Research Highlights |
Featured
-
-
Research Highlights |
Cancer biology: Ovarian cancer culprits
-
News |
 US clinics quietly embrace whole-genome sequencing
US clinics quietly embrace whole-genome sequencing
Physicians are turning to genomic tools to diagnose puzzling conditions.
- Brendan Borrell
-
News & Views |
 Holes with an edge
Holes with an edge
Tiny holes have been drilled through individual layers of graphene — atomically thin sheets of carbon — using an electron beam. These nanopores might be useful for the ultrarapid sequencing of single DNA molecules.
- Hagan Bayley
-
News |
 What does it mean to be an ant?
What does it mean to be an ant?
Genome sequences offer clues on how to be a queen and live a long life.
- Alla Katsnelson
-
News |
 The gut's 'friendly' viruses revealed
The gut's 'friendly' viruses revealed
DNA sequencing reveals a new world of bacterial viruses in our intestines.
- Amy Maxmen
-
Feature |
 The promise of T. cruzi genomics
The promise of T. cruzi genomics
The publishing of the first Trypanosoma cruzi genome sequence was hailed as “a huge intellectual triumph”, but what has it delivered?
- Julie Clayton
-
News Feature |
 Human genome at ten: Science after the sequence
Human genome at ten: Science after the sequence
The completion of the draft human genome sequence was announced ten years ago. Nature's survey of life scientists reveals that biology will never be the same again. Declan Butler reports.
- Declan Butler
-
News |
 Sequencing Napoleon's nemesis
Sequencing Napoleon's nemesis
Body-louse genome offers a glimpse into the genetic legacy of life as a permanent parasite.
- Heidi Ledford
-
Research Highlights |
Genomics: Genetic editing
-
Careers and Recruitment |
 The Sequencers
The Sequencers
Rapid technological developments have spurred big changes in the requisite genome-sequencing jobs. Kelly Rae Chi assesses the sequencing assembly line.
- Kelly Rae Chi
-
News |
 Ancient DNA set to rewrite human history
Ancient DNA set to rewrite human history
Discovery that some humans are part-Neanderthal reveals the promise of comparing genomes old and new.
- Rex Dalton
-
News |
 Genomics goes beyond DNA sequence
Genomics goes beyond DNA sequence
A technology that simultaneously reads a DNA sequence and its crucial modifications makes its debut.
- Alla Katsnelson
-
Research Highlights |
Genomics: Rat sequencing redux
-
News |
 It's a microbial world
It's a microbial world
Worldwide census ups diversity estimates for marine microbes one-hundred-fold.
- Jane Qiu
-
News Feature |
 Human genome at ten: The sequence explosion
Human genome at ten: The sequence explosion
-
News Feature |
 Human genome at ten: Life is complicated
Human genome at ten: Life is complicated
The more biologists look, the more complexity there seems to be. Erika Check Hayden asks if there's a way to make life simpler.
- Erika Check Hayden
-
News & Views |
 Stranger from Siberia
Stranger from Siberia
The sequencing of ancient DNA is generating dramatic results. The sequence from a bone fragment has revealed the existence of an unknown type of extinct human ancestor that lived in Asia 40,000 years ago.
- Terence A. Brown
-
Letter |
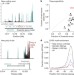 Understanding mechanisms underlying human gene expression variation with RNA sequencing
Understanding mechanisms underlying human gene expression variation with RNA sequencing
There is much interest in understanding the genetic mechanisms that underlie individual variations in gene expression. Here, RNA sequencing has been used to study gene expression in lymphoblastoid cell lines derived from Nigerian individuals for whom extensive genotype information is known. Numerous genetic determinants of variation in gene expression were identified, including variation in transcription, splicing and allele-specific expression.
- Joseph K. Pickrell
- , John C. Marioni
- & Jonathan K. Pritchard
-
Letter
| Open Access Whole-genome resequencing reveals loci under selection during chicken domestication
Whole-genome resequencing reveals loci under selection during chicken domestication
Here, the genomes of birds representing eight populations of domestic chickens are compared with the genome of their wild ancestor, the red jungle fowl. The results reveal selective sweeps of favourable alleles and mutations that may have contributed to domestication. One selective sweep, for instance, occurred at the locus encoding the thyroid stimulating hormone receptor, which is important in metabolism and in the timing of vertebrate reproduction.
- Carl-Johan Rubin
- , Michael C. Zody
- & Leif Andersson
-
Letter |
 Transcriptome genetics using second generation sequencing in a Caucasian population
Transcriptome genetics using second generation sequencing in a Caucasian population
Here, sequencing has been used to characterize the mRNA fraction of the transcriptome in Caucasian individuals, to provide a fine-scale view of transcriptomes and to identify genetic variants that affect alternative splicing. Measuring allele-specific expression identified rare expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) and allelic differences in transcript structure, revealing new properties of genetic effects on the transcriptome.
- Stephen B. Montgomery
- , Micha Sammeth
- & Emmanouil T. Dermitzakis
-
Article
| Open Access A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing
A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing
Deep metagenomic sequencing and characterization of the human gut microbiome from healthy and obese individuals, as well as those suffering from inflammatory bowel disease, provide the first insights into this gene set and how much of it is shared among individuals. The minimal gut metagenome as well as the minimal gut bacterial genome is also described.
- Junjie Qin
- , Ruiqiang Li
- & Jun Wang
-
News |
 Ancient polar-bear fossil yields genome
Ancient polar-bear fossil yields genome
Oldest mammalian DNA sequence reveals link to brown bears.
- Matt Kaplan
-
News |
 Personalized biomarkers monitor cancer
Personalized biomarkers monitor cancer
Pilot study harnesses sequencing power to track tumours.
- Heidi Ledford
-
News |
 Africa yields two full human genomes
Africa yields two full human genomes
Sequences show rich diversity among the population.
- Heidi Ledford
-
Article |
 The primary transcriptome of the major human pathogen Helicobacter pylori
The primary transcriptome of the major human pathogen Helicobacter pylori
The transcriptome of Helicobacter pylori, an important human pathogen involved in gastric ulcers and cancer, is presented. The approach establishes a model for mapping and annotating the primary transcriptomes of many living species.
- Cynthia M. Sharma
- , Steve Hoffmann
- & Jörg Vogel
-
Article
| Open Access Ancient human genome sequence of an extinct Palaeo-Eskimo
Ancient human genome sequence of an extinct Palaeo-Eskimo
The first genome sequence of an ancient human is reported. It comes from an approximately 4,000-year-old permafrost-preserved hair from a male from the first known culture to settle in Greenland. Functional single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) assessment is used to assign possible phenotypic characteristics and high-confidence SNPs are compared to those of contemporary populations to find those most closely related to the individual.
- Morten Rasmussen
- , Yingrui Li
- & Eske Willerslev
-
Article |
 Genome sequencing and analysis of the model grass Brachypodium distachyon
Genome sequencing and analysis of the model grass Brachypodium distachyon
The genome of the wild grass Brachypodium distachyon (Brachypodium), a member of the Pooideae subfamily, is sequenced. The Pooideae are one of three subfamilies of grasses that provide the bulk of human nutrition and may become major sources of renewable energy. Availability of the genome sequence should help establish Brachypodium as a model for developing new energy and food crops.
- John P. Vogel
- , David F. Garvin
- & Ivan Baxter
-
News & Views |
 Decoding a national treasure
Decoding a national treasure
The giant-panda genome is the first reported de novo assembly of a large mammalian genome achieved using next-generation sequencing methods. The feat reflects a trend towards ever-decreasing genome-sequencing costs.
- Kim C. Worley
- & Richard A. Gibbs
-
Article
| Open Access Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean
Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean
Soybean is an important crop plant, providing seed protein and oil and fixing atmospheric nitrogen through symbioses with soil-borne microorganisms. Using a whole-genome shotgun approach, its 1.1-gigabase genome is now sequenced and integrated with physical and high-density genetic maps to create a chromosome-scale draft sequence assembly.
- Jeremy Schmutz
- , Steven B. Cannon
- & Scott A. Jackson
-
Research Highlights |
Materials science: Sequencing with carbon
-
-
-
Letter |
 Systematic sequencing of renal carcinoma reveals inactivation of histone modifying genes
Systematic sequencing of renal carcinoma reveals inactivation of histone modifying genes
Clear cell renal carcinoma, the most common form of adult kidney cancer, is often characterized by the presence of inactivating mutations in the VHL gene. A large survey for somatic mutations now identifies inactivating mutations in two genes encoding enzymes involved in histone modification, highlighting the role of mutations in components of the chromatin modification machinery in human cancer.
- Gillian L. Dalgliesh
- , Kyle Furge
- & P. Andrew Futreal

 Michael Stratton & Peter Campbell
Michael Stratton & Peter Campbell The fickle Y chromosome
The fickle Y chromosome