Featured
-
-
Letter |
 Control of valley polarization in monolayer MoS2 by optical helicity
Control of valley polarization in monolayer MoS2 by optical helicity
Circularly polarized light has been used to confine charge carriers in single-layer molybdenum disulphide entirely to a single energy-band valley, representing full valley polarization.
- Kin Fai Mak
- , Keliang He
- & Tony F. Heinz
-
Article |
 Dual-gated bilayer graphene hot-electron bolometer
Dual-gated bilayer graphene hot-electron bolometer
An infrared bolometer made using bilayer graphene compares favourably to existing devices in terms of sensitivity, noise equivalent power and speed.
- Jun Yan
- , M-H. Kim
- & H. D. Drew
-
Article |
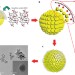 Emissive ZnO–graphene quantum dots for white-light-emitting diodes
Emissive ZnO–graphene quantum dots for white-light-emitting diodes
Quantum dots with a zinc oxide core and a strained graphene shell are used as an emissive layer in a white-light-emitting diode.
- Dong Ick Son
- , Byoung Wook Kwon
- & Won Kook Choi
-
Letter |
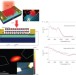 Hybrid graphene–quantum dot phototransistors with ultrahigh gain
Hybrid graphene–quantum dot phototransistors with ultrahigh gain
A phototransistor in which electric charges are absorbed by colloidal quantum dots and circulated in graphene exhibits high values for gain, responsivity and specific detectivity.
- Gerasimos Konstantatos
- , Michela Badioli
- & Frank H. L. Koppens
-
Letter |
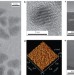 Red, green and blue lasing enabled by single-exciton gain in colloidal quantum dot films
Red, green and blue lasing enabled by single-exciton gain in colloidal quantum dot films
Films of densely packed core–shell quantum dots demonstrate full-colour amplified spontaneous emission with single-exciton gain, and are used to build vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers operating at very low optical pumping thresholds.
- Cuong Dang
- , Joonhee Lee
- & Arto Nurmikko
-
Research Highlights |
Diffusive light made simple
-
News & Views |
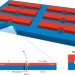 Tiny holes with great promise
Tiny holes with great promise
Sensors that combine solid-state nanopores and nanowire field-effect transistors can be used to detect single DNA molecules quickly and with high sensitivity.
- Dario Anselmetti
-
Letter |
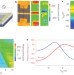 Ultrafast hot-carrier-dominated photocurrent in graphene
Ultrafast hot-carrier-dominated photocurrent in graphene
Hot carriers dominate energy transport across graphene p–n junctions that are excited by ultrafast laser pulses, and set fundamental limits on device speeds.
- Dong Sun
- , Grant Aivazian
- & Xiaodong Xu
-
Letter |
 Direct visualization of large-area graphene domains and boundaries by optical birefringency
Direct visualization of large-area graphene domains and boundaries by optical birefringency
The domain structure of macroscopic graphene samples can be simply observed by covering them with liquid-crystal molecules.
- Dae Woo Kim
- , Yun Ho Kim
- & Hee-Tae Jung
-
Article |
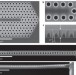 One- and two-dimensional photonic crystal microcavities in single crystal diamond
One- and two-dimensional photonic crystal microcavities in single crystal diamond
Optical microcavities have been fabricated in single-crystal diamond and tuned into resonance with the zero phonon line of an ensemble of silicon-vacancy colour centres, which results in an enhancement of spontaneous emission.
- Janine Riedrich-Möller
- , Laura Kipfstuhl
- & Christoph Becher
-
Letter |
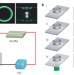 Detecting single viruses and nanoparticles using whispering gallery microlasers
Detecting single viruses and nanoparticles using whispering gallery microlasers
It is possible to detect single viruses and single nanoparticles in air and in water by measuring how they change the output of a whispering-gallery-mode microlaser.
- Lina He
- , Şahin Kaya Özdemir
- & Lan Yang
-
Article |
 Virus-templated self-assembled single-walled carbon nanotubes for highly efficient electron collection in photovoltaic devices
Virus-templated self-assembled single-walled carbon nanotubes for highly efficient electron collection in photovoltaic devices
Composites composed of single-walled carbon nanotubes and titania nanocrystals can be synthesized using a genetically engineered M13 virus as a template, and used to create highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells.
- Xiangnan Dang
- , Hyunjung Yi
- & Angela M. Belcher
-
News & Views |
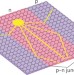 Making light of electrons
Making light of electrons
Electrons have been channelled through graphene wires using the principles of optical guiding by fibre optic cables.
- David Goldhaber-Gordon
-
News & Views |
 Terahertz radiation gets shaken up
Terahertz radiation gets shaken up
Mechanical vibrations in piezoelectric structures induced by green laser light can efficiently produce electromagnetic radiation at terahertz frequencies.
- Peter Uhd Jepsen
-
Letter |
 Plasmonic Luneburg and Eaton lenses
Plasmonic Luneburg and Eaton lenses
Grey-scale lithography has been used to make Luneburg and Eaton lenses that have lower losses than previously reported plasmonic elements.
- Thomas Zentgraf
- , Yongmin Liu
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Research Highlights |
A better shot in the dark
-
Article |
 Single-walled carbon nanotubes as excitonic optical wires
Single-walled carbon nanotubes as excitonic optical wires
Experiments have shown that carbon nanotubes are ideal optical wires, with properties affected by excitonic and other intrinsic properties, as well as by shape.
- Daniel Y. Joh
- , Jesse Kinder
- & Jiwoong Park
-
Letter |
 Vibrational and electronic heating in nanoscale junctions
Vibrational and electronic heating in nanoscale junctions
Surface-enhanced Raman emission can measure the effective temperatures both of the vibrational modes and the flowing electrons in a nanoscale junction.
- Daniel R. Ward
- , David A. Corley
- & Douglas Natelson
-
News & Views |
 Moving into the red
Moving into the red
Can silicon ever be a true direct-bandgap semiconductor? The first observation of a new, short-lived photoluminescence band from silicon nanocrystals offers fresh hope.
- Dmitry Kovalev
-
Letter |
 Electroluminescence from a single nanotube–molecule–nanotube junction
Electroluminescence from a single nanotube–molecule–nanotube junction
Voltage-induced light emission has been observed from a molecule attached to two carbon-nanotube electrodes.
- Christoph W. Marquardt
- , Sergio Grunder
- & Ralph Krupke
-
Article |
 Red spectral shift and enhanced quantum efficiency in phonon-free photoluminescence from silicon nanocrystals
Red spectral shift and enhanced quantum efficiency in phonon-free photoluminescence from silicon nanocrystals
An ultrafast visible band in the photoluminescence spectrum of silicon nanocrystals increases in intensity and shifts to longer wavelengths as the size of the nanocrystals decreases.
- W. D. A. M. de Boer
- , D. Timmerman
- & T. Gregorkiewicz
-
Research Highlights |
A repulsive trap
-
Research Highlights |
Quantum dots beat the limit
-
News & Views |
 Plasmons offer a helping hand
Plasmons offer a helping hand
Arrays of metallic nanostructures allow chiral biomolecules to be detected and characterized with increased sensitivity.
- Romain Quidant
- & Mark Kreuzer
-
Research Highlights |
LEDs learn to relax
-
Letter |
 Optical rectification and field enhancement in a plasmonic nanogap
Optical rectification and field enhancement in a plasmonic nanogap
Optical rectification and electric-field enhancements in excess of 1,000 are observed when a subnanometre gap between gold electrodes is illuminated with infrared radiation.
- Daniel R. Ward
- , Falco Hüser
- & Douglas Natelson
-
News & Views |
 Written with light
Written with light
An array of polymer tips that can channel light to an underlying substrate can be used to generate intricate nanostructures with high throughput and over large areas.
- Aaron Hernandez-Santana
- & Duncan Graham
-
Research Highlights |
In hot pursuit
-
News & Views |
 New twist on nanoscale motors
New twist on nanoscale motors
Linearly polarized light that does not possess any angular momentum can be used to rotate a gold nanostructure that can, in turn, rotate a much larger silica microdisk.
- Erez Hasman
-
Letter |
 Beam pen lithography
Beam pen lithography
A technique based on scanning probe microscopy, which uses a two-dimensional array of nanoscopic apertures fabricated at the end of polymer tips to channel light to an underlying substrate, can be used to generate arbitrary patterns with both sub-diffraction limit and larger feature sizes over large areas.
- Fengwei Huo
- , Gengfeng Zheng
- & Chad A. Mirkin
-
Research Highlights |
Electric entanglement
-
Letter |
 Light-driven nanoscale plasmonic motors
Light-driven nanoscale plasmonic motors
Linearly polarized light can be used to generate a rotational force in a plasmonic nanostructure that is capable of rotating a much larger microdisk.
- Ming Liu
- , Thomas Zentgraf
- & Xiang Zhang
-
News & Views |
 Plasmonics gets transformed
Plasmonics gets transformed
A high degree of control over plasmons can be achieved at the nanoscale by engineering the properties of adjacent dielectric layers.
- Wenshan Cai
- & Mark L. Brongersma
-
News & Views |
 The third plasmonic revolution
The third plasmonic revolution
Combining nanostructured magnetic media with nanoplasmonic antennas has propelled commercially viable data-storage densities beyond one terabit per square inch.
- Daniel O'Connor
- & Anatoly V. Zayats
-
Research Highlights |
To the limit and beyond
-
Editorial |
The many aspects of quantum dots
From fundamental physics and chemistry to digital cameras, improved displays and more natural lighting, nanoscale semiconductor structures called quantum dots are having an impact on many areas of science and technology.
-
Letter |
 Mimicking the colourful wing scale structure of the Papilio blumei butterfly
Mimicking the colourful wing scale structure of the Papilio blumei butterfly
Colour mixing and other optical effects displayed by the wings of the Papilio blumei butterfly have now been replicated by a combination of colloid self-assembly and other standard layer-deposition techniques.
- Mathias Kolle
- , Pedro M. Salgard-Cunha
- & Ullrich Steiner
-
Letter |
 Spectroscopy of few-electron single-crystal silicon quantum dots
Spectroscopy of few-electron single-crystal silicon quantum dots
By controlling the density of phosphorus dopant atoms in single-crystal silicon it is possible to fabricate quantum dots that do not contain interfaces between different materials.
- Martin Fuechsle
- , S. Mahapatra
- & Michelle Y. Simmons
-
-
News & Views |
 Switching blinking on and off
Switching blinking on and off
Diamonds with a diameter of just 5 nm are capable of supporting colour centres and emitting fluorescence, and encapsulating these nanodiamonds in a polymer stops them blinking.
- Joerg Wrachtrup
-
Letter |
 Optical heating and rapid transformation of functionalized fullerenes
Optical heating and rapid transformation of functionalized fullerenes
The response of polyhydroxy fullerene and other functionalized fullerenes to low levels of laser irradiation could be exploited in a variety of applications.
- Vijay Krishna
- , Nathanael Stevens
- & Brij Moudgil
-
Letter |
 Lipid multilayer gratings
Lipid multilayer gratings
Diffraction gratings composed of lipid multilayers can be fabricated by dip-pen nanolithography and used for label-free biosensing.
- Steven Lenhert
- , Falko Brinkmann
- & Harald Fuchs
-
News & Views |
 Focusing on the objective
Focusing on the objective
Placing colloidal spheres in the immediate proximity of fluorescent molecules makes it possible to achieve single-molecule imaging at high temperatures with a low-cost system.
- Yuval Ebenstein
- & Laurent A. Bentolila
-
Article |
 Above-bandgap voltages from ferroelectric photovoltaic devices
Above-bandgap voltages from ferroelectric photovoltaic devices
Steps in the electrostatic potential at domain walls in a ferroelectric material give rise to a new kind of photovoltaic effect that produces voltages significantly higher than the bandgap of the material.
- S. Y. Yang
- , J. Seidel
- & R. Ramesh

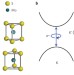 Valley polarization in MoS2 monolayers by optical pumping
Valley polarization in MoS2 monolayers by optical pumping