Featured
-
-
Research Highlights |
 Racemization on the rack
Racemization on the rack
Thermally stable stereoisomers can be interconverted by the application of a mechanical force using ultrasound irradiation.
- Stephen Davey
-
Research Highlights |
 The krypton factor
The krypton factor
A krypton difluoride coordination compound — where it acts as a ligand to a bromine atom — has been synthesized and studied.
- Neil Withers
-
-
Blogroll |
Blogroll: Lessons learnt
-
News & Views |
 Stitching together palau'amine
Stitching together palau'amine
The long-awaited first total synthesis of the structurally intriguing natural product palau'amine has now been achieved. The synthesis features cascade reactions and an 'across ring' stitching of a 'macropalau'amine', and sets the bar for future efforts towards an enantioselective variant.
- Daniel Romo
-
News & Views |
 Seizing the caesium
Seizing the caesium
Public acceptance of the expansion of nuclear power may hinge on the safe disposal of nuclear waste. Ion exchangers that remove radioactive metals — such as caesium ions — from the waste could provide part of the answer, so a flexible-framework material that selectively grab them from solution is a step in the right direction.
- Abraham Clearfield
-
News & Views |
 Caught in a trap
Caught in a trap
Monitoring the dynamics of a single molecule is impeded by their motion in solution, and immobilizing them without changing their properties is problematic. By using a trapping method that counteracts a molecule's Brownian motion, the complex dynamics of a fluorescent protein, allophycocyanin, have been investigated.
- Peter Dedecker
- & Johan Hofkens
-
News & Views |
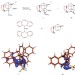 The same but different
The same but different
Electromerism is an unfamiliar concept to many chemists and refers to molecules that are not conventional isomers but instead differ in how the electrons are distributed across their structure. A novel example of such electromers has now been demonstrated.
- Thomas Bally
-
News & Views |
 Building bridges
Building bridges
Supramolecular gels, which rely on non-covalent interactions, are typically fragile. Now, hydrogels that possess remarkable mechanical strength combined with the ability to rapidly self-heal have been built through multiple non-covalent interactions.
- David K. Smith
-
Editorial |
 Cover story
Cover story
As the saying goes, a picture is worth a thousand words, but when that picture appears on the front cover of a scientific journal, that estimate is probably a little on the low side.
-
In Your Element |
 A flourish of fluorine
A flourish of fluorine
Herbert Roesky relates how the small, highly electronegative fluorine atom unveiled the chemical reactivity of noble gases and found many practical applications. but it can also render organic compounds highly toxic or pollutants.
- Herbert W. Roesky
-
-
News & Views |
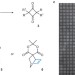 Facilitating functionality
Facilitating functionality
Monomers that contain masked ketene groups provide new opportunities for facile crosslinking and post-synthetic modification of polymers in a wide variety of materials applications.
- Steve Rimmer
-
Research Highlights |
 Our choice from the recent literature
Our choice from the recent literature
-
Commentary |
 Virtual conferences becoming a reality
Virtual conferences becoming a reality
Traditional scientific conferences can be costly and time-consuming, and certainly aren't 'green', with participants travelling long distances to attend. Are there advantages to meetings held in the virtual world, and can they really offer equally satisfying — or even better — experiences compared with the real world?
- Christopher J. Welch
- , Sanjoy Ray
- & Martin Leach
-
Article |
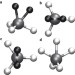 Quantum-induced symmetry breaking explains infrared spectra of CH5+ isotopologues
Quantum-induced symmetry breaking explains infrared spectra of CH5+ isotopologues
Stepwise deuteration of protonated methane CH5+ — a fluxional structure that undergoes ‘hydrogen scrambling’ — leads to dramatic changes in the infrared spectra of the isotopologues. The spectra can be assigned using ab initio quantum simulations that account for the non-classical occupation — by H and D atoms — of topologically different sites within the molecule.
- Sergei D. Ivanov
- , Oskar Asvany
- & Stephan Schlemmer
-
Article |
 Stereoinduction by distortional asymmetry
Stereoinduction by distortional asymmetry
Steric, torsion, stereoelectronic and polar effects are widely used to explain and predict the stereochemical outcome of synthetic organic reactions. Here, the asymmetric distortion of the reactant is considered and used to explain the observed stereoselectivity where these accepted models are unable to provide a clear prediction.
- Robert V. Kolakowski
- & Lawrence J. Williams
-
Article |
 Nanocrystalline intermetallics on mesoporous carbon for direct formic acid fuel cell anodes
Nanocrystalline intermetallics on mesoporous carbon for direct formic acid fuel cell anodes
Formic acid fuel cells require nanosized intermetallic nanoparticles as anode catalysts, but current techniques are poor at producing the small size required. Now, surface-modified ordered mesoporous carbons have been used to produce nanocrystallites as small as 1.5 nm that are extremely active catalysts.
- Xiulei Ji
- , Kyu Tae Lee
- & Linda F. Nazar
-
Article |
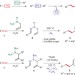 Triflimide-catalysed sigmatropic rearrangement of N-allylhydrazones as an example of a traceless bond construction
Triflimide-catalysed sigmatropic rearrangement of N-allylhydrazones as an example of a traceless bond construction
A triflimide-catalysed rearrangement of N-allylhydrazones has been developed that allows for the generation of a sigma bond between two unfunctionalized sp3 carbons such that no clear marker remains for how the bond was formed. This traceless bond construction offers new avenues for convergent fragment coupling in synthetic strategies.
- Devon A. Mundal
- , Christopher T. Avetta Jr
- & Regan J. Thomson
-
Research Highlights |
 An illuminating twist
An illuminating twist
The slow oxidation of tellurium in semiconductor cadmium telluride nanoparticles, accompanied by the replacement of tellurium by sulfur, has led to CdS/CdTe nanoparticles that self-assemble under visible light into twisted nanoribbons.
- Anne Pichon
-
Research Highlights |
 Hot to trot
Hot to trot
The motion of a molecule on a hot surface is investigated using molecular dynamics, revealing a regime of fast rolling and vibrational excitation.
- Gavin Armstrong
-
Article |
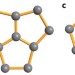 Chlorofullerenes featuring triple sequentially fused pentagons
Chlorofullerenes featuring triple sequentially fused pentagons
Fullerene cages that break the isolated pentagon rule are rare and often unstable. Now a range of fullerenes that feature three sequentially fused pentagons of carbon have been stabilized by chlorination.
- Yuan-Zhi Tan
- , Jia Li
- & Lan-Sun Zheng
-
Article |
 Total synthesis of the large non-ribosomal peptide polytheonamide B
Total synthesis of the large non-ribosomal peptide polytheonamide B
Polytheonamide B is a large non-ribosomal peptide with very high bioactivity. The synthesis described here includes the first preparation of several non-proteinogenic amino acids and a general coupling strategy for large non-natural peptides. The synthesis is a key step necessary to understand and utilize the bioactivity of this and similar compounds.
- Masayuki Inoue
- , Naoki Shinohara
- & Shigeru Matsuoka
-
Research Highlights |
 Surface conversion
Surface conversion
The reversible conversion between guanine-based extended ribbons and macrocyclic G-quartets has been directly observed at a liquid–solid interface by scanning tunnelling microscopy.
- Anne Pichon
-
Research Highlights |
 Ice ice maybe
Ice ice maybe
Positive charges lower, and negative charges raise the freezing temperature of supercooled water on a pyroelectric surface, as well as affecting at which interface nucleation takes place.
- Gavin Armstrong
-
Review Article |
 Organocatalytic cascade reactions as a new tool in total synthesis
Organocatalytic cascade reactions as a new tool in total synthesis
The field of organocatalysis has grown rapidly in the past decade to become, along with metal catalysis and biocatalysis, a third pillar of asymmetric catalysis. Here, progress in the use of organocatalytic cascade reactions for total synthesis is reviewed. The elegance and efficiency of such cascades mean that they have emerged as a powerful tool in synthetic organic chemistry.
- Christoph Grondal
- , Matthieu Jeanty
- & Dieter Enders
-
Research Highlights |
 Furans furnished
Furans furnished
A Brønsted acid co-catalyst is the key to the synthesis of furans by alkene cross-metathesis.
- Laura Croft
-
Research Highlights |
 X-ray ordering
X-ray ordering
Exposing supramolecular filaments to X-rays results in spontaneous and reversible crystalline ordering.
- Neil Withers
-
News & Views |
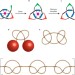 Tying up some loose ends
Tying up some loose ends
A linear molecule containing three bipyridine ligands can be wrapped around a single metal-ion template to form an open-knot complex. The loose ends of the knot can be 'tied' together through esterification or olefin-metathesis reactions to form closed knots that do not unravel when the metal template is removed.
- Edward E. Fenlon
-
Article |
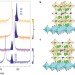 Anisotropic oxygen diffusion at low temperature in perovskite-structure iron oxides
Anisotropic oxygen diffusion at low temperature in perovskite-structure iron oxides
The movement of oxygen ions through materials is important in electrolytes and separation membranes, but is rare at lower temperatures. Two different low-temperature diffusion pathways are revealed during the reduction process of CaFeO2.5 to CaFeO2. The two pathways are significantly different, resulting in anisotropy.
- Satoru Inoue
- , Masanori Kawai
- & Yuichi Shimakawa
-
Article |
 Exceptional ammonia uptake by a covalent organic framework
Exceptional ammonia uptake by a covalent organic framework
The uptake of ammonia by a covalent–organic framework (COF) containing a high density of Lewis-acidic boron sites has been found to be significantly greater than that exhibited by other state-of-the-art porous materials. The ammonia can be removed by heating under vacuum and the structural integrity of the COF is maintained during adsorption/desorption cycles.
- Christian J. Doonan
- , David J. Tranchemontagne
- & Omar M. Yaghi
-
Article |
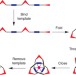 Synthesis of a molecular trefoil knot by folding and closing on an octahedral coordination template
Synthesis of a molecular trefoil knot by folding and closing on an octahedral coordination template
The synthesis of interlocked compounds such as catenanes and rotaxanes has undergone much development in recent years, but molecular knots are still relatively hard to make. It has now been shown that a linear bipyridine oligomer can fold around a single zinc-ion template to form a complex that can be cyclized to give a molecular trefoil knot.
- Jun Guo
- , Paul C. Mayers
- & Christopher A. Hunter
-
Article |
 Exploring local currents in molecular junctions
Exploring local currents in molecular junctions
A methodology for describing local electronic transmission through bridging molecules between metallic electrodes is presented. Its application to simple alkane, phenyl and cross-conjugated systems highlights an unexpected number of cases whereby ‘through space’, rather than ‘through bond’ terms dominate and that interference effects coincide with the reversal of ring currents.
- Gemma C. Solomon
- , Carmen Herrmann
- & Mark A. Ratner
-
Research Highlights |
 Practical honeycombs
Practical honeycombs
Silicon-based polymers have been assembled into honeycomb films that exhibit good flexibility, stability and thermal conductivity, showing great promise for industrial applications.
- Anne Pichon
-
Research Highlights |
Advancing vaccines
Replacing readily hydrolysable ester linkages with amides in a natural adjuvant has resulted in not only more stable, but significantly more active and less toxic analogues.
- Georgia Tsoukala
-
-
Blogroll |
Blogroll: Take a deep breath
-
News & Views |
 Chemistry from photons
Chemistry from photons
The use of conventional computers to calculate molecular properties is hindered by the exponential increase in computational cost on increasing the size of the molecules studied. Using quantum computers could be the solution and the initial steps are now being taken.
- Kenneth R. Brown
-
News & Views |
 Unearthing the unconventional
Unearthing the unconventional
Quantum tunnelling can at times be the cause of kinetic isotope effects, and in these cases conventional wisdom has been that molecules with isotopes of larger mass will react more slowly. New calculations, however, predict that sometimes the reverse should be true.
- Barry K. Carpenter
-
News & Views |
 Visualizing fullerene chemistry
Visualizing fullerene chemistry
Chemical reactions of fullerenes and metallofullerenes lined up inside single-walled carbon nanotubes can be monitored at the atomic scale inside an aberration-corrected transmission electron microscope.
- Mauricio Terrones
-
News & Views |
 A controlled sequence of events
A controlled sequence of events
Yttrium-based catalysts can be used to stitch together two different lactone monomers in an alternating fashion to produce polyesters with well-defined primary structures. The ability to control the sequence of building blocks in polymers with increasing levels of precision offers new opportunities for tailoring the properties of designer synthetic macromolecules.
- Jean-François Lutz
-
News & Views |
 Stereochemistry by remote control
Stereochemistry by remote control
The stereochemical lability of cycloalkylzinc reagents combined with a large difference in reactivity between epimers has been exploited to form a wide variety of interesting organic compounds with both high yields and diastereoselectivities.
- Frank Glorius
-
News & Views |
 Sweet flexibility
Sweet flexibility
An enzyme that is unusually tolerant of a truly broad range of substrates can catalyse aldol-type chemistry on sugars in which the various hydroxyl groups are protected. The new methodology combines some of the most important advantages of enzyme and small-molecule catalysis.
- Benjamin G. Davis
-
-
In Your Element |
 Welcome copernicium?
Welcome copernicium?
In the search for superheavy elements, element 112 was a stepping stone towards the 'islands of stability'. Sigurd Hofmann now relates the steps that led to its 'creation' and detection.
- Sigurd Hofmann
-
News & Views |
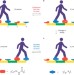 Tiny steps
Tiny steps
A molecular 'walker' can be made to move up and down a molecular 'track' by alternately locking and unlocking the two different types of covalent bonds that join the two components together. By changing the conditions under which one of the bond-forming/bond-breaking processes occurs, a directional bias for walking can be achieved.
- Sijbren Otto
-
Editorial |
A Dickens of a funding problem
The financial crisis that continued to grip the world in 2009 has brought the question of who should pay for scientific research — and what it should set out to achieve — into sharper focus than ever.
-
Thesis |
 Men of mystery
Men of mystery
Michelle Francl wonders why people almost inevitably draw scientists as men with weird hair and glasses, and why there is no such thing as a 'draw a lawyer' test.
- Michelle Francl
-
Research Highlights |
 Our choice from the recent literature
Our choice from the recent literature

 Binding energies, lifetimes and implications of bulk and interface solvated electrons in water
Binding energies, lifetimes and implications of bulk and interface solvated electrons in water Nanoparticles ring the changes
Nanoparticles ring the changes Tomography reveals all
Tomography reveals all