Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of Kekulé vortices around hydrogen adatoms in graphene
Observation of Kekulé vortices around hydrogen adatoms in graphene
Kekulé vortices in hexagonal lattices can host fractionalized charges at zero magnetic field, but have remained out of experimental reach. Here, the authors report a Kekulé vortex in the local density states of graphene around a chemisorbed hydrogen adatom.
- Yifei Guan
- , Clement Dutreix
- & Vincent T. Renard
-
Article
| Open Access Benchtop mesoSPIM: a next-generation open-source light-sheet microscope for cleared samples
Benchtop mesoSPIM: a next-generation open-source light-sheet microscope for cleared samples
The demand to image large biological samples at high resolution requires improvement in current light-sheet microscopy tools. Here, the authors present an improved, benchtop mesoSPIM with a significantly increased field-of-view, improved resolution and improved throughput.
- Nikita Vladimirov
- , Fabian F. Voigt
- & Fritjof Helmchen
-
Article
| Open Access Photoswitchable polyynes for multiplexed stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with reversible light control
Photoswitchable polyynes for multiplexed stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with reversible light control
Bioimaging with photocontrol and multiplexing capability is vital for studying cellular interactions and dynamics, but multiplexed stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) imaging with reversible photocontrol is elusive. Here, the authors report SRS microscopy with Carbow-switch enabling multiplexed SRS imaging and tracking in live cells with reversible photocontrol and high spatiotemporal selectivity.
- Yueli Yang
- , Xueyang Bai
- & Fanghao Hu
-
Article
| Open Access In-section Click-iT detection and super-resolution CLEM analysis of nucleolar ultrastructure and replication in plants
In-section Click-iT detection and super-resolution CLEM analysis of nucleolar ultrastructure and replication in plants
Application of correlative light and electron microscopy (CLEM) in plants remains challenging. Here, the authors use Click-iT chemistry as a tool for CLEM, due to its unique properties in resin permeability and super-resolution microscopy. They use this approach to study cellular physiology in Arabidopsis.
- Michal Franek
- , Lenka Koptašíková
- & Jíří Fajkus
-
Article
| Open Access Atomically precise engineering of spin–orbit polarons in a kagome magnetic Weyl semimetal
Atomically precise engineering of spin–orbit polarons in a kagome magnetic Weyl semimetal
Defect engineering in topological materials is a frontier that promises tunable physical properties with rich applications. Here, the authors demonstrate the atomically precise engineering of vacancies in a topological semimetal, which locally tunes the magnetic properties.
- Hui Chen
- , Yuqing Xing
- & Hong-Jun Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Fast topographic optical imaging using encoded search focal scan
Fast topographic optical imaging using encoded search focal scan
Quickly acquiring topographical information from a sample remains a challenge in optics. Here, the authors introduce encoded search focal scan, a technique for sub-micrometric imaging of tens of topographies per second based on collecting a reduced set of images.
- Narcís Vilar
- , Roger Artigas
- & Guillem Carles
-
Article
| Open Access Spectral-temporal-spatial customization via modulating multimodal nonlinear pulse propagation
Spectral-temporal-spatial customization via modulating multimodal nonlinear pulse propagation
The authors introduce a method for modulating the multimodal nonlinear pulse propagation in fibers by controlled bending, achieving a tunable broadband high-peak-power femtosecond light source that could empower nonlinear imaging and spectroscopy.
- Tong Qiu
- , Honghao Cao
- & Sixian You
-
Article
| Open Access Light-field flow cytometry for high-resolution, volumetric and multiparametric 3D single-cell analysis
Light-field flow cytometry for high-resolution, volumetric and multiparametric 3D single-cell analysis
Current imaging flow cytometry approaches remain limited in their ability to reveal subcellular information with high-resolution and instrumental simplicity. Here, the authors present a light-field flow cytometer capable of high-content, multi-color imaging of cells with high-resolution in 3D.
- Xuanwen Hua
- , Keyi Han
- & Shu Jia
-
Article
| Open Access High-density volumetric super-resolution microscopy
High-density volumetric super-resolution microscopy
Current approaches for volumetric super-resolution microscopy can yield large and complex PSF spatial footprints. Here, the authors show a super-resolution microscopy approach using a hexagonal microlens array, which offers speed improvements in volumetric imaging compared to other single-molecule methods.
- Sam Daly
- , João Ferreira Fernandes
- & Steven F. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access SEMORE: SEgmentation and MORphological fingErprinting by machine learning automates super-resolution data analysis
SEMORE: SEgmentation and MORphological fingErprinting by machine learning automates super-resolution data analysis
There is a lack of universal tools to analyse protein assemblies and quantify underlying structures in single-molecule localization microscopy. Here, the authors present SEMORE, a semi-automatic machine learning framework for system- and input-dependent analysis of super-resolution data.
- Steen W. B. Bender
- , Marcus W. Dreisler
- & Nikos S. Hatzakis
-
Article
| Open Access Swept coded aperture real-time femtophotography
Swept coded aperture real-time femtophotography
The researchers showcase swept-coded aperture real-time femtophotography—an all-optical single-shot computational imaging modality at up to 156.3 trillion frames per second—video-records transient absorption in a semiconductor and ultrafast demagnetization of a metal alloy.
- Jingdan Liu
- , Miguel Marquez
- & Jinyang Liang
-
Article
| Open Access Open-source microscope add-on for structured illumination microscopy
Open-source microscope add-on for structured illumination microscopy
Researchers developed an open-hardware structured illumination microscopy add-on. This affordable upgrade provides super-resolution capabilities for normal optical microscopes. Detailed instructions enable easy reproduction to help democratize advanced microscopy.
- Mélanie T. M. Hannebelle
- , Esther Raeth
- & Georg E. Fantner
-
Article
| Open Access Rejuvenation as the origin of planar defects in the CrCoNi medium entropy alloy
Rejuvenation as the origin of planar defects in the CrCoNi medium entropy alloy
High and medium-entropy alloys have shown excellent mechanical performance, yet the role of short-range order (SRO) on these properties has been unclear. Here, the authors demonstrate that the reduction of SRO by deformation leads to rejuvenation, explaining their remarkable damage tolerance.
- Yang Yang
- , Sheng Yin
- & Andrew M. Minor
-
Article
| Open Access Mesoscopic calcium imaging in a head-unrestrained male non-human primate using a lensless microscope
Mesoscopic calcium imaging in a head-unrestrained male non-human primate using a lensless microscope
Current systems for imaging calcium dynamics in the brains of non-human primates require the animal’s movement to be restricted. Here, the authors demonstrate a mesoscale calcium imaging device in a freely moving non-human primate which features a 20 mm2 field of view.
- Jimin Wu
- , Yuzhi Chen
- & Jacob T. Robinson
-
Article
| Open Access Ultracompact mirror device for forming 20-nm achromatic soft-X-ray focus toward multimodal and multicolor nanoanalyses
Ultracompact mirror device for forming 20-nm achromatic soft-X-ray focus toward multimodal and multicolor nanoanalyses
Optics used for X-ray focusing suffer from wavelength dependent effects like chromatic aberration. Here the authors demonstrate fabrication of a ultracompact Kirkpatrick-Baez mirror and use it for achromatic focusing to 20 nm spot for the soft X-ray at 2-keV photon energy.
- Takenori Shimamura
- , Yoko Takeo
- & Hidekazu Mimura
-
Article
| Open Access N2FXm, a method for joint nuclear and cytoplasmic volume measurements, unravels the osmo-mechanical regulation of nuclear volume in mammalian cells
N2FXm, a method for joint nuclear and cytoplasmic volume measurements, unravels the osmo-mechanical regulation of nuclear volume in mammalian cells
Cells exert tight control over the size of their compartments in order to regulate their function. Here, nuclear fluorescence exclusion microscopy is able to measure the nuclear and cytoplasmic volumes of live cells in a high-throughput way.
- Fabrizio A. Pennacchio
- , Alessandro Poli
- & Paolo Maiuri
-
Article
| Open Access Geometric transformation adaptive optics (GTAO) for volumetric deep brain imaging through gradient-index lenses
Geometric transformation adaptive optics (GTAO) for volumetric deep brain imaging through gradient-index lenses
The GRIN lenses widely used for deep brain functional imaging suffer from a small measurement field of view due to strong fourth-order astigmatism. Here the authors report Geometric Transformation Adaptive Optics (GTAO) that corrects field-dependent astigmatism and enables large-volume in vivo imaging of deep mouse brain through 0.5 mm GRIN lenses.
- Yuting Li
- , Zongyue Cheng
- & Meng Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasmall single-layered NbSe2 nanotubes flattened within a chemical-driven self-pressurized carbon nanotube
Ultrasmall single-layered NbSe2 nanotubes flattened within a chemical-driven self-pressurized carbon nanotube
The chemical-driven large pressure arising inside carbon nanotubes creates energetically stable, flattened, single-layered NbSe2 nanotubes with enhanced intermolecular electronic interactions, suggesting a chemical approach to produce materials with tailored structural and electronic properties.
- Yaxin Jiang
- , Hao Xiong
- & Fei Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of strong surface reconstruction in partially reduced nickelate films
Direct observation of strong surface reconstruction in partially reduced nickelate films
Surface polarity affects the electronic and structural properties of oxide thin films through electrostatic effects, which is challenging to control. Here, the authors probe the tunable surface polarity at the atomic scale.
- Chao Yang
- , Rebecca Pons
- & Peter A. van Aken
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell mapping of lipid metabolites using an infrared probe in human-derived model systems
Single-cell mapping of lipid metabolites using an infrared probe in human-derived model systems
Current metabolic imaging studies are limited by low resolution and low specificity. Here, the authors present a single-cell metabolic imaging platform to monitor lipid metabolism with high specificity in various human-derived 2D and 3D culture systems.
- Yeran Bai
- , Carolina M. Camargo
- & Kenneth S. Kosik
-
Article
| Open Access Exact inversion of partially coherent dynamical electron scattering for picometric structure retrieval
Exact inversion of partially coherent dynamical electron scattering for picometric structure retrieval
By combining real and diffraction space data recorded in electron microscopes, ptychography retrieves specimen details with super-resolution. Here, the inverse problem is solved in the presence of thermal diffuse scattering and applied to measure ferroelectric displacements with picometer precision.
- Benedikt Diederichs
- , Ziria Herdegen
- & Knut Müller-Caspary
-
Article
| Open Access AI-driven projection tomography with multicore fibre-optic cell rotation
AI-driven projection tomography with multicore fibre-optic cell rotation
Conventional optical tomography can have disadvantages, including anisotropic resolution and incomplete imaging of cellular structures. Here, the authors propose an AI-driven 3D cell imaging system with a cell rotator, which offers improved resolution and automated processing.
- Jiawei Sun
- , Bin Yang
- & Juergen W. Czarske
-
Article
| Open Access Voltage sensors of a Na+ channel dissociate from the pore domain and form inter-channel dimers in the resting state
Voltage sensors of a Na+ channel dissociate from the pore domain and form inter-channel dimers in the resting state
It is believed that voltage sensor domains (VSD) of voltage-gated Na+ channels are always attached to the channel. Here, authors find that VSDs detach from the channel to form inter-channel dimers.
- Ayumi Sumino
- , Takashi Sumikama
- & Katsumasa Irie
-
Article
| Open Access Atypical flagella assembly and haploid genome coiling during male gamete formation in Plasmodium
Atypical flagella assembly and haploid genome coiling during male gamete formation in Plasmodium
Gametogenesis is critical for sexual reproduction. Using volume electron microscopy, Hair et al report the structural organisation of the haploid nucleus coiled around the axoneme of the Plasmodium berghei male microgamete.
- Molly Hair
- , Flávia Moreira-Leite
- & Sue Vaughan
-
Article
| Open Access Single-photon microscopy to study biomolecular condensates
Single-photon microscopy to study biomolecular condensates
The wide variety of cellular processes involving biomolecular condensation makes their quantification a challenging task. Here, the authors present an integrated platform based on single-photon microscopy to study complex biomolecular processes.
- Eleonora Perego
- , Sabrina Zappone
- & Giuseppe Vicidomini
-
Article
| Open Access Hot luminescence from single-molecule chromophores electrically and mechanically self-decoupled by tripodal scaffolds
Hot luminescence from single-molecule chromophores electrically and mechanically self-decoupled by tripodal scaffolds
A fundamental challenge for molecular electronics is the change in photophysical properties of molecules upon direct electrical contact. Here, the authors observe hot luminescence emitted by single-molecule chromophores that are electrically and mechanically self-decoupled by a tripodal scaffold.
- Vibhuti Rai
- , Nico Balzer
- & Michal Valášek
-
Article
| Open Access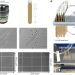 ComplexEye: a multi-lens array microscope for high-throughput embedded immune cell migration analysis
ComplexEye: a multi-lens array microscope for high-throughput embedded immune cell migration analysis
Video microscopy is key in studying cell migration, but accomplishing this in a high-throughput manner is still challenging. Here, the authors present an array microscope that can track the movements of thousands of individual cells simultaneously, and that can be used for drug screening studies.
- Zülal Cibir
- , Jacqueline Hassel
- & Matthias Gunzer
-
Article
| Open Access A minority of final stacks yields superior amplitude in single-particle cryo-EM
A minority of final stacks yields superior amplitude in single-particle cryo-EM
Here the authors develop an iterative particle sieving method called CryoSieve, demonstrating this method outperforms other cryo-EM particle sorting algorithms to reveal that most particles are unnecessary in final stacks.
- Jianying Zhu
- , Qi Zhang
- & Chenglong Bao
-
Article
| Open Access In-plane charged antiphase boundary and 180° domain wall in a ferroelectric film
In-plane charged antiphase boundary and 180° domain wall in a ferroelectric film
The correlation between charged and antiphase states in BiFeO3 remain elusive. Here, the authors report a fabrication of in-plane charged antiphase boundaries in BiFeO3 thin films, revealing the atomic bonding configurations and atomically sharp 180° polarization reversal of such boundaries.
- Xiangbin Cai
- , Chao Chen
- & Deyang Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Incommensurate grain-boundary atomic structure
Incommensurate grain-boundary atomic structure
Grain boundary atomic structures of crystalline materials have long been believed to be commensurate with the crystal periodicity of the adjacent crystals. Here, the authors discover an incommensurate grain boundary structure based on direct observations and theoretical calculations.
- Takehito Seki
- , Toshihiro Futazuka
- & Naoya Shibata
-
Article
| Open Access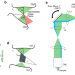 Blazed oblique plane microscopy reveals scale-invariant inference of brain-wide population activity
Blazed oblique plane microscopy reveals scale-invariant inference of brain-wide population activity
Recording neuronal activity at cellular resolution across an entire adult vertebrate brain is challenging. Here, the authors develop a blazed oblique plane microscope to perform brain-wide activity measurements in an adult vertebrate at high cellular resolution.
- Maximilian Hoffmann
- , Jörg Henninger
- & Benjamin Judkewitz
-
Article
| Open Access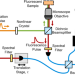 Fluorescence lifetime Hong-Ou-Mandel sensing
Fluorescence lifetime Hong-Ou-Mandel sensing
Standard techniques for Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy are limited by the electronics to 100’s of picoseconds time resolution. Here, the authors show how to use two-photon interference to perform fluorescence lifetime sensing with picosecond-scale resolution.
- Ashley Lyons
- , Vytautas Zickus
- & Daniele Faccio
-
Article
| Open Access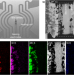 Operando analysis of a solid oxide fuel cell by environmental transmission electron microscopy
Operando analysis of a solid oxide fuel cell by environmental transmission electron microscopy
By contacting a solid oxide fuel cell to a microelectromechanical system inside an environmental electron microscope, the authors establish links between environmental conditions (gas atmosphere, temperature), cell voltage and atomic-scale structure.
- Q. Jeangros
- , M. Bugnet
- & M. Duchamp
-
Article
| Open Access Defining a core configuration for human centromeres during mitosis
Defining a core configuration for human centromeres during mitosis
The detailed 3D organization of human centromere components is unknown. Here, the authors use super-resolution microscopy to present a working model for a common core centromere structure.
- Ayantika Sen Gupta
- , Chris Seidel
- & Jennifer L. Gerton
-
Article
| Open Access A fungal plant pathogen discovered in the Devonian Rhynie Chert
A fungal plant pathogen discovered in the Devonian Rhynie Chert
Here, the authors describe a pathogenic fungus from a 400-million-year-old fossil plant from the Devonian Rhynie Chert in Scotland. They use advanced imaging methods to determine that the fungus belongs to the sac fungi, the most diverse group of Fungi today.
- Christine Strullu-Derrien
- , Tomasz Goral
- & David L. Hawksworth
-
Article
| Open Access iU-ExM: nanoscopy of organelles and tissues with iterative ultrastructure expansion microscopy
iU-ExM: nanoscopy of organelles and tissues with iterative ultrastructure expansion microscopy
Current expansion microscopy approaches need further optimization to achieve the precision of nanoscopy techniques. Here, the authors develop an iterative ultrastructure expansion microscopy (iU-ExM) approach that achieves SMLM-level resolution.
- Vincent Louvel
- , Romuald Haase
- & Paul Guichard
-
Article
| Open Access Solving complex nanostructures with ptychographic atomic electron tomography
Solving complex nanostructures with ptychographic atomic electron tomography
Transmission electron microscopy is essential for three-dimensional atomic structure determination, but solving complex heterogeneous structures containing light elements remains challenging. Here, authors solve a complex nanostructure using atomic resolution ptychographic electron tomography.
- Philipp M. Pelz
- , Sinéad M. Griffin
- & Colin Ophus
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-level polarization in electric fields of defects for electrocatalysis
Atomic-level polarization in electric fields of defects for electrocatalysis
The visible evidence bridging atomic defects with catalytic properties has been scarcely explored. Using differential phase contrast technology, this work discloses the existence of a polarized electric field surrounding the antisite defects of a monolayer MoS2 material and its correlation to its electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution property.
- Jie Xu
- , Xiong-Xiong Xue
- & Jun Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Label-free identification of protein aggregates using deep learning
Label-free identification of protein aggregates using deep learning
The authors use deep learning to detect and segment unlabeled and unaltered protein aggregates in living cells from transmitted-light images. The method provides a way to quantitatively study protein aggregation dynamics in a simple, fast and accurate way.
- Khalid A. Ibrahim
- , Kristin S. Grußmayer
- & Aleksandra Radenovic
-
Article
| Open Access 3D reconstructions of parasite development and the intracellular niche of the microsporidian pathogen Encephalitozoon intestinalis
3D reconstructions of parasite development and the intracellular niche of the microsporidian pathogen Encephalitozoon intestinalis
Microsporidia are obligate intracellular parasitic fungi that can cause opportunistic infections in humans. Here, Antao et al. investigate the intracellular life cycle of human-infecting Encephalitozoon intestinalis using serial block-face scanning electron microscopy to characterize parasite organelle development and host-cell mitochondrial remodeling.
- Noelle V. Antao
- , Cherry Lam
- & Gira Bhabha
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic scale volume and grain boundary diffusion elucidated by in situ STEM
Atomic scale volume and grain boundary diffusion elucidated by in situ STEM
Here authors explore volume diffusion within crystalline solids at the atomic scale. They use high resolution microscopy techniques to provide insights into the movement of individual atoms within a crystal lattice, revealing the intricate dynamics of volume diffusion processes.
- Peter Schweizer
- , Amit Sharma
- & Xavier Maeder
-
Article
| Open Access Topotactically transformable antiphase boundaries with enhanced ionic conductivity
Topotactically transformable antiphase boundaries with enhanced ionic conductivity
Antiphase boundaries (APBs) have been considered major obstacles to optimizing the ionic conductivity of conductors. Here authors reveal that ionic conductivity can be enhanced through engineering APBs by topotactical transformation at the atomic scale.
- Kun Xu
- , Shih-Wei Hung
- & Jing Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Long-term cargo tracking reveals intricate trafficking through active cytoskeletal networks in the crowded cellular environment
Long-term cargo tracking reveals intricate trafficking through active cytoskeletal networks in the crowded cellular environment
Leveraging a label-free interferometric scattering microscope, scientists tracked numerous cargos within a crowded cellular environment. Intriguingly, cells employ effective strategies echoing human transportation systems to manage such transportation hurdles.
- Jin-Sung Park
- , Il-Buem Lee
- & Minhaeng Cho
-
Article
| Open Access CLOOME: contrastive learning unlocks bioimaging databases for queries with chemical structures
CLOOME: contrastive learning unlocks bioimaging databases for queries with chemical structures
Artificial intelligence can assist in obtaining knowledge from bioimaging data, but need human annotation. Here the authors use multimodal contrastive learning to link chemical structures and cell phenotypes, which can lead to foundation models for microscopy images.
- Ana Sanchez-Fernandez
- , Elisabeth Rumetshofer
- & Günter Klambauer
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing ultrafast photothermal dynamics with decoupled optical force nanoscopy
Visualizing ultrafast photothermal dynamics with decoupled optical force nanoscopy
Diving deep into material insights, the authors introduce the ‘Decoupled Optical Force Nanoscopy’. This innovation uncovers the physical origins of light induced forces and captures dynamic thermal details with unparalleled nanometer precision.
- Hanwei Wang
- , Sean M. Meyer
- & Yang Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Multipole engineering by displacement resonance: a new degree of freedom of Mie resonance
Multipole engineering by displacement resonance: a new degree of freedom of Mie resonance
Mie resonances are typically manipulated through varying nanostructure shape/size. Here, authors found that Gaussian beam displacement excites higher-order multipolar modes, not accessible by plane wave, featuring maximal linear and nonlinear scattering efficiency when the focus is misaligned.
- Yu-Lung Tang
- , Te-Hsin Yen
- & Shi-Wei Chu
-
Article
| Open Access In situ imaging of the atomic phase transition dynamics in metal halide perovskites
In situ imaging of the atomic phase transition dynamics in metal halide perovskites
Phase transition dynamics are an important concern in the wide applications of metal halide perovskites. Here authors apply low-dose imaging technique to reveal the phase transition dynamics of CsPbI3 during in-situ heating process with atomic resolution.
- Mengmeng Ma
- , Xuliang Zhang
- & Boyuan Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Tracing multiple scattering trajectories for deep optical imaging in scattering media
Tracing multiple scattering trajectories for deep optical imaging in scattering media
Deep imaging in complex scattering media is hindered by multiple light scattering. Here, the authors proposed a method to trace multiple scattering trajectories in situ using a recorded reflection matrix and achieved enhanced imaging depth by converting these multiple scattering to signal waves.
- Sungsam Kang
- , Yongwoo Kwon
- & Wonshik Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical organization and assembly of the archaeal cell sheath from an amyloid-like protein
Hierarchical organization and assembly of the archaeal cell sheath from an amyloid-like protein
Cellular cryoET reveals how an amyloid-like protein of the prototypical archaeon, Methanospirillum hungatei, oligomerizes into a ring containing a giant 2700-strand β sheet, and how rings stack into hoops and into the cylindrical sheath of the cell.
- Hui Wang
- , Jiayan Zhang
- & Z. Hong Zhou
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Atomic force microscopy
- Ca2+ imaging
- Confocal microscopy
- Cryoelectron microscopy
- Interference microscopy
- Light-sheet microscopy
- Multiphoton microscopy
- Phase-contrast microscopy
- Polarization microscopy
- Scanning electron microscopy
- Scanning probe microscopy
- Super-resolution microscopy
- Total internal reflection microscopy
- Transmission electron microscopy
- Transmission light microscopy
- Wide-field fluorescence microscopy

 Atomic-scale observation of localized phonons at FeSe/SrTiO3 interface
Atomic-scale observation of localized phonons at FeSe/SrTiO3 interface