Focus Review |
Featured
-
-
Original Article |
 Phase separation in benzoxazine/epoxy resin blending systems
Phase separation in benzoxazine/epoxy resin blending systems
The possibility of phase separation of benzoxazine (BZ)/epoxy resin (ER) blends were investigated via model components. The experiment result indicated that if the molecular weight of ER can increase to a higher extent (for example, ⩾4370 g mol−1) before the polymerization of BZ resin occurs, phase separation of BZ/ER blends can take place in-situ. By varying the ER content in the system, sea-island structure, ribbon weave-like bi- continuous structure and inverted-phase structure can be obtained.
- Pei Zhao
- , Qian Zhou
- & Yi Gu
-
Original Article |
 In situ small-angle X-ray and neutron scattering measurements on a blend of deuterated and hydrogenated polyethylenes during uniaxial drawing
In situ small-angle X-ray and neutron scattering measurements on a blend of deuterated and hydrogenated polyethylenes during uniaxial drawing
In situ small-angle X-ray and neutron scattering (SAXS and SANS) measurements were conducted on an isotropic blend of deuterated polyethylene (97 wt%) and hydrogenated polyethylene (3 wt%) during uniaxial drawing at 125 °C to clarify the formation mechanism of shish-kebab from isotropic film. Figure shows that 2D SANS and SAXS patterns in the various drawing ratio, RD, conditions. The drawing direction is longitudinal. In RD=8, the streak-like scattering in the normal direction of drawing became stronger only in the SANS, showing that more hydrogenated polyethylene chains were merged into the shish.
- Go Matsuba
- , Chie Ito
- & Toshiji Kanaya
-
Original Article |
 Complete NMR assignment of a sulfonated aromatic block copolymer via heteronuclear single-quantum correlation, heteronuclear multiple-bond correlation and heteronuclear single-quantum correlation total correlation spectroscopy
Complete NMR assignment of a sulfonated aromatic block copolymer via heteronuclear single-quantum correlation, heteronuclear multiple-bond correlation and heteronuclear single-quantum correlation total correlation spectroscopy
A sulfonated aromatic block copolymer (SABC), consisting of hydrophobic and hydrophilic blocks, was analyzed by 2D NMR techniques of HSQC, HMBC and HSQC–TOCSY. Because of its complicated chemical structure with five different phenylene rings, 12 types of 1H signals and 24 types of 13C signals were observed in a narrow chemical shift range (7.0–8.0 p.p.m. for 1H and 118–162 p.p.m. for 13C). As a result of these studies, complete 1H and 13C NMR signal assignment of SABC was performed.
- Mari Takasaki
- , Kazuo Kimura
- & Masahiro Watanabe
-
Original Article |
 Structural studies of amphiphilic oligopeptides composed of alternating alanine and ionizable amino-acid residues using CD and 13C CP/MAS NMR spectroscopy
Structural studies of amphiphilic oligopeptides composed of alternating alanine and ionizable amino-acid residues using CD and 13C CP/MAS NMR spectroscopy
It was observed that the peptides resulted in β-sheet structure when the peptide solutions were mixed in combination of the side-chain charges being neutralized by each other. Additionally, formation speeds of the β-sheet structure were different between systems, AD12 and AK12 or AE12 and AK12. These phenomena were also observed under the higher concentration condition by 13C CP/MAS NMR. These results indicate that the mixing of the two kinds of peptide solutions will be a trigger for the peptide self-assembly and will be able to control the formation speed by the combination.
- Chikako T Nakazawa
- , Atsushi Asano
- & Takuzo Kurotsu
-
Original Article |
 Structural characterization of silk-polyurethane composite material for biomaterials using solid-state NMR
Structural characterization of silk-polyurethane composite material for biomaterials using solid-state NMR
In this study, we investigated the molecular structure of the composite material of silk fibroin and polyurethane as coating agent of vascular grafts by using solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) techniques. To elucidate the structure and dynamics, 13C cross-polarization (CP)/magic angle spinning (MAS) NMR studies including NMR relaxation experiments were performed. These observations showed that there is a partial interacted portion between soft segment of PU and SF, in particular, the domain size of PU:SU=1:1 composite was smaller than that of the other composites. This study gave basic information on development of new silk-like materials for vascular grafts.
- Yasumoto Nakazawa
- , Atsushi Asano
- & Tetsuo Asakura
-
Note |
 A two-dimensional spin-diffusion NMR study on the local structure of a water-soluble model peptide for Nephila clavipes dragline silk (MaSp1) before and after spinning
A two-dimensional spin-diffusion NMR study on the local structure of a water-soluble model peptide for Nephila clavipes dragline silk (MaSp1) before and after spinning
The local structure of the acidic-treated model peptides,(E)8GGLGGQGAG(A)6GGAGQGGYGG, derived from the consensus sequence of Nephila clavipes fibroin major ampullate spidroin 1 was determined using two-dimensional proton-driven spin-diffusion solid-state NMR under off-magic-angle spinning coupled with 13C isotope double labeling of specific residues. We observed a positional dependence on the torsion angles of Ala residues in the β sheet. Torsion angle of the Ala residue at the center of poly-Ala domain concentrates around at (ϕ, ψ) = (−150°, 150°), while that of its periphery is distorted and more distributed.
- Koji Yazawa
- , Erika Yamaguchi
- & Tetsuo Asakura
-
Review |
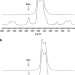 Some aspects of the NMR chemical shift/structure correlation in the structural characterization of polymers and biopolymers
Some aspects of the NMR chemical shift/structure correlation in the structural characterization of polymers and biopolymers
Studies on NMR methodology of characterizing the structure of polymers and biopolymers based on understanding of NMR chemical shift/structure correlation by solution-state and solid-state NMR experiments, development of NMR chemical shift theory and their combination have been reviewed.
- Isao Ando
-
Original Article |
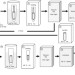 1H MRI study of small-diameter silk vascular grafts in water
1H MRI study of small-diameter silk vascular grafts in water
The images of 1H spin density, 1H T2 and diffusion coefficient (D) of water molecules in the layer of silk-based vascular grafts (VG) coated by different materials that are silk fibroin or polyurethane were non-destructively observed in water using 1H MR imaging. The inner and outer coating materials affect significantly the amount and mobility of water molecules in the VG.
- Shigeki Kuroki
- , Masahito Kanekiyo
- & Tetsuo Asakura
-
Original Article |
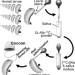 Quantifying the fraction of alanine residues in an α-helical conformation in hornet silk using solid-state NMR
Quantifying the fraction of alanine residues in an α-helical conformation in hornet silk using solid-state NMR
An isotope-labeled hornet (Vespa) cocoon in which the Ala carbons of silk proteins were substituted with 13C was successfully obtained by feeding a mixture of larval saliva with [13C3]Ala to mature larvae. The Ala fraction in the α-helix conformation of hornet silk was estimated by obtaining high-resolution 13C solid-state NMR spectra of the labeled cocoon, which also helped in understanding the molecular structure of hornet silk.
- Tsunenori Kameda
-
Original Article
| Open Access Statistical approach for solid-state NMR spectra of cellulose derived from a series of variable parameters
Statistical approach for solid-state NMR spectra of cellulose derived from a series of variable parameters
A multivariate analysis was used to extract components in solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra from bacterial cellulose (BC). Polymers such as cellulose have several domain structures, and their structure and dynamics are reflected in the variety of solid-state spectra derived from different parameters. Multivariate analysis, such as principle component analysis (PCA), is suggested as an option to improve analyses of complex NMR spectra from relaxation measurements. In this study we demonstrate the extraction of peak components using PCA from cross polarization experiment data with variable contact time spectra of BC.
- Keiko Okushita
- , Takanori Komatsu
- & Jun Kikuchi
-
Original Article |
 Field-dependent 19F NMR study of sperm whale myoglobin reconstituted with a ring-fluorinated heme
Field-dependent 19F NMR study of sperm whale myoglobin reconstituted with a ring-fluorinated heme
A fluorinated heme was incorporated into Mb, and the field dependence of the line width of 19F NMR signals of the protein with S values ranging from 0 to 5/2 was analyzed in order to gain a quantitative insight into the 19F transverse relaxation mechanism in the protein. In the cases of S=2 and S=5/2 forms, the significant contribution of Curie spin relaxation to the relaxation was demonstrated and analysis of the Curie spin relaxation was useful to estimate the overall correlation time of the protein.
- Yasuhiko Yamamoto
- , Satoshi Nagao
- & Akihiro Suzuki

 Direct observation and mutual diffusion of cyclic polymers
Direct observation and mutual diffusion of cyclic polymers