News & Views |
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Twin experiments reveal twin electron dynamics
Twin experiments reveal twin electron dynamics
Two studies of electrons generated from laser-triggered emitters have found highly predictable electron–electron energy correlations. These studies, at vastly different energy scales, may lead to heralded electron sources, enabling quantum free-electron optics and low-noise, low-damage electron beam lithography and microscopy.
- John W. Simonaitis
- & Phillip D. Keathley
-
Article
| Open Access Coulomb-correlated electron number states in a transmission electron microscope beam
Coulomb-correlated electron number states in a transmission electron microscope beam
Coulomb interactions in free-electron beams are usually seen as an adverse effect. The creation of distinctive number states with one, two, three and four electrons now reveals unexpected opportunities for electron microscopy and lithography from Coulomb correlations.
- Rudolf Haindl
- , Armin Feist
- & Claus Ropers
-
Article |
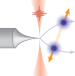 Few-electron correlations after ultrafast photoemission from nanometric needle tips
Few-electron correlations after ultrafast photoemission from nanometric needle tips
Even a few electrons confined to a tight space and time interval interact strongly, often causing issues for applications. The resulting repulsion has now been shown to allow strong electron–electron correlations, enabling shot-noise reduction.
- Stefan Meier
- , Jonas Heimerl
- & Peter Hommelhoff
-
Research Briefing |
 Accessing quantum information of field theories with ultracold atoms
Accessing quantum information of field theories with ultracold atoms
It’s a long-standing theoretical prediction that mutual information in locally interacting, many-body quantum systems follows an area law. Using cold-atom quantum-field simulators on an atom chip to measure the scaling of von Neumann entropy and mutual information, that prediction is now proved true.
-
News & Views |
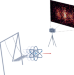 A picture of a swinging atom
A picture of a swinging atom
Reconstructing the motional quantum states of massive particles has important implications for quantum information science. Motional tomography of a single atom in an optical tweezer has now been demonstrated.
- Hannes Bernien
-
Article |
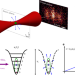 Time-of-flight quantum tomography of an atom in an optical tweezer
Time-of-flight quantum tomography of an atom in an optical tweezer
A tomography protocol that exploits the control offered by optical tweezers allows the reconstruction of motional states of a single trapped atom. This has implications for the study of non-classical states of massive trapped and levitated particles.
- M. O. Brown
- , S. R. Muleady
- & C. A. Regal
-
Review Article |
 Laser cooling for quantum gases
Laser cooling for quantum gases
Laser cooling underpins the field of ultracold quantum gases. This Review surveys recent methodological advances that are pushing quantum gases into new regimes.
- Florian Schreck
- & Klaasjan van Druten
-
Letter |
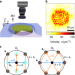 Pattern formation in a driven Bose–Einstein condensate
Pattern formation in a driven Bose–Einstein condensate
Two-dimensional density patterns with two-, four- and six-fold symmetries emerge in homogeneous Bose–Einstein condensates when the atomic interactions are modulated at multiple frequencies causing the coherent mixing of excitations.
- Zhendong Zhang
- , Kai-Xuan Yao
- & Cheng Chin
-
Letter |
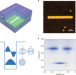 Observation of exciton polariton condensation in a perovskite lattice at room temperature
Observation of exciton polariton condensation in a perovskite lattice at room temperature
Non-equilibrium Bose–Einstein condensation of exciton polaritons in chains of lead halide perovskite pillars can occur at room temperature. These condensates have long spatial coherence.
- Rui Su
- , Sanjib Ghosh
- & Qihua Xiong
-
-
Letter |
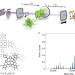 Quantum superposition of molecules beyond 25 kDa
Quantum superposition of molecules beyond 25 kDa
Matter-wave interference experiments demonstrate quantum superposition of molecules consisting of up to 2,000 atoms—the heaviest objects to show this quantum behaviour to date. This provides a bound on potential modifications to quantum mechanics.
- Yaakov Y. Fein
- , Philipp Geyer
- & Markus Arndt
-
-
Article |
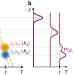 Quantum formulation of the Einstein equivalence principle
Quantum formulation of the Einstein equivalence principle
The physical conditions that support a geometric interpretation of spacetime, such as the equivalence between rest and inertial mass, are shown not to be necessarily valid in the quantum regime, and a quantum formulation is provided.
- Magdalena Zych
- & Časlav Brukner
-
Letter |
 Neural-network quantum state tomography
Neural-network quantum state tomography
Unsupervised machine learning techniques can efficiently perform quantum state tomography of large, highly entangled states with high accuracy, and allow the reconstruction of many-body quantities from simple experimentally accessible measurements.
- Giacomo Torlai
- , Guglielmo Mazzola
- & Giuseppe Carleo
-
Letter
| Open Access Attractive force on atoms due to blackbody radiation
Attractive force on atoms due to blackbody radiation
The effect of blackbody radiation is expected to be very weak. The acceleration due to the attractive optical forces from blackbody radiation is measured in an atom interferometer and, surprisingly, it dominates gravity and radiation pressure
- Philipp Haslinger
- , Matt Jaffe
- & Holger Müller
-
Letter |
 Testing sub-gravitational forces on atoms from a miniature in-vacuum source mass
Testing sub-gravitational forces on atoms from a miniature in-vacuum source mass
Atomic interferometry measurements of the gravitational force on free-falling atoms provide improved constraints on certain scalar field theories trying to explain dark energy.
- Matt Jaffe
- , Philipp Haslinger
- & Holger Müller
-
Letter |
 Ramsey-type phase control of free-electron beams
Ramsey-type phase control of free-electron beams
Using a technique inspired by Ramsey spectroscopy it is now possible to coherently control free electrons in an electron microscope.
- Katharina E. Echternkamp
- , Armin Feist
- & Claus Ropers
-
Letter |
 Single-shot simulations of dynamic quantum many-body systems
Single-shot simulations of dynamic quantum many-body systems
A simulation method connects single-shot measurements in ultracold atom experiments to the probability distribution of the many-body wavefunction, elucidating the role of the fluctuations in different experimental situations.
- Kaspar Sakmann
- & Mark Kasevich
-
Progress Article |
 Structured quantum waves
Structured quantum waves
Similar to orbital angular momentum-carrying optical beams, it is now possible to engineer structured electron beams that could find applications in imaging, nanofabrication and the study of fundamental phenomena.
- Jérémie Harris
- , Vincenzo Grillo
- & Ebrahim Karimi
-
Article |
 Measurement of the mobility edge for 3D Anderson localization
Measurement of the mobility edge for 3D Anderson localization
The mobility edge characterizes the transition from localization to diffusion. This key parameter in Anderson localization was measured for a system of ultracold atoms in a tunable disordered potential created by laser speckles.
- G. Semeghini
- , M. Landini
- & G. Modugno
-
News & Views |
 These crashing waves
These crashing waves
Solitons in attractive Bose–Einstein condensates are mesoscopic quantum objects that may prove useful as tools for precision measurement. A new experiment shows that collisions of matter-wave bright solitons depend crucially on their relative phase.
- Thomas P. Billam
- & Christoph Weiss

 Quantum optics meets attosecond science
Quantum optics meets attosecond science