Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Anisotropic exchange interaction of two hole-spin qubits
Anisotropic exchange interaction of two hole-spin qubits
A successful silicon spin qubit design should be rapidly scalable by benefiting from industrial transistor technology. This investigation of exchange interactions between two FinFET qubits provides a guide to implementing two-qubit gates for hole spins.
- Simon Geyer
- , Bence Hetényi
- & Andreas V. Kuhlmann
-
Research Briefing |
 A compact neutral-atom fault-tolerant quantum computer based on new quantum codes
A compact neutral-atom fault-tolerant quantum computer based on new quantum codes
A practical and hardware-efficient blueprint for fault-tolerant quantum computing has been developed, using quantum low-density-parity-check codes and reconfigurable neutral-atom arrays. The scheme requires ten times fewer qubits and paves the way towards large-scale quantum computing using existing experimental technologies.
-
Article |
 Constant-overhead fault-tolerant quantum computation with reconfigurable atom arrays
Constant-overhead fault-tolerant quantum computation with reconfigurable atom arrays
Quantum low-density parity-check codes are highly efficient in principle but challenging to implement in practice. This proposal shows that these codes could be implemented in the near term using recently demonstrated neutral-atom arrays.
- Qian Xu
- , J. Pablo Bonilla Ataides
- & Hengyun Zhou
-
News & Views |
 Search for rule-breaking electrons
Search for rule-breaking electrons
Questioning the validity of axioms can teach us about physics beyond the standard model. A recent search for the violation of charge conservation and the Pauli exclusion principle yields limits on these scenarios.
- Alessio Porcelli
-
Article |
 Search for charge non-conservation and Pauli exclusion principle violation with the Majorana Demonstrator
Search for charge non-conservation and Pauli exclusion principle violation with the Majorana Demonstrator
The Majorana Demonstrator experiment reports searches for the violation of the Pauli exclusion principle and of charge conservation. In the absence of a signal, exclusion limits for these processes are reported.
- I. J. Arnquist
- , F. T. Avignone III
- & B. X. Zhu
-
Comment |
 A call for responsible quantum technology
A call for responsible quantum technology
The time has come to consider appropriate guardrails to ensure quantum technology benefits humanity and the planet. With quantum development still in flux, the science community shares a responsibility in defining principles and practices.
- Urs Gasser
- , Eline De Jong
- & Mauritz Kop
-
Article |
 Observation of the 2D–1D crossover in strongly interacting ultracold bosons
Observation of the 2D–1D crossover in strongly interacting ultracold bosons
Quantum systems exhibit vastly different properties depending on their dimensionality. An experimental study with ultracold bosons now tracks quantum correlation properties during the crossover from two dimensions to one dimension.
- Yanliang Guo
- , Hepeng Yao
- & Hanns-Christoph Nägerl
-
Article
| Open Access Leggett modes in a Dirac semimetal
Leggett modes in a Dirac semimetal
Leggett modes can occur when superconductivity arises in more than one band in a material and represent oscillation of the relative phases of the two superconducting condensates. Now, this mode is observed in Cd3As2, a Dirac semimetal.
- Joseph J. Cuozzo
- , W. Yu
- & Enrico Rossi
-
Article |
 Search for decoherence from quantum gravity with atmospheric neutrinos
Search for decoherence from quantum gravity with atmospheric neutrinos
Interactions of atmospheric neutrinos with quantum-gravity-induced fluctuations of the metric of spacetime would lead to decoherence. The IceCube Collaboration constrains such interactions with atmospheric neutrinos.
- R. Abbasi
- , M. Ackermann
- & M. Zimmerman
-
News & Views |
 Efficient learning of many-body systems
Efficient learning of many-body systems
The Hamiltonian describing a quantum many-body system can be learned using measurements in thermal equilibrium. Now, a learning algorithm applicable to many natural systems has been found that requires exponentially fewer measurements than existing methods.
- Sitan Chen
-
Article |
 Protecting entanglement between logical qubits via quantum error correction
Protecting entanglement between logical qubits via quantum error correction
Despite being essential to many applications in quantum science, entanglement can be easily disrupted by decoherence. A protocol based on repetitive quantum error correction now demonstrates enhanced coherence times of entangled logical qubits.
- Weizhou Cai
- , Xianghao Mu
- & Luyan Sun
-
Article |
Learning quantum Hamiltonians from high-temperature Gibbs states and real-time evolutions
Complexity of learning Hamiltonians from Gibbs states is an important issue for both many-body physics and machine learning. The optimal sample and time complexities of quantum Hamiltonian learning for high temperature has now been proven.
- Jeongwan Haah
- , Robin Kothari
- & Ewin Tang
-
Perspective |
 Drug design on quantum computers
Drug design on quantum computers
Quantum computers promise to efficiently predict the structure and behaviour of molecules. This Perspective explores how this could overcome existing challenges in computational drug discovery.
- Raffaele Santagati
- , Alan Aspuru-Guzik
- & Clemens Utschig-Utschig
-
Article
| Open Access Graph states of atomic ensembles engineered by photon-mediated entanglement
Graph states of atomic ensembles engineered by photon-mediated entanglement
Photon-mediated entanglement in atomic ensembles coupled to cavities enables the engineering of quantum states with a graph-like entanglement structure. This offers potential advantages in quantum computation and metrology.
- Eric S. Cooper
- , Philipp Kunkel
- & Monika Schleier-Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Cavity-mediated long-range interactions in levitated optomechanics
Cavity-mediated long-range interactions in levitated optomechanics
Combining multiparticle levitation with cavity control enables cavity-mediated interaction between levitated nanoparticles, whose strength can be tailored via optical detuning and position of the two particles.
- Jayadev Vijayan
- , Johannes Piotrowski
- & Lukas Novotny
-
Article |
 Observation of spin polarons in a frustrated moiré Hubbard system
Observation of spin polarons in a frustrated moiré Hubbard system
Spin polarons, bound states of a doped carrier and a spin flip excitation, are observed in a transition metal moiré bilayer.
- Zui Tao
- , Wenjin Zhao
- & Kin Fai Mak
-
Article |
 Nonclassical near-field dynamics of surface plasmons
Nonclassical near-field dynamics of surface plasmons
Most applications of surface plasmons are based on their near-field properties. These properties are now shown to be governed by nonclassical scattering between multiparticle plasmonic subsystems.
- Mingyuan Hong
- , Riley B. Dawkins
- & Omar S. Magaña-Loaiza
-
Article |
 Deterministic generation of multidimensional photonic cluster states with a single quantum emitter
Deterministic generation of multidimensional photonic cluster states with a single quantum emitter
Cluster states made from multiple photons with a special entanglement structure are a useful resource for quantum technologies. Two-dimensional cluster states of microwave photons have now been deterministically generated using a superconducting circuit.
- Vinicius S. Ferreira
- , Gihwan Kim
- & Oskar Painter
-
Article |
 Non-classical microwave–optical photon pair generation with a chip-scale transducer
Non-classical microwave–optical photon pair generation with a chip-scale transducer
A transducer that generates microwave–optical photon pairs is demonstrated. This could provide an interface between optical communication networks and superconducting quantum devices that operate at microwave frequencies.
- Srujan Meesala
- , Steven Wood
- & Oskar Painter
-
News & Views |
 Sound interactions across multiple modes
Sound interactions across multiple modes
Some quantum acoustic resonators possess a large number of phonon modes at different frequencies. Direct interactions between modes similar to those available for photonic devices have now been demonstrated. This enables manipulation of multimode states.
- Audrey Bienfait
-
Article |
 Superradiant and subradiant states in lifetime-limited organic molecules through laser-induced tuning
Superradiant and subradiant states in lifetime-limited organic molecules through laser-induced tuning
Laser-induced tuning of pairs of lifetime-limited organic emitters allows the controlled creation of superradiant and subradiant entangled states.
- Christian M. Lange
- , Emma Daggett
- & Jonathan D. Hood
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of Josephson harmonics in tunnel junctions
Observation of Josephson harmonics in tunnel junctions
The standard current–phase relation in tunnel Josephson junctions involves a single sinusoidal term, but real junctions are more complicated. The effects of higher Josephson harmonics have now been identified in superconducting qubit devices.
- Dennis Willsch
- , Dennis Rieger
- & Ioan M. Pop
-
News & Views |
 Symmetry matters
Symmetry matters
Quantum simulators can provide new insights into the complicated dynamics of quantum many-body systems far from equilibrium. A recent experiment reveals that underlying symmetries dictate the nature of universal scaling dynamics.
- Maximilian Prüfer
-
Article |
 Tunable quantum simulation of spin models with a two-dimensional ion crystal
Tunable quantum simulation of spin models with a two-dimensional ion crystal
Most quantum simulations of spin models with trapped ions have been restricted to one dimension. Now, tunable simulations of Ising models with single-site detection have been demonstrated in two-dimensional ion crystals.
- Mu Qiao
- , Zhengyang Cai
- & Kihwan Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering multimode interactions in circuit quantum acoustodynamics
Engineering multimode interactions in circuit quantum acoustodynamics
Quantum gates require controlled interactions between different degrees of freedom. A tunable coupling has now been demonstrated between the phonon modes of a mechanical resonator designed for storing and manipulating quantum information.
- Uwe von Lüpke
- , Ines C. Rodrigues
- & Yiwen Chu
-
Article |
 Raman sideband cooling of molecules in an optical tweezer array
Raman sideband cooling of molecules in an optical tweezer array
Raman sideband cooling is a method used to prepare atoms and ions in their vibrational ground state. This technique has now been extended to molecules trapped in optical tweezer arrays.
- Yukai Lu
- , Samuel J. Li
- & Lawrence W. Cheuk
-
News & Views |
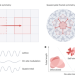 A kicked quasicrystal
A kicked quasicrystal
Quasicrystals are ordered but not periodic, which makes them fascinating objects at the interface between order and disorder. Experiments with ultracold atoms zoom in on this interface by driving a quasicrystal and exploring its fractal properties.
- Julian Léonard
-
Article |
 Covariant quantum kernels for data with group structure
Covariant quantum kernels for data with group structure
The kernel method in machine learning can be implemented on near-term quantum computers. A 27-qubit device has now been used to solve learning problems using kernels that have the potential to be practically useful.
- Jennifer R. Glick
- , Tanvi P. Gujarati
- & Kristan Temme
-
Article
| Open Access Inverse design of high-dimensional quantum optical circuits in a complex medium
Inverse design of high-dimensional quantum optical circuits in a complex medium
Light passing through complex media is subject to scattering processes that mix together different photonic modes. This complexity can be harnessed to implement quantum operations.
- Suraj Goel
- , Saroch Leedumrongwatthanakun
- & Mehul Malik
-
Article |
 Universality class of a spinor Bose–Einstein condensate far from equilibrium
Universality class of a spinor Bose–Einstein condensate far from equilibrium
The dynamics of isolated quantum many-body systems far from equilibrium is the object of intense research. Magnetization measurements in a spinor atomic gas now offer a way to classify universal dynamics based on symmetry and topology.
- SeungJung Huh
- , Koushik Mukherjee
- & Jae-yoon Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Second-scale rotational coherence and dipolar interactions in a gas of ultracold polar molecules
Second-scale rotational coherence and dipolar interactions in a gas of ultracold polar molecules
Coherence between rotational states of polar molecules has previously been limited by light shifts in optical traps. A magic-wavelength trap is able to maximize the coherence time and enables the observation of tunable dipolar interactions.
- Philip D. Gregory
- , Luke M. Fernley
- & Simon L. Cornish
-
Article
| Open Access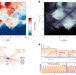 Anomalous localization in a kicked quasicrystal
Anomalous localization in a kicked quasicrystal
Phases of matter can host different transport behaviours, ranging from diffusion to localization. Anomalous transport has now been observed in an interacting Bose gas in a one-dimensional lattice subject to a pulsed incommensurate potential.
- Toshihiko Shimasaki
- , Max Prichard
- & David M. Weld
-
Article
| Open Access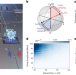 Programmable Heisenberg interactions between Floquet qubits
Programmable Heisenberg interactions between Floquet qubits
External driving of qubits can exploit their nonlinearity to generate different forms of interqubit interactions, broadening the capabilities of the platform.
- Long B. Nguyen
- , Yosep Kim
- & Irfan Siddiqi
-
Measure for Measure |
 Squeeze it tight
Squeeze it tight
Quantum technologies change our notion of measurement. Chenyu Wang elaborates on how quantum squeezing enhances the precision of gravitational-wave interferometers.
- Chenyu Wang
-
News & Views |
 A new way to use old codes
A new way to use old codes
Scalable quantum computers require quantum error-correcting codes that can robustly store information. Exploiting the structure of well-known classical codes may help create more efficient approaches to quantum error correction.
- Anirudh Krishna
-
Article
| Open Access Time-Efficient Constant-Space-Overhead Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computation
Time-Efficient Constant-Space-Overhead Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computation
Large quantum computers will require error correcting codes, but most proposals have prohibitive requirements for overheads in the number of qubits, processing time or both. A way to combine smaller codes now gives a much more efficient protocol.
- Hayata Yamasaki
- & Masato Koashi
-
News & Views |
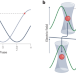 Parallel quantum control meets optical atomic clocks
Parallel quantum control meets optical atomic clocks
Optical atomic clocks are extremely accurate sensors despite the poor use of their resources. A parallel quantum control approach might help to optimize the resources of optical atomic clocks, which could lead to an exponential improvement in their performance.
- Simone Colombo
-
Article |
 Probing many-body correlations using quantum-cascade correlation spectroscopy
Probing many-body correlations using quantum-cascade correlation spectroscopy
Quantum-correlated photons typically characterize strongly nonlinear quantum emitters. A two-photon correlation spectroscopy method now provides a powerful probe of weakly nonlinear many-body quantum systems.
- Lorenzo Scarpelli
- , Cyril Elouard
- & Thomas Volz
-
Article |
 Emergence of highly coherent two-level systems in a noisy and dense quantum network
Emergence of highly coherent two-level systems in a noisy and dense quantum network
Quantum coherence is hard to maintain in solid-state systems, as interactions usually lead to fast dephasing. Exploiting disorder effects and interactions, highly coherent two-level systems have now been realized in a rare-earth insulator compound.
- A. Beckert
- , M. Grimm
- & G. Aeppli
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-ensemble metrology by programming local rotations with atom movements
Multi-ensemble metrology by programming local rotations with atom movements
Addressing optical transitions at the level of a single site is crucial to unlock the potential of quantum computers and atomic clocks. A scheme based on atom rearrangement now demonstrates such control with demonstrable metrological benefits.
- Adam L. Shaw
- , Ran Finkelstein
- & Manuel Endres
-
News & Views |
 Precisely simple
Precisely simple
Precise frequencies of nearly forbidden transitions have been ascertained in the simplest molecule, the molecular hydrogen ion. This work offers a new perspective on precision measurements and fundamental physical tests with molecular spectroscopy.
- Xin Tong
-
Article |
 Laser spectroscopy of a rovibrational transition in the molecular hydrogen ion \({\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{2}}^{\mathbf{+}}\)
Laser spectroscopy of a rovibrational transition in the molecular hydrogen ion \({\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{2}}^{\mathbf{+}}\)
Vibrational laser spectroscopy of the molecular hydrogen ion \({\rm{H}}_{2}^{+}\) offers new prospects for fundamental physics studies.
- M. R. Schenkel
- , S. Alighanbari
- & S. Schiller
-
Article |
 Direct comparison of two spin-squeezed optical clock ensembles at the 10−17 level
Direct comparison of two spin-squeezed optical clock ensembles at the 10−17 level
Noise is a fundamental obstacle to the stability of atomic optical clocks. An experiment now realizes the design of a spin-squeezed clock that improves interrogation times and enables direct comparisons of performance between different clocks.
- John M. Robinson
- , Maya Miklos
- & Jun Ye
-
Article |
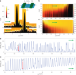 Edge supercurrent reveals competition between condensates in a Weyl superconductor
Edge supercurrent reveals competition between condensates in a Weyl superconductor
How superconducting states with different order parameter symmetries can interact with each other is not well understood. Now, the edge mode of a Weyl superconductor serves as a probe for competing condensates.
- Stephan Kim
- , Shiming Lei
- & N. P. Ong
-
Article |
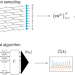 Quantum-inspired classical algorithms for molecular vibronic spectra
Quantum-inspired classical algorithms for molecular vibronic spectra
It has been suggested that Gaussian boson sampling may provide a quantum computational advantage for calculating the vibronic spectra of molecules. Now, an equally efficient classical algorithm has been identified.
- Changhun Oh
- , Youngrong Lim
- & Liang Jiang
-
Article |
 Protecting expressive circuits with a quantum error detection code
Protecting expressive circuits with a quantum error detection code
An error detecting code running on a trapped-ion quantum computer protects expressive circuits of eight logical qubits with a high-fidelity and partially fault-tolerant implementation of a universal gate set.
- Chris N. Self
- , Marcello Benedetti
- & David Amaro
-
Article |
 Realization of the Haldane Chern insulator in a moiré lattice
Realization of the Haldane Chern insulator in a moiré lattice
The Haldane model is a paradigmatic example of topological behaviour but has not previously been implemented in condensed-matter experiments. Now a moiré bilayer is shown to realize this model with the accompanying quantized transport response.
- Wenjin Zhao
- , Kaifei Kang
- & Kin Fai Mak
-
Matters Arising |
 Gauge non-invariance due to material truncation in ultrastrong-coupling quantum electrodynamics
Gauge non-invariance due to material truncation in ultrastrong-coupling quantum electrodynamics
- Adam Stokes
- & Ahsan Nazir
-
Comment |
 The tangled state of quantum hypothesis testing
The tangled state of quantum hypothesis testing
Quantum hypothesis testing—the task of distinguishing quantum states—enjoys surprisingly deep connections with the theory of entanglement. Recent findings have reopened the biggest questions in hypothesis testing and reversible entanglement manipulation.
- Mario Berta
- , Fernando G. S. L. Brandão
- & Marco Tomamichel

 Strong tunable coupling between two distant superconducting spin qubits
Strong tunable coupling between two distant superconducting spin qubits