Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access 3D atomic structure from a single X-ray free electron laser pulse
3D atomic structure from a single X-ray free electron laser pulse
X-ray Free Electron Lasers allow fast structure determination. Here, the authors push the temporal limit of atomic level structure determination to 25 fs, the length of a single pulse, paving the way to the study of fast, non-repeatable processes.
- Gábor Bortel
- , Miklós Tegze
- & Gyula Faigel
-
Article
| Open Access Impact of palladium/palladium hydride conversion on electrochemical CO2 reduction via in-situ transmission electron microscopy and diffraction
Impact of palladium/palladium hydride conversion on electrochemical CO2 reduction via in-situ transmission electron microscopy and diffraction
The evolution of Pd-based material during CO2 electroreduction requires further investigation. Here the authors use in-situ liquid-phase transmission electron microscopy and select area diffraction characterization techniques to visualize the morphological and phase structure evolution of the Pd/PdHx catalysts under CO2 electroreduction conditions.
- Ahmed M. Abdellah
- , Fatma Ismail
- & Drew Higgins
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate additive manufacturing of lightweight and elastic carbons using plastic precursors
Accurate additive manufacturing of lightweight and elastic carbons using plastic precursors
This work reports a simple method to produce 3D printed complex carbon materials with low dimensional shrinkage (<4%) from printed to carbonized state, using commercially available carbon fiber-reinforced polypropylene precursors and a fused filament fabrication-based process.
- Paul Smith
- , Jiayue Hu
- & Zhe Qiang
-
Article
| Open Access Self-poled piezoelectric polymer composites via melt-state energy implantation
Self-poled piezoelectric polymer composites via melt-state energy implantation
Lightweight flexible piezoelectric polymers are demanded for various applications, but restricted by the low instinctively piezoelectric coefficient and complex poling process. Here, the authors develop a high performance lightweight, flexible self-poled piezoelectric polymer composite towards sustainable self-powered sensing and energy harvesting.
- Zhao-Xia Huang
- , Lan-Wei Li
- & Jin-Ping Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Stable and efficient pure blue quantum-dot LEDs enabled by inserting an anti-oxidation layer
Stable and efficient pure blue quantum-dot LEDs enabled by inserting an anti-oxidation layer
Blue QD-LEDs suffer from poor operational stability due to the carrier accumulation at transport layers. Here, the authors propose a strategy to mitigate the hole accumulation driven oxidation in hole transport layer, effectively elongating the operational lifetime of blue QD-LEDs.
- Wenjing Zhang
- , Bo Li
- & Huaibin Shen
-
Article
| Open Access EUV-induced hydrogen desorption as a step towards large-scale silicon quantum device patterning
EUV-induced hydrogen desorption as a step towards large-scale silicon quantum device patterning
Scanning tunnelling microscopy-based H desorption lithography is used for atomic-scale patterning of quantum devices in Si, but its time-consuming nature hinders scalability. Here the authors report H desorption from Si(001):H surface using extreme-UV light and explore implications for patterning.
- Procopios Constantinou
- , Taylor J. Z. Stock
- & Steven R. Schofield
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerating process development for 3D printing of new metal alloys
Accelerating process development for 3D printing of new metal alloys
Process development for 3D printing of new metal alloys can be time-consuming and variability in the printing outcome makes it even more challenging. Here, authors demonstrate an in-situ method using high-speed imaging and deep learning to accelerate the process design for a more consistent quality.
- David Guirguis
- , Conrad Tucker
- & Jack Beuth
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasmall single-layered NbSe2 nanotubes flattened within a chemical-driven self-pressurized carbon nanotube
Ultrasmall single-layered NbSe2 nanotubes flattened within a chemical-driven self-pressurized carbon nanotube
The chemical-driven large pressure arising inside carbon nanotubes creates energetically stable, flattened, single-layered NbSe2 nanotubes with enhanced intermolecular electronic interactions, suggesting a chemical approach to produce materials with tailored structural and electronic properties.
- Yaxin Jiang
- , Hao Xiong
- & Fei Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Single-sided magnetic resonance-based sensor for point-of-care evaluation of muscle
Single-sided magnetic resonance-based sensor for point-of-care evaluation of muscle
Magnetic resonance imaging is a useful clinical tool, but its widespread use is constrained by size, cost, and time. Here, the authors report the development of a magnetic resonance sensor for the clinical detection of muscle tissue, allowing for new point-of-care quantitative diagnostic measurements
- Sydney E. Sherman
- , Alexa S. Zammit
- & Michael J. Cima
-
Article
| Open Access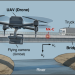 Drone-based displacement measurement of infrastructures utilizing phase information
Drone-based displacement measurement of infrastructures utilizing phase information
Drones are an effective and flexible tool for safety assessment of aging infrastructure, especially in locations with challenging accessibility. Here, authors demonstrate a phase-based sampling moiré technique with a drone for measurement of millimeter-scale infrastructural displacement in bridges.
- Shien Ri
- , Jiaxing Ye
- & Norihiko Ogura
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of strong surface reconstruction in partially reduced nickelate films
Direct observation of strong surface reconstruction in partially reduced nickelate films
Surface polarity affects the electronic and structural properties of oxide thin films through electrostatic effects, which is challenging to control. Here, the authors probe the tunable surface polarity at the atomic scale.
- Chao Yang
- , Rebecca Pons
- & Peter A. van Aken
-
Article
| Open Access Switchable tribology of ferroelectrics
Switchable tribology of ferroelectrics
The interaction of flexoelectric polarization arising from strain gradients with ferroelectricity impacts tribological properties and facilitates fine physical lithography without masks or chemicals, with potential applications in various fields.
- Seongwoo Cho
- , Iaroslav Gaponenko
- & Seungbum Hong
-
Article
| Open Access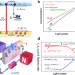 Resolving electron and hole transport properties in semiconductor materials by constant light-induced magneto transport
Resolving electron and hole transport properties in semiconductor materials by constant light-induced magneto transport
Here, the authors introduce a constant light-induced magneto-transport method which seamlessly integrates light, current, and a magnetic field to characterize electron and hole properties across an expansive array of materials.
- Artem Musiienko
- , Fengjiu Yang
- & Antonio Abate
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative analysis of printed nanostructured networks using high-resolution 3D FIB-SEM nanotomography
Quantitative analysis of printed nanostructured networks using high-resolution 3D FIB-SEM nanotomography
The physical properties of devices made of printed nanosheets and nanowires are determined by their intrinsic nanostructured network morphology. Here, the authors use FIB-SEM nanotomography to quantitatively analyze printed nanostructured networks via 3D reconstructions.
- Cian Gabbett
- , Luke Doolan
- & Jonathan N. Coleman
-
Article
| Open Access Exact inversion of partially coherent dynamical electron scattering for picometric structure retrieval
Exact inversion of partially coherent dynamical electron scattering for picometric structure retrieval
By combining real and diffraction space data recorded in electron microscopes, ptychography retrieves specimen details with super-resolution. Here, the inverse problem is solved in the presence of thermal diffuse scattering and applied to measure ferroelectric displacements with picometer precision.
- Benedikt Diederichs
- , Ziria Herdegen
- & Knut Müller-Caspary
-
Article
| Open Access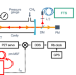 Sub-Doppler optical-optical double-resonance spectroscopy using a cavity-enhanced frequency comb probe
Sub-Doppler optical-optical double-resonance spectroscopy using a cavity-enhanced frequency comb probe
Probing molecules in excited vibrational states requires precise methods to extract the spectroscopic parameters. Here the authors demonstrate optical-optical double-resonance spectroscopy of excited-bands of methane using single pass high power continuous wave pump and cavity-enhanced frequency comb probe.
- Vinicius Silva de Oliveira
- , Isak Silander
- & Aleksandra Foltynowicz
-
Article
| Open Access Tensile straining of iridium sites in manganese oxides for proton-exchange membrane water electrolysers
Tensile straining of iridium sites in manganese oxides for proton-exchange membrane water electrolysers
The acidic oxygen evolution reaction plays a crucial role in proton-exchange membrane water electrolysis devices. The authors developed a low-iridium catalyst with tensile-strain able to trigger a localized lattice oxygen-mediated mechanism to realize efficient and stable acid-OER performance.
- Hui Su
- , Chenyu Yang
- & Qinghua Liu
-
Article
| Open Access 3D microprinting of inorganic porous materials by chemical linking-induced solidification of nanocrystals
3D microprinting of inorganic porous materials by chemical linking-induced solidification of nanocrystals
3D microprinting is considered a next generation manufacturing process for microscale components. Here, authors develop a generalised microscale 3D printing method to produce purely inorganic nanocrystal-linked porous materials that exhibit excellent functionality and hierarchical porosity.
- Minju Song
- , Yoonkyum Kim
- & Jae Sung Son
-
Article
| Open Access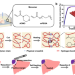 3D printing of self-healing personalized liver models for surgical training and preoperative planning
3D printing of self-healing personalized liver models for surgical training and preoperative planning
High-fidelity personalized anatomical models can offer invaluable support for precision medicine. Here, the authors show the 3D printing of self-healing liver models, which can be resected in a trial and-error manner for surgical training to enhance the safety of hepatic surgery.
- Yahui Lu
- , Xing Chen
- & Yuhua Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Roll-to-plate 0.1-second shear-rolling process at elevated temperature for highly aligned nanopatterns
Roll-to-plate 0.1-second shear-rolling process at elevated temperature for highly aligned nanopatterns
In this work, authors demonstrate a 0.1-second shear rolling process capable of shearing without peeling up to 280 °C. This enables roll-to-plate fabrication of highly and unidirectionally aligned sub−10 nm block copolymer patterns over large wafer areas.
- Junghyun Cho
- , Jinwoo Oh
- & Jeong Gon Son
-
Article
| Open Access UV-curable thiol-ene system for broadband infrared transparent objects
UV-curable thiol-ene system for broadband infrared transparent objects
Processing of conventional infrared-transparent materials limits their applicability. The authors demonstrate 3D printing of thiol-ene optical components with mid- and long-wave infrared transparency with applications such as reaction temperature monitoring.
- Piaoran Ye
- , Zhihan Hong
- & Rongguang Liang
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular sensitised probe for amino acid recognition within peptide sequences
Molecular sensitised probe for amino acid recognition within peptide sequences
Chemical identification of the building blocks of biopolymers often considerably relies on the presence of markers, extensive simulations, or is not possible at all. Here, the authors report a molecular probe-sensitisation approach addressing the identification of a specific amino acid within different peptides.
- Xu Wu
- , Bogdana Borca
- & Uta Schlickum
-
Article
| Open Access Hot luminescence from single-molecule chromophores electrically and mechanically self-decoupled by tripodal scaffolds
Hot luminescence from single-molecule chromophores electrically and mechanically self-decoupled by tripodal scaffolds
A fundamental challenge for molecular electronics is the change in photophysical properties of molecules upon direct electrical contact. Here, the authors observe hot luminescence emitted by single-molecule chromophores that are electrically and mechanically self-decoupled by a tripodal scaffold.
- Vibhuti Rai
- , Nico Balzer
- & Michal Valášek
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired rational design of bi-material 3D printed soft-hard interfaces
Bioinspired rational design of bi-material 3D printed soft-hard interfaces
Stress concentrations make the design of durable interfaces between hard and soft materials a challenging task. Here, the authors, inspired by nature, combine mechanical tests and simulations on multiple geometries to generate design guidelines that yield strong and tough soft-hard interfaces.
- M. C. Saldívar
- , E. Tay
- & A. A. Zadpoor
-
Article
| Open Access In-plane charged antiphase boundary and 180° domain wall in a ferroelectric film
In-plane charged antiphase boundary and 180° domain wall in a ferroelectric film
The correlation between charged and antiphase states in BiFeO3 remain elusive. Here, the authors report a fabrication of in-plane charged antiphase boundaries in BiFeO3 thin films, revealing the atomic bonding configurations and atomically sharp 180° polarization reversal of such boundaries.
- Xiangbin Cai
- , Chao Chen
- & Deyang Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Harmonizing sound and light: X-ray imaging unveils acoustic signatures of stochastic inter-regime instabilities during laser melting
Harmonizing sound and light: X-ray imaging unveils acoustic signatures of stochastic inter-regime instabilities during laser melting
In the pursuit of advancing laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) technology, researchers have successfully converged the realms of sound and light. Here, the authors unveil the synergistic potential of synchronized x-ray imaging and acoustics to illuminate hidden instabilities in LPBF process.
- Milad Hamidi Nasab
- , Giulio Masinelli
- & Roland E. Logé
-
Article
| Open Access Incommensurate grain-boundary atomic structure
Incommensurate grain-boundary atomic structure
Grain boundary atomic structures of crystalline materials have long been believed to be commensurate with the crystal periodicity of the adjacent crystals. Here, the authors discover an incommensurate grain boundary structure based on direct observations and theoretical calculations.
- Takehito Seki
- , Toshihiro Futazuka
- & Naoya Shibata
-
Article
| Open Access Operando dynamics of trapped carriers in perovskite solar cells observed via infrared optical activation spectroscopy
Operando dynamics of trapped carriers in perovskite solar cells observed via infrared optical activation spectroscopy
Conventional spectroscopic techniques are not sufficiently selective to follow the dynamics of trapped carriers in working perovskite solar cells. Here, authors use infrared optical activation spectroscopy to observe real time evolution of trapped carriers and compare the behaviour of trapped holes.
- Jiaxin Pan
- , Ziming Chen
- & Artem A. Bakulin
-
Article
| Open Access Operando analysis of a solid oxide fuel cell by environmental transmission electron microscopy
Operando analysis of a solid oxide fuel cell by environmental transmission electron microscopy
By contacting a solid oxide fuel cell to a microelectromechanical system inside an environmental electron microscope, the authors establish links between environmental conditions (gas atmosphere, temperature), cell voltage and atomic-scale structure.
- Q. Jeangros
- , M. Bugnet
- & M. Duchamp
-
Article
| Open Access Enabling direct-growth route for highly efficient ethanol upgrading to long-chain alcohols in aqueous phase
Enabling direct-growth route for highly efficient ethanol upgrading to long-chain alcohols in aqueous phase
Achieving efficient carbon chain propagation remains a grand challenge for ethanol upgrading. Here, the authors report sulfur doped Ni@C-Sx catalysts with controllably exposed nickel sites that can dramatically improve direct-growth probability towards long-chain alcohols production.
- Juwen Gu
- , Wanbing Gong
- & Yujie Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access Solving complex nanostructures with ptychographic atomic electron tomography
Solving complex nanostructures with ptychographic atomic electron tomography
Transmission electron microscopy is essential for three-dimensional atomic structure determination, but solving complex heterogeneous structures containing light elements remains challenging. Here, authors solve a complex nanostructure using atomic resolution ptychographic electron tomography.
- Philipp M. Pelz
- , Sinéad M. Griffin
- & Colin Ophus
-
Article
| Open Access Unraveling the synergistic effects of Cu-Ag tandem catalysts during electrochemical CO2 reduction using nanofocused X-ray probes
Unraveling the synergistic effects of Cu-Ag tandem catalysts during electrochemical CO2 reduction using nanofocused X-ray probes
Combining in situ nanoprobe techniques paves the way for gaining insights into structure-selectivity relations for electrocatalysts. Herein, the dynamic evolution of lattice strain in individual nanoparticles is directly visualized with nanoscale resolution in Cu-Ag tandem catalysts during the electrocatalytic conversion of CO2 into value-added chemicals.
- Marvin L. Frisch
- , Longfei Wu
- & Peter Strasser
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-level polarization in electric fields of defects for electrocatalysis
Atomic-level polarization in electric fields of defects for electrocatalysis
The visible evidence bridging atomic defects with catalytic properties has been scarcely explored. Using differential phase contrast technology, this work discloses the existence of a polarized electric field surrounding the antisite defects of a monolayer MoS2 material and its correlation to its electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution property.
- Jie Xu
- , Xiong-Xiong Xue
- & Jun Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Emulator-based Bayesian inference on non-proportional scintillation models by compton-edge probing
Emulator-based Bayesian inference on non-proportional scintillation models by compton-edge probing
Scintillators are widely used for radiation detection and require proper calibration in such applications. Here the authors discuss a Bayesian inference and machine learning method in combination with the Compton-edge probing that can describe the non-proportional scintillation response of inorganic scintillators.
- David Breitenmoser
- , Francesco Cerutti
- & Sabine Mayer
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic scale volume and grain boundary diffusion elucidated by in situ STEM
Atomic scale volume and grain boundary diffusion elucidated by in situ STEM
Here authors explore volume diffusion within crystalline solids at the atomic scale. They use high resolution microscopy techniques to provide insights into the movement of individual atoms within a crystal lattice, revealing the intricate dynamics of volume diffusion processes.
- Peter Schweizer
- , Amit Sharma
- & Xavier Maeder
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative three-dimensional imaging of chemical short-range order via machine learning enhanced atom probe tomography
Quantitative three-dimensional imaging of chemical short-range order via machine learning enhanced atom probe tomography
Quantifying chemical short-range order (CSRO) remains a formidable for volume-averaged or 2D microscopy methods. Here the authors introduce a machine-learning approach that breaks the resolution limitations of atom probe tomography to reveal the 3D atomistic architecture of CSRO in Fe-based alloys.
- Yue Li
- , Ye Wei
- & Baptiste Gault
-
Article
| Open Access Topotactically transformable antiphase boundaries with enhanced ionic conductivity
Topotactically transformable antiphase boundaries with enhanced ionic conductivity
Antiphase boundaries (APBs) have been considered major obstacles to optimizing the ionic conductivity of conductors. Here authors reveal that ionic conductivity can be enhanced through engineering APBs by topotactical transformation at the atomic scale.
- Kun Xu
- , Shih-Wei Hung
- & Jing Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Lead-free Zr-doped ceria ceramics with low permittivity displaying giant electrostriction
Lead-free Zr-doped ceria ceramics with low permittivity displaying giant electrostriction
Electrostrictors are materials that develop mechanical strain proportional to the square of the applied electric field. Here authors report. Zr-doped-Ceria as a new lead-free electrostrictive material with a similar electrostriction coefficient to the best electrostrictor material currently in use.
- Maxim Varenik
- , Boyuan Xu
- & Igor Lubomirsky
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing ultrafast photothermal dynamics with decoupled optical force nanoscopy
Visualizing ultrafast photothermal dynamics with decoupled optical force nanoscopy
Diving deep into material insights, the authors introduce the ‘Decoupled Optical Force Nanoscopy’. This innovation uncovers the physical origins of light induced forces and captures dynamic thermal details with unparalleled nanometer precision.
- Hanwei Wang
- , Sean M. Meyer
- & Yang Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access High-speed mapping of surface charge dynamics using sparse scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy
High-speed mapping of surface charge dynamics using sparse scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy
Dynamic mapping of charge motion across multiple length- and timescales is essential for understanding a variety of phenomena. Here, the authors introduce sparse scanning KPFM, which enables fast nanoscale charge mapping at 3 frames per second to track ion migration.
- Marti Checa
- , Addis S. Fuhr
- & Liam Collins
-
Article
| Open Access In situ imaging of the atomic phase transition dynamics in metal halide perovskites
In situ imaging of the atomic phase transition dynamics in metal halide perovskites
Phase transition dynamics are an important concern in the wide applications of metal halide perovskites. Here authors apply low-dose imaging technique to reveal the phase transition dynamics of CsPbI3 during in-situ heating process with atomic resolution.
- Mengmeng Ma
- , Xuliang Zhang
- & Boyuan Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning at the edge enables real-time streaming ptychographic imaging
Deep learning at the edge enables real-time streaming ptychographic imaging
Next-generation light sources and fast detectors enable unparalleled materials characterization, but increased data rates and compute needs preclude real-time analysis. Here, Babu et al. leverage high-performance computing and AI@Edge to achieve real-time, low-dose imaging on streaming data at 2 KHz.
- Anakha V. Babu
- , Tao Zhou
- & Mathew J. Cherukara
-
Article
| Open Access A general large-scale synthesis approach for crystalline porous materials
A general large-scale synthesis approach for crystalline porous materials
The large-scale production of crystalline porous materials remains a challenge. Here the authors report a general approach of high-pressure homogenization that can realize large-scale synthesis of crystalline porous materials under benign conditions.
- Xiongli Liu
- , An Wang
- & Shengqian Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Defects and nanostrain gradients control phase transition mechanisms in single crystal high-voltage lithium spinel
Defects and nanostrain gradients control phase transition mechanisms in single crystal high-voltage lithium spinel
Lithiation dynamics and phase transition mechanisms in battery materials remain poorly understood. Here authors use operando X-ray nanodiffraction microscopy to reveal how domains relate to defects and how cycling affects the lattice domain reorientation in LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 single crystals.
- Isaac Martens
- , Nikita Vostrov
- & Tobias U. Schulli
-
Article
| Open Access Autonomous and dynamic precursor selection for solid-state materials synthesis
Autonomous and dynamic precursor selection for solid-state materials synthesis
Solid-state materials synthesis relies on effective precursor design. Here, the authors introduce an algorithm that combines ab-initio computations with insights gained from experimental outcomes to efficiently optimize the selection of precursors.
- Nathan J. Szymanski
- , Pragnay Nevatia
- & Gerbrand Ceder
-
Article
| Open Access SEI growth on Lithium metal anodes in solid-state batteries quantified with coulometric titration time analysis
SEI growth on Lithium metal anodes in solid-state batteries quantified with coulometric titration time analysis
In lithium-metal batteries, it is vital to quantify electrolyte side reactions occurring at the metal anode surface. Here, the authors introduce an electrochemical technique, using a series of small-step lithium deposition followed by open circuit voltage analysis, to accurately measure these reactions.
- Burak Aktekin
- , Luise M. Riegger
- & Jürgen Janek
-
Article
| Open Access Additive manufacturing of alloys with programmable microstructure and properties
Additive manufacturing of alloys with programmable microstructure and properties
The traditional way of beating metals to improve their properties is not practical to 3D printed parts with intricate geometry. Here, the authors demonstrate how to program microstructural modifications of metals site-specifically during 3D printing to tune their properties.
- Shubo Gao
- , Zhi Li
- & Matteo Seita
-
Article
| Open Access Elucidating the active phases of CoOx films on Au(111) in the CO oxidation reaction
Elucidating the active phases of CoOx films on Au(111) in the CO oxidation reaction
Supported CoOx catalysts display higher reactivities towards CO oxidation, yet, corresponding catalytically active phases are still unclear, especially under reaction conditions. Here, by means of in-situ APXPS and ResPES, the authors demonstrate that the topographic restructuring and chemical restructuring occur on these CoOx working catalysts, and also highlight the unique catalytic properties of Co3+ sites.
- Hao Chen
- , Lorenz J. Falling
- & Miquel Salmeron
-
Article
| Open Access The practice of reaction window in an electrocatalytic on-chip microcell
The practice of reaction window in an electrocatalytic on-chip microcell
Here, the authors investigate frequently observed variations in data between different electrochemical cells using in-situ electronic/electrochemical measurements, developing a vertical microcell strategy to eliminate the conductance issue and enhance measurement reproducibility.
- Hang Xia
- , Xiaoru Sang
- & Yongmin He

 Development of multifunctional membranes via plasma-assisted nonsolvent induced phase separation
Development of multifunctional membranes via plasma-assisted nonsolvent induced phase separation