Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Design-rules for stapled peptides with in vivo activity and their application to Mdm2/X antagonists
Design-rules for stapled peptides with in vivo activity and their application to Mdm2/X antagonists
Stapled α-helical peptides are promising for targeting challenging targets such as transcription factors, but achieving sufficient cell permeability while avoiding off-target cleavage is difficult. Here, the authors present workflows for identifying stapled peptides against Mdm2(X) with in vivo activity and no off-target effects based on comprehensive investigations of their properties.
- Arun Chandramohan
- , Hubert Josien
- & Anthony W. Partridge
-
Article
| Open Access Direct-to-biology, automated, nano-scale synthesis, and phenotypic screening-enabled E3 ligase modulator discovery
Direct-to-biology, automated, nano-scale synthesis, and phenotypic screening-enabled E3 ligase modulator discovery
Targeted protein degradation (TPD) is an emerging therapeutic that can lead to proteasomal degradation of target proteins. Here, the authors combine nano-scale, automated synthesis and cell-based, direct-to-biology screening, allowing them to discover and profile Molecular Glues (MGs) degrading substrates via the Cereblon E3 ubiquitin ligase.
- Zefeng Wang
- , Shabnam Shaabani
- & Alexander Dömling
-
Article
| Open Access C5 methylation confers accessibility, stability and selectivity to picrotoxinin
C5 methylation confers accessibility, stability and selectivity to picrotoxinin
Minor changes to complex structures can exert major influences on synthesis strategy and functional properties but synthetic difficulties can obstruct the exploration of natural product function. Here the authors explore two parallel series of picrotoxinin analogs and identify leads with selectivity between mammalian and insect ion channels.
- Guanghu Tong
- , Samantha Griffin
- & Ryan A. Shenvi
-
Article
| Open Access Catalytic 4-exo-dig carbocyclization for the construction of furan-fused cyclobutanones and synthetic applications
Catalytic 4-exo-dig carbocyclization for the construction of furan-fused cyclobutanones and synthetic applications
Aromatic ring fused cyclobutanone is a strained motif with broad applications. Here, the authors report a catalytic 4- exo-dig process, which proved successful to access furan-fused cyclobutanones that can serve as versatile synthetic blocks.
- Kemiao Hong
- , Yi Zhou
- & Xinfang Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Diversity-oriented synthesis encoded by deoxyoligonucleotides
Diversity-oriented synthesis encoded by deoxyoligonucleotides
Most DNA-encoded library (DEL) syntheses are limited by the presence of sensitive DNA-based constructs. Here, the authors develop DOSEDO, a diverse 3.7 million compound DEL, generated through diversity-oriented synthesis that provides enhanced scaffold and exit vector diversity and gives validated binding hits for multiple protein targets.
- Liam Hudson
- , Jeremy W. Mason
- & Karin Briner
-
Article
| Open Access Smart thrombosis inhibitors without bleeding side effects via charge tunable ligand design
Smart thrombosis inhibitors without bleeding side effects via charge tunable ligand design
Treatments to prevent thrombosis are suboptimal. Here, the authors identify a lead an antithrombotic drug targeting polyphosphate based on switchable protonation states for the anion-binding groups, demonstrating antithrombotic activity in multiple mouse models, not causing bleeding, and well tolerated.
- Chanel C. La
- , Stephanie A. Smith
- & Jayachandran N. Kizhakkedathu
-
Article
| Open Access Reference compounds for characterizing cellular injury in high-content cellular morphology assays
Reference compounds for characterizing cellular injury in high-content cellular morphology assays
Cellular nuisance compounds are a burden in chemical biology and drug screening. Here the authors profile prototypical cytotoxic and nuisance compounds using the cell painting assay to systematically characterise cellular morphologies associated with compound-dependent cellular injury and nuisance activity.
- Jayme L. Dahlin
- , Bruce K. Hua
- & Bridget K. Wagner
-
Article
| Open Access Oxygen mediated oxidative couplings of flavones in alkaline water
Oxygen mediated oxidative couplings of flavones in alkaline water
Catalysed oxidative C-C bond formation reactions are important in the synthesis of natural products, but poorly tolerated by polyphenolic flavones. Here the authors report the reactivity of molecular oxygen in alkaline water without added catalyst for the synthesis of a collection of flavone dimers and trimers.
- Xin Yang
- , Sophie Hui Min Lim
- & Dejian Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Generating experimentally unrelated target molecule-binding highly functionalized nucleic-acid polymers using machine learning
Generating experimentally unrelated target molecule-binding highly functionalized nucleic-acid polymers using machine learning
In vitro library screening is a powerful approach to identify functional biopolymers, but only covers a fraction of possible sequences. Here, the authors use experimental in vitro selection results to train a conditional variational autoencoder machine learning model that generates biopolymers with no apparent sequence similarity to experimentally derived examples, but that nevertheless bind the target molecule with similar potent binding affinity.
- Jonathan C. Chen
- , Jonathan P. Chen
- & David R. Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis and direct assay of large macrocycle diversities by combinatorial late-stage modification at picomole scale
Synthesis and direct assay of large macrocycle diversities by combinatorial late-stage modification at picomole scale
Macrocycles have potential as therapeutics, but their libraries are currently not large enough for high-throughput screening. Here, the authors show a combinatorial approach to generate a library of almost 20’000 macrocycles by conjugating carboxylic-acid fragments to macrocyclic scaffolds, identifying nanomolar inhibitors against thrombin and binders of MDM2.
- Sevan Habeshian
- , Manuel Leonardo Merz
- & Christian Heinis
-
Article
| Open Access Metabolic drug survey highlights cancer cell dependencies and vulnerabilities
Metabolic drug survey highlights cancer cell dependencies and vulnerabilities
Metabolic reprogramming contributes to cancer development and progression. Here, the authors show the utility of a metabolic drug library to uncover metabolic vulnerabilities and obtain functional insights into myeloid leukemia biology.
- Tea Pemovska
- , Johannes W. Bigenzahn
- & Giulio Superti-Furga
-
Article
| Open Access Difluorocarbene enables to access 2-fluoroindoles from ortho-vinylanilines
Difluorocarbene enables to access 2-fluoroindoles from ortho-vinylanilines
2-Fluoroindoles are an important structural scaffold in many bioactive or therapeutic agents, but efficient constructions of 2-fluoroindole derivatives are very sparce. Here the authors report an efficient and general strategy for the construction of 2-fluoroindoles in which a wide variety of 2-fluoroindoles were accessed with high efficiency and chemoselectivity.
- Jianke Su
- , Xinyuan Hu
- & Qiuling Song
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring protein hotspots by optimized fragment pharmacophores
Exploring protein hotspots by optimized fragment pharmacophores
Fragment-based drug discovery employs screening of small polar compounds typically exhibiting low affinity towards protein targets. Here, the authors combine the use of protein-based binding pharmacophores with the theory of protein hotspots to develop a design protocol for fragment libraries, called SpotXplorer, and validate their approach on common and emerging drug targets.
- Dávid Bajusz
- , Warren S. Wade
- & György M. Keserű
-
Article
| Open Access Natural product fragment combination to performance-diverse pseudo-natural products
Natural product fragment combination to performance-diverse pseudo-natural products
Natural products inspire the development of pseudo-natural products through combinations of fragments of compound classes that are chemically and biologically distinct. Here, the authors report a library of 244 pseudo-natural products, evaluate them in the cell painting essays and identify the phenotypic role of individual fragments.
- Michael Grigalunas
- , Annina Burhop
- & Herbert Waldmann
-
Article
| Open Access Lasso-grafting of macrocyclic peptide pharmacophores yields multi-functional proteins
Lasso-grafting of macrocyclic peptide pharmacophores yields multi-functional proteins
RaPID (Random non-standard Peptides Integrated Discovery) enables discovery of small macrocyclic peptides binding desired targets. Here, the authors propose lasso-grafting: the RaPID-derived peptides are implanted onto diverse proteins and maintain both the binding properties of the cyclic peptide and the host protein function.
- Emiko Mihara
- , Satoshi Watanabe
- & Junichi Takagi
-
Article
| Open Access Nature-inspired remodeling of (aza)indoles to meta-aminoaryl nicotinates for late-stage conjugation of vitamin B3 to (hetero)arylamines
Nature-inspired remodeling of (aza)indoles to meta-aminoaryl nicotinates for late-stage conjugation of vitamin B3 to (hetero)arylamines
Vitamin B3 derivatives display a range of biological activities. Here, the authors report the synthesis of meta-aminoaryl nicotinates, derivatives of vitamin B3, and their late-stage conjugation with (hetero)arylamines, ultimately expanding the chemical space for biomedical research.
- Begur Vasanthkumar Varun
- , Kannan Vaithegi
- & Seung Bum Park
-
Article
| Open Access A combined high-throughput and high-content platform for unified on-chip synthesis, characterization and biological screening
A combined high-throughput and high-content platform for unified on-chip synthesis, characterization and biological screening
On-chip synthesis and screening has been used to automate drug discovery but on-chip analysis still remains a major limitation. Here, the authors report on a dendrimer-based surface patterning method to create nanodroplet arrays on materials which allow for on-chip high-throughput analysis.
- Maximilian Benz
- , Arndt Asperger
- & Pavel A. Levkin
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of gramicidin A analogues with altered activities by multidimensional screening of a one-bead-one-compound library
Discovery of gramicidin A analogues with altered activities by multidimensional screening of a one-bead-one-compound library
The strong hemolytic activity and mammalian cytotoxicity of gramicidin A, a peptide antibiotic, has hindered its non-topical clinical application. Here, the authors report a high-throughput strategy for the discovery of gramicidin A analogues with altered biological activity profiles.
- Yuri Takada
- , Hiroaki Itoh
- & Masayuki Inoue
-
Article
| Open Access Unsymmetrical polysulfidation via designed bilateral disulfurating reagents
Unsymmetrical polysulfidation via designed bilateral disulfurating reagents
The functionalization of a sulfur-sulfur motif is synthetically challenging but highly desired for the production of bioactive compounds. Here, the authors report a disulfurating reagent for sequential and modular assembly of polysulfides where the S-S motif is functionalized with different C-, N- and S-nucleophiles.
- Jiahui Xue
- & Xuefeng Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-large chemical libraries for the discovery of high-affinity peptide binders
Ultra-large chemical libraries for the discovery of high-affinity peptide binders
Synthetic peptide libraries can access broad chemical space, but generally examine only ~ 106 compounds. Here, the authors show that in-solution affinity selection, interfaced with nLC-MS/MS sequencing, can identify binders from fully randomized synthetic libraries of 108 members.
- Anthony J. Quartararo
- , Zachary P. Gates
- & Bradley L. Pentelute
-
Article
| Open Access Stereospecific Si-C coupling and remote control of axial chirality by enantioselective palladium-catalyzed hydrosilylation of maleimides
Stereospecific Si-C coupling and remote control of axial chirality by enantioselective palladium-catalyzed hydrosilylation of maleimides
Catalytic asymmetric hydrosilylation of internal alkenes has proven elusive due to more favourable double bond reduction or isomerization. Here, the authors show an enantioselective Si-C coupling by hydrosilylation of activated alkenes using a palladium/phosphoramidite catalyst affording axially chiral succinimides.
- Xing-Wei Gu
- , Yu-Li Sun
- & Li-Wen Xu
-
Article
| Open Access A modular biomimetic strategy for the synthesis of macrolide P-glycoprotein inhibitors via Rh-catalyzed C-H activation
A modular biomimetic strategy for the synthesis of macrolide P-glycoprotein inhibitors via Rh-catalyzed C-H activation
One strategy to address multidrug resistance in cancer is the development of modular methods to access bioactive scaffolds. Here, the authors report a Rh(III)-catalyzed carboxylic acid-directed C(sp2)−H allylation and apply it to the modular synthesis of (Z)-allylic macrolides which enhance antitumoral drug activity.
- Lu Chen
- , Haitian Quan
- & Weibo Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis and evaluation of designed PKC modulators for enhanced cancer immunotherapy
Synthesis and evaluation of designed PKC modulators for enhanced cancer immunotherapy
Bryostatin 1 is a unique therapeutic lead, however its scarce natural sources have hampered its use in treatment of human disease. Here, the authors use a scalable synthesis of bryostatin 1 to make close-in analogs which potently induce increased cell surface expression holding potential for immunotherapy.
- Clayton Hardman
- , Stephen Ho
- & Paul A. Wender
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic biology based construction of biological activity-related library of fungal decalin-containing diterpenoid pyrones
Synthetic biology based construction of biological activity-related library of fungal decalin-containing diterpenoid pyrones
Combining genome mining and heterologous expression in a genetically tractable host can lead to bioactive natural products discovery and production. Here, the authors employ this strategy for new decalin-containing diterpenoid pyrenes production by expressing native, extended, and shunt pathways in Aspergillus oryzae.
- Kento Tsukada
- , Shono Shinki
- & Teigo Asai
-
Article
| Open Access Boron-mediated directed aromatic C–H hydroxylation
Boron-mediated directed aromatic C–H hydroxylation
Transition metal-catalysed C–H hydroxylation is one of the most notable synthetic advances to access alcohols and phenols. Here, the authors report a metal-free, mild C–H hydroxylation of (hetero)arenes via boron-mediated chelation.
- Jiahang Lv
- , Binlin Zhao
- & Zhuangzhi Shi
-
Article
| Open Access A synthetic peptide library for benchmarking crosslinking-mass spectrometry search engines for proteins and protein complexes
A synthetic peptide library for benchmarking crosslinking-mass spectrometry search engines for proteins and protein complexes
Validating crosslinking-mass spectrometry workflows is hampered by the lack of a ground truth to assess the robustness of the crosslink identifications. Here, the authors present a synthetic library of crosslinked peptides, enabling unambiguous discrimination of correct and incorrect crosslink identifications.
- Rebecca Beveridge
- , Johannes Stadlmann
- & Karl Mechtler
-
Article
| Open Access A general strategy for diversifying complex natural products to polycyclic scaffolds with medium-sized rings
A general strategy for diversifying complex natural products to polycyclic scaffolds with medium-sized rings
Derivatization of natural products is a powerful approach to generate new molecules for biological screenings. Here, the authors employ C-H oxidation and ring expansion methods for the preparation of a library of medium-sized ring skeleta, which occupy a unique chemical space based on chemoinformatic analysis.
- Changgui Zhao
- , Zhengqing Ye
- & Weiping Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Rhodium-catalysed direct hydroarylation of alkenes and alkynes with phosphines through phosphorous-assisted C−H activation
Rhodium-catalysed direct hydroarylation of alkenes and alkynes with phosphines through phosphorous-assisted C−H activation
Dialkyl biaryl phosphines find wide application in catalysis as ligands. Here, the authors report a rhodium-catalysed hydroarylation of alkenes and alkynes with tertiary phosphines through P(III)-chelation assisted C-H activation affording a library of functionalized phosphines which hold potential in catalytic applications.
- Dingyi Wang
- , Ben Dong
- & Zhuangzhi Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Development of a high-throughput strategy for discovery of potent analogues of antibiotic lysocin E
Development of a high-throughput strategy for discovery of potent analogues of antibiotic lysocin E
The depsipeptide Lysocin E has antibacterial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Here, the authors developed a high-throughput one-bead-on-compound method for the synthesis and screening lysocin E derivatives, with several hits being more active than the parent compound.
- Hiroaki Itoh
- , Kotaro Tokumoto
- & Masayuki Inoue
-
Article
| Open Access Marrying chemistry with biology by combining on-chip solution-based combinatorial synthesis and cellular screening
Marrying chemistry with biology by combining on-chip solution-based combinatorial synthesis and cellular screening
High-throughput cell-based screening of compound libraries is utilised in drug development; however, a lack of compatible methods limits direct synthesis and testing. Here, the authors present a diverse chip based synthesis system which can be combined with cell screening and demonstrate the application.
- Maximilian Benz
- , Mijanur R. Molla
- & Pavel A. Levkin
-
Article
| Open Access A diversity-oriented rhodamine library for wide-spectrum bactericidal agents with low inducible resistance against resistant pathogens
A diversity-oriented rhodamine library for wide-spectrum bactericidal agents with low inducible resistance against resistant pathogens
Preparation of xanthene-containing compounds has been limited due to structural bias existing methods pose. Here, the authors developed a mild, diversity-oriented method for rhodamines synthesis, leading to the finding of compounds with antibacterial potency against a variety of bacterial species.
- Xiao Luo
- , Liujia Qian
- & Youjun Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Multicomponent reactions provide key molecules for secret communication
Multicomponent reactions provide key molecules for secret communication
Designing molecular keys and combining advanced encryption standard cryptography with molecular steganography is a secure way for encoding messages. Here, the authors use the Ugi four-component reaction of perfluorinated acids to create a library of 500,000 molecular keys for encryption and decryption.
- Andreas C. Boukis
- , Kevin Reiter
- & Michael A. R. Meier
-
Article
| Open Access A modular synthesis of tetracyclic meroterpenoid antibiotics
A modular synthesis of tetracyclic meroterpenoid antibiotics
Polycyclic meroterpenoids show a wide range of biological activities. Here, the authors report a modular approach to synthesize a number of natural and non-natural tetracyclic meroterpenoids, which display antibiotic activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
- Raphael Wildermuth
- , Klaus Speck
- & Thomas Magauer
-
Article
| Open Access Multicomponent mapping of boron chemotypes furnishes selective enzyme inhibitors
Multicomponent mapping of boron chemotypes furnishes selective enzyme inhibitors
Heteroatom-rich organoboron compounds are promising modulators of enzyme activity. Here, the authors report a library of aminocyanoboronates as serine hydrolases inhibitors with the most potent compound showing in vivo and in vitro nanomolar activity and high selectivity towards human ABHD3 hydrolase.
- Joanne Tan
- , Armand B. Cognetta III
- & Andrei K. Yudin
-
Article
| Open Access Prioritizing multiple therapeutic targets in parallel using automated DNA-encoded library screening
Prioritizing multiple therapeutic targets in parallel using automated DNA-encoded library screening
Encoded Library Technology (ELT) has streamlined the identification of chemical ligands for protein targets in drug discovery. Here, the authors optimize the ELT approach to screen multiple proteins in parallel and identify promising targets and antibacterial compounds forS. aureus, A. baumannii and M. tuberculosis.
- Carl A. Machutta
- , Christopher S. Kollmann
- & Ghotas Evindar
-
Article
| Open Access Facile access to potent antiviral quinazoline heterocycles with fluorescence properties via merging metal-free domino reactions
Facile access to potent antiviral quinazoline heterocycles with fluorescence properties via merging metal-free domino reactions
Heterocycles are ubiquitous in bioactive compounds and routes to different substitution patterns are important to access the full substrate space. Here the authors report a route to 4,5,7,8-substituted antiviral fluorescent quinazolines, to allow cellular uptake visualization without external marker.
- Felix E. Held
- , Anton A. Guryev
- & Svetlana B. Tsogoeva
-
Article
| Open Access A ligand-directed divergent catalytic approach to establish structural and functional scaffold diversity
A ligand-directed divergent catalytic approach to establish structural and functional scaffold diversity
Synthetic methods that efficiently construct structurally diverse molecular scaffolds are attractive routes to diversely bioactive molecules. Here the authors report a method whereby common starting materials are converted to structurally and functionally diverse products by changing the catalyst ligand.
- Yen-Chun Lee
- , Sumersing Patil
- & Herbert Waldmann
-
Article
| Open Access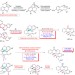 Radical aryl migration enables diversity-oriented synthesis of structurally diverse medium/macro- or bridged-rings
Radical aryl migration enables diversity-oriented synthesis of structurally diverse medium/macro- or bridged-rings
Medium-sized ring systems are common in natural products, however their synthesis is challenging, largely due to entropic factors. Here the authors report a radical-based method for the synthesis of medium to large functionalized, carbon or heterocyclic scaffolds.
- Lei Li
- , Zhong-Liang Li
- & Xin-Yuan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Total synthesis of teixobactin
Total synthesis of teixobactin
Teixobactin is a recently identified antibiotic that shows activity against drug resistant strains of bacteria. Here, the authors report a highly convergent total synthesis of this natural product, with sufficient flexibility to also allow the synthesis of a number of analogues.
- Kang Jin
- , Iek Hou Sam
- & Xuechen Li
-
Article |
 De novo branching cascades for structural and functional diversity in small molecules
De novo branching cascades for structural and functional diversity in small molecules
Generating diverse structures with a minimum amount of synthetic effort is an important goal for drug discovery. Here, the authors report a two-phase synthesis for the generation of skeletally diverse small molecules—forming molecular scaffolds and subsequently diversifying each into multiple structures.
- Miguel Garcia-Castro
- , Lea Kremer
- & Kamal Kumar
-
Article |
 CaV1.3-selective L-type calcium channel antagonists as potential new therapeutics for Parkinson's disease
CaV1.3-selective L-type calcium channel antagonists as potential new therapeutics for Parkinson's disease
L-type calcium channels comprising the CaV1.3 subunit have been linked to the generation of mitochondrial oxidant stress in Parkinson’s disease. Kang et al. identify pyrimidine-2,4,6-triones as a potential molecular scaffold, which they modify to develop a potent and highly selective CaV1.3 antagonist.
- Soosung Kang
- , Garry Cooper
- & Richard B. Silverman

 Targeted sampling of natural product space to identify bioactive natural product-like polyketide macrolides
Targeted sampling of natural product space to identify bioactive natural product-like polyketide macrolides