Featured
-
-
Article |
 Giant spin Hall effect in graphene grown by chemical vapour deposition
Giant spin Hall effect in graphene grown by chemical vapour deposition
Manipulating spin currents in graphene by the spin–orbit interaction is important for many technological developments. Here, the authors show that the presence of residual metallic adatoms in chemical vapour deposition graphene enhances its spin–orbit coupling by three orders of magnitude.
- Jayakumar Balakrishnan
- , Gavin Kok Wai Koon
- & Barbaros Özyilmaz
-
Article
| Open Access Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy with single spin sensitivity
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy with single spin sensitivity
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is a powerful technique that can identify the presence of certain atoms in a sample by their magnetic properties. Müller et al.now take this concept to its ultimate limit by measuring individual nuclear spins near the surface of diamond.
- C. Müller
- , X. Kong
- & F. Jelezko
-
Article |
 The uncertainty principle enables non-classical dynamics in an interferometer
The uncertainty principle enables non-classical dynamics in an interferometer
In quantum mechanics, the uncertainty principle is considered a limiting factor forbidding a system from being in a state where all possible measurements have perfectly predictable outcomes. Here, Dahlsten et al. show its positive role as the enabler of non-classical dynamics in an interferometer.
- Oscar C. O. Dahlsten
- , Andrew J. P. Garner
- & Vlatko Vedral
-
Article |
 Edge and confinement effects allow in situ measurement of size and thickness of liquid-exfoliated nanosheets
Edge and confinement effects allow in situ measurement of size and thickness of liquid-exfoliated nanosheets
Liquid phase exfoliation is frequently used to produce 2D nanosheets from layered materials, but determining sheet thickness in situhas not been possible. Here, the authors report a spectroscopic technique capable of determining sheet thickness, sheet lengths and concentrations directly from dispersions.
- Claudia Backes
- , Ronan J. Smith
- & Jonathan N. Coleman
-
Article |
 In operando tracking phase transformation evolution of lithium iron phosphate with hard X-ray microscopy
In operando tracking phase transformation evolution of lithium iron phosphate with hard X-ray microscopy
Lithium iron phosphate is an extensively studied battery electrode material, but its phase transformation mechanism in the delithiation process is under debate. Here, Wang et al.use hard X-ray microscopy to produce direct real-time phase evolution, which clarifies the delithiation mechanisms.
- Jiajun Wang
- , Yu-chen Karen Chen-Wiegart
- & Jun Wang
-
Article |
 Multinuclear in situ magnetic resonance imaging of electrochemical double-layer capacitors
Multinuclear in situ magnetic resonance imaging of electrochemical double-layer capacitors
Electric double-layer capacitors are promising energy storage devices with high-power density. Here, the authors report in situmagnetic resonance imaging experiments on a working electric double-layer capacitor, revealing insights into the charge storage mechanism and cell-aging effects.
- Andrew J. Ilott
- , Nicole M. Trease
- & Alexej Jerschow
-
Article
| Open Access Theory of rapid force spectroscopy
Theory of rapid force spectroscopy
Dynamic force spectroscopy is widely applied to probe molecular interactions by forcible bond breaking, but it currently lacks an analytical theory that spans the divide between experiment and simulation. Here, such a unified framework is developed and shown to be accurate for slow and fast loading.
- Jakob T. Bullerjahn
- , Sebastian Sturm
- & Klaus Kroy
-
Article |
 Vertical atomic manipulation with dynamic atomic-force microscopy without tip change via a multi-step mechanism
Vertical atomic manipulation with dynamic atomic-force microscopy without tip change via a multi-step mechanism
Understanding vertical manipulation mechanisms in atomic-force microscopy applications is a serious challenge. Here, the authors report vertical extraction and deposition processes of copper atoms at an oxidized copper surface, and rationalize the processes with a multi-step manipulation mechanism.
- J. Bamidele
- , S.H. Lee
- & L. Kantorovich
-
Article
| Open Access A moiré deflectometer for antimatter
A moiré deflectometer for antimatter
Measuring forces on antimatter is vital to testing our understanding of fundamental physics. Towards this aim, Aghion et al.present a method to measure the deflection of antiprotons based on an atom optical tool, the moiré deflectometer, which could be extended to future antihydrogen gravity measurements.
- S. Aghion
- , O. Ahlén
- & J. Zmeskal
-
Article |
 Designed synthesis of large-pore crystalline polyimide covalent organic frameworks
Designed synthesis of large-pore crystalline polyimide covalent organic frameworks
Covalent organic frameworks are a potentially useful class of materials, although they are currently synthesized using relatively few reactions. Here, the authors show that the imidization reaction can be used to prepare a series of large pore polyimide frameworks with high surface area and thermal stability.
- Qianrong Fang
- , Zhongbin Zhuang
- & Yushan Yan
-
Article |
 Tabletop imaging of structural evolutions in chemical reactions demonstrated for the acetylene cation
Tabletop imaging of structural evolutions in chemical reactions demonstrated for the acetylene cation
Femto-chemistry allows researchers to probe the individual transitions in a molecule during a chemical reaction. Here, the authors show that a relatively simple tabletop experiment is capable of capturing the dynamics of isomerization and fragmentation of the acetylene cation to record a molecular movie.
- Heide Ibrahim
- , Benji Wales
- & François Légaré
-
Article |
 Atom manipulation on an insulating surface at room temperature
Atom manipulation on an insulating surface at room temperature
Atomic manipulation can be used to fabricate unique structures at the atomic level but has previously been limited to conductive surfaces, mainly at low temperatures. Here, the authors present a systematic manipulation on an insulating surface using atomic force microscopy to construct complex patterns.
- Shigeki Kawai
- , Adam S. Foster
- & Ernst Meyer
-
Article |
 Coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering with single-molecule sensitivity using a plasmonic Fano resonance
Coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering with single-molecule sensitivity using a plasmonic Fano resonance
The field enhancements arising in plasmonic nanostructures make them ideal as substrates for molecular sensors. In this study, Zhang et al.achieve single molecule sensitivity with Fano resonances in a quadrumer nanostructure and coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy.
- Yu Zhang
- , Yu-Rong Zhen
- & Naomi J. Halas
-
Article |
 Mechanical gate control for atom-by-atom cluster assembly with scanning probe microscopy
Mechanical gate control for atom-by-atom cluster assembly with scanning probe microscopy
Nanoclusters supported on substrates are important for a range of applications, as well as of interest for their fundamental physics and chemistry. Here, the authors demonstrate the use of a scanning probe microscope for the assembly of nanoclusters on an atom-by-atom basis.
- Yoshiaki Sugimoto
- , Ayhan Yurtsever
- & Seizo Morita
-
Article
| Open Access Visualization of asymmetric wetting ridges on soft solids with X-ray microscopy
Visualization of asymmetric wetting ridges on soft solids with X-ray microscopy
Wetting on soft surfaces exhibits a ridge structure at the contact line and the underlying mechanism is not yet fully understood. Here, Park et al.visualize the evolution of the ridge tip with high spatial and temporal resolution and identity its asymmetric shape independent of surface softness.
- Su Ji Park
- , Byung Mook Weon
- & Jung Ho Je
-
Article |
 Enantioselective control of lattice and shape chirality in inorganic nanostructures using chiral biomolecules
Enantioselective control of lattice and shape chirality in inorganic nanostructures using chiral biomolecules
Inorganic structured nanomaterials with chiral symmetry groups may have interesting optical activities. Here, the authors use biomolecules to synthesize chiral tellurium and selenium nanostructures, which exhibit visible optical and chiroptical responses and may be used as templates for mixed metal structures.
- Assaf Ben-Moshe
- , Sharon Grayer Wolf
- & Gil Markovich
-
Article |
 Functional ferroic heterostructures with tunable integral symmetry
Functional ferroic heterostructures with tunable integral symmetry
Crystal symmetries play an important role in the properties of materials, but allow little dynamic control once the materials have been grown. Here, the authors show that conducting oxides sandwiched between independently switchable ferroelectric films achieve tunable symmetry for controllable properties.
- C. Becher
- , M. Trassin
- & D. Meier
-
Article |
 Approaching the limits of transparency and conductivity in graphitic materials through lithium intercalation
Approaching the limits of transparency and conductivity in graphitic materials through lithium intercalation
Graphene-based materials have potential as transparent electrodes, but still fall short of desired performance goals. Here, Bao et al.report that upon intercalation of lithium into few-layer graphene, desired sheet resistance and optical transmittance may be achieved.
- Wenzhong Bao
- , Jiayu Wan
- & Liangbing Hu
-
Article |
 Wigner and Kondo physics in quantum point contacts revealed by scanning gate microscopy
Wigner and Kondo physics in quantum point contacts revealed by scanning gate microscopy
The electrical conductance across quantum point contacts shows quantum steps that are well understood except for some anomalies. Here, the authors are able to explain their origin in terms of spontaneously localized electron states by tuning the potential landscape of the contact with a scanning gate microscope.
- B. Brun
- , F. Martins
- & H. Sellier
-
Article |
 Ultra-high aspect ratio high-resolution nanofabrication for hard X-ray diffractive optics
Ultra-high aspect ratio high-resolution nanofabrication for hard X-ray diffractive optics
The increasing use of hard X-ray sources for scientific and biomedical imaging applications requires the development of suitable optical devices to focus and shape these high-energy beams. Here, Chang and Sakdinawat have fabricated ultra-high aspect ratio nanostructures for hard X-ray focusing.
- Chieh Chang
- & Anne Sakdinawat
-
Article |
 High-strength carbon nanotube fibre-like ribbon with high ductility and high electrical conductivity
High-strength carbon nanotube fibre-like ribbon with high ductility and high electrical conductivity
There is strong interest in carbon nanotube assemblies for a variety of applications, many of which require combined high mechanical and electrical properties. Here, the authors demonstrate a rolling technique for performance improvement, reporting tensile strength of 4.34 GPa, ductility of 10% and electrical conductivity of 2.0 × 104 S cm−1.
- J. N. Wang
- , X. G. Luo
- & Y. Chen
-
Article |
 Stress-induced phase transformation and optical coupling of silver nanoparticle superlattices into mechanically stable nanowires
Stress-induced phase transformation and optical coupling of silver nanoparticle superlattices into mechanically stable nanowires
Silver nanowires are commonly synthesized via chemical routes. Here, the authors report nanowire formation via a physical method involving stress-induced phase transformation and sintering of spherical silver nanoparticle superlattices.
- Binsong Li
- , Xiaodong Wen
- & Hongyou Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Microwave spectroscopic observation of distinct electron solid phases in wide quantum wells
Microwave spectroscopic observation of distinct electron solid phases in wide quantum wells
Confining electrons to two dimensions can drastically alter the way they interact with each other. Here, the authors show that electrons in quantum wells can form into two distinct solid-like phases when placed in a large magnetic field.
- A. T. Hatke
- , Yang Liu
- & K. W. Baldwin
-
Article
| Open Access Probing the solar corona with very long baseline interferometry
Probing the solar corona with very long baseline interferometry
Very long baseline interferometry is an astronomical technique that uses radio telescopes on Earth to observe extragalactic radio sources. Here, the authors show that it can be used to measure the electron density of the Sun’s corona and compare their findings to models from spacecraft tracking data.
- B. Soja
- , R. Heinkelmann
- & H. Schuh
-
Article |
 Determination of energy level alignment at metal/molecule interfaces by in-device electrical spectroscopy
Determination of energy level alignment at metal/molecule interfaces by in-device electrical spectroscopy
Probing energy level alignment in metal/molecular semiconductor interfaces via electron photoemission spectroscopy requires conditions removed from those during device operation. Here, the authors report a three-terminal device for obtaining this information under real operating conditions.
- M. Gobbi
- , L. Pietrobon
- & L. E. Hueso
-
Article |
 An elasto-mechanical unfeelability cloak made of pentamode metamaterials
An elasto-mechanical unfeelability cloak made of pentamode metamaterials
Cloaking of a range of stimuli have been demonstrated in various metamaterials recently. Here, the authors report mechanical cloaking in a pentamode structure, leading to ‘unfeelability’ of a core in an elasto-mechanical core-shell system.
- T. Bückmann
- , M. Thiel
- & M. Wegener
-
Article |
 Extremely confined gap surface-plasmon modes excited by electrons
Extremely confined gap surface-plasmon modes excited by electrons
Electron energy-loss spectroscopy gives important information on plasmonic modes in metal nanostructures. Raza et al. use it to study the confined gap surface-plasmon modes in ultra-sharp convex grooves in gold and find asymmetric modes existing down to nanometre-sized gaps.
- Søren Raza
- , Nicolas Stenger
- & N. Asger Mortensen
-
Article |
 Visible-frequency asymmetric transmission devices incorporating a hyperbolic metamaterial
Visible-frequency asymmetric transmission devices incorporating a hyperbolic metamaterial
Optical devices with asymmetric transmission are desirable for many applications, but fabrication difficulties impede visible frequency operation. Xu and Lezec overcome this by combining nonsymmetric subwavelength gratings with a hyperbolic metamaterial to realize efficient asymmetric transmission.
- Ting Xu
- & Henri J. Lezec
-
Article |
 Biomimetic block copolymer particles with gated nanopores and ultrahigh protein sorption capacity
Biomimetic block copolymer particles with gated nanopores and ultrahigh protein sorption capacity
Porous particles can be capable of selectivity encapsulating various guests. Here, the authors report a strategy to make block copolymer microparticles with pH-responsive pores, study and rationalize their assembly process and furthermore demonstrate separation of differently charged proteins.
- Haizhou Yu
- , Xiaoyan Qiu
- & Klaus-Viktor Peinemann
-
Article |
 Using nanoscale and mesoscale anisotropy to engineer the optical response of three-dimensional plasmonic metamaterials
Using nanoscale and mesoscale anisotropy to engineer the optical response of three-dimensional plasmonic metamaterials
The geometry of periodic plasmonic nanostructures in three dimensions can be exploited to give tailored optical properties. Here, the authors study the role of anisotropy on the nano- and mesoscale to provide a framework for designing the optical response of metamaterials formed from plasmonic building blocks.
- Michael B. Ross
- , Martin G. Blaber
- & George C. Schatz
-
Article
| Open Access Encapsulation kinetics and dynamics of carbon monoxide in clathrate hydrate
Encapsulation kinetics and dynamics of carbon monoxide in clathrate hydrate
Carbon monoxide clathrate hydrate has been widely studied and although the structure-II gas hydrate is predicted to be thermodynamically favourable, it is the structure-I hydrate that has been observed. Here, the authors synthesize the structure-II carbon monoxide hydrate and probe its structure and formation.
- Jinlong Zhu
- , Shiyu Du
- & Yusheng Zhao
-
Article |
 Incorporation and redistribution of impurities into silicon nanowires during metal-particle-assisted growth
Incorporation and redistribution of impurities into silicon nanowires during metal-particle-assisted growth
Understanding the incorporation of metal atoms into silicon nanowires during metal-catalysed growth is of importance. Here, the authors find that the metal atom concentration dissolved into the silicon nanowires increases with growth rate and is two orders of magnitude higher than their equilibrium solubility.
- Wanghua Chen
- , Linwei Yu
- & Pere Roca i Cabarrocas
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-micron phase coexistence in small-molecule organic thin films revealed by infrared nano-imaging
Sub-micron phase coexistence in small-molecule organic thin films revealed by infrared nano-imaging
The grain boundaries between two coexisting phases in organic semiconductor pentacene are expected to obstruct charge transport in its thin-film devices. Westermeier et al. use infrared-spectroscopic nano-imaging to show an interlocking morphology, which is uncorrelated with its grain structures.
- Christian Westermeier
- , Adrian Cernescu
- & Bert Nickel
-
Article |
 Picometre-precision analysis of scanning transmission electron microscopy images of platinum nanocatalysts
Picometre-precision analysis of scanning transmission electron microscopy images of platinum nanocatalysts
The structural characterization of materials with picometre precision is vital for the development of structure–property relationships. Here, the authors present results demonstrating sub-picometre precision measurements of atomic position based on a non-rigid registration technique.
- Andrew B. Yankovich
- , Benjamin Berkels
- & Paul M. Voyles
-
Article |
 Collective fluorescence switching of counterion-assembled dyes in polymer nanoparticles
Collective fluorescence switching of counterion-assembled dyes in polymer nanoparticles
Fluorescent organic nanoparticles are attractive alternatives to quantum dots for imaging applications. Here, the authors assemble dyes with bulky counterions inside polymer nanoparticles to achieve high fluorescence brightness, as well as a photoinducible and reversible on/off switching.
- Andreas Reisch
- , Pascal Didier
- & Andrey S. Klymchenko
-
Article |
 Graphitic nanostripes in silicon carbide surfaces created by swift heavy ion irradiation
Graphitic nanostripes in silicon carbide surfaces created by swift heavy ion irradiation
Defects alter the properties of silicon carbide structures, but the introduction of these defects in a controlled manner remains a challenge. Here, the authors show that swift heavy ions can create graphitic grooves if the irradiation is at grazing angles of incidence.
- Oliver Ochedowski
- , Orkhan Osmani
- & Marika Schleberger
-
Article |
 Single-shot three-dimensional structure determination of nanocrystals with femtosecond X-ray free-electron laser pulses
Single-shot three-dimensional structure determination of nanocrystals with femtosecond X-ray free-electron laser pulses
Three-dimensional imaging is typically complex and time consuming. Here, the authors report the use of X-ray free-electron laser pulses for single-shot three-dimensional imaging of nanocrystals at ~5.5 nm resolution, using the symmetry in the nanocrystal and the curvature of the Ewald sphere.
- Rui Xu
- , Huaidong Jiang
- & Jianwei Miao
-
Article
| Open Access All-printable band-edge modulated ZnO nanowire photodetectors with ultra-high detectivity
All-printable band-edge modulated ZnO nanowire photodetectors with ultra-high detectivity
Nanowire photodetectors offer a high sensitivity arising from their geometry that makes them of interest for optoelectronic devices. Here, the authors demonstrate the printable fabrication of ZnO nanowires with high detectivity, making them suitable for high-performance flexible electronics applications.
- Xi Liu
- , Leilei Gu
- & Zhiyong Fan
-
Article |
 Design amphiphilic dipolar π-systems for stimuli-responsive luminescent materials using metastable states
Design amphiphilic dipolar π-systems for stimuli-responsive luminescent materials using metastable states
Some π-conjugated molecules exhibit tunable luminescence—a property that is useful for the next generation of optical devices. Yagai et al. propose a strategy to design these materials on a molecular level, which tailors the emission colour via structural changes in response to mechanical stimuli.
- Shiki Yagai
- , Satoru Okamura
- & Hajime Ito
-
Article |
 Capturing carbon dioxide as a polymer from natural gas
Capturing carbon dioxide as a polymer from natural gas
Natural gas is a widely used fossil fuel, but its extraction results in the venting of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. Here, the authors demonstrate that nucleophilic porous carbons can store this carbon dioxide as a polymer, and that the polymerization requires lower pressures than previously observed.
- Chih-Chau Hwang
- , Josiah J. Tour
- & James M. Tour
-
Article |
 Magnetocaloric effects in a freestanding and flexible graphene-based superlattice synthesized with a spatially confined reaction
Magnetocaloric effects in a freestanding and flexible graphene-based superlattice synthesized with a spatially confined reaction
Superlattices are made of alternating thin-film layers and offer a broader range of properties than natural materials. Here, the authors present a method for fabricating free-standing graphene–vanadium oxide superlattices, which could be used in smart windows or as temperature sensors.
- Haiou Zhu
- , Chong Xiao
- & Yi Xie
-
Article
| Open Access In situ observation of step-edge in-plane growth of graphene in a STEM
In situ observation of step-edge in-plane growth of graphene in a STEM
Direct visualization of graphene growth is highly desired, though, extremely high growth rates during chemical vapour deposition make atomic resolution analysis infeasible. Here, Liu et al. report the visualization of the in situin-plane growth of graphene in a scanning transmission electron microscope.
- Zheng Liu
- , Yung-Chang Lin
- & Kazu Suenaga
-
Article |
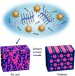 Rapid fabrication of hierarchically structured supramolecular nanocomposite thin films in one minute
Rapid fabrication of hierarchically structured supramolecular nanocomposite thin films in one minute
There is significant research into fabrication methods for the rapid, scalable preparation of composite nanomaterials. Here, the authors probe the assembly of supramolecular nanocomposites in thin films and are able to optimize parameters to produce hierarchically structured thin films in one minute.
- Joseph Kao
- , Kari Thorkelsson
- & Ting Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of half-metallicity in the Heusler compound Co2MnSi
Direct observation of half-metallicity in the Heusler compound Co2MnSi
Spintronics requires materials in which most of the spins at the Fermi edge are aligned with each other at room temperatures. Jourdan et al. observe such a spin polarization of 93% in Co2MnSi—a Heusler alloy amenable to many spintronic applications; evidence of the material’s half-metallicity.
- M. Jourdan
- , J. Minár
- & M. Kläui
-
Article
| Open Access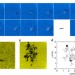 Imaging atomic-level random walk of a point defect in graphene
Imaging atomic-level random walk of a point defect in graphene
Observing the movement of defects through a crystal lattice in real time presents significant difficulties. Here, the authors use an ultra-high vacuum and low-voltage scanning transmission microscope setup to observe the migration of a divacancy defect in real time through graphene.
- Jani Kotakoski
- , Clemens Mangler
- & Jannik C. Meyer
-
Article |
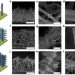 Maximizing omnidirectional light harvesting in metal oxide hyperbranched array architectures
Maximizing omnidirectional light harvesting in metal oxide hyperbranched array architectures
The development of structured electrode architectures is one of the strategies for improving photovoltaic performance. Here, the authors report hierarchical hyperbranced titania materials, composed of nanowires and nanosheets, linked by nanorods, and assess their solar energy conversion efficiency.
- Wu-Qiang Wu
- , Hao-Lin Feng
- & Cheng-Yong Su
-
Article |
 Modular assembly of optical nanocircuits
Modular assembly of optical nanocircuits
Lumped circuit elements provide a simple tool to design complex electronic systems; a similar approach has been proposed for nanophotonics. Here, the authors demonstrate the modularized design and assembly of photonic nanocircuits using metal and dielectric nanoparticles as the constituent lumped elements.
- Jinwei Shi
- , Francesco Monticone
- & Andrea Alù
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-15-nm patterning of asymmetric metal electrodes and devices by adhesion lithography
Sub-15-nm patterning of asymmetric metal electrodes and devices by adhesion lithography
Electron-beam lithography is often used for patterning of asymmetric metal electrodes for nanoscale devices, but suffers from several limitations. Here, the authors report a new adhesion lithography process, which allows for high-throughput and simple fabrication of nanogap metal electrodes.
- David J. Beesley
- , James Semple
- & John C. deMello
-
Article |
 A design strategy for the hierarchical fabrication of colloidal hybrid mesostructures
A design strategy for the hierarchical fabrication of colloidal hybrid mesostructures
Achieving a high degree of control over the self-assembly process is a challenging task, but one that can give access to precisely defined structures. Here, the authors show the generation of hybrid materials with controlled morphology and hierarchy based on the assembly of block copolymers on silica cores.
- Lin Jia
- , Guangyao Zhao
- & Mitchell A. Winnik

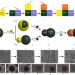 Hierarchical synthesis of non-centrosymmetric hybrid nanostructures and enabled plasmon-driven photocatalysis
Hierarchical synthesis of non-centrosymmetric hybrid nanostructures and enabled plasmon-driven photocatalysis