Article |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 In situ detection of hydrogen-induced phase transitions in individual palladium nanocrystals
In situ detection of hydrogen-induced phase transitions in individual palladium nanocrystals
In situ electron energy-loss spectroscopy in an environmental transmission electron microscope reveals that palladium nanocrystals undergo sharp phase transitions during hydrogen absorption and desorption, and that surface effects dictate the size dependence of the hydrogen absorption pressures.
- Andrea Baldi
- , Tarun C. Narayan
- & Jennifer A. Dionne
-
Letter |
 Entropy-driven formation of large icosahedral colloidal clusters by spherical confinement
Entropy-driven formation of large icosahedral colloidal clusters by spherical confinement
Experiments with colloidal nano- and microparticles and computer simulations show that, unexpectedly, confinement and entropy are sufficient for the formation of icosahedral crystalline clusters of up to about 100,000 particles.
- Bart de Nijs
- , Simone Dussi
- & Marjolein Dijkstra
-
Letter |
 Redox shuttle mechanism enhances photocatalytic H2 generation on Ni-decorated CdS nanorods
Redox shuttle mechanism enhances photocatalytic H2 generation on Ni-decorated CdS nanorods
Photocatalytic efficiency can be limited by slow transfer of photoexcited holes and high charge recombination rates. Using a hydroxyl anion–radical redox couple leads to enhanced photocatalytic H2 generation on Ni-decorated CdS nanorods.
- Thomas Simon
- , Nicolas Bouchonville
- & Jochen Feldmann
-
-
Article |
 Visualization of oscillatory behaviour of Pt nanoparticles catalysing CO oxidation
Visualization of oscillatory behaviour of Pt nanoparticles catalysing CO oxidation
Many catalytic reactions exhibit oscillatory behaviour but these oscillations are not well understood for catalysts consisting of supported nanoparticles. The study of oscillatory CO oxidation catalysed by Pt nanoparticles now reveals that periodic changes in the CO oxidation are synchronous with a periodic refacetting of the Pt nanoparticles.
- S. B. Vendelbo
- , C. F. Elkjær
- & S. Helveg
-
Letter |
 Reconfigurable 3D plasmonic metamolecules
Reconfigurable 3D plasmonic metamolecules
Until now, it has not been possible to switch chirality in plasmonic nanostructures at will and repeatedly. Now, thanks to DNA-regulated conformational changes, reconfigurable 3D plasmonic metamolecules with switchable chirality have been created.
- Anton Kuzyk
- , Robert Schreiber
- & Na Liu
-
Article |
 Etchable plasmonic nanoparticle probes to image and quantify cellular internalization
Etchable plasmonic nanoparticle probes to image and quantify cellular internalization
Nanoparticle-based fluorescence imaging does not usually allow cell membrane-bound particles and intracellular particles to be distinguished from each other. Now, using functionalized silver nanoparticles as plasmonic probes, this distinction can be made following a rapid, non-toxic etching process that selectively removes the extracellular nanoparticles but leaves the intracellular nanoparticles unharmed.
- Gary B. Braun
- , Tomas Friman
- & Erkki Ruoslahti
-
Article |
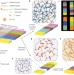 Universal process-inert encoding architecture for polymer microparticles
Universal process-inert encoding architecture for polymer microparticles
The use of encoded microparticles in industrial settings is hampered by issues of scalability, decoding robustness and encoding density. Now, easily decodable microparticles with spatially patterned rare-earth upconversion nanocrystals, exponentially scalable encoding capacities and ultralow decoding false-alarm rates that are insensitive to harsh processing environments and can be used in practical applications such as durable anti-counterfeiting labels and multiplexed bioassays are reported.
- Jiseok Lee
- , Paul W. Bisso
- & Patrick S. Doyle
-
News & Views |
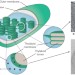 Boosting plant biology
Boosting plant biology
Chloroplasts with extended photosynthetic activity beyond the visible absorption spectrum, and living leaves that perform non-biological functions, are made possible by localizing nanoparticles within plant organelles.
- Gregory D. Scholes
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
-
News & Views |
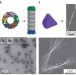 A loop of two rods
A loop of two rods
The spontaneous organization of semiconductor nanoparticles into uniform pairs of parallel nanorods bridged at their ends illustrates the potential of hierarchical self-assembly processes for the formation of inorganic superstructures with complexity comparable to that of small self-organized biological aggregates.
- Bongjun Yeom
- & Nicholas A. Kotov
-
-
Article |
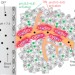 A nanoparticle-based strategy for the imaging of a broad range of tumours by nonlinear amplification of microenvironment signals
A nanoparticle-based strategy for the imaging of a broad range of tumours by nonlinear amplification of microenvironment signals
The imaging of tumours is challenging because of the wide range of different cancers. Now, the rapid detection of tumours, independent of type, is achieved using a nonlinear amplification strategy that employs ultrasensitive pH-responsive fluorescent nanoparticles that illuminate within tumour neovasculature or in response to the tumour’s acidic extracellular environment.
- Yiguang Wang
- , Kejin Zhou
- & Jinming Gao
-
Article |
 Water-mediated structuring of bone apatite
Water-mediated structuring of bone apatite
Proteins from bone extracellular matrix are known to mediate the organization of apatite crystals in bone. Now, electron microscopy, X-ray scattering and nuclear magnetic resonance measurements of the structure and organization of apatite nanoparticles and intact bone samples show that water also plays a significant role in orienting the apatite crystals, and that such structuring is mediated by a disordered mineral layer that coats the crystalline core of bone apatite.
- Yan Wang
- , Stanislas Von Euw
- & Nadine Nassif
-
Letter |
 Enhanced oxidation of nanoparticles through strain-mediated ionic transport
Enhanced oxidation of nanoparticles through strain-mediated ionic transport
Size effects and geometry can significantly modify the properties of nanoparticles with direct impact on their biocompatibility and chemical reactivity. Using high-resolution electron microscopy it is now shown that strain gradients induced in the oxide shell of cuboid Fe nanoparticles can lead to oxide domain formation and shape evolution of the particles.
- Andrew Pratt
- , Leonardo Lari
- & Roland Kröger
-
-
Commentary |
 Translating materials design to the clinic
Translating materials design to the clinic
Many materials-based therapeutic systems have reached the clinic or are in clinical trials. Here we describe materials design principles and the construction of delivery vehicles, as well as their adaptation and evaluation for human use.
- Jeffrey A. Hubbell
- & Robert Langer
-
Commentary |
 Strategies for advancing cancer nanomedicine
Strategies for advancing cancer nanomedicine
Cancer nanomedicines approved so far minimize toxicity, but their efficacy is often limited by physiological barriers posed by the tumour microenvironment. Here, we discuss how these barriers can be overcome through innovative nanomedicine design and through creative manipulation of the tumour microenvironment.
- Vikash P. Chauhan
- & Rakesh K. Jain
-
Review Article |
 Delivery materials for siRNA therapeutics
Delivery materials for siRNA therapeutics
Therapeutics based on small interfering RNA (siRNA), which in principle are able to reversibly silence any gene of interest, are under development for the treatment of cancers, viral infections, hereditary disorders and many other diseases. This Review discusses the biological challenges that siRNA delivery materials aim to overcome, as well as the most clinically advanced classes of siRNA delivery systems, including cyclodextrin–polymer nanoparticles, lipid nanoparticles and siRNA conjugates.
- Rosemary Kanasty
- , Joseph Robert Dorkin
- & Daniel Anderson
-
Article |
 Uncovering the intrinsic size dependence of hydriding phase transformations in nanocrystals
Uncovering the intrinsic size dependence of hydriding phase transformations in nanocrystals
Although quantitative understanding of nanocrystal phase transformations is important for efficient energy conversion and catalysis, difficulties in directly monitoring nanoscale systems in reactive environments remain. Direct quantification of hydriding transformations in palladium nanocrystals now clearly reveals that the transformation rates are governed by nanocrystal dimensions.
- Rizia Bardhan
- , Lester O. Hedges
- & Jeffrey J. Urban
-
Article |
 The effect of particle proximity on the oxygen reduction rate of size-selected platinum clusters
The effect of particle proximity on the oxygen reduction rate of size-selected platinum clusters
The catalytic activity of highly dispersed platinum nanoparticles is not yet well understood. Now, a unique approach that allows precise control of both the size and coverage of platinum nanoclusters reveals that particle proximity influences the oxygen reduction rate of these size-selected clusters, especially in terms of mass normalized activity.
- Markus Nesselberger
- , Melanie Roefzaad
- & Matthias Arenz
-
Article |
 Identifying champion nanostructures for solar water-splitting
Identifying champion nanostructures for solar water-splitting
Assessing the effect of nanometre-scale structure on charge transport across micrometre-scale distances remains a fundamental challenge for many energy-conversion technologies. By correlating the structure and the charge transport with nanometre resolution across micrometre-scale distances, nanoparticle aggregates responsible for the high photoelectrochemical water-splitting activity of α-Fe2O3 electrodes are identified.
- Scott C. Warren
- , Kislon Voïtchovsky
- & Michael Grätzel
-
Letter |
 Hybrid nanocolloids with programmed three-dimensional shape and material composition
Hybrid nanocolloids with programmed three-dimensional shape and material composition
Making colloidal nanoparticles with controlled composition and shape is challenging because at the nanoscale surface energy favours highly symmetric structures. Now, a fast, wafer-scale fabrication scheme that combines low-temperature shadow deposition with nanoscale patterning has been developed that produces anisotropic hybrid nanocolloids with designed composition and feature sizes down to 20 nm.
- Andrew G. Mark
- , John G. Gibbs
- & Peer Fischer
-
-
Article |
 Compositional segregation in shaped Pt alloy nanoparticles and their structural behaviour during electrocatalysis
Compositional segregation in shaped Pt alloy nanoparticles and their structural behaviour during electrocatalysis
Although site-dependent metal surface segregation in bimetallic nanoalloys affects catalytic activity and stability, segregation on shaped nanocatalysts and their atomic-scale evolution is largely unexplored. PtxNi1−x alloy nanoparticle electrocatalysts with unique activity for oxygen reduction reactions exhibit an unexpected compositional segregation structure across the {111} facets.
- Chunhua Cui
- , Lin Gan
- & Peter Strasser
-
-
Letter |
 A general approach to DNA-programmable atom equivalents
A general approach to DNA-programmable atom equivalents
Progress in DNA-mediated nanoparticle self-assembly has been hampered by the lack of a general method to control the bonding of nanoparticles of different chemical composition into lattices by means of DNA linkers. An approach that makes possible the functionalization of any nanoparticle that has hydrophobic capping ligands with a dense monolayer of DNA, and allows for independent control of composition, particle size and lattice parameters for a variety of lattices, is now demonstrated.
- Chuan Zhang
- , Robert J. Macfarlane
- & Chad A. Mirkin
-
News & Views |
 Going active
Going active
The spiking phenomena associated with neural activity are characterized by an impressive degree of efficiency. The fabrication of a neuristor consisting of nanoscale components represents a step towards implementing such devices in integrated circuit applications.
- Wei Lu
-
News & Views |
 Death by magnetism
Death by magnetism
A magnetic on/off switch for cell-death signalling in cancer cells is developed using antibodies conjugated to magnetic nanoparticles. The control of cell death in in vivo systems is demonstrated by a tell-tale morphological change within the zebrafish.
- Jon Dobson
-
Article |
 Self-assembled nanoparticle arrays for multiphase trace analyte detection
Self-assembled nanoparticle arrays for multiphase trace analyte detection
Nanoplasmonic structures that can detect trace analytes via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy typically require sophisticated nanofabrication techniques. Self-assembly of gold nanoparticles into close-packed arrays at liquid/liquid and liquid/air interfaces is now used for the detection of multi-analytes from aqueous, organic or air phases.
- Michael P. Cecchini
- , Vladimir A. Turek
- & Joshua B. Edel
-
Letter |
 Towards stable catalysts by controlling collective properties of supported metal nanoparticles
Towards stable catalysts by controlling collective properties of supported metal nanoparticles
Supported metal nanoparticles play a pivotal role in areas such as nanoelectronics, energy storage and conversion, and catalysis, but their tendency to grow into larger crystallites is an issue for their stable performance. A strategy based on controlling not only size and composition but also the location of the metal nanoparticles, now reveals the impact of their three-dimensional nanospatial distribution on their catalytic stability.
- Gonzalo Prieto
- , Jovana Zečević
- & Petra E. de Jongh
-
Article |
 Structurally ordered intermetallic platinum–cobalt core–shell nanoparticles with enhanced activity and stability as oxygen reduction electrocatalysts
Structurally ordered intermetallic platinum–cobalt core–shell nanoparticles with enhanced activity and stability as oxygen reduction electrocatalysts
Enhancing and optimizing the performance and durability of nanocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction is crucial for fuel-cell applications. A class of Pt–Co nanocatalysts consisting of ordered Pt3Co intermetallic cores with a 2–3 atomic-layer-thick platinum shell now exhibit a large increase in mass activity and specific activity when compared with disordered alloy nanoparticles.
- Deli Wang
- , Huolin L. Xin
- & Héctor D. Abruña
-
-
News & Views |
 Striped cation-trappers
Striped cation-trappers
Toxic metal cations in environmental samples can be detected with ultrahigh sensitivity through measurements of the tunnelling current across crosslinked films of nanoparticles decorated with striped monolayers of organic ligands.
- Knut Rurack
-
Letter |
 Atomic-scale determination of surface facets in gold nanorods
Atomic-scale determination of surface facets in gold nanorods
The atomic structure of nanoparticles considerably influences their properties. A new methodology that is now able to measure the full three-dimensional atomic structure of free-standing nanoparticles will therefore provide a much better connection between their structure and properties.
- Bart Goris
- , Sara Bals
- & Gustaaf Van Tendeloo
-
Letter |
 A magnetic switch for the control of cell death signalling in in vitro and in vivo systems
A magnetic switch for the control of cell death signalling in in vitro and in vivo systems
On application of a focused magnetic field, zinc-doped iron oxide nanoparticles with targeting antibodies attached are shown to activate cell death signalling in a spatially controlled manner. This triggering of apoptosis signalling, via the magnetically activated aggregation of receptors, is observed in both in vitro and in vivo systems.
- Mi Hyeon Cho
- , Eun Jung Lee
- & Jinwoo Cheon
-
News & Views |
 Upconversion goes broadband
Upconversion goes broadband
Upconversion nanoparticles that convert low-energy light into high-energy light hold promise for boosting solar-cell efficiency and enabling highly sensitive biological assays. But their spectral conversion under broadband excitation has been challenging, until now.
- Xiaoji Xie
- & Xiaogang Liu
-
News & Views |
 Combo combat
Combo combat
Nanoparticle-enabled, sustained delivery of soluble hydrophilic cytokines and hydrophobic inhibitors engages the innate and adaptive immune systems to fight cancer.
- C. Jeffrey Brinker
-
Article |
 Ultrasensitive detection of toxic cations through changes in the tunnelling current across films of striped nanoparticles
Ultrasensitive detection of toxic cations through changes in the tunnelling current across films of striped nanoparticles
Solid-state sensors for the detection of heavy-metal cations require for the most part sophisticated chemistry and equipment. It is now shown that toxic cations in environmental samples can be detected with ultrahigh sensitivity and over a broad range of cation concentrations by measuring the tunnelling current across films of nanoparticles decorated with striped monolayers of organic ligands.
- Eun Seon Cho
- , Jiwon Kim
- & Bartosz A. Grzybowski
-
-
News & Views |
 Polarizability reveals identity
Polarizability reveals identity
Improvements in electrostatic force microscopy now make it possible to measure the dielectric constant of isolated low-polarizable nanoparticles and viruses, thus enabling the label-free identification of dielectric nanomaterials of similar morphology.
- Enrique Sahagún
- & Juan José Sáenz
-
Article |
 Atomic origins of the high catalytic activity of nanoporous gold
Atomic origins of the high catalytic activity of nanoporous gold
Although nanoparticulate gold possesses remarkable catalytic activity towards oxidation reactions, catalytic activity usually cannot be observed in particles larger than 5 nm. Atomic insights into dealloyed nanoporous gold catalysts by transmission electron microscopy now demonstrate that surface defects are active sites for the catalytic oxidation of carbon monoxide and that residual silver stabilizes atomic steps.
- Takeshi Fujita
- , Pengfei Guan
- & Mingwei Chen
-
-
Article |
 Label-free identification of single dielectric nanoparticles and viruses with ultraweak polarization forces
Label-free identification of single dielectric nanoparticles and viruses with ultraweak polarization forces
Electrostatic force microscopy with sub-piconewton resolution can now be used for the label-free identification of single dielectric nanoparticles of similar morphology but distinct low-polarizable materials. The technique can also distinguish between empty and DNA-containing virus capsids, and should be extensible to the characterization of surface and subsurface dielectric properties of nanoscale dielectrics and biological macromolecules in general.
- Laura Fumagalli
- , Daniel Esteban-Ferrer
- & Gabriel Gomila
-
-
Letter |
 Experimental realization of optical lumped nanocircuits at infrared wavelengths
Experimental realization of optical lumped nanocircuits at infrared wavelengths
Lumped elements such as resistors, capacitors and inductors play a crucial role in electronic circuits. Now, inspired by metamaterials technology, the experimental realization of lumped circuit elements for optical frequencies provides a standardized platform for applications such as mixing and multiplexing of optical signals.
- Yong Sun
- , Brian Edwards
- & Nader Engheta
-
Letter |
 Charged nanoparticles as supramolecular surfactants for controlling the growth and stability of microcrystals
Charged nanoparticles as supramolecular surfactants for controlling the growth and stability of microcrystals
The growth of microcrystals can be controlled by various agents such as ions, small charged molecules and polyelectrolytes. However, their use is specific to the crystallizing material. It is now shown that oppositely charged nanoparticles can act as ‘universal’ surfactants for controlling the growth and stability of microcrystals of inorganic salts and of charged organic molecules.
- Bartlomiej Kowalczyk
- , Kyle J. M. Bishop
- & Bartosz A. Grzybowski
-
-

 Digital metamaterials
Digital metamaterials Stains of authenticity
Stains of authenticity Aerobic oxidation
Aerobic oxidation Nano contraception
Nano contraception Coiled-coil balls
Coiled-coil balls Particle perfection
Particle perfection A flare for cancer
A flare for cancer Optimized for the clinic
Optimized for the clinic