News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 On-surface synthesis of ballbot-type N-heterocyclic carbene polymers
On-surface synthesis of ballbot-type N-heterocyclic carbene polymers
Monomeric N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) can act as molecular modifiers of metal surfaces and thus affect heterogeneous catalytic behaviour. Now NHC polymers have been formed on gold surfaces, consisting of ballbot-type repeating units bound to single gold adatoms. Conformational, electronic and charge transport properties explain the high surface mobility of the incommensurate NHC polymers.
- Jindong Ren
- , Maximilian Koy
- & Frank Glorius
-
Article |
 Hybrid organic–inorganic two-dimensional metal carbide MXenes with amido- and imido-terminated surfaces
Hybrid organic–inorganic two-dimensional metal carbide MXenes with amido- and imido-terminated surfaces
Functionalizing two-dimensional transition-metal carbide (MXene) surfaces can alter their properties, but covalent functionalization has been synthetically challenging. Now, it has been shown that various organic groups can be covalently attached to MXene surfaces through amido and imido bonds. The resulting hybrid organic–inorganic structures exhibit Fano resonances and superior stability compared with traditional MXenes with a mixture of –F, –O and –OH surface terminations.
- Chenkun Zhou
- , Di Wang
- & Dmitri V. Talapin
-
Article |
 Autonomous and directional flow of water and transport of particles across a subliming dynamic crystal surface
Autonomous and directional flow of water and transport of particles across a subliming dynamic crystal surface
Crystals of hexachlorobenzene have now been shown to support the autonomous motion of water and particulate matter over their surface. Parallel microchannels present at the surface of the crystal gradually widen by sublimation, propelling droplets of condensed ambient water that can also transport microscopic amounts of material such as silver microparticles.
- Patrick Commins
- , Marieh B. Al-Handawi
- & Panče Naumov
-
Article
| Open Access On-surface synthesis of disilabenzene-bridged covalent organic frameworks
On-surface synthesis of disilabenzene-bridged covalent organic frameworks
Incorporating silicon into organic molecules and materials leads to interesting changes in electronic structure and properties; silabenzenes are attractive species for this purpose, but their high reactivity in solution poses challenges. Now, 1D and 2D covalent organic frameworks featuring disilabenzene rings (C4Si2) as linkers have been prepared by reacting silicon atoms and polyaromatic hydrocarbon precursors on a Au(111) surface.
- Kewei Sun
- , Orlando J. Silveira
- & Shigeki Kawai
-
Article |
 Controlling anisotropic properties by manipulating the orientation of chiral small molecules
Controlling anisotropic properties by manipulating the orientation of chiral small molecules
The properties of chiral conjugated molecules, such as the absorption and/or emission of circularly polarized light or electron transport, are highly anisotropic. Now it has been shown that templating layers can control the orientation and anisotropic properties of small chiral molecules in bulk thin films useful for a range of emerging technologies.
- Jessica Wade
- , Francesco Salerno
- & Matthew J. Fuchter
-
Review Article |
 Covalent on-surface polymerization
Covalent on-surface polymerization
Growing polymers directly on surfaces has emerged as a powerful tool because it can provide a route to otherwise inaccessible structures such as defect-free linear chains, graphene nanoribbons and two-dimensional networks. This Review Article describes general principles and key aspects of this method from the perspectives of surface science and polymer chemistry.
- Leonhard Grill
- & Stefan Hecht
-
Article |
 On-water surface synthesis of crystalline, few-layer two-dimensional polymers assisted by surfactant monolayers
On-water surface synthesis of crystalline, few-layer two-dimensional polymers assisted by surfactant monolayers
It is difficult to prepare 2D polymers that are crystalline over large areas. Now, few-layer 2D polyimides and polyamides with good crystallinity on the micrometre scale have been synthesized on a water surface. A surfactant monolayer is used to organize amine monomers before their polymerization with anhydride moieties.
- Kejun Liu
- , Haoyuan Qi
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Article |
 Tuning underwater adhesion with cation–π interactions
Tuning underwater adhesion with cation–π interactions
Cation–π interactions are critical for the adhesion proteins of marine organisms, yet the energetics of cation–π interactions in underwater environments remains uncharted. Nanoscale force measurements and NMR spectroscopy reveal that interfacial confinement fundamentally alters the energetics of cation–π mediated assembly.
- Matthew A. Gebbie
- , Wei Wei
- & Jacob N. Israelachvili
-
News & Views |
 Single handedness in flatland
Single handedness in flatland
Planar molecules may break mirror symmetry when aligned on a surface, but both right- and left-handed forms will be created. Starting with a single-handed precursor, chiral adsorbates of planar hydrocarbons with a single handedness are formed in on-surface reactions.
- Karl-Heinz Ernst
-
Article |
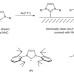 Ballbot-type motion of N-heterocyclic carbenes on gold surfaces
Ballbot-type motion of N-heterocyclic carbenes on gold surfaces
STM investigations and first principles calculations provide an understanding of the microscopic mechanism behind the mobility of N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) on gold surfaces. Now, it is shown that a ballbot-type motion allows the formation of self-assembled monolayers due to the NHC extracting a gold atom from the surface, leading to a ligated gold adatom.
- Gaoqiang Wang
- , Andreas Rühling
- & Harald Fuchs
-
Article |
 Homochiral polymerization-driven selective growth of graphene nanoribbons
Homochiral polymerization-driven selective growth of graphene nanoribbons
Metal surfaces have been believed to be catalytic, but the mechanism of catalysis is unknown. Now, graphene nanoribbons (GNRs) can be grown on Au(111) from a ‘Z-bar-linkage' precursor through a conformation-controlled mechanism. Chemical vapour deposition of precursors adopting a chiral conformation produced homochiral polymers, which are dehydrogenated to form GNRs.
- Hiroshi Sakaguchi
- , Shaotang Song
- & Takahiro Nakae
-
Article |
 Dynamic control over supramolecular handedness by selecting chiral induction pathways at the solution–solid interface
Dynamic control over supramolecular handedness by selecting chiral induction pathways at the solution–solid interface
The formation of homochiral supramolecular networks at solution–solid interfaces typically relies on the soldier-and-sergeant approach, in which a small amount of chiral modifier defines the handedness of the network. Now, judicious choice of the sergeant, solvent, temperature and concentration has enabled chiral induction pathways to be controlled so that a homochiral surface of either handedness can be assembled from the same system.
- Yuan Fang
- , Elke Ghijsens
- & Steven De Feyter
-
Article |
 Microscopic origin of chiral shape induction in achiral crystals
Microscopic origin of chiral shape induction in achiral crystals
Achiral minerals often adopt a chiral shape when crystal growth proceeds in contact with chiral molecules. Now, detailed microscopic insight is provided into how the chiral footprint of hemifullerene (a buckybowl that is essentially half of C60) rearranges atoms at step edges on a copper surface into chiral motifs.
- Wende Xiao
- , Karl-Heinz Ernst
- & Roman Fasel
-
Article |
 Transfer of molecular recognition information from DNA nanostructures to gold nanoparticles
Transfer of molecular recognition information from DNA nanostructures to gold nanoparticles
DNA nanostructures are typically used as molecular scaffolds. Now, it has been shown that they can also act as reusable templates for ‘molecular printing’ of DNA strands onto gold nanoparticles. The products inherit the recognition elements of the parent template: number, orientation and sequence asymmetry of DNA strands. This converts isotropic nanoparticles into complex building blocks.
- Thomas G. W. Edwardson
- , Kai Lin Lau
- & Hanadi F. Sleiman
-
Article |
 Light-controlled self-assembly of non-photoresponsive nanoparticles
Light-controlled self-assembly of non-photoresponsive nanoparticles
Controlling the self-assembly of nanoparticles using light has been demonstrated in many systems where the particle surfaces are functionalized with photoswitchable ligands. Now, it has been shown that the light-controlled self-assembly of non-photoresponsive nanoparticles can be achieved in a quantitative and reversible fashion by placing them in a photoresponsive medium.
- Pintu K. Kundu
- , Dipak Samanta
- & Rafal Klajn
-
News & Views |
 Self-assembling Sierpiński triangles
Self-assembling Sierpiński triangles
Defect-free Sierpiński triangles can be self-assembled on a silver surface through a combination of molecular design and thermal annealing. Three-fold halogen-bonding arrays and precise surface epitaxy preclude structural errors, thus enabling the high-level complexity of these supramolecular fractal patterns.
- Steven L. Tait
-
Article |
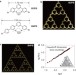 Assembling molecular Sierpiński triangle fractals
Assembling molecular Sierpiński triangle fractals
A series of molecular fractals, specifically Sierpiński triangles, can be assembled on a Ag(111) surface from small, bent oligophenyls with a bromo group at each end. The self-assembly is driven by the formation of synergistic halogen and hydrogen bonds between the molecular building blocks, and defect-free structures with more than 100 individual components are observed.
- Jian Shang
- , Yongfeng Wang
- & Kai Wu
-
Article |
 Supramolecular nesting of cyclic polymers
Supramolecular nesting of cyclic polymers
Biopolymers adopt functional tertiary structures through folding and multiplex formation. Synthetic molecules with protein-like dimensions — monodisperse cyclic porphyrin polymers with diameters of 13–21 nm — have now been shown to exhibit biomimetic self-organization by forming nested structures on a gold surface. These assemblies are formed both under vacuum and during deposition from solution.
- Dmitry V. Kondratuk
- , Luís M. A. Perdigão
- & Harry L. Anderson
-
Review Article |
 Porphyrins at interfaces
Porphyrins at interfaces
Bringing porphyrins in contact with well-defined interfaces generates a rich playground of chemical behaviour and properties for exploration and exploitation. This Review examines our current understanding of surface-confined tetrapyrroles and their embedding in nanoarchitectures - discussing both the structural and functional attributes, and methods by which to manipulate their intramolecular and organizational features.
- Willi Auwärter
- , David Écija
- & Johannes V. Barth
-
-
News & Views |
 From rods to sheets in a flash
From rods to sheets in a flash
The controlled synthesis of two-dimensional carbon nanomaterials enables their properties to be tailored for potential device applications. Functionalized graphene-like nanosheets with controlled thickness have now been obtained by irradiating monolayers of carbon-rich molecular precursors at room temperature.
- Jean-François Morin
-
Article |
 Ultra stable self-assembled monolayers of N-heterocyclic carbenes on gold
Ultra stable self-assembled monolayers of N-heterocyclic carbenes on gold
Thiol-based self-assembled monolayers have a huge variety of potential applications but are hampered by oxidative and thermal instability. Now, N-heterocyclic carbenes are shown to form densely packed layers on Au(111) that are considerably more stable than thiol films, resisting hot organic solvents, acid, base, oxidant and oxidative electrohemical etching.
- Cathleen M. Crudden
- , J. Hugh Horton
- & Gang Wu
-

 Towards zero droplet friction
Towards zero droplet friction Laying down the law
Laying down the law