Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Topotactically transformable antiphase boundaries with enhanced ionic conductivity
Topotactically transformable antiphase boundaries with enhanced ionic conductivity
Antiphase boundaries (APBs) have been considered major obstacles to optimizing the ionic conductivity of conductors. Here authors reveal that ionic conductivity can be enhanced through engineering APBs by topotactical transformation at the atomic scale.
- Kun Xu
- , Shih-Wei Hung
- & Jing Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Lead-free Zr-doped ceria ceramics with low permittivity displaying giant electrostriction
Lead-free Zr-doped ceria ceramics with low permittivity displaying giant electrostriction
Electrostrictors are materials that develop mechanical strain proportional to the square of the applied electric field. Here authors report. Zr-doped-Ceria as a new lead-free electrostrictive material with a similar electrostriction coefficient to the best electrostrictor material currently in use.
- Maxim Varenik
- , Boyuan Xu
- & Igor Lubomirsky
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing ultrafast photothermal dynamics with decoupled optical force nanoscopy
Visualizing ultrafast photothermal dynamics with decoupled optical force nanoscopy
Diving deep into material insights, the authors introduce the ‘Decoupled Optical Force Nanoscopy’. This innovation uncovers the physical origins of light induced forces and captures dynamic thermal details with unparalleled nanometer precision.
- Hanwei Wang
- , Sean M. Meyer
- & Yang Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access High-speed mapping of surface charge dynamics using sparse scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy
High-speed mapping of surface charge dynamics using sparse scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy
Dynamic mapping of charge motion across multiple length- and timescales is essential for understanding a variety of phenomena. Here, the authors introduce sparse scanning KPFM, which enables fast nanoscale charge mapping at 3 frames per second to track ion migration.
- Marti Checa
- , Addis S. Fuhr
- & Liam Collins
-
Article
| Open Access In situ imaging of the atomic phase transition dynamics in metal halide perovskites
In situ imaging of the atomic phase transition dynamics in metal halide perovskites
Phase transition dynamics are an important concern in the wide applications of metal halide perovskites. Here authors apply low-dose imaging technique to reveal the phase transition dynamics of CsPbI3 during in-situ heating process with atomic resolution.
- Mengmeng Ma
- , Xuliang Zhang
- & Boyuan Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning at the edge enables real-time streaming ptychographic imaging
Deep learning at the edge enables real-time streaming ptychographic imaging
Next-generation light sources and fast detectors enable unparalleled materials characterization, but increased data rates and compute needs preclude real-time analysis. Here, Babu et al. leverage high-performance computing and AI@Edge to achieve real-time, low-dose imaging on streaming data at 2 KHz.
- Anakha V. Babu
- , Tao Zhou
- & Mathew J. Cherukara
-
Article
| Open Access A general large-scale synthesis approach for crystalline porous materials
A general large-scale synthesis approach for crystalline porous materials
The large-scale production of crystalline porous materials remains a challenge. Here the authors report a general approach of high-pressure homogenization that can realize large-scale synthesis of crystalline porous materials under benign conditions.
- Xiongli Liu
- , An Wang
- & Shengqian Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Defects and nanostrain gradients control phase transition mechanisms in single crystal high-voltage lithium spinel
Defects and nanostrain gradients control phase transition mechanisms in single crystal high-voltage lithium spinel
Lithiation dynamics and phase transition mechanisms in battery materials remain poorly understood. Here authors use operando X-ray nanodiffraction microscopy to reveal how domains relate to defects and how cycling affects the lattice domain reorientation in LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 single crystals.
- Isaac Martens
- , Nikita Vostrov
- & Tobias U. Schulli
-
Article
| Open Access Autonomous and dynamic precursor selection for solid-state materials synthesis
Autonomous and dynamic precursor selection for solid-state materials synthesis
Solid-state materials synthesis relies on effective precursor design. Here, the authors introduce an algorithm that combines ab-initio computations with insights gained from experimental outcomes to efficiently optimize the selection of precursors.
- Nathan J. Szymanski
- , Pragnay Nevatia
- & Gerbrand Ceder
-
Article
| Open Access SEI growth on Lithium metal anodes in solid-state batteries quantified with coulometric titration time analysis
SEI growth on Lithium metal anodes in solid-state batteries quantified with coulometric titration time analysis
In lithium-metal batteries, it is vital to quantify electrolyte side reactions occurring at the metal anode surface. Here, the authors introduce an electrochemical technique, using a series of small-step lithium deposition followed by open circuit voltage analysis, to accurately measure these reactions.
- Burak Aktekin
- , Luise M. Riegger
- & Jürgen Janek
-
Article
| Open Access Additive manufacturing of alloys with programmable microstructure and properties
Additive manufacturing of alloys with programmable microstructure and properties
The traditional way of beating metals to improve their properties is not practical to 3D printed parts with intricate geometry. Here, the authors demonstrate how to program microstructural modifications of metals site-specifically during 3D printing to tune their properties.
- Shubo Gao
- , Zhi Li
- & Matteo Seita
-
Article
| Open Access Elucidating the active phases of CoOx films on Au(111) in the CO oxidation reaction
Elucidating the active phases of CoOx films on Au(111) in the CO oxidation reaction
Supported CoOx catalysts display higher reactivities towards CO oxidation, yet, corresponding catalytically active phases are still unclear, especially under reaction conditions. Here, by means of in-situ APXPS and ResPES, the authors demonstrate that the topographic restructuring and chemical restructuring occur on these CoOx working catalysts, and also highlight the unique catalytic properties of Co3+ sites.
- Hao Chen
- , Lorenz J. Falling
- & Miquel Salmeron
-
Article
| Open Access The practice of reaction window in an electrocatalytic on-chip microcell
The practice of reaction window in an electrocatalytic on-chip microcell
Here, the authors investigate frequently observed variations in data between different electrochemical cells using in-situ electronic/electrochemical measurements, developing a vertical microcell strategy to eliminate the conductance issue and enhance measurement reproducibility.
- Hang Xia
- , Xiaoru Sang
- & Yongmin He
-
Article
| Open Access Realistic prediction and engineering of high-Q modes to implement stable Fano resonances in acoustic devices
Realistic prediction and engineering of high-Q modes to implement stable Fano resonances in acoustic devices
The authors demonstrate that laser Doppler vibrometer measurements are a powerful tool for predicting the maximum pressure enhancement of high-Q modes. The results presented enable future applications of acoustic BICs by filling the missing data gap on field enhancement.
- Felix Kronowetter
- , Marcus Maeder
- & Steffen Marburg
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial photosynthetic cells with biotic–abiotic hybrid energy modules for customized CO2 conversion
Artificial photosynthetic cells with biotic–abiotic hybrid energy modules for customized CO2 conversion
The design of programmable artificial photosynthetic cells is hindered by the requirement for cofactor generation for the biocatalytic module. Here, the authors report on the design of artificial photosynthetic cells using biotic–abiotic thylakoid–CdTe as hybrid energy modules, which enhance the regeneration of NADPH, NADH and ATP cofactors without external supplements by promoting proton-coupled electron transfer.
- Feng Gao
- , Guangyu Liu
- & Yujie Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access Lorentz microscopy of optical fields
Lorentz microscopy of optical fields
Electron holography and microscopy have long been used to map static electric and magnetic fields. Here, authors establish Lorentz Microscopy of Optical Fields, a new technique that uses the deflection and interference of an electron beam to obtain phase-resolved images of nanoscale optical fields.
- John H. Gaida
- , Hugo Lourenço-Martins
- & Claus Ropers
-
Article
| Open Access Remote inspection of adversary-controlled environments
Remote inspection of adversary-controlled environments
Physical unclonable functions (PUFs) normally ensure authentication of small physical objects. Here, instead, the authors observe that also rooms and buildings can serve as PUFs. They apply this insight to monitor the integrity of enclosed environments, such as art galleries, bank vaults, or data centers.
- Johannes Tobisch
- , Sébastien Philippe
- & Ulrich Rührmair
-
Article
| Open Access Material-agnostic machine learning approach enables high relative density in powder bed fusion products
Material-agnostic machine learning approach enables high relative density in powder bed fusion products
Exploring laser powder bed fusion in manufacturing, the authors demonstrate a machine learning-based method to optimize processing conditions achieving materials with relative density greater than 98% and experimentally verify its generality for multiple distinct powder materials.
- Jaemin Wang
- , Sang Guk Jeong
- & Byeong-Joo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative three-dimensional local order analysis of nanomaterials through electron diffraction
Quantitative three-dimensional local order analysis of nanomaterials through electron diffraction
Correlated disorder can lead to phenomena that are inaccessible to ordered structures. Here the authors show that local order principles can be directly derived from the three-dimensional difference pair distribution function based on the single crystal diffuse scattering in 3D electron diffraction data from nanometre sized crystals.
- Ella Mara Schmidt
- , Paul Benjamin Klar
- & Lukas Palatinus
-
Article
| Open Access Fast and versatile electrostatic disc microprinting for piezoelectric elements
Fast and versatile electrostatic disc microprinting for piezoelectric elements
In this work, authors demonstrate a fast and versatile microprinting technique to produce high-performance and customizable piezoelectric elements by employing a conductive spiny disc to electrostatically trigger instability to the liquid-air interface of the ink.
- Xuemu Li
- , Zhuomin Zhang
- & Zhengbao Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Fully automatic transfer and measurement system for structural superlubric materials
Fully automatic transfer and measurement system for structural superlubric materials
A critical step to enable practical structural superlubricity (SSL) applications is to enable high throughput to both fabrication and performance evaluation. Here, the authors demonstrate an automated system for efficient and multiple SSL materials transfer and tribological measurement.
- Li Chen
- , Cong Lin
- & Ming Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal dissolution by particle detachment
Crystal dissolution by particle detachment
Crystal dissolution has been predominately viewed as a process of ion-by-ion detachment into a surrounding solvent. Here, the authors report an alternative mechanism of dissolution by particle detachment.
- Guomin Zhu
- , Benjamin A. Legg
- & James J. De Yoreo
-
Article
| Open Access Joining of metallic glasses in liquid via ultrasonic vibrations
Joining of metallic glasses in liquid via ultrasonic vibrations
Under-liquid joining of metals has far-reaching implications for energy storage, space exploration, offshore mining and defense. Here, the authors report an alternative method to join metallic glasses firmly under water, seawater, flammable alcohol and even cryogenic liquid nitrogen.
- Luyao Li
- , Xin Li
- & Jiang Ma
-
Article
| Open Access In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors
In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors
Nanodiamonds containing NV centers are promising electron paramagnetic resonance sensors, however applications are hindered by their random orientation. Qin et al. propose a new protocol that makes the technique insensitive to the sensor’s orientation and present a proof-of-principle in situ demonstration.
- Zhuoyang Qin
- , Zhecheng Wang
- & Jiangfeng Du
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of the noncatalytic oxidation of soot using in situ transmission electron microscopy
Mechanism of the noncatalytic oxidation of soot using in situ transmission electron microscopy
In this work, authors investigate mechanisms of noncatalytic soot oxidation and establish models applicable to different types of soot based on the particles oxidation behaviour using in-situ transmission electron microscopy.
- Ming Gao
- , Yongjun Jang
- & Fuchen Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Inverse design of chiral functional films by a robotic AI-guided system
Inverse design of chiral functional films by a robotic AI-guided system
Chiral materials with strong and tunable chiroptical activities are highly desirable. Here, the authors employ an AI-guided robotic platform to fully execute a cyclic process to perform inverse design and fabricate chiral films with target chiroptical performance.
- Yifan Xie
- , Shuo Feng
- & Gang Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing the aging process of solid electrolyte interphase on SiOx anode
Revealing the aging process of solid electrolyte interphase on SiOx anode
Observing the evolution of the solid electrolyte interphase on SiOx-based electrodes in Li-ion batteries is challenging. Here, authors use three-dimensional tomography to visualize the growth of the interphase on single SiOx particles and propose a mechanical confinement strategy to prevent aging.
- Guoyu Qian
- , Yiwei Li
- & Feng Pan
-
Article
| Open Access Mending cracks atom-by-atom in rutile TiO2 with electron beam radiolysis
Mending cracks atom-by-atom in rutile TiO2 with electron beam radiolysis
Radiolysis is known for damaging crystals. Here, using STEM, researchers observed radiolysis-driven bond-breakage, atomic movements, & crystal restructuring in rutile TiO2, and proposed a “2-step rolling” model of building blocks. These results open possibilities for constructive use of radiolysis.
- Silu Guo
- , Hwanhui Yun
- & K. Andre Mkhoyan
-
Article
| Open Access Reassessing chain tilt in the lamellar crystals of polyethylene
Reassessing chain tilt in the lamellar crystals of polyethylene
The mechanical and thermal properties of semicrystalline polymers are governed by the hierarchical structure comprising lamellar crystals, but the tilt angles of the molecular chains in the lamellae and their origin remains controversial. Here, the authors report a direct determination of molecular chain orientation in the lamellar crystals of high-density polyethylene using electron-diffraction based imaging with nanometre-scale positional resolution.
- Shusuke Kanomi
- , Hironori Marubayashi
- & Hiroshi Jinnai
-
Article
| Open Access Metal-organic framework template-guided electrochemical lithography on substrates for SERS sensing applications
Metal-organic framework template-guided electrochemical lithography on substrates for SERS sensing applications
Templating method holds great promise for fabricating surface nanopatterns. Here authors present a guiding growth mode using metal-organic framework microparticles as templates during metal electrodeposition, where metals exclusively grow underneath the microparticles.
- Youyou Lu
- , Xuan Zhang
- & Shikuan Yang
-
Article
| Open Access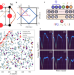 Capturing dynamical correlations using implicit neural representations
Capturing dynamical correlations using implicit neural representations
Analysis of experimental data in condensed matter is often challenging due to system complexity and slow character of physical simulations. The authors propose a framework that combines machine learning with theoretical calculations to enable real-time analysis for electron, neutron, and x-ray spectroscopies.
- Sathya R. Chitturi
- , Zhurun Ji
- & Joshua J. Turner
-
Article
| Open Access Probing three-dimensional mesoscopic interfacial structures in a single view using multibeam X-ray coherent surface scattering and holography imaging
Probing three-dimensional mesoscopic interfacial structures in a single view using multibeam X-ray coherent surface scattering and holography imaging
The authors observe X-ray coherent scattering speckles from substrate-supported planar patterns in grazing incidence reflection geometry, which constitutes hard X-ray holograms revealing three-dimensional high-resolution structural information in a single image.
- Miaoqi Chu
- , Zhang Jiang
- & Jin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access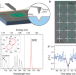 Photoluminescence imaging of single photon emitters within nanoscale strain profiles in monolayer WSe2
Photoluminescence imaging of single photon emitters within nanoscale strain profiles in monolayer WSe2
Here, the authors correlate the position and spectral emission properties of single photon emitters in monolayer WSe2 with the surrounding local strain potential by combining deep-subwavelength photoluminescence imaging and atomic force microscopy, providing insights on the microscopic mechanisms behind the formation of the quantum emitters.
- Artem N. Abramov
- , Igor Y. Chestnov
- & Vasily Kravtsov
-
Article
| Open Access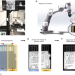 Robotic-OCT guided inspection and microsurgery of monolithic storage devices
Robotic-OCT guided inspection and microsurgery of monolithic storage devices
Demand for data recovery from monolithic storage devices is high but current methods are inefficient. Here, authors develop a robotic OCT-guided inspection and microsurgery method, minimizing damage to device and enhancing data recovery efficiency.
- Bin He
- , Yuxin Zhang
- & Ning Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of bifunctionality of carbons and metal atoms in catalyzed acetylene hydrochlorination
Evidence of bifunctionality of carbons and metal atoms in catalyzed acetylene hydrochlorination
Carbon is a key support for metal-catalyzed acetylene hydrochlorination to vinyl chloride but its role remains elusive. Here, the authors, by means of operando spectroscopy, demonstrate the co-catalytic function of neighboring carbon and isolated metal atoms, constituting the active ensemble.
- Vera Giulimondi
- , Andrea Ruiz-Ferrando
- & Javier Pérez-Ramírez
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration of an AI-driven workflow for autonomous high-resolution scanning microscopy
Demonstration of an AI-driven workflow for autonomous high-resolution scanning microscopy
Modern microscopes can image a sample with sub-Angstrom and sub-picosecond resolutions, but this often requires analysis of tremendously large datasets. Here, the authors demonstrate that an autonomous experiment can yield over a 70% reduction in dataset size while still producing high-fidelity images of the sample.
- Saugat Kandel
- , Tao Zhou
- & Mathew J. Cherukara
-
Comment
| Open Access Guidelines for measuring and reporting particle removal efficiency in fibrous media
Guidelines for measuring and reporting particle removal efficiency in fibrous media
Adopting standardized and reliable methodologies to accurately measure particle removal efficiency when developing fibrous materials for controlling airborne contamination is crucial. Here, the authors recommend best practices for experimental assessments and reporting to ensure a reliable evaluation of new airborne particle filtration media and technologies.
- Paolo Tronville
- , Vincenzo Gentile
- & Jesus Marval
-
Article
| Open Access Unconventional specular optical rotation in the charge ordered state of Kagome metal CsV3Sb5
Unconventional specular optical rotation in the charge ordered state of Kagome metal CsV3Sb5
Kagome materials, such as CsV3Sb5, a rich array of correlated phase, including a time-reversal symmetry breaking phase, which could possibly be the result of loop currents. Attempts to verify this with magneto-optical measurements have yielded mixed results. Here, Farhang et al show that the magneto-optical signals are due to specular optical rotation. ‘
- Camron Farhang
- , Jingyuan Wang
- & Jing Xia
-
Article
| Open Access Drug classification with a spectral barcode obtained with a smartphone Raman spectrometer
Drug classification with a spectral barcode obtained with a smartphone Raman spectrometer
Smartphones are ubiquitous devices that have permeated into our daily life. Here, the authors demonstrate that a Smartphone Raman spectrometer can be used for drug classification by using a convolutional neural network to process its spectral barcode.
- Un Jeong Kim
- , Suyeon Lee
- & Hyuck Choo
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing intrinsic domains and fluctuations of moiré magnetism by a wide-field quantum microscope
Revealing intrinsic domains and fluctuations of moiré magnetism by a wide-field quantum microscope
By carefully inducing twists or lattice stacking offsets between two adjacent van der Waals crystals, a superlattice potential can be introduced. This Moire lattice offers an incredibly rich physics, ranging from superconductivity to exotic magnetism, depending on van der Waals materials in question. Here, Du et al. study the magnetic domains in twisted CrI3, and show that despite this domain structure, spin fluctuations are spatially homogenous.
- Mengqi Huang
- , Zeliang Sun
- & Chunhui Rita Du
-
Article
| Open Access Electron counting detectors in scanning transmission electron microscopy via hardware signal processing
Electron counting detectors in scanning transmission electron microscopy via hardware signal processing
Electron detectors used in electron microscope are often unable to provide quantified information without calibration. Here, by combining existing detectors with hardware signal processing, the authors demonstrated that the detectors can be run in an electron counting mode enabling imaging at faster speeds, at lower electron doses, and reduces the barrier to quantitative measurements.
- Jonathan J. P. Peters
- , Tiarnan Mullarkey
- & Lewys Jones
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneous magnetic resonance imaging of pH, perfusion and renal filtration using hyperpolarized 13C-labelled Z-OMPD
Simultaneous magnetic resonance imaging of pH, perfusion and renal filtration using hyperpolarized 13C-labelled Z-OMPD
pH alterations are a hallmark of many pathologies including cancer and kidney disease. Here the authors describe [1,5- 13 C2]Z-OMPD as a probe for hyperpolarized 13C-MRI with good pH sensitivity and hyperpolarization properties which combined with tailored MRI protocols allow sub-minute imaging of pH, renal perfusion and filtration simultaneously.
- Martin Grashei
- , Pascal Wodtke
- & Franz Schilling
-
Article
| Open Access Crackling noise microscopy
Crackling noise microscopy
The authors present crackling noise microscopy, a method for measurement of the crackling of individual nanoscale features based on AFM nanoindentation. They use it to investigate crackling noise and avalanches in the domains and domain walls of ferroelectric materials.
- Cam-Phu Thi Nguyen
- , Peggy Schoenherr
- & Jan Seidel
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-wideband optical coherence elastography from acoustic to ultrasonic frequencies
Ultra-wideband optical coherence elastography from acoustic to ultrasonic frequencies
Understanding the mechanical properties of materials is critical in many fields, from soft hydrogels to biological tissues, yet current measurement methods lack the spatial and time resolution to characterize samples with complex structures. Here, the authors show non-invasive elastography technique offering advancements in resolution, sensitivity, and measurement frequencies.
- Xu Feng
- , Guo-Yang Li
- & Seok-Hyun Yun
-
Article
| Open Access Operando neutron diffraction reveals mechanisms for controlled strain evolution in 3D printing
Operando neutron diffraction reveals mechanisms for controlled strain evolution in 3D printing
Residual stress affects most manufactured goods and is prevalent in casting, welding, and additive manufacturing. Here, the authors use operando neutron diffraction to elucidate mechanisms for lattice strain evolution during printing of a low-temperature transformation steel.
- A. Plotkowski
- , K. Saleeby
- & S. S. Babu
-
Article
| Open Access Metal 3D nanoprinting with coupled fields
Metal 3D nanoprinting with coupled fields
Manufacturing metallized arrays of 3D nanoarchitectures is generally limited by existing lithographic methods. Here, by manipulating applied electric and flow fields, authors demonstrate fast 3D nanoprinting of nanostructured arrays of multiple materials and geometries over millimetre-scale areas.
- Bingyan Liu
- , Shirong Liu
- & Jicheng Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Non-destructive erosive wear monitoring of multi-layer coatings using AI-enabled differential split ring resonator based system
Non-destructive erosive wear monitoring of multi-layer coatings using AI-enabled differential split ring resonator based system
Real-time monitoring of coatings erosive wear is critical to mitigate safety and financial concerns in many applications. Here, authors show a non-destructive inspection system with AI-enabled microwave resonators and a smart monitoring circuitry to identify and estimate wear depth and rate of eroded layers.
- Vishal Balasubramanian
- , Omid Niksan
- & Mohammad H. Zarifi
-
Article
| Open Access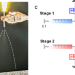 Efficient electrospray deposition of surfaces smaller than the spray plume
Efficient electrospray deposition of surfaces smaller than the spray plume
Electrospray deposition is a promising technique for depositing functional coatings at the micro-/nano-scale. Here, the authors establish the necessary conditions for high efficiency electrospray deposition of small targets, establishing promise as an alternative to other conformal coating methods.
- Sarah H. Park
- , Lin Lei
- & Jonathan P. Singer
-
Article
| Open Access Non-interferometric stand-alone single-shot holographic camera using reciprocal diffractive imaging
Non-interferometric stand-alone single-shot holographic camera using reciprocal diffractive imaging
An ideal holographic camera acquires depth information about an object by measuring the light field. Here, the authors present a reference-free single-shot holographic image sensor that freely focuses the image of real-world objects via reciprocal diffractive imaging.
- Jeonghun Oh
- , Herve Hugonnet
- & YongKeun Park

 Quantitative three-dimensional imaging of chemical short-range order via machine learning enhanced atom probe tomography
Quantitative three-dimensional imaging of chemical short-range order via machine learning enhanced atom probe tomography