News & Views |
Featured
-
-
-
Article |
 Bond-selective fluorescence imaging with single-molecule sensitivity
Bond-selective fluorescence imaging with single-molecule sensitivity
Two-photon excitation with mid- and near-infrared pulses encodes bond selectivity in fluorescence imaging. Single-molecule imaging and spectroscopy is demonstrated on individual fluorophores as well as various labelled biological targets.
- Haomin Wang
- , Dongkwan Lee
- & Lu Wei
-
Letter
| Open Access Cavity-enhanced field-resolved spectroscopy
Cavity-enhanced field-resolved spectroscopy
An ultrabroadband femtosecond enhancement cavity is developed, using gold-coated mirrors and a wedged-diamond-plate input coupler. Simultaneous enhancement of a 22–40 THz offset-free frequency comb allows cavity-enhanced time-domain spectroscopy of gas mixtures based on electro-optic sampling in the mid-infrared range.
- Philipp Sulzer
- , Maximilian Högner
- & Ioachim Pupeza
-
Article |
 A wavelength-scale black phosphorus spectrometer
A wavelength-scale black phosphorus spectrometer
A single-photodetector spectrometer based on black phosphorus is demonstrated in the wavelength range from 2 to 9 μm. The footprint is 9 × 16 μm2. The spectrometer is free from bulky interferometers and gratings, and is electrically reconfigurable.
- Shaofan Yuan
- , Doron Naveh
- & Fengnian Xia
-
Article |
 High-resolution, high-contrast mid-infrared imaging of fresh biological samples with ultraviolet-localized photoacoustic microscopy
High-resolution, high-contrast mid-infrared imaging of fresh biological samples with ultraviolet-localized photoacoustic microscopy
Photoacoustic detection highly localized with a pulsed ultraviolet laser based on the Grüneisen relaxation effect allows water-background suppressed mid-infrared (MIR) imaging of lipids and proteins at ultraviolet resolution, at least an order of magnitude finer than the MIR diffraction limits.
- Junhui Shi
- , Terence T. W. Wong
- & Lihong V. Wang
-
Letter |
 Coherent injection locking of quantum cascade laser frequency combs
Coherent injection locking of quantum cascade laser frequency combs
Quantum cascade laser frequency combs are coherently locked to an external radio-frequency source even in extremely high-feedback conditions. The internal phase-locking mechanism and the possibility of all-electric stabilization are investigated.
- Johannes Hillbrand
- , Aaron Maxwell Andrews
- & Benedikt Schwarz
-
Article |
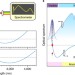 Mid-infrared frequency comb via coherent dispersive wave generation in silicon nitride nanophotonic waveguides
Mid-infrared frequency comb via coherent dispersive wave generation in silicon nitride nanophotonic waveguides
The direct generation of mid-infrared optical frequency combs in the region 2.5–4.0 μm from a 1.55-μm conventional and compact erbium-fibre-based femtosecond laser is demonstrated via coherent dispersive wave generation in silicon nitride nanophotonic waveguides.
- Hairun Guo
- , Clemens Herkommer
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article |
 High-coherence mid-infrared dual-comb spectroscopy spanning 2.6 to 5.2 μm
High-coherence mid-infrared dual-comb spectroscopy spanning 2.6 to 5.2 μm
By employing difference-frequency generation, a mid-infrared dual-comb spectrometer covering the 2.6 to 5.2 µm range is demonstrated with comb-tooth resolution, sub-MHz frequency precision and accuracy, and a spectral signal-to-noise ratio as high as 6,500.
- Gabriel Ycas
- , Fabrizio R. Giorgetta
- & Nathan R. Newbury
-
-
-
Letter |
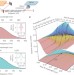 Generation and multi-octave shaping of mid-infrared intense single-cycle pulses
Generation and multi-octave shaping of mid-infrared intense single-cycle pulses
The conversion of shaped near-infrared pulses to shaped, energetic, multi-octave-spanning mid-infrared pulses lasting as little as 1.2 optical cycles is made possible by adiabatic difference frequency generation.
- Peter Krogen
- , Haim Suchowski
- & Jeffrey Moses
-
Article |
 Optical microresonators as single-particle absorption spectrometers
Optical microresonators as single-particle absorption spectrometers
Single-particle double-modulation absorption spectrometers based on whispering-gallery-mode microresonators achieve sub-100-Hz sensitivity to photothermal resonance shifts and allow for the study of arrays of Fano resonances in the context of plasmonic–photonic hybridization.
- Kevin D. Heylman
- , Niket Thakkar
- & Randall H. Goldsmith
-
-
Article |
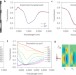 Ultrafast switching of tunable infrared plasmons in indium tin oxide nanorod arrays with large absolute amplitude
Ultrafast switching of tunable infrared plasmons in indium tin oxide nanorod arrays with large absolute amplitude
Ultrafast plasmon modulation has been realized in the near- to mid-infrared range by intraband pumping of indium tin oxide nanorod arrays.
- Peijun Guo
- , Richard D. Schaller
- & Robert P. H. Chang
-
Letter |
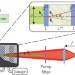 Infrared spectroscopy with visible light
Infrared spectroscopy with visible light
The refractive index and absorption coefficient of a medium in the infrared range are measured using visible spectral range components. The technique relies on nonlinear interference of infrared and visible photons, produced by down-conversion.
- Dmitry A. Kalashnikov
- , Anna V. Paterova
- & Leonid A. Krivitsky
-
Letter |
 High-power sub-two-cycle mid-infrared pulses at 100 MHz repetition rate
High-power sub-two-cycle mid-infrared pulses at 100 MHz repetition rate
A compact source that generates sub-two-cycle-duration pulses with an average power of 0.1 W spanning 6.8–16.4 μm combines the properties of power scalability, high repetition rate and phase coherence for the first time in this spectral region.
- I. Pupeza
- , D. Sánchez
- & J. Biegert
-
Article |
 Quantum cascade laser frequency stabilization at the sub-Hz level
Quantum cascade laser frequency stabilization at the sub-Hz level
A 10 μm quantum cascade laser is phase-locked to a remote ultrastable laser referenced to primary frequency standards using an optical frequency comb. The obtained relative stability of 2 × 10−15 is record-breaking in the mid-infrared region.
- Bérengère Argence
- , Bruno Chanteau
- & Anne Amy-Klein
-
News & Views |
 Entering the mid-infrared
Entering the mid-infrared
The demonstration of chalcogenide fibre-based supercontinuum sources that reach beyond a wavelength of ten micrometres is set to have a major impact on spectroscopy and molecular sensing.
- Günter Steinmeyer
- & Julia S. Skibina
-
Letter |
 Ultrafast multi-terahertz nano-spectroscopy with sub-cycle temporal resolution
Ultrafast multi-terahertz nano-spectroscopy with sub-cycle temporal resolution
The authors demonstrate ultrabroadband time-resolved THz spectroscopy on a single InAs nanowire with 10 nm spatial resolution and sub-100 fs time resolution.
- M. Eisele
- , T. L. Cocker
- & R. Huber
-
-
-
Letter |
 Tip-enhanced infrared nanospectroscopy via molecular expansion force detection
Tip-enhanced infrared nanospectroscopy via molecular expansion force detection
Mid-infrared spectroscopy with nanometre spatial resolution is highly desired for materials and life sciences applications. A nanoscale mid-infrared spectrometer is demonstrated that detects mechanical forces exerted by molecules on an atomic force microscope tip upon light excitation. It operates under ambient conditions with a high sensitivity and a spatial resolution of better than 25 nm.
- Feng Lu
- , Mingzhou Jin
- & Mikhail A. Belkin
-

 Metasurfaces for edge encoding with incoherent light
Metasurfaces for edge encoding with incoherent light Turning night into day
Turning night into day Dense comb on a chip
Dense comb on a chip Chip-based thermal emitter
Chip-based thermal emitter Tunable spectrometer
Tunable spectrometer