Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access The key role of the scaffold on the efficiency of dendrimer nanodrugs
The key role of the scaffold on the efficiency of dendrimer nanodrugs
The biological properties of dendrimers are thought to be largely dependent on the chemical nature of their surface. Here, the authors show that the internal scaffold of dendritic nanodrugs strongly influences their bioactivity, based on convergent information from biology and computation results.
- Anne-Marie Caminade
- , Séverine Fruchon
- & Rémy Poupot
-
Article
| Open Access Lansoprazole is an antituberculous prodrug targeting cytochrome bc1
Lansoprazole is an antituberculous prodrug targeting cytochrome bc1
Tuberculosis control is threatened by the continued emergence of drug-resistant strains. Here, Rybniker et al. screen a library of FDA-approved drugs and identify a gastric proton pump inhibitor that also has antituberculosis activity and targets the bacterial cytochrome bc1complex.
- Jan Rybniker
- , Anthony Vocat
- & Stewart T. Cole
-
Article
| Open Access Asymmetric synthesis of N-allylic indoles via regio- and enantioselective allylation of aryl hydrazines
Asymmetric synthesis of N-allylic indoles via regio- and enantioselective allylation of aryl hydrazines
N-allylic indoles are important in medicinal and synthetic chemistry, but selective N-allylation of indoles can be difficult to achieve. Here, the authors report a catalytic asymmetric synthesis of these compounds through an enantioselective addition of aryl hydrazines to allenes, followed by indole formation.
- Kun Xu
- , Thomas Gilles
- & Bernhard Breit
-
Article
| Open Access Crystallographic structure of a small molecule SIRT1 activator-enzyme complex
Crystallographic structure of a small molecule SIRT1 activator-enzyme complex
Sirtuins are NAD+-dependent deacylases implicated in the regulation of stress responses, bioenergetics and epigenetic control. Here the authors describe the crystal structure of a sirtuin-activating compounds (STAC)-sirtuin complex and begin to elucidate the mechanism of sirtuins activation by STACs.
- Han Dai
- , April W. Case
- & James L. Ellis
-
Article
| Open Access Protein conformational plasticity and complex ligand-binding kinetics explored by atomistic simulations and Markov models
Protein conformational plasticity and complex ligand-binding kinetics explored by atomistic simulations and Markov models
Conformational plasticity influences several aspects of protein function. Here the authors combine extensive MD simulations with Markov state models—using trypsin as model—to reveal new mechanistic details of how conformational plasticity influence ligand-receptors interactions.
- Nuria Plattner
- & Frank Noé
-
Article
| Open Access Caenorhabditis elegans is a useful model for anthelmintic discovery
Caenorhabditis elegans is a useful model for anthelmintic discovery
Screening for new anthelmintic compounds that are active against parasitic nematodes is costly and labour intensive. Here, the authors use the non-parasitic nematode Caenorhabditis elegansto identify 30 anthelmintic lead compounds in an effective and cost-efficient manner.
- Andrew R. Burns
- , Genna M. Luciani
- & Peter J. Roy
-
Article
| Open Access Rhodium-catalysed C(sp2)–C(sp2) bond formation via C–H/C–F activation
Rhodium-catalysed C(sp2)–C(sp2) bond formation via C–H/C–F activation
Fluoroalkenes are found widely in biologically active compounds, but their introduction can be difficult or laborious. Here, the authors report a C–H/C–F activation strategy to introduce monofluoroalkenes into organic molecules in one step with good to excellent yields.
- Panpan Tian
- , Chao Feng
- & Teck-Peng Loh
-
Article
| Open Access Photoswitchable fatty acids enable optical control of TRPV1
Photoswitchable fatty acids enable optical control of TRPV1
Fatty acids are ancient lipids with numerous functions, from metabolic processes as a source of energy to structural and signalling roles within cell membranes. Here, the authors present azobenzene-modified fatty acids and their application as photoswitchable agonists of the Vanilloid Receptor 1.
- James Allen Frank
- , Mirko Moroni
- & Dirk Trauner
-
Article
| Open Access New peptide architectures through C–H activation stapling between tryptophan–phenylalanine/tyrosine residues
New peptide architectures through C–H activation stapling between tryptophan–phenylalanine/tyrosine residues
Macrocyclic, constrained peptides show promise in therapeutic applications due to the stable and defined conformations that can be produced. Here, the authors report a method to form macrocyclic peptides through C–H activation on tryptophan and coupling with iodo-substituted aryl amino acids
- Lorena Mendive-Tapia
- , Sara Preciado
- & Rodolfo Lavilla
-
Article
| Open Access Direct synthesis of imino-C-nucleoside analogues and other biologically active iminosugars
Direct synthesis of imino-C-nucleoside analogues and other biologically active iminosugars
Iminosugars are biologically and medicinally important compounds but methods for their synthesis are often laborious. Here, the authors report a simple, rapid route for the enantioselective synthesis of multiple biologically active iminosugars and C-nucleoside analogues.
- Milan Bergeron-Brlek
- , Michael Meanwell
- & Robert Britton
-
Article |
 Glycopeptide analogues of PSGL-1 inhibit P-selectin in vitro and in vivo
Glycopeptide analogues of PSGL-1 inhibit P-selectin in vitro and in vivo
Inhibiting the interaction between the membrane protein P-selectin and its ligand PSGL-1 is thought to block inflammation. Here the authors report an efficient stereoselective synthesis for PSGL-1 glycopeptide mimics and show that these compounds inhibit PSGL-1/P-selectin in vitro and in vivo.
- Venkata R. Krishnamurthy
- , Mohammed Y. R. Sardar
- & Elliot L. Chaikof
-
Article
| Open Access Triaminopyrimidine is a fast-killing and long-acting antimalarial clinical candidate
Triaminopyrimidine is a fast-killing and long-acting antimalarial clinical candidate
The emergence of resistant Plasmodiumstrains fuels the search for new antimalarials. Here, the authors present a new class of potent antimalarial compounds, the triaminopyrimidines, that display low toxicity and long half-life in animal models.
- Shahul Hameed P.
- , Suresh Solapure
- & Vasan K. Sambandamurthy
-
Article
| Open Access Transfer hydrogenation catalysis in cells as a new approach to anticancer drug design
Transfer hydrogenation catalysis in cells as a new approach to anticancer drug design
Organometallic complexes are effective hydrogenation catalysts for organic reactions. Here the authors report for the first time that transfer hydrogenation catalysis can take place inside the cell and could be used as a novel anticancer strategy.
- Joan J. Soldevila-Barreda
- , Isolda Romero-Canelón
- & Peter J. Sadler
-
Article |
 De novo branching cascades for structural and functional diversity in small molecules
De novo branching cascades for structural and functional diversity in small molecules
Generating diverse structures with a minimum amount of synthetic effort is an important goal for drug discovery. Here, the authors report a two-phase synthesis for the generation of skeletally diverse small molecules—forming molecular scaffolds and subsequently diversifying each into multiple structures.
- Miguel Garcia-Castro
- , Lea Kremer
- & Kamal Kumar
-
Article
| Open Access Total synthesis of clostrubin
Total synthesis of clostrubin
Due to rising resistance, efficient routes to new antibiotics is a vital task for human health. Here, the authors report a short, convergent and elegant synthesis of a very recently reported antibiotic, successfully giving access to this material on scale.
- Ming Yang
- , Jian Li
- & Ang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Triggering HIV polyprotein processing by light using rapid photodegradation of a tight-binding protease inhibitor
Triggering HIV polyprotein processing by light using rapid photodegradation of a tight-binding protease inhibitor
The study of HIV proteolysis during maturation and replication can be difficult since different steps in these processes occur simultaneously. Here, the authors present a photolabile HIV protease inhibitor which can be deactivated by light irradiation, allowing synchronized induction of viral maturation.
- Jiří Schimer
- , Marcela Pávová
- & Jan Konvalinka
-
Article
| Open Access Stereochemical bias introduced during RNA synthesis modulates the activity of phosphorothioate siRNAs
Stereochemical bias introduced during RNA synthesis modulates the activity of phosphorothioate siRNAs
Therapeutic oligonucleotides can be made more stable by substituting their achiral phosphodiester groups for chiral phosphorothioate linkages. Here, the authors present a synthesis of phosphorothioated RNAs, where the activator controls strand stereochemistry, and also the activity of assembled siRNAs.
- Hartmut Jahns
- , Martina Roos
- & Jonathan Hall
-
Article
| Open Access Total synthesis of periploside A, a unique pregnane hexasaccharide with potent immunosuppressive effects
Total synthesis of periploside A, a unique pregnane hexasaccharide with potent immunosuppressive effects
Periploside A is a natural pregnane glycoside with promising immunosuppressive properties, but the presence of a seven-membered formyl acetal bridged orthoester makes it difficult to chemically synthesize. Here, the authors present a 76-step total synthesis of periploside A.
- Xiaheng Zhang
- , Yu Zhou
- & Biao Yu
-
Article |
 Comprehensive bioimaging with fluorinated nanoparticles using breathable liquids
Comprehensive bioimaging with fluorinated nanoparticles using breathable liquids
Perfluorinated organic molecules have shown many uses, including as imaging agents. Here, the authors report that fluorinated gold nanoparticles offer an effective means of mass spectrometry tissue imaging, in addition to facilitating X-ray analysis providing complementary information to mass spectral images.
- Michael E. Kurczy
- , Zheng-Jiang Zhu
- & Gary Siuzdak
-
Article |
 Late-stage C–H functionalization of complex alkaloids and drug molecules via intermolecular rhodium-carbenoid insertion
Late-stage C–H functionalization of complex alkaloids and drug molecules via intermolecular rhodium-carbenoid insertion
The ability to functionalize a C–H bond is useful in complex organic syntheses, but the scope of this approach is sometimes limited by its sensitivity to basic amines. Here, the authors achieve functionalization of amine-containing natural products by site-selective rhodium-carbene-mediated C–H insertion.
- Jing He
- , Lawrence G. Hamann
- & Rohan E. J. Beckwith
-
Article
| Open Access Cell type-specific delivery of short interfering RNAs by dye-functionalised theranostic nanoparticles
Cell type-specific delivery of short interfering RNAs by dye-functionalised theranostic nanoparticles
A potential drug should specifically interact with its intended target in order to limit unwanted side effects. Here, the authors fabricate a biodegradable polymer nanoparticle with a fluorescent hepatic uptake transporter ligand to achieve targeted in vivosiRNA delivery and imaging of delivery.
- Adrian T. Press
- , Anja Traeger
- & Michael Bauer
-
Article
| Open Access Pyrazoleamide compounds are potent antimalarials that target Na+ homeostasis in intraerythrocytic Plasmodium falciparum
Pyrazoleamide compounds are potent antimalarials that target Na+ homeostasis in intraerythrocytic Plasmodium falciparum
Novel antimalarial drugs are urgently needed to combat parasite drug resistance. Here, Vaidya et al. describe a new chemical class of potent antimalarial compounds that act by disrupting the parasite's sodium homeostasis.
- Akhil B. Vaidya
- , Joanne M. Morrisey
- & Lawrence W. Bergman
-
Article |
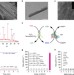 An antioxidant nanozyme that uncovers the cytoprotective potential of vanadia nanowires
An antioxidant nanozyme that uncovers the cytoprotective potential of vanadia nanowires
It is known that some nanomaterials can exhibit enzyme-like activities, prompting interest in the novel applications this property may allow. Here, the authors show how vanadia nanowires possess glutathione peroxidase-like activity, and can effectively protect cells from oxidative damage.
- Amit A. Vernekar
- , Devanjan Sinha
- & Govindasamy Mugesh
-
Article |
 Semi-permeable coatings fabricated from comb-polymers efficiently protect proteins in vivo
Semi-permeable coatings fabricated from comb-polymers efficiently protect proteins in vivo
The attachment of polymers to protein molecules is known to shield them from biological breakdown. Here, the authors apply this concept to an asparaginase, in order to prevent its deactiviation by host immune responses during leukaemia treatment.
- Mi Liu
- , Pål Johansen
- & Marc A. Gauthier
-
Article |
 Catalytic activation of pre-substrates via dynamic fragment assembly on protein templates
Catalytic activation of pre-substrates via dynamic fragment assembly on protein templates
The identification of protein-binding fragments during drug development can be hampered by poor binding affinities before optimization. Here, the authors have designed pre-substrates to release fluorescent signals whenever a nucleophile fragment binds next to the active site of the enzyme.
- Edyta Burda
- & Jörg Rademann
-
Article
| Open Access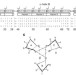 Structural basis of IL-23 antagonism by an Alphabody protein scaffold
Structural basis of IL-23 antagonism by an Alphabody protein scaffold
Protein scaffolds can serve as alternatives to antibodies in a range of applications. Here, the authors report the design and development of Alphabody™, a protein scaffold featuring a single-chain antiparallel triple-helix coiled-coil fold that the authors use to develop Alphabodies that can neutralize human IL-23 with high specificity and affinity.
- Johan Desmet
- , Kenneth Verstraete
- & Savvas N. Savvides
-
Article |
 Structure-guided discovery of potent and dual-acting human parainfluenza virus haemagglutinin–neuraminidase inhibitors
Structure-guided discovery of potent and dual-acting human parainfluenza virus haemagglutinin–neuraminidase inhibitors
Human parainfluenza viruses (hPIVs) cause common respiratory diseases in children. Here the authors rationally design small molecules targeting the hPIV haemagglutinin–neuraminidase protein, and show that the compounds inhibit viral entry and exit from cultured cells.
- Patrice Guillon
- , Larissa Dirr
- & Mark von Itzstein
-
Article
| Open Access Optical control of insulin release using a photoswitchable sulfonylurea
Optical control of insulin release using a photoswitchable sulfonylurea
Sulfonylureas are widely used anti-diabetic drugs, which promote insulin release by blocking a pancreatic ion channel. Here the authors create a photoswitchable sulfonylurea derivative and use it to control insulin release from cultured cells and isolated pancreatic islets by illumination with blue light.
- Johannes Broichhagen
- , Matthias Schönberger
- & Dirk Trauner
-
Article
| Open Access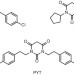 Modest CaV1.342-selective inhibition by compound 8 is β-subunit dependent
Modest CaV1.342-selective inhibition by compound 8 is β-subunit dependent
Compound 8-1-(3-chlorophenethyl)-3-cyclopentylpyrimidine-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-trione was previously reported to be a selective inhibitor of the CaV1.3 calcium channel. Now, Huang et al. demonstrate that selectivity towards CaV1.3 relative to CaV1.2 is dependent on the type of β-subunit and CaV1.3 splice variant assayed.
- Hua Huang
- , Cheng Yang Ng
- & Tuck Wah Soong
-
Article
| Open Access Protein painting reveals solvent-excluded drug targets hidden within native protein–protein interfaces
Protein painting reveals solvent-excluded drug targets hidden within native protein–protein interfaces
Identifying the site where a protein binds to another molecule is an important factor for the design of therapeutics intended to prevent this interaction. Here, the authors coat protein–receptor complexes with surface-binding molecules, and determine their interacting regions using mass spectrometry.
- Alessandra Luchini
- , Virginia Espina
- & Lance A. Liotta
-
Article |
 Spirocyclic hypervalent iodine(III)-mediated radiofluorination of non-activated and hindered aromatics
Spirocyclic hypervalent iodine(III)-mediated radiofluorination of non-activated and hindered aromatics
Fluorine-18 containing molecules are important for PET imaging, but due to the short half-life it is necessary to develop rapid methods for its introduction. Here, the authors use spirocyclic iodine(III) precursors, allowing direct 18F labelling of highly functionalized non-activated arenes and PET radiopharmaceuticals.
- Benjamin H. Rotstein
- , Nickeisha A. Stephenson
- & Steven H. Liang
-
Article |
 In vivo imaging of specific drug–target binding at subcellular resolution
In vivo imaging of specific drug–target binding at subcellular resolution
The ability to image the action of drugs in cells in real time could yield valuable information on their efficacy and mode of action. Here, the authors use multiphoton fluorescence anisotropy microscopy to image drug distribution and target engagement in real time at the cellular level in vivo.
- J. M. Dubach
- , C. Vinegoni
- & R. Weissleder
-
Article
| Open Access Ligand substitutions between ruthenium–cymene compounds can control protein versus DNA targeting and anticancer activity
Ligand substitutions between ruthenium–cymene compounds can control protein versus DNA targeting and anticancer activity
Ruthenium-cymene-based compounds are investigated as potential anticancer drugs. Here, Adhireksan et al.study two ruthenium-containing compounds with varying cytotoxicity and show that differences in ligand structure may explain their activity and binding to different subcellular targets.
- Zenita Adhireksan
- , Gabriela E. Davey
- & Curt A. Davey
-
Article |
 Regioselective trifluoromethylation of N-heteroaromatic compounds using trifluoromethyldifluoroborane activator
Regioselective trifluoromethylation of N-heteroaromatic compounds using trifluoromethyldifluoroborane activator
Trifluoromethyl groups greatly alter the properties of organic molecules and are commonly used in the preparation of drugs and agrochemicals. Here the authors report a method for the activation of nitrogen heterocycles to nucleophilic attack, allowing regioselective trifluoromethylation.
- Tomoaki Nishida
- , Haruka Ida
- & Motomu Kanai
-
Article |
 Transition-metal-substituted polyoxometalate derivatives as functional anti-amyloid agents for Alzheimer’s disease
Transition-metal-substituted polyoxometalate derivatives as functional anti-amyloid agents for Alzheimer’s disease
Beta amyloid aggregation, a process implicated in Alzheimer’s disease pathology, is inhibted by polyoxometalate with a Wells–Dawson structure. Gao et al.show that transition metal-functionalized derivatives are more effective at inhibiting beta amyloid aggregation than non-functionalized derivatives.
- Nan Gao
- , Hanjun Sun
- & Xiaogang Qu
-
Article |
 Activation pathway of Src kinase reveals intermediate states as targets for drug design
Activation pathway of Src kinase reveals intermediate states as targets for drug design
Activation of c-src kinase is associated with uncontrolled growth and metastasis of tumour cells. Shukla et al.model conformational changes in c-src during activation, and identify an allosteric site in an intermediate state that may provide a target for small molecule therapeutics.
- Diwakar Shukla
- , Yilin Meng
- & Vijay S. Pande
-
Article
| Open Access Extracellular palladium-catalysed dealkylation of 5-fluoro-1-propargyl-uracil as a bioorthogonally activated prodrug approach
Extracellular palladium-catalysed dealkylation of 5-fluoro-1-propargyl-uracil as a bioorthogonally activated prodrug approach
A bioorthogonal organometallic reaction is a biocompatible and chemospecific process. Here, the authors report the bioorthogonal generation of 5-fluorouracil from a biologically inert alkylated precursor by extracellular palladium catalysis, and assess its antiproliferative properties in vitro.
- Jason T. Weiss
- , John C. Dawson
- & Asier Unciti-Broceta
-
Article |
 Selenoether oxytocin analogues have analgesic properties in a mouse model of chronic abdominal pain
Selenoether oxytocin analogues have analgesic properties in a mouse model of chronic abdominal pain
Peptide drugs are attractive as therapeutics for gut-based applications, although they may be susceptible to reduction and degradation. Here, the authors develop seleno-oxytocin analogues, with enhanced stability at no cost to potency, and demonstrate their efficacy at colonic nociceptor inhibition in a mouse model.
- Aline Dantas de Araujo
- , Mehdi Mobli
- & Paul F. Alewood
-
Article |
 Probing backbone hydrogen bonding in PDZ/ligand interactions by protein amide-to-ester mutations
Probing backbone hydrogen bonding in PDZ/ligand interactions by protein amide-to-ester mutations
PDZ domains facilitate numerous protein-binding interactions, and their prevalence in the human genome has led to their investigation as drug targets. Here, the authors generate semisynthetic PDZ domains containing backbone mutations for the identification of important ligand-binding interactions.
- Søren W. Pedersen
- , Stine B. Pedersen
- & Kristian Strømgaard
-
Article
| Open Access 4′-O-substitutions determine selectivity of aminoglycoside antibiotics
4′-O-substitutions determine selectivity of aminoglycoside antibiotics
Aminoglycoside antibiotics target the ribosome but their limited selectivity for the bacterial ribosome can cause side effects in humans. Here, the authors synthesize 4′-O-ether or 4′,6′-O-acetal modifications and show that these compounds possess increased selectivity against bacterial ribosomes.
- Déborah Perez-Fernandez
- , Dmitri Shcherbakov
- & Erik C. Böttger
-
Article |
 Supramolecular high-aspect ratio assemblies with strong antifungal activity
Supramolecular high-aspect ratio assemblies with strong antifungal activity
Efficient and pathogen-specific antifungal agents are required to mitigate drug resistance problems. Here the authors present a series of cationic small molecules, which are easy to isolate and characterize, and which can self-assemble to give polymer-like antifungal activity and specificity.
- Kazuki Fukushima
- , Shaoqiong Liu
- & James L. Hedrick
-
Article |
 Downsizing a human inflammatory protein to a small molecule with equal potency and functionality
Downsizing a human inflammatory protein to a small molecule with equal potency and functionality
Replicating the functionality of bioactive proteins using rationally designed small molecule mimics is both economically valuable and synthetically challenging. Here the authors develop a mimic of the inflammatory protein C3a with equal biological potency but enhanced stability and bioavailability.
- Robert C. Reid
- , Mei-Kwan Yau
- & David P. Fairlie
-
Article |
 The first total synthesis of the cyclodepsipeptide pipecolidepsin A
The first total synthesis of the cyclodepsipeptide pipecolidepsin A
Pipecolidepsin A—commonly isolated from a marine sponge—is a promising anticancer agent but is challenging to synthesise in the lab. Here the authors describe the first total synthesis of this cyclodepsipeptide using a versatile strategy applicable to other similar compounds.
- Marta Pelay-Gimeno
- , Yésica García-Ramos
- & Fernando Albericio
-
Article
| Open Access Tetrasaccharide iteration synthesis of a heparin-like dodecasaccharide and radiolabelling for in vivo tissue distribution studies
Tetrasaccharide iteration synthesis of a heparin-like dodecasaccharide and radiolabelling for in vivo tissue distribution studies
Heparin-like oligosaccharides are implicated in various diseases. Hansen et al. report an efficient two-cycle [4+4+4] tetrasaccharide-iteration-based approach to synthesize a structurally defined heparin dodecasaccharide with a latent aldehyde tag for labelling and conjugation.
- Steen U. Hansen
- , Gavin J. Miller
- & John M. Gardiner
-
Article |
 Identification and optimization of small-molecule agonists of the human relaxin hormone receptor RXFP1
Identification and optimization of small-molecule agonists of the human relaxin hormone receptor RXFP1
The peptide hormone relaxin has potential in the treatment of acute heart failure, but it must be intravenously injected and has a short half-life after administration. Now, small-molecule alternatives to relaxin are reported with similar efficacies to the natural hormone in functional assays.
- Jingbo Xiao
- , Zaohua Huang
- & Juan J. Marugan
-
Article |
 An influenza virus-inspired polymer system for the timed release of siRNA
An influenza virus-inspired polymer system for the timed release of siRNA
Small interfering RNA is degraded by plasma and can’t cross the cell membrane due to its negative charge. Here, the authors present an influenza inspired polymer carrier, capable of local RNA delivery, which degrades to a non-toxic by-product, and is thus suitable for multiple doses.
- Nghia P Truong
- , Wenyi Gu
- & Michael J Monteiro
-
Article
| Open Access Assembly of a π–π stack of ligands in the binding site of an acetylcholine-binding protein
Assembly of a π–π stack of ligands in the binding site of an acetylcholine-binding protein
AChBP is used as a structurally accessible prototype for studying ligand binding to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Stornaiuolo et al. report that a small molecule binds AChBP in an ordered p–p stack of three molecules per binding site, which may lead to new approaches in drug design.
- Mariano Stornaiuolo
- , Gerdien E. De Kloe
- & Titia K. Sixma
-
Article |
 Externally controlled on-demand release of anti-HIV drug using magneto-electric nanoparticles as carriers
Externally controlled on-demand release of anti-HIV drug using magneto-electric nanoparticles as carriers
Magneto-electric nanoparticles may facilitate the low-energy and dissipation-free field-triggered release of drugs across the blood–brain barrier. Here, the authors demonstrate the a.c. field-triggered release of anti-HIV drugs and confirm the in vitrodrug integrity after release.
- Madhavan Nair
- , Rakesh Guduru
- & Sakhrat Khizroev
-
Article |
 Influenza neuraminidase operates via a nucleophilic mechanism and can be targeted by covalent inhibitors
Influenza neuraminidase operates via a nucleophilic mechanism and can be targeted by covalent inhibitors
New influenza neuramidase inhibitors may increase preparedness against influenza outbreaks. Vavricka et al.confirm the catalytic mechanism of neuramidase and show that it can be inhibited irreversibly with covalent inhibitors.
- Christopher J. Vavricka
- , Yue Liu
- & George F. Gao

 Carbohydrate scaffolds as glycosyltransferase inhibitors with in vivo antibacterial activity
Carbohydrate scaffolds as glycosyltransferase inhibitors with in vivo antibacterial activity