Featured
-
-
News |
 Behind the scenes of a brain-mapping moon shot
Behind the scenes of a brain-mapping moon shot
Critics fear that a proposed megaproject could crowd out other biological research.
- Meredith Wadman
-
Article |
 Dynamic regulatory network controlling TH17 cell differentiation
Dynamic regulatory network controlling TH17 cell differentiation
A global view of the genetic networks regulating the differentiation of TH17 cells is presented, based on temporal expression profiling, computational network reconstruction and validation of predicted interactions by nanowire-mediated siRNA perturbation.
- Nir Yosef
- , Alex K. Shalek
- & Aviv Regev
-
Letter |
 Dynamics extracted from fixed cells reveal feedback linking cell growth to cell cycle
Dynamics extracted from fixed cells reveal feedback linking cell growth to cell cycle
A mathematical method, known as ergodic rate analysis, has been developed and used to study the rates of molecular events from single time measurements of large populations of fixed cells; this new method is able to overcome some of the previous limitations with regards to studying cell-size control.
- Ran Kafri
- , Jason Levy
- & Marc W. Kirschner
-
News |
 Influential few predict behaviour of the many
Influential few predict behaviour of the many
Technique helps to untangle complexity in systems from metabolism to social networks.
- Julie Rehmeyer
-
Letter |
 The spatial architecture of protein function and adaptation
The spatial architecture of protein function and adaptation
A high-throughput mutagenesis study in a PDZ domain shows that biochemical function and adaptation primarily originate from a collectively evolving amino acid network within the structure termed a protein sector.
- Richard N. McLaughlin Jr
- , Frank J. Poelwijk
- & Rama Ranganathan
-
Letter |
 In vivo genome editing using a high-efficiency TALEN system
In vivo genome editing using a high-efficiency TALEN system
Although zebrafish is an important animal model for basic vertebrate biology and human disease modelling, rapid targeted genome modification has not been possible in this species; here a technique based on improved artificial transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) allows precise sequence modifications at pre-determined genomic locations.
- Victoria M. Bedell
- , Ying Wang
- & Stephen C. Ekker
-
Article
| Open Access Architecture of the human regulatory network derived from ENCODE data
Architecture of the human regulatory network derived from ENCODE data
A description is given of the ENCODE consortium’s efforts to examine the principles of human transcriptional regulatory networks; the results are integrated with other genomic information to form a hierarchical meta-network where different levels have distinct properties.
- Mark B. Gerstein
- , Anshul Kundaje
- & Michael Snyder
-
News & Views |
 A cell in a computer
A cell in a computer
The small genomes of some bacteria could provide the first complete understanding of a biological system. A new computer model brings this goal closer, by calculating every process in a dividing Mycoplasma cell.
- Mark Isalan
-
Letter |
 Interpreting cancer genomes using systematic host network perturbations by tumour virus proteins
Interpreting cancer genomes using systematic host network perturbations by tumour virus proteins
Combining analysis of host proteome and transcriptome perturbations induced by tumour virus proteins with ongoing genome-wide studies of cancer facilitates the prioritization of cancer genes.
- Orit Rozenblatt-Rosen
- , Rahul C. Deo
- & Marc Vidal
-
Article |
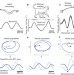 Neural population dynamics during reaching
Neural population dynamics during reaching
- Mark M. Churchland
- , John P. Cunningham
- & Krishna V. Shenoy
-
Review Article |
 Engineering the third wave of biocatalysis
Engineering the third wave of biocatalysis
Over the past ten years, protein engineering has established biocatalysis as a practical and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional forms of catalysis both in the laboratory and in industry.
- U. T. Bornscheuer
- , G. W. Huisman
- & K. Robins
-
News & Views |
 Tighter ties that bind
Tighter ties that bind
A stepwise process of mutation and structural analysis has modulated a flexible binding interface of an immune-cell signalling protein, interleukin-2, and generated mutant proteins with enhanced anticancer activity. See Article p.529
- Eric T. Boder
-
News & Views |
 A ratchet for protein complexity
A ratchet for protein complexity
Molecular machines containing related protein subunits are common in cells. Reconstruction of ancient proteins suggests that this type of complexity can evolve in the absence of any initial selective advantage. See Letter p.360
- W. Ford Doolittle
-
Outlook |
 Perspective: All systems go
Perspective: All systems go
Systems science can provide guidance in capturing the complementary approaches to healthcare, says Jan van der Greef.
- Jan van der Greef
-
News |
 India to cut out animal dissection
India to cut out animal dissection
University funding body recommends a phase-out, but gives no final date.
- Priya Shetty
-
Article |
 A sensing array of radically coupled genetic ‘biopixels’
A sensing array of radically coupled genetic ‘biopixels’
Thousands of quorum-sensing Escherichia coli colonies are synchronized over centimetres using redox signalling to create ‘biopixels’ that can sense trace amounts of arsenic in water.
- Arthur Prindle
- , Phillip Samayoa
- & Jeff Hasty
-
Feature |
 Single-cell analysis: Imaging is everything
Single-cell analysis: Imaging is everything
Advances in single-cell imaging bring opportunities for physicists, biologists and chemists alike.
- Amy Maxmen
-
News & Views |
A yeast for all reasons
Scientists have begun to overhaul a yeast's genome to make it more stable, engineerable and evolvable. Remarkably, the part-natural, part-synthetic yeast cells function and reproduce without obvious ill effects. See Letter p.471
- Peter J. Enyeart
- & Andrew D. Ellington
-
News & Views |
 How to escape treatment
How to escape treatment
Even during effective treatment with antiretroviral drugs, low levels of HIV persist. In part, this could be due to cell-to-cell transfer of multiple virions and the drugs' inability to inhibit replication when virus levels are high. See Letter p.95
- Steven G. Deeks
-
Letter |
 Cell-to-cell spread of HIV permits ongoing replication despite antiretroviral therapy
Cell-to-cell spread of HIV permits ongoing replication despite antiretroviral therapy
- Alex Sigal
- , Jocelyn T. Kim
- & David Baltimore
-
News & Views |
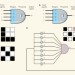 DNA and the brain
DNA and the brain
The idea that artificial neural networks could be based on molecular components is not new, but making such a system has been difficult. A network of four artificial neurons made from DNA has now been created. See Letter p.368
- Anne Condon
-
Letter |
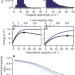 Excess digestive capacity in predators reflects a life of feast and famine
Excess digestive capacity in predators reflects a life of feast and famine
- Jonathan B. Armstrong
- & Daniel E. Schindler
-
Article |
 A conditional knockout resource for the genome-wide study of mouse gene function
A conditional knockout resource for the genome-wide study of mouse gene function
- William C. Skarnes
- , Barry Rosen
- & Allan Bradley
-
-
Technology Feature |
 The next step for the synthetic genome
The next step for the synthetic genome
Biologists have copied an existing genetic code, but haven't yet commercialized it or written their own. What will it take for a tour de force to reach industrial force?
- Monya Baker
-
Books & Arts |
 Culture: Art that touches a nerve
Culture: Art that touches a nerve
Anthony King explores a Dublin exhibition that exposes the controversies of synthetic biology.
- Anthony King
-
Books & Arts |
 Cosmology: The untestable multiverse
Cosmology: The untestable multiverse
George Ellis reminds us that Brian Greene's beguiling book on parallel worlds is more theory than fact.
- George Ellis
-
News & Views |
 Catalytic detoxification
Catalytic detoxification
Protein engineering of an enzyme that catalytically detoxifies organophosphate compounds in the body opens up fresh opportunities in the search for therapeutic protection against nerve agents used in chemical warfare.
- Frank M. Raushel
-
News & Views |
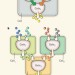 Division of logic labour
Division of logic labour
Cellular compartmentalization is an effective way to build gene circuits capable of complex logic operations, in which binary inputs are converted into binary outputs according to user-defined rules. See Letters p.207 & p.212
- Bochong Li
- & Lingchong You
-
News & Views |
 DNA as a logic operator
DNA as a logic operator
Computers use transistor-based logic gates as the basis of their functions, but molecular logic gates would make them much faster. A report of DNA-based logic gates could be a first step towards molecular computing.
- Thomas Carell
-
Comment |
 Build life to understand it
Build life to understand it
Biologists and engineers should work together: synthetic biology reveals how organisms develop and function, argue Michael Elowitz and Wendell A. Lim.
- Michael Elowitz
- & Wendell A. Lim
-
News |
 Germans cook up liver project
Germans cook up liver project
Biologists join physicists in a bid to map the workings of the human organ at all scales.
- Alison Abbott
-
Letter |
 Robust multicellular computing using genetically encoded NOR gates and chemical ‘wires’
Robust multicellular computing using genetically encoded NOR gates and chemical ‘wires’
For synthetic biologists' creativity to be unleashed, basic circuits must become truly interchangeable, that is, modular and scalable. This study, one of two linked papers, has harnessed bacterial 'quorum sensing' to achieve complex computation through communication between individual cells performing simple logic functions. Such extracellular 'chemical wiring' is one promising way to get around intracellular noise when building more complex genetic circuitry.
- Alvin Tamsir
- , Jeffrey J. Tabor
- & Christopher A. Voigt
-
Article |
 Genetic dissection of an amygdala microcircuit that gates conditioned fear
Genetic dissection of an amygdala microcircuit that gates conditioned fear
The central amygdala relies on inhibitory circuitry to encode fear memories, but how this information is acquired and expressed in these connections is unknown. Two new papers use a combination of cutting-edge technologies to reveal two distinct microcircuits within the central amygdala, one required for fear acquisition and the other critical for conditioned fear responses. Understanding this architecture provides a strong link between activity in a specific circuit and particular behavioural consequences.
- Wulf Haubensak
- , Prabhat S. Kunwar
- & David J. Anderson
-
News & Views |
 Longer-lived proteins
Longer-lived proteins
Short residence times in the bloodstream reduce the effectiveness of protein drugs. Application of an approach that combines protein and polymer engineering prolongs circulation time and increases drug uptake by tumours.
- Jeffrey A. Hubbell
-
-
News & Views |
 Ocean biomes blended
Ocean biomes blended
The ratio of nutrient elements in marine subsurface waters is much the same everywhere, even though biogeochemically distinct ocean biomes exist. A modelling study that includes mixing solves this conundrum. See Article p.550
- Raymond N. Sambrotto
-
News & Views |
 Foreseeing tipping points
Foreseeing tipping points
Theory suggests that the risk of critical transitions in complex systems can be revealed by generic indicators. A lab study of extinction in plankton populations provides experimental support for that principle. See Letter p. 456
- Marten Scheffer
-
-
-
News & Views |
The cost of feedback control
Noise in biochemical processes can compromise precision in cellular functions. An analysis involving information theory suggests that there is a strict limit to how far noise can be suppressed by feedback.
- Li Sun
- & Attila Becskei
-
News & Views |
Making black holes from scratch
The means by which supermassive black holes form and grow have remained largely unclear. Numerical simulations show that the collision of massive galaxies can naturally lead to the creation of these objects.
- Marta Volonteri
-
News & Views |
 A signal take on speech
A signal take on speech
Approaches that abandon traditional speech categories offer promise for developing statistical descriptions that encapsulate how speech conveys information. Grandparents would be among the beneficiaries.
- Michael S. Lewicki
-
News & Views |
 Closing in on evaders
Closing in on evaders
A simple model highlights the pros and cons of chasing — and escaping — in groups. It shows that, for a given number of prey animals, an optimal number of predators exists that maximizes the success of the catch.
- Tamás Vicsek
-
News |
 Ancient macrofossils unearthed in West Africa
Ancient macrofossils unearthed in West Africa
Two-billion-year-old fossils could indicate steps towards multicellularity.
- Amy Maxmen
-
-
News |
 Synthetic-biology competition launches
Synthetic-biology competition launches
Genome-design contest aims to engineer cress for commercial uses.
- David Cyranoski
-
News & Views |
 Wider role for airborne chlorine
Wider role for airborne chlorine
Unexpected chlorine chemistry in the lowest part of the atmosphere can affect the cycling of nitrogen oxides and the production of ozone, and reduce the lifetime of the greenhouse gas methane.
- Roland von Glasow
-
News |
 Plant biologists fear for cress project
Plant biologists fear for cress project
Is enthusiasm withering for funding studies into Arabidopsis thaliana?
- Heidi Ledford
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Bayesian inference
- Biobricks
- Biochemical networks
- Bioenergetics
- Cellular noise
- Complexity
- Computer modelling
- Computer science
- Control theory
- Criticality
- Differential equations
- DNA computing and cryptography
- Dynamic networks
- Dynamical systems
- Emergence
- Evolvability
- Genetic circuit engineering
- Genetic interaction
- Genomic engineering
- Information theory
- Logic gates
- Metabolic engineering
- Modularity
- Molecular engineering
- Molecular fluctuations
- Multicellular systems
- Multistability
- Nonlinear dynamics
- Numerical simulations
- Oscillators
- Population dynamics
- Programming language
- Protein engineering
- Regulatory networks
- Reverse engineering
- Robustness
- Signal processing
- Single-cell imaging
- Software
- Standardization
- Stochastic modelling
- Stochastic networks
- Synthetic biology
- Systems analysis
- Time series

 High-level semi-synthetic production of the potent antimalarial artemisinin
High-level semi-synthetic production of the potent antimalarial artemisinin A molecular calculator
A molecular calculator The energetics of genome complexity
The energetics of genome complexity Functional roles for noise in genetic circuits
Functional roles for noise in genetic circuits Saliva at a stretch
Saliva at a stretch