Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Temporal trends of SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence during the first wave of the COVID-19 epidemic in Kenya
Temporal trends of SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence during the first wave of the COVID-19 epidemic in Kenya
The reported burden of SARS-CoV-2 has been relatively low in tropical Africa compared to Europe and the Americas, but estimating true infection rates is challenging. Here, the authors screen blood donors in Kenya for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and describe spatiotemporal seroprevalence dynamics.
- Ifedayo M. O. Adetifa
- , Sophie Uyoga
- & George M. Warimwe
-
Article
| Open Access The architecture of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA genome inside virion
The architecture of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA genome inside virion
Secondary structures and long-range RNA interactions of the SARS-CoV-2 genome have been investigated by various sequencing methods. Here the authors use an RNA-RNA hybrid sequencing method to predict the secondary and tertiary structure of the SRAS-CoV-2 RNA genome in the virion.
- Changchang Cao
- , Zhaokui Cai
- & Yuanchao Xue
-
Article
| Open Access Improved pyrrolysine biosynthesis through phage assisted non-continuous directed evolution of the complete pathway
Improved pyrrolysine biosynthesis through phage assisted non-continuous directed evolution of the complete pathway
Pyrrolysine (Pyl) exists in nature as the 22nd proteinogenic amino acid, but studies of Pyl have been hindered by the difficulty and inefficiency of both its chemical and biological syntheses. Here, the authors developed an improved PANCE approach to evolve the pylBCD pathway for increased production of Pyl proteins in E. coli.
- Joanne M. L. Ho
- , Corwin A. Miller
- & Matthew R. Bennett
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid proliferation due to better metabolic adaptation results in full virulence of a filament-deficient Candida albicans strain
Rapid proliferation due to better metabolic adaptation results in full virulence of a filament-deficient Candida albicans strain
The ability of the fungal pathogen Candida albicans to undergo yeast-to-hypha transition is believed to be a key virulence factor. Here, Dunker et al. show that a filament-deficient strain is attenuated in a mouse model of intraperitoneal infection, but remains virulent in a mouse model of systemic candidiasis.
- Christine Dunker
- , Melanie Polke
- & Ilse D. Jacobsen
-
Review Article
| Open Access Antipathogenic properties and applications of low-dimensional materials
Antipathogenic properties and applications of low-dimensional materials
Antimicrobial resistance is a growing global problem and low dimensional materials have emerged as a potential solution. Here, the authors review the progress which has been made on low dimensional antimicrobials looking at the materials synthesis, modes of action and currently applications.
- Z. L. Shaw
- , Sruthi Kuriakose
- & Sumeet Walia
-
Article
| Open Access Human cytomegalovirus-induced host protein citrullination is crucial for viral replication
Human cytomegalovirus-induced host protein citrullination is crucial for viral replication
Citrullination is a posttranslational modification of arginines. Here, the authors show that HCMV infection increases citrullination of host and virus proteins to promote infection and that citrullinated interferon-inducible protein IFIT1 is impaired in RNA binding, as a potential mechanism of evasion.
- Gloria Griffante
- , Francesca Gugliesi
- & Santo Landolfo
-
Article
| Open Access COVseq is a cost-effective workflow for mass-scale SARS-CoV-2 genomic surveillance
COVseq is a cost-effective workflow for mass-scale SARS-CoV-2 genomic surveillance
Genomic surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 is crucial to monitor the spread of variants of concern. A new sequencing method enables cost-effective SARS-CoV-2 genomic surveillance at scale and is easily adaptable to other viruses.
- Michele Simonetti
- , Ning Zhang
- & Nicola Crosetto
-
Article
| Open Access A high-throughput screen for TMPRSS2 expression identifies FDA-approved compounds that can limit SARS-CoV-2 entry
A high-throughput screen for TMPRSS2 expression identifies FDA-approved compounds that can limit SARS-CoV-2 entry
The serine protease TMPRSS2 primes SARS-CoV-2 glycoprotein for cell entry. Here, the authors perform a screen to identify drugs that reduce TMPRSS2 expression and find that halofuginone modulates proteasome-mediated degradation of TMPRSS2 and reduces entry of SARS-CoV-2.
- Yanwen Chen
- , Travis B. Lear
- & Bill B. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Gut microbiota mediate the FGF21 adaptive stress response to chronic dietary protein-restriction in mice
Gut microbiota mediate the FGF21 adaptive stress response to chronic dietary protein-restriction in mice
Dietary protein restriction induces a hepatic stress response mediated by the endocrine molecule FGF21, which triggers host adaptive pathways. Here the authors demonstrate that the gut microbiome is required to trigger the FGF21 response and can be manipulated through dietary fiber supplementation.
- Anthony Martin
- , Gertrude Ecklu-Mensah
- & Suzanne Devkota
-
Article
| Open Access Oncolytic H-1 parvovirus binds to sialic acid on laminins for cell attachment and entry
Oncolytic H-1 parvovirus binds to sialic acid on laminins for cell attachment and entry
Rat H-1 parvovirus (H-1PV) is in clinical development for oncolytic therapy. Here, Kulkarni et al. identify LAMC1 as a modulator of H-1PV cell attachment and entry and find that LAMC1 levels and H-1PV oncolytic activity correlate in 59 tested cancer cell lines.
- Amit Kulkarni
- , Tiago Ferreira
- & Antonio Marchini
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid evolution of bacterial mutualism in the plant rhizosphere
Rapid evolution of bacterial mutualism in the plant rhizosphere
Beneficial plant-microbe interactions are common in nature, but direct evidence for the evolution of mutualism is scarce. Here, Li et al. experimentally evolve a rhizospheric bacterium and find that it can evolve into a mutualist on a relatively short timescale.
- Erqin Li
- , Ronnie de Jonge
- & Alexandre Jousset
-
Article
| Open Access Intracellular localisation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis affects efficacy of the antibiotic pyrazinamide
Intracellular localisation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis affects efficacy of the antibiotic pyrazinamide
Effective chemotherapies against tuberculosis must kill the pathogen’s intracellular population. Here, Santucci et al. show that bacterial localisation within human macrophages impact pyrazinamide (PZA) accumulation and efficacy, and that combination with a second antibiotic (bedaquiline) enhances PZA accumulation via a host-dependent process.
- Pierre Santucci
- , Daniel J. Greenwood
- & Maximiliano G. Gutierrez
-
Article
| Open Access Composition and stage dynamics of mitochondrial complexes in Plasmodium falciparum
Composition and stage dynamics of mitochondrial complexes in Plasmodium falciparum
Applying complexome profiling, Evers et al. unravel the composition of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation complexes in P. falciparum asexual and sexual blood stages. Abundance of these complexes differs between both stages, supporting the hypothesis that a mitochondrial metabolic switch is central to gametocyte development and functioning.
- Felix Evers
- , Alfredo Cabrera-Orefice
- & Taco W. A. Kooij
-
Article
| Open Access A catalog of the diversity and ubiquity of bacterial microcompartments
A catalog of the diversity and ubiquity of bacterial microcompartments
Bacterial microcompartments (BMCs) are organelles consisting of a protein shell in which certain metabolic reactions take place separated from the cytoplasm. Here, Sutter et al. present a comprehensive catalog of BMC loci, substantially expanding the number of known BMCs and describing distinct types and compartmentalized reactions.
- Markus Sutter
- , Matthew R. Melnicki
- & Cheryl A. Kerfeld
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered ACE2 receptor therapy overcomes mutational escape of SARS-CoV-2
Engineered ACE2 receptor therapy overcomes mutational escape of SARS-CoV-2
Hoshino et al., engineer a human virus receptor, hACE2, and demonstrate its potential for overcoming SARS-CoV-2 mutations that otherwise hinder therapeutic interventions. Overall, the data provide insights in to the therapeutic potential of engineered receptors.
- Yusuke Higuchi
- , Tatsuya Suzuki
- & Atsushi Hoshino
-
Article
| Open Access SARS-CoV-2-mediated dysregulation of metabolism and autophagy uncovers host-targeting antivirals
SARS-CoV-2-mediated dysregulation of metabolism and autophagy uncovers host-targeting antivirals
Viruses manipulate host cell pathways to support infection. Here the authors show that SARS-CoV-2 infection modulates cellular metabolism and limits autophagy, and identify druggable host pathways for virus inhibition.
- Nils C. Gassen
- , Jan Papies
- & Marcel A. Müller
-
Article
| Open Access Sequence signatures of two public antibody clonotypes that bind SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain
Sequence signatures of two public antibody clonotypes that bind SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain
Public antibody clonotypes that recognize SARS-CoV-2 spike protein are important for protection against COVID-19. Here, the authors characterize sequence motifs in the heavy chain complementarity-determining region (CDR) H3s of two public clonotypes and their association with light chain identity.
- Timothy J. C. Tan
- , Meng Yuan
- & Nicholas C. Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Acinetobacter baylyi regulates type IV pilus synthesis by employing two extension motors and a motor protein inhibitor
Acinetobacter baylyi regulates type IV pilus synthesis by employing two extension motors and a motor protein inhibitor
Type IV pili (T4P) are retractile appendages used by bacteria for DNA uptake and other purposes. T4P extension is thought to occur through the action of a single motor protein, PilB. Here, Ellison et al. show that T4P synthesis in Acinetobacter baylyi depends not only on PilB but also on an additional, distinct motor, TfpB.
- Courtney K. Ellison
- , Triana N. Dalia
- & Ankur B. Dalia
-
Article
| Open Access Design of COVID-19 staged alert systems to ensure healthcare capacity with minimal closures
Design of COVID-19 staged alert systems to ensure healthcare capacity with minimal closures
Selection of COVID-19 mitigation measures requires balancing health outcomes with economic impacts. Here, the authors derive a system to set triggers for increasing mitigation measures to preserve healthcare capacity, and describe how it has been used to support public health decision making in Austin, Texas.
- Haoxiang Yang
- , Özge Sürer
- & Lauren Ancel Meyers
-
Article
| Open Access The extracellular contractile injection system is enriched in environmental microbes and associates with numerous toxins
The extracellular contractile injection system is enriched in environmental microbes and associates with numerous toxins
The extracellular Contractile Injection System (eCIS) is a toxin-delivery particle that mediates interactions between bacteria and their invertebrate hosts. Here, the authors catalogue eCIS loci from 1,249 prokaryotic genomes, showing enrichment in non-pathogenic environmental microbes, and identifying eCIS-associated toxins that inhibit the growth of bacteria and/or yeast.
- Alexander Martin Geller
- , Inbal Pollin
- & Asaf Levy
-
Article
| Open Access Community factors and excess mortality in first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in England
Community factors and excess mortality in first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in England
COVID-19-related mortality in England shows geographical variation but the reasons for this are not well understood. This study estimated excess mortality in the first wave of the pandemic and found associations with higher density of care homes, overcrowding, and economic deprivation, but not with population density or air pollution.
- Bethan Davies
- , Brandon L. Parkes
- & Paul Elliott
-
Article
| Open Access Association of social distancing and face mask use with risk of COVID-19
Association of social distancing and face mask use with risk of COVID-19
Estimating the effectiveness of COVID-19 control measures requires large prospective data including symptoms and personal risk factors. Here, the authors used data from smartphone-based application and found that individual face mask use was associated with a 64% reduced risk of COVID-19 symptoms.
- Sohee Kwon
- , Amit D. Joshi
- & Andrew T. Chan
-
Article
| Open Access Serum amyloid P component is an essential element of resistance against Aspergillus fumigatus
Serum amyloid P component is an essential element of resistance against Aspergillus fumigatus
Serum Amyloid P is a humoral component with established roles in the response to bacterial infection and regulation of tissue remodeling. Here the authors provide evidence to a further crucial role of serum amyloid P in the context of fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus.
- Andrea Doni
- , Raffaella Parente
- & Alberto Mantovani
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into an atypical secretory pathway kinase crucial for Toxoplasma gondii invasion
Structural insights into an atypical secretory pathway kinase crucial for Toxoplasma gondii invasion
Host cell invasion by Toxoplasma gondii depends on the heavily phosphorylated RON complex, but the relevance and regulation of these modifications are not understood. Here, the authors identify the kinase RON13 as a key virulence factor, determine its structure and show that it phosphorylates the RON complex.
- Gaëlle Lentini
- , Rouaa Ben Chaabene
- & Dominique Soldati-Favre
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for CSPG4 as a receptor for TcdB and a therapeutic target in Clostridioides difficile infection
Structural basis for CSPG4 as a receptor for TcdB and a therapeutic target in Clostridioides difficile infection
Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 (CSPG4) is a potential receptor for C. difficile toxin B (TcdB) during C. difficile infections (CDIs). Here, the cryo-EM structure of a TcdB–CSPG4 complex and CDI mouse models offer insights into CSPG4 role in CDIs and suggest a therapeutic strategy targeting TcdB.
- Peng Chen
- , Ji Zeng
- & Rongsheng Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Influenza virus infection expands the breadth of antibody responses through IL-4 signalling in B cells
Influenza virus infection expands the breadth of antibody responses through IL-4 signalling in B cells
The reasons why influenza infection promotes a broader antibody response compared with vaccines are not fully understood. Here the authors show that unmasking of haemagglutinin epitopes and IL-4 signals in the germinal centre contribute to broader antibody responses after infection.
- Kosuke Miyauchi
- , Yu Adachi
- & Masato Kubo
-
Article
| Open Access BNT162b2 vaccine uptake and effectiveness in UK healthcare workers – a single centre cohort study
BNT162b2 vaccine uptake and effectiveness in UK healthcare workers – a single centre cohort study
Several vaccines for COVID-19 have received emergency approval. Here, the authors describe BNT162B2 vaccine uptake and effectiveness among UK healthcare workers in a single centre cohort study during a time of high community COVID-19 prevalence.
- Tariq Azamgarhi
- , Michelle Hodgkinson
- & Simon Warren
-
Article
| Open Access Tick extracellular vesicles enable arthropod feeding and promote distinct outcomes of bacterial infection
Tick extracellular vesicles enable arthropod feeding and promote distinct outcomes of bacterial infection
Extracellular vesicles have been implicated in the transmission of pathogens from the arthropod to the human host. Here the authors show that tick-derived extracellular vesicles play a role in feeding and modulate the outcome of bacterial infection.
- Adela S. Oliva Chávez
- , Xiaowei Wang
- & Joao H. F. Pedra
-
Article
| Open Access Triboelectrification induced self-powered microbial disinfection using nanowire-enhanced localized electric field
Triboelectrification induced self-powered microbial disinfection using nanowire-enhanced localized electric field
Air-transmitted pathogens are a recognized threat to public health. Here, the authors develop a self-powered, rapid disinfection method toward air-transmitted microbes using the localized electric field to damage the outer structures of microbes driven by a triboelectric nanogenerator.
- Zheng-Yang Huo
- , Young-Jun Kim
- & Sang-Woo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Vpr counteracts the restriction of LAPTM5 to promote HIV-1 infection in macrophages
Vpr counteracts the restriction of LAPTM5 to promote HIV-1 infection in macrophages
Here, using proteomics and cell-based assays, the authors show that HIV accessory protein Vpr mediates the degradation of host lysosomal-associated transmembrane protein 5 (LAPTM5) in monocyte-derived macrophages (MDM) to enhance infection in macrophages.
- Li Zhao
- , Shumei Wang
- & Guoxin Liang
-
Article
| Open Access In-depth single-cell analysis of translation-competent HIV-1 reservoirs identifies cellular sources of plasma viremia
In-depth single-cell analysis of translation-competent HIV-1 reservoirs identifies cellular sources of plasma viremia
To provide in depth characterization of HIV reservoir cells, the authors here develop a single-cell approach to simultaneously sequence TCR, integration sites and proviral genomes, called STIP-Seq, and show that the translation-competent reservoir mainly consists of proviruses with short deletions at the 5’-end of the genome.
- Basiel Cole
- , Laurens Lambrechts
- & Linos Vandekerckhove
-
Article
| Open Access CRISPR-Associated Primase-Polymerases are implicated in prokaryotic CRISPR-Cas adaptation
CRISPR-Associated Primase-Polymerases are implicated in prokaryotic CRISPR-Cas adaptation
CAPPs are putative Primase-Polymerases associated with CRISPR-Cas operons. Here, the authors show CAPPs genetic and physical association with Cas1 and Cas2, their capacity to function as DNA-dependent DNA primases and DNA polymerases, and that Cas1-Cas2 complex adjacent to CAPP has bona fide spacer integration activity.
- Katerina Zabrady
- , Matej Zabrady
- & Aidan J. Doherty
-
Article
| Open Access A distinct growth physiology enhances bacterial growth under rapid nutrient fluctuations
A distinct growth physiology enhances bacterial growth under rapid nutrient fluctuations
Here the authors use microfluidics and single-cell microscopy to quantify the growth dynamics of individual E. coli cells exposed to nutrient fluctuations with periods as short as 30 seconds, finding that nutrient fluctuations reduce growth rates up to 50% compared to a steady nutrient delivery of equal average concentration, implying that temporal variability is an important parameter in bacterial growth.
- Jen Nguyen
- , Vicente Fernandez
- & Roman Stocker
-
Article
| Open Access PGC-1α mediates a metabolic host defense response in human airway epithelium during rhinovirus infections
PGC-1α mediates a metabolic host defense response in human airway epithelium during rhinovirus infections
Epithelial host defense to rhinovirus infections is enhanced by targeting the mitochondrial metabolic regulator, PGC-1a. Using metabolomics and proteomics, Michi et al show that human airway epithelial cells mount a barrier-protective early glycolysis-shift in response to rhinovirus, and that by targeting PGC-1a early in infection, epithelial barrier function, viral defense and pathology are improved.
- Aubrey N. Michi
- , Bryan G. Yipp
- & David Proud
-
Article
| Open Access Multivalency transforms SARS-CoV-2 antibodies into ultrapotent neutralizers
Multivalency transforms SARS-CoV-2 antibodies into ultrapotent neutralizers
Here, the authors combine three different antibody specificities and an Fc domain on a single multivalent molecule, resulting in high neutralization activity despite viral sequence variability.
- Edurne Rujas
- , Iga Kucharska
- & Jean-Philippe Julien
-
Article
| Open Access 4D analysis of malaria parasite invasion offers insights into erythrocyte membrane remodeling and parasitophorous vacuole formation
4D analysis of malaria parasite invasion offers insights into erythrocyte membrane remodeling and parasitophorous vacuole formation
Here, Geoghegan, Evelyn et al. provide a lattice light-sheet microscopy based 4D imaging pipeline to quantitatively investigate Plasmodium spp. invasion and show that the nascent parasitophorous vacuole is predominantly formed from host’s erythrocyte membrane and undergoes continuous remodeling throughout invasion.
- Niall D. Geoghegan
- , Cindy Evelyn
- & Kelly L. Rogers
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular benchmarks of a SARS-CoV-2 epidemic
Molecular benchmarks of a SARS-CoV-2 epidemic
The concentration of SARS-CoV-2 changes during an individual’s infection, and mutations accumulate as viruses are transmitted between people. Here, the authors use data from Iceland to demonstrate how this information can be exploited at the population-level to determine the phase of the epidemic.
- Hakon Jonsson
- , Olafur T. Magnusson
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access Seasonality of agricultural exposure as an important predictor of seasonal yellow fever spillover in Brazil
Seasonality of agricultural exposure as an important predictor of seasonal yellow fever spillover in Brazil
Yellow fever virus (YFV) is an arbovirus affecting humans and non-human primates (NHPs) with seasonal transmission. Here Hamlet et al. model the monthly occurrence of YF in humans and NHPs across Brazil and show that seasonality of agriculture is an important predictor of seasonal YF transmission.
- Arran Hamlet
- , Daniel Garkauskas Ramos
- & Neil M. Ferguson
-
Article
| Open Access Insights into household transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from a population-based serological survey
Insights into household transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from a population-based serological survey
Household-based studies can provide insights into SARS-CoV-2 transmission. Here, the authors fit transmission models to serological data from Geneva, Switzerland, and estimate that the risk of infection from single household exposure (17.3%) was higher than for extra-household exposure (5.1%).
- Qifang Bi
- , Justin Lessler
- & Didier Trono
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated omics endotyping of infants with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis and risk of childhood asthma
Integrated omics endotyping of infants with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis and risk of childhood asthma
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) bronchiolitis during infancy is a major risk factor for asthma development. Here, Raita et al. integrate clinical data with airway microbiome, transcriptome, and metabolome data and identity four endotypes with differential risks for developing asthma.
- Yoshihiko Raita
- , Marcos Pérez-Losada
- & Kohei Hasegawa
-
Article
| Open Access SARS-CoV-2 infection and transmission in the North American deer mouse
SARS-CoV-2 infection and transmission in the North American deer mouse
Deer mice are natural hosts for a number of human pathogens. Here, Griffin et al. report that intranasal exposure of the North American deer mouse to SARS-CoV-2 results in virus replication and shedding, despite causing only mild or asymptomatic illness. Additionally, infected deer mice can transmit SARS-CoV-2 to naïve deer mice.
- Bryan D. Griffin
- , Mable Chan
- & Darwyn Kobasa
-
Article
| Open Access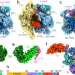 Distinct mechanisms of the human mitoribosome recycling and antibiotic resistance
Distinct mechanisms of the human mitoribosome recycling and antibiotic resistance
High-resolution cryo-EM structures and biochemical analyses of the human mitoribosome, in complex with mitochondria-specific factors mediating mitoribosome recycling, RRFmt and EF-G2mt, offer insight into mechanisms of mitoribosome recycling and resistance to antibiotic fusidic acid.
- Ravi Kiran Koripella
- , Ayush Deep
- & Rajendra K. Agrawal
-
Article
| Open Access Role of meteorological factors in the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in the United States
Role of meteorological factors in the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in the United States
The role of meteorological factors in SARS-COV-2 transmission is not well understood. Here, the authors use county-level data from the United States to the end of 2020 and find evidence of a moderate association between increased transmissibility and cold, dry weather and low ultraviolet radiation.
- Yiqun Ma
- , Sen Pei
- & Kai Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Distinct clinical and immunological profiles of patients with evidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in sub-Saharan Africa
Distinct clinical and immunological profiles of patients with evidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in sub-Saharan Africa
Clinical management of COVID-19 in resource-poor settings has distinct challenges and detailed patient characterisation is needed. Here, the authors describe the clinical and immunological profiles of patients at a hospital in Malawi with confirmed and suspected COVID-19.
- Ben Morton
- , Kayla G. Barnes
- & Kondwani C. Jambo
-
Article
| Open Access Benchmarking microbiome transformations favors experimental quantitative approaches to address compositionality and sampling depth biases
Benchmarking microbiome transformations favors experimental quantitative approaches to address compositionality and sampling depth biases
Here, the authors use simulated quantitative gut microbial communities to benchmark the performance of 13 common data transformations in determining diversity as well as microbe-microbe and microbe-metadata associations, finding that quantitative approaches incorporating microbial load variation outperform computational strategies in downstream analyses, urging for a widespread adoption of quantitative approaches, or recommending specific computational transformations whenever determination of microbial load of samples is not feasible.
- Verónica Lloréns-Rico
- , Sara Vieira-Silva
- & Jeroen Raes
-
Article
| Open Access SARS-CoV-2 RBD trimer protein adjuvanted with Alum-3M-052 protects from SARS-CoV-2 infection and immune pathology in the lung
SARS-CoV-2 RBD trimer protein adjuvanted with Alum-3M-052 protects from SARS-CoV-2 infection and immune pathology in the lung
Efficient vaccines for SARS-CoV-2 are needed. Here, the authors show that a trimeric form of the receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike adjuvanted with alum-3M-052 protects non-human primates from disease and inhibits infection.
- Nanda Kishore Routhu
- , Narayanaiah Cheedarla
- & Rama Rao Amara
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of specific non-pharmaceutical intervention policies on SARS-CoV-2 transmission in the counties of the United States
Effect of specific non-pharmaceutical intervention policies on SARS-CoV-2 transmission in the counties of the United States
Disentangling the impacts of non-pharmaceutical interventions on COVID-19 transmission is challenging as they have been used in different combinations across time and space. This study shows that, early in the epidemic, school/daycare closures and stopping nursing home visits were associated with the biggest reduction in transmission in the United States.
- Bingyi Yang
- , Angkana T. Huang
- & Derek A. T. Cummings
-
Article
| Open Access Citywide serosurveillance of the initial SARS-CoV-2 outbreak in San Francisco using electronic health records
Citywide serosurveillance of the initial SARS-CoV-2 outbreak in San Francisco using electronic health records
Population-based surveys are the gold standard for estimating seroprevalence but are expensive and often only capture a small geographic area or window of time. This study describes a new platform, SCALE-IT, for serosurveillance based on algorithmic sampling of electronic health records, and uses it to estimate the seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in San Francisco.
- Isobel Routledge
- , Adrienne Epstein
- & Isabel Rodriguez-Barraquer
-
Article
| Open Access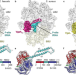 Structural basis of ABCF-mediated resistance to pleuromutilin, lincosamide, and streptogramin A antibiotics in Gram-positive pathogens
Structural basis of ABCF-mediated resistance to pleuromutilin, lincosamide, and streptogramin A antibiotics in Gram-positive pathogens
Mitochondrial ribosomes (mitoribosomes) are characterized by a distinct architecture and thus biogenesis pathway. Here, cryo-EM structures of mitoribosome large subunit assembly intermediates elucidate final steps of 16 S rRNA folding, methylation and peptidyl transferase centre (PTC) completion, as well as functions of several mitoribosome assembly factors.
- Caillan Crowe-McAuliffe
- , Victoriia Murina
- & Daniel N. Wilson
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Antimicrobials
- Applied microbiology
- Archaea
- Bacteria
- Bacteriology
- Bacteriophages
- Biofilms
- Biogeochemistry
- Cellular microbiology
- Clinical microbiology
- Microbial communities
- CRISPR-Cas systems
- Environmental microbiology
- Fungi
- Industrial microbiology
- Infectious-disease diagnostics
- Microbial genetics
- Parasitology
- Pathogens
- Phage biology
- Policy and public health in microbiology
- Vaccines
- Virology

 Control of membrane barrier during bacterial type-III protein secretion
Control of membrane barrier during bacterial type-III protein secretion