Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
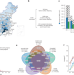 The Born in Guangzhou Cohort Study enables generational genetic discoveries
The Born in Guangzhou Cohort Study enables generational genetic discoveries
Analysis of data from the Born in Guangzhou Cohort Study comprising mainly of trios and mother–infant pairs reveals novel East Asian-specific genetic associations with maternal bile acid, gestational weight gain and infant cord blood traits.
- Shujia Huang
- , Siyang Liu
- & Xiu Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access Alternative splicing of latrophilin-3 controls synapse formation
Alternative splicing of latrophilin-3 controls synapse formation
Latrophilin-3 organizes synapses through a convergent dual-pathway mechanism in which Gαs signalling is activated and phase-separated postsynaptic protein scaffolds are recruited.
- Shuai Wang
- , Chelsea DeLeon
- & Thomas C. Südhof
-
Article
| Open Access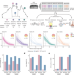 The landscape of genomic structural variation in Indigenous Australians
The landscape of genomic structural variation in Indigenous Australians
Population-scale whole-genome sequencing across four remote Indigenous Australian communities reveals a large fraction of structural variants that are unique to these populations, emphasizing the genetic distinctiveness of and diversity among Indigenous Australians.
- Andre L. M. Reis
- , Melissa Rapadas
- & Ira W. Deveson
-
Article
| Open Access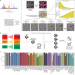 Ultra-fast deep-learned CNS tumour classification during surgery
Ultra-fast deep-learned CNS tumour classification during surgery
Sturgeon is a pretrained neural network that uses incremental results from nanopore sequencing to rapidly classify central nervous system tumours and can be used to aid critical decision-making during surgery.
- C. Vermeulen
- , M. Pagès-Gallego
- & J. de Ridder
-
Article
| Open Access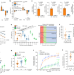 Transgenic ferret models define pulmonary ionocyte diversity and function
Transgenic ferret models define pulmonary ionocyte diversity and function
Conditional genetic ferret models enable ionocyte lineage tracing, ionocyte ablation and ionocyte-specific deletion of CFTR to elucidate the roles of pulmonary ionocyte biology and function during human health and disease.
- Feng Yuan
- , Grace N. Gasser
- & John F. Engelhardt
-
Article
| Open Access Gut microbial carbohydrate metabolism contributes to insulin resistance
Gut microbial carbohydrate metabolism contributes to insulin resistance
Faecal carbohydrates, particularly host-accessible monosaccharides, are increased in individuals with insulin resistance and are associated with microbial carbohydrate metabolisms and host inflammatory cytokines.
- Tadashi Takeuchi
- , Tetsuya Kubota
- & Hiroshi Ohno
-
Article
| Open Access Spatially resolved multiomics of human cardiac niches
Spatially resolved multiomics of human cardiac niches
Single-cell and spatial transcriptomic analysis of eight human heart tissues reveals the cellular profiles and tissue architecture of niches including the cardiac conduction system, and a new tool, drug2cell, identifies drug target expression.
- Kazumasa Kanemaru
- , James Cranley
- & Sarah A. Teichmann
-
Article
| Open Access A pangenome reference of 36 Chinese populations
A pangenome reference of 36 Chinese populations
A study reports data from the first phase of the Chinese Pangenome Consortium including 116 de novo assemblies from 58 core samples representing 36 minority Chinese ethnic groups.
- Yang Gao
- , Xiaofei Yang
- & Shuhua Xu
-
Article |
 Adeno-associated virus type 2 in US children with acute severe hepatitis
Adeno-associated virus type 2 in US children with acute severe hepatitis
A retrospective analysis using PCR testing, viral enrichment-based sequencing and agnostic metagenomic sequencing finds an association between adeno-associated virus type 2 and paediatric hepatitis of unknown cause.
- Venice Servellita
- , Alicia Sotomayor Gonzalez
- & Charles Y. Chiu
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Reply to: When did mammoths go extinct?
Reply to: When did mammoths go extinct?
- Yucheng Wang
- , Ana Prohaska
- & Eske Willerslev
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial profiling of chromatin accessibility in mouse and human tissues
Spatial profiling of chromatin accessibility in mouse and human tissues
Spatial-ATAC-seq—spatially resolved chromatin accessibility profiling of tissue sections using next-generation sequencing—delineated tissue-region-specific epigenetic landscapes in mouse embryos and identified gene regulators involved in the development of the central nervous system and the lymphoid tissue.
- Yanxiang Deng
- , Marek Bartosovic
- & Rong Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Late Quaternary dynamics of Arctic biota from ancient environmental genomics
Late Quaternary dynamics of Arctic biota from ancient environmental genomics
A large-scale metagenomic analysis of plant and mammal environmental DNA reveals complex ecological changes across the circumpolar region over the past 50,000 years, as biota responded to changing climates, culminating in the postglacial extinction of large mammals and emergence of modern ecosystems.
- Yucheng Wang
- , Mikkel Winther Pedersen
- & Eske Willerslev
-
Article
| Open Access Sequencing of 53,831 diverse genomes from the NHLBI TOPMed Program
Sequencing of 53,831 diverse genomes from the NHLBI TOPMed Program
The goals, resources and design of the NHLBI Trans-Omics for Precision Medicine (TOPMed) programme are described, and analyses of rare variants detected in the first 53,831 samples provide insights into mutational processes and recent human evolutionary history.
- Daniel Taliun
- , Daniel N. Harris
- & Gonçalo R. Abecasis
-
Article |
 High-depth African genomes inform human migration and health
High-depth African genomes inform human migration and health
Whole-genome sequencing analyses of African populations provide insights into continental migration, gene flow and the response to human disease, highlighting the importance of including diverse populations in genomic analyses to understand human ancestry and improve health.
- Ananyo Choudhury
- , Shaun Aron
- & Neil A. Hanchard
-
Article |
 The landscape of RNA Pol II binding reveals a stepwise transition during ZGA
The landscape of RNA Pol II binding reveals a stepwise transition during ZGA
Binding of RNA polymerase II during zygotic genome activation in mouse embryos is determined using the newly developed method Stacc–seq.
- Bofeng Liu
- , Qianhua Xu
- & Wei Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Exome sequencing and characterization of 49,960 individuals in the UK Biobank
Exome sequencing and characterization of 49,960 individuals in the UK Biobank
Exome sequences from the first 49,960 participants in the UK Biobank highlight the promise of genome sequencing in large population-based studies and are now accessible to the scientific community.
- Cristopher V. Van Hout
- , Ioanna Tachmazidou
- & Aris Baras
-
Matters Arising |
 APP gene copy number changes reflect exogenous contamination
APP gene copy number changes reflect exogenous contamination
- Junho Kim
- , Boxun Zhao
- & Eunjung Alice Lee
-
Article |
 Position-specific oxidation of miR-1 encodes cardiac hypertrophy
Position-specific oxidation of miR-1 encodes cardiac hypertrophy
The 8-oxoguanine modification of the microRNA miR-1 results in redirected recognition and silencing of target genes and leads to cardiac hypertrophy in mice.
- Heeyoung Seok
- , Haejeong Lee
- & Sung Wook Chi
-
Letter |
 Genome architecture and stability in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae knockout collection
Genome architecture and stability in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae knockout collection
Whole-genome sequencing of the strains of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene-knockout collection reveals the effects of the deletion of non-essential genes on genome stability.
- Fabio Puddu
- , Mareike Herzog
- & Stephen P. Jackson
-
Letter |
 Molecular architecture of lineage allocation and tissue organization in early mouse embryo
Molecular architecture of lineage allocation and tissue organization in early mouse embryo
Spatially resolved transcriptomes of cell populations at defined positions in the early mouse embryo reveal molecular bases of lineage specification and tissue patterning.
- Guangdun Peng
- , Shengbao Suo
- & Naihe Jing
-
Letter |
 Palaeo-Eskimo genetic ancestry and the peopling of Chukotka and North America
Palaeo-Eskimo genetic ancestry and the peopling of Chukotka and North America
DNA analysis of ancient individuals and modern populations suggests that the population history of North America can be explained by the admixture of two ancestral lineages—Palaeo-Eskimos and First Peoples.
- Pavel Flegontov
- , N. Ezgi Altınışık
- & Stephan Schiffels
-
Article
| Open Access Exome sequencing of 20,791 cases of type 2 diabetes and 24,440 controls
Exome sequencing of 20,791 cases of type 2 diabetes and 24,440 controls
Exome-sequencing analyses of a large cohort of patients with type 2 diabetes and control individuals without diabetes from five ancestries are used to identify gene-level associations of rare variants that are associated with type 2 diabetes.
- Jason Flannick
- , Josep M. Mercader
- & Michael Boehnke
-
Letter
| Open Access Genome organization and DNA accessibility control antigenic variation in trypanosomes
Genome organization and DNA accessibility control antigenic variation in trypanosomes
Long-read sequencing allows the assembly of antigen-gene arrays in Trypanosoma brucei and, coupled with deletion experiments, demonstrates that histone variants act as a molecular link between genome architecture, chromatin conformation and antigen variation.
- Laura S. M. Müller
- , Raúl O. Cosentino
- & T. Nicolai Siegel
-
Article |
 The genetic basis and cell of origin of mixed phenotype acute leukaemia
The genetic basis and cell of origin of mixed phenotype acute leukaemia
A large-scale genomics study shows that the cell of origin and founding mutations determine disease subtype and lead to the expression of multiple haematopoietic lineage-defining antigens in mixed phenotype acute leukaemia.
- Thomas B. Alexander
- , Zhaohui Gu
- & Charles G. Mullighan
-
Letter
| Open Access Sooty mangabey genome sequence provides insight into AIDS resistance in a natural SIV host
Sooty mangabey genome sequence provides insight into AIDS resistance in a natural SIV host
Whole-genome sequencing and comparative genomic analysis of immune-related genes of Cercocebus atys and Macaca mulatta identify candidate genes, such as ICAM2 and TLR4, that may explain the AIDS resistance of C. atys.
- David Palesch
- , Steven E. Bosinger
- & Guido Silvestri
-
Letter |
 Terminal Pleistocene Alaskan genome reveals first founding population of Native Americans
Terminal Pleistocene Alaskan genome reveals first founding population of Native Americans
An Ancient Beringian population from Late Pleistocene Alaska and the ancestors of other Native American groups descended from a single founding population that diversified around twenty thousand years ago.
- J. Víctor Moreno-Mayar
- , Ben A. Potter
- & Eske Willerslev
-
Letter |
 Genetic diversity of the African malaria vector Anopheles gambiae
Genetic diversity of the African malaria vector Anopheles gambiae
Genome sequencing analyses from 765 specimens of Anopheles gambiae and Anopheles coluzzii from 15 locations across Africa characterize patterns of gene flow and variations in population size, and provide a resource for studying the evolution of natural malaria vector populations.
- Alistair Miles
- , Nicholas J. Harding
- & Dominic P. Kwiatkowski
-
Letter
| Open Access Sequencing and de novo assembly of 150 genomes from Denmark as a population reference
Sequencing and de novo assembly of 150 genomes from Denmark as a population reference
A report of high-depth, short-read sequencing and de novo assemblies for 150 individuals from 50 parent–offspring trios as part of establishing a population reference genome for the GenomeDenmark project.
- Lasse Maretty
- , Jacob Malte Jensen
- & Mikkel Heide Schierup
-
Letter |
 Global profiling of SRP interaction with nascent polypeptides
Global profiling of SRP interaction with nascent polypeptides
Here, the selection of substrates by the protein–RNA complex known as the signal recognition particle (SRP) is investigated in the bacterium Escherichia coli, revealing that the SRP has a strong preference for hydrophobic transmembrane domains of inner membrane proteins.
- Daniela Schibich
- , Felix Gloge
- & Günter Kramer
-
Letter |
 Dynamics of ribosome scanning and recycling revealed by translation complex profiling
Dynamics of ribosome scanning and recycling revealed by translation complex profiling
A translation complex sequencing approach has been developed enabling intermediates of all mRNA-associated processes of translation to be isolated and localized across the transcriptome; the results support longstanding models of initiation and termination and offer new mechanistic insights.
- Stuart K. Archer
- , Nikolay E. Shirokikh
- & Thomas Preiss
-
Article |
 The genetic architecture of type 2 diabetes
The genetic architecture of type 2 diabetes
Sequencing data from two large-scale studies show that most of the genetic variation influencing the risk of type 2 diabetes involves common alleles and is found in regions previously identified by genome-wide association studies, clarifying the genetic architecture of this disease.
- Christian Fuchsberger
- , Jason Flannick
- & Mark I. McCarthy
-
Article |
 DNA methylation on N6-adenine in mammalian embryonic stem cells
DNA methylation on N6-adenine in mammalian embryonic stem cells
The prevalence of N6-adenine DNA methylation in mammals was previously unknown; this study reveals that N6-methyladenine can be found in mouse embryonic stem cells, especially at subfamilies of young (<1.5 million years old) LINE-1 transposons.
- Tao P. Wu
- , Tao Wang
- & Andrew Z. Xiao
-
Letter |
 Real-time, portable genome sequencing for Ebola surveillance
Real-time, portable genome sequencing for Ebola surveillance
A nanopore DNA sequencer is used for real-time genomic surveillance of the Ebola virus epidemic in the field in Guinea; the authors demonstrate that it is possible to pack a genomic surveillance laboratory in a suitcase and transport it to the field for on-site virus sequencing, generating results within 24 hours of sample collection.
- Joshua Quick
- , Nicholas J. Loman
- & Miles W. Carroll
-
Letter |
 Whole‐genome sequencing identifies EN1 as a determinant of bone density and fracture
Whole‐genome sequencing identifies EN1 as a determinant of bone density and fracture
Human population genomic studies, including whole‐genome sequencing, were undertaken to identify determinants of bone mineral density (BMD), a major predictor of osteoporotic fractures. Non‐coding variants with large effects on BMD and fractures were identified near the EN1 locus and mouse studies confirmed this gene has an important role in skeletal biology.
- Hou‐Feng Zheng
- , Vincenzo Forgetta
- & J. Brent Richards
-
Article
| Open Access The UK10K project identifies rare variants in health and disease
The UK10K project identifies rare variants in health and disease
Low read depth sequencing of whole genomes and high read depth exomes of nearly 10,000 extensively phenotyped individuals are combined to help characterize novel sequence variants, generate a highly accurate imputation reference panel and identify novel alleles associated with lipid-related traits; in addition to describing population structure and providing functional annotation of rare and low-frequency variants the authors use the data to estimate the benefits of sequencing for association studies.
- Klaudia Walter
- , Josine L. Min
- & Weihua Zhang
-
Letter |
 NAD captureSeq indicates NAD as a bacterial cap for a subset of regulatory RNAs
NAD captureSeq indicates NAD as a bacterial cap for a subset of regulatory RNAs
A newly developed method, NAD captureSeq, has been used to show that bacteria cap the 5′-ends of some RNAs to protect against degradation, much as happens with eukaryotic messenger RNAs, although with a different modification: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.
- Hana Cahová
- , Marie-Luise Winz
- & Andres Jäschke
-
Letter |
 Exome sequencing identifies rare LDLR and APOA5 alleles conferring risk for myocardial infarction
Exome sequencing identifies rare LDLR and APOA5 alleles conferring risk for myocardial infarction
Exome sequence analysis of nearly 10,000 people was carried out to identify alleles associated with early-onset myocardial infarction; mutations in low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) or apolipoprotein A-V (APOA5) were associated with disease risk, identifying the key roles of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins.
- Ron Do
- , Nathan O. Stitziel
- & Sekar Kathiresan
-
Letter |
 Role of TP53 mutations in the origin and evolution of therapy-related acute myeloid leukaemia
Role of TP53 mutations in the origin and evolution of therapy-related acute myeloid leukaemia
Somatic TP53 mutations are highly prevalent in therapy-related acute myeloid leukaemia and myelodysplastic syndrome, which arise as complications of cytotoxic chemotherapy or radiotherapy; although it was believed that these TP53 mutations are directly induced by cytotoxic therapy, new data indicate that they predate cytotoxic therapy and that haematopoietic progenitors harbouring these pre-existing mutations may selectively expand after exposure to chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
- Terrence N. Wong
- , Giridharan Ramsingh
- & Richard K. Wilson
-
Article |
 Synaptic, transcriptional and chromatin genes disrupted in autism
Synaptic, transcriptional and chromatin genes disrupted in autism
Whole-exome sequencing in a large autism study identifies over 100 autosomal genes that are likely to affect risk for the disorder; these genes, which show unusual evolutionary constraint against mutations, carry de novo loss-of-function mutations in over 5% of autistic subjects and many function in synaptic, transcriptional and chromatin-remodelling pathways.
- Silvia De Rubeis
- , Xin He
- & Joseph D. Buxbaum
-
Letter |
 Multiplex single-molecule interaction profiling of DNA-barcoded proteins
Multiplex single-molecule interaction profiling of DNA-barcoded proteins
Single-molecular-interaction-sequencing involves attaching DNA barcodes to proteins, assaying these barcoded proteins en masse in an aqueous solution, followed by immobilization in a polyacrylamide film and amplifying and analysing the barcoding DNAs—the method allows for precise protein quantification and simultaneous interrogation of molecular binding affinity and specificity.
- Liangcai Gu
- , Chao Li
- & George M. Church
-
Article
| Open Access Gibbon genome and the fast karyotype evolution of small apes
Gibbon genome and the fast karyotype evolution of small apes
The genome of the gibbon, a tree-dwelling ape from Asia positioned between Old World monkeys and the great apes, is presented, providing insights into the evolutionary history of gibbon species and their accelerated karyotypes, as well as evidence for selection of genes such as those for forelimb development and connective tissue that may be important for locomotion through trees.
- Lucia Carbone
- , R. Alan Harris
- & Richard A. Gibbs
-
Letter |
 Pseudouridine profiling reveals regulated mRNA pseudouridylation in yeast and human cells
Pseudouridine profiling reveals regulated mRNA pseudouridylation in yeast and human cells
The modification of uridine to pseudouridine is widespread in transfer and ribosomal RNAs but not observed so far in a coding RNA; here a new technique is used to detect this modification on a genome-wide scale, leading to the identification of pseudouridylation in messenger RNAs as well as almost 100 new sites in non-coding RNAs.
- Thomas M. Carlile
- , Maria F. Rojas-Duran
- & Wendy V. Gilbert
-
Letter |
 Genome sequencing identifies major causes of severe intellectual disability
Genome sequencing identifies major causes of severe intellectual disability
Whole-genome sequencing is used to identify genetic alterations in patients with severe intellectual disability for whom all other tests, including array and exome sequencing, returned negative results; de novo single-nucleotide and copy number variations affecting the coding region seem to be a major cause of this disorder.
- Christian Gilissen
- , Jayne Y. Hehir-Kwa
- & Joris A. Veltman
-
Article |
 Poly(A)-tail profiling reveals an embryonic switch in translational control
Poly(A)-tail profiling reveals an embryonic switch in translational control
A new high-throughput sequencing method to determine mRNA poly(A)-tail length enabled studies of individual RNAs across species and developmental stages to investigate the role of poly(A) length in translational regulation; the relationship between poly(A) length and translational efficiency shown in early embryo systems does not occur later in development, a finding that explains different regulatory consequences of microRNAs acting at different developmental times.
- Alexander O. Subtelny
- , Stephen W. Eichhorn
- & David P. Bartel
-
Article |
 De novo mutations in schizophrenia implicate synaptic networks
De novo mutations in schizophrenia implicate synaptic networks
The authors report the largest family-trio exome sequencing study of schizophrenia to date; mutations are overrepresented in genes for glutamatergic synaptic proteins and also genes mutated in autism and intellectual disability, providing insights into aetiological mechanisms and pathopshyisology shared with other neurodevelopmental disorders.
- Menachem Fromer
- , Andrew J. Pocklington
- & Michael C. O’Donovan
-
Article |
 A polygenic burden of rare disruptive mutations in schizophrenia
A polygenic burden of rare disruptive mutations in schizophrenia
Exome sequence analysis of more than 5,000 schizophrenia cases and controls identifies a polygenic burden primarily arising from rare, disruptive mutations distributed across many genes, among which are those encoding voltage-gated calcium ion channels and the signalling complex formed by the ARC protein of the postsynaptic density; as in autism, mutations were also found in homologues of known targets of the fragile X mental retardation protein.
- Shaun M. Purcell
- , Jennifer L. Moran
- & Pamela Sklar
-
Letter |
 The haplotype-resolved genome and epigenome of the aneuploid HeLa cancer cell line
The haplotype-resolved genome and epigenome of the aneuploid HeLa cancer cell line
Haplotype-resolved whole-genome sequencing of the HeLa CCL-2 strain shows that HeLa is relatively stable in terms of point variation; integration of several data sets reveals strong, haplotype-specific activation of the proto-oncogene MYC by the human papilloma virus type 18 genome, and enables the relationship between gene dosage and expression to be examined.
- Andrew Adey
- , Joshua N. Burton
- & Jay Shendure
-
Article
| Open Access Comprehensive molecular characterization of clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Comprehensive molecular characterization of clear cell renal cell carcinoma
The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network reports an integrative analysis of more than 400 samples of clear cell renal cell carcinoma based on genomic, DNA methylation, RNA and proteomic characterisation; frequent mutations were identified in the PI(3)K/AKT pathway, suggesting this pathway might be a potential therapeutic target, among the findings is also a demonstration of metabolic remodelling which correlates with tumour stage and severity.
- Chad J. Creighton
- , Margaret Morgan
- & Heidi J. Sofia.
-
Letter |
 Negligible impact of rare autoimmune-locus coding-region variants on missing heritability
Negligible impact of rare autoimmune-locus coding-region variants on missing heritability
A search for variants in coding exons of 25 genome-wide association study risk genes in a large cohort of autoimmune patients finds that rare coding-region variants at known loci have a negligible role in common autoimmune disease susceptibility, arguing against the previously proposed rare-variant synthetic genome-wide association hypothesis.
- Karen A. Hunt
- , Vanisha Mistry
- & David A. van Heel

 Whole-cortex in situ sequencing reveals input-dependent area identity
Whole-cortex in situ sequencing reveals input-dependent area identity