertinent advices for DNA ChIP. This work was supported by grants awarded by the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), the Institut National du Cancer (grant PL06-125), Ligue Contre le Cancer Puy de Dôme and the Université Blaise Pascal (UBP). L Léotoing is recipient of a doctoral fellowship from the Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer (ARC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Léotoing, L., Meunier, L., Manin, M. et al. Influence of nucleophosmin/B23 on DNA binding and transcriptional activity of the androgen receptor in prostate cancer cell. Oncogene 27, 2858–2867 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210942
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210942
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
NPM1 upregulates the transcription of PD-L1 and suppresses T cell activity in triple-negative breast cancer
Nature Communications (2020)
-
NPM1 Biology in Myeloid Neoplasia
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2020)
-
NPM1 alternative transcripts are upregulated in acute myeloid and lymphoblastic leukemia and their expression level affects patient outcome
Journal of Translational Medicine (2018)
-
Analysis of the oligomeric states of nucleophosmin using size exclusion chromatography
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Nucleophosmin: from structure and function to disease development
BMC Molecular Biology (2016)