Featured
-
-
All Minerals Considered |
 Quartz for all time
Quartz for all time
From the tools of Stone Age ancestors to records of Earth’s history, Yang Li and Xian-Hua Li explore how the properties of quartz place it at the heart of human innovation.
- Yang Li
- & Xian-Hua Li
-
Perspective |
 Formation of necromass-derived soil organic carbon determined by microbial death pathways
Formation of necromass-derived soil organic carbon determined by microbial death pathways
Microbial death pathways affect the quantity and composition of microbial necromass and its associated soil organic carbon.
- Tessa Camenzind
- , Kyle Mason-Jones
- & Johannes Lehmann
-
Article |
 Formation of manganese oxides on early Mars due to active halogen cycling
Formation of manganese oxides on early Mars due to active halogen cycling
Manganese oxidation experiments in Mars-like fluids suggest that chlorate and bromate may have been more effective oxidants of manganese on early Mars than atmospheric oxygen and explain observed manganese oxide deposits.
- Kaushik Mitra
- , Eleanor L. Moreland
- & Jeffrey G. Catalano
-
News & Views |
 Abiotic path of Archean nitrogen
Abiotic path of Archean nitrogen
Mediation by iron minerals in the non-biological production of nitrous and nitric oxides may have driven the nitrogen cycle in the Archean ocean. This system may also have shaped the function and composition of the early marine ecosystem.
- Manabu Nishizawa
-
Article |
 Formation of oxidized sulfur-rich magmas in Neoarchaean subduction zones
Formation of oxidized sulfur-rich magmas in Neoarchaean subduction zones
Neoarchaean arc magmas in Superior Province, Canada, were relatively oxidized and sulfur rich, reaching compositions comparable to modern subduction zones by approximately 2.7 Ga, according to analysis of sulfur speciation in zircon-hosted apatite grains.
- Xuyang Meng
- , Adam C. Simon
- & Jeremy P. Richards
-
Perspective |
 Diverse geochemical conditions for prebiotic chemistry in shallow-sea alkaline hydrothermal vents
Diverse geochemical conditions for prebiotic chemistry in shallow-sea alkaline hydrothermal vents
The spatial and temporal geochemical variability of alkaline hydrothermal systems in shallow waters could support prebiotic chemical reactions required for the emergence of life.
- Laura M. Barge
- & Roy E. Price
-
Q&A |
 Digging into deep water
Digging into deep water
Nature Geoscience spoke with Dr Qingyang Hu, a high-pressure mineralogist at HPSTAR; Prof. Suzan van der Lee, a geophysicist at Northwestern University; and Prof. Katherine Kelley, a geochemist at the University of Rhode Island about their work and what the future of deep-water research might bring.
- Rebecca Neely
-
Editorial |
 Deep Earth bound by water
Deep Earth bound by water
Research efforts from across the geosciences are uncovering how water deep within the Earth affects its fundamental workings.
-
-
All Minerals Considered |
 Cycles of serpentines
Cycles of serpentines
Jörg Hermann suggests that as the process of serpentinization leads to clean energy generation, metal separation and carbon sequestration, it could serve as a natural analogue for a sequential economy.
- Jörg Hermann
-
Article |
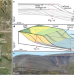 High rates of organic carbon burial in submarine deltas maintained on geological timescales
High rates of organic carbon burial in submarine deltas maintained on geological timescales
Organic carbon burial rates in an Upper Cretaceous river delta are similar to those in modern deltas, suggesting that high burial rates can persist over geological timescales in these common settings, according to stratigraphic and geochemical analysis of exhumed delta sediments.
- Sophie Hage
- , Brian W. Romans
- & Stephen M. Hubbard
-
Editorial |
 Minerals matter
Minerals matter
Permeating every aspect of life – and each with a multitude of stories to tell – we celebrate the utility, beauty and wonder of minerals in a new column: all minerals considered.
-
Perspective |
 Orange hydrogen is the new green
Orange hydrogen is the new green
Enhancing natural subsurface hydrogen production through water injection could make a substantial contribution to achieving the low-carbon energy transition that is required to limit global warming.
- F. Osselin
- , C. Soulaine
- & M. Pichavant
-
All Minerals Considered |
 An apatite for kidney stones
An apatite for kidney stones
Bruce Fouke explores the biomineralization of calcium oxalate and apatite kidney stones and the opportunities that lie at the intersection of geology, biology and medicine; a transdisciplinary effort traced back some 350 years.
- Bruce W. Fouke
-
News & Views |
 Plant fingerprints in the deep Earth
Plant fingerprints in the deep Earth
The colonization of Earth landmasses by vascular plants around 430 million years ago substantially impacted erosion and sediment transport mechanisms. This left behind fingerprints in magmatic rocks, linking the evolution of Earth’s biosphere with its internal processes.
- Nicolas D. Greber
-
Article |
 Composition of continental crust altered by the emergence of land plants
Composition of continental crust altered by the emergence of land plants
Colonization of continents by plants some 430 Myr ago enhanced the complexity of weathering and sedimentary systems, and altered the composition of continental crust, according to statistical assessment of zircon compositions.
- Christopher J. Spencer
- , Neil S. Davies
- & Gui-Mei Lu
-
Article |
 Astronomically controlled aridity in the Sahara since at least 11 million years ago
Astronomically controlled aridity in the Sahara since at least 11 million years ago
Pulses of Saharan dust have been entering the North Atlantic since at least 11 Ma, a result of astronomically paced cycles between arid and humid conditions in northern Africa, according to a terrigenous input record from an ocean core off west Africa.
- Anya J. Crocker
- , B. David A. Naafs
- & Paul A. Wilson
-
Article |
 Transient mobilization of subcrustal carbon coincident with Palaeocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum
Transient mobilization of subcrustal carbon coincident with Palaeocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum
A change in the style of rifting in the North Atlantic led to carbon fluxes from subcrustal melting that helped trigger the Palaeocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum, according to geochemical analyses of volcanic sequences as well as melting and tectonic modelling.
- Thomas M. Gernon
- , Ryan Barr
- & Martin R. Palmer
-
Article |
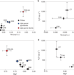 High water content of arc magmas recorded in cumulates from subduction zone lower crust
High water content of arc magmas recorded in cumulates from subduction zone lower crust
The water content of arc magmas in the lower crust can reach up to 20 wt% during crystallization, according to geochemical analyses of minerals from the Kohistan palaeo-arc, Pakistan, underscoring the role of water in porphyry deposits formation.
- B. M. Urann
- , V. Le Roux
- & E. J. Chin
-
Article |
 Thermochemical structure and evolution of cratonic lithosphere in central and southern Africa
Thermochemical structure and evolution of cratonic lithosphere in central and southern Africa
Cratons in central and southern Africa exhibit diverse structures, compositions and responses to geodynamic settings, according to a high-resolution thermochemical regional model constructed from land- and satellite-based geophysical observations.
- Juan C. Afonso
- , Walid Ben-Mansour
- & Yingjie Yang
-
Article |
 Sea-level stability over geological time owing to limited deep subduction of hydrated mantle
Sea-level stability over geological time owing to limited deep subduction of hydrated mantle
Accounting for experimental data on hydrous peridotites reduces the estimated water recycled into the deep mantle during subduction and suggests sea-level stability over geological time, according to subduction zone thermopetrological modelling.
- N. G. Cerpa
- , D. Arcay
- & J. A. Padrón-Navarta
-
Article |
 Fluocerite as a precursor to rare earth element fractionation in ore-forming systems
Fluocerite as a precursor to rare earth element fractionation in ore-forming systems
Experiments under simulated hydrothermal conditions suggest that the mineral fluocerite may serve as an intermediate phase that fractionates the rare earth elements in ore-forming systems.
- Andrew C. Strzelecki
- , Artas Migdisov
- & Xiaofeng Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Slab-derived devolatilization fluids oxidized by subducted metasedimentary rocks
Slab-derived devolatilization fluids oxidized by subducted metasedimentary rocks
Metasedimentary rocks atop the downgoing slab oxidize ascending slab-derived dehydration fluids by removing reduced species, according to petrological analysis of subduction complex metasedimentary rocks and reactive transport modelling.
- Jay J. Ague
- , Santiago Tassara
- & Timm John
-
Article |
 Earth’s Great Oxidation Event facilitated by the rise of sedimentary phosphorus recycling
Earth’s Great Oxidation Event facilitated by the rise of sedimentary phosphorus recycling
Recycling of sedimentary phosphorus driven by increasing oceanic sulfide availability contributed to the persistent oxygenation of Earth’s atmosphere, according to analysis of Archean drill-core samples and biogeochemical modelling
- Lewis J. Alcott
- , Benjamin J. W. Mills
- & Simon W. Poulton
-
Article |
 Emergence of felsic crust and subaerial weathering recorded in Palaeoarchaean barite
Emergence of felsic crust and subaerial weathering recorded in Palaeoarchaean barite
Chemical weathering of subaerial felsic crust modified the composition of Palaeoarchaean seawater, suggesting possible Eoarchaean crustal emergence, according to the radiogenic strontium isotope composition of 3.5–3.2 Ga barite deposits.
- Desiree L. Roerdink
- , Yuval Ronen
- & Paul R. D. Mason
-
Article |
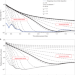 A nitrogen-rich atmosphere on ancient Mars consistent with isotopic evolution models
A nitrogen-rich atmosphere on ancient Mars consistent with isotopic evolution models
The isotopic composition of nitrogen in the Martian atmosphere can be explained by a nitrogen-rich ancient atmosphere, according to models of atmospheric evolution.
- Renyu Hu
- & Trent B. Thomas
-
News & Views |
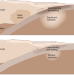 Top-down control on water subduction
Top-down control on water subduction
The structure of the overriding plate may control bending and water ingress into the subducting plate based on an exceptional 3D velocity model of the Nankai subduction zone.
- Donna J. Shillington
-
Article |
 Earth’s missing argon paradox resolved by recycling of oceanic crust
Earth’s missing argon paradox resolved by recycling of oceanic crust
Oceanic crust subduction sequesters substantial amounts of argon in the Earth’s mantle, while atmosphere-derived argon affects only the isotopic composition and not the overall budget, according to geodynamic–geochemical models of mantle convection.
- Jonathan M. Tucker
- , Peter E. van Keken
- & Chris J. Ballentine
-
Article |
 Lunar compositional asymmetry explained by mantle overturn following the South Pole–Aitken impact
Lunar compositional asymmetry explained by mantle overturn following the South Pole–Aitken impact
The compositional asymmetry between the Moon’s near- and farsides can be explained as the result of impact-induced mantle convection and gravitational instability, according to numerical modelling of the South Pole–Aitken impact and the ensuing mantle evolution.
- Nan Zhang
- , Min Ding
- & Zongyu Yue
-
News & Views |
 Sulfur evaporation in planetesimals
Sulfur evaporation in planetesimals
Evaporative loss of sulfur from molten planetesimals can explain the sub-chondritic sulfur isotope composition of the bulk silicate mantle, suggesting an important role for planetesimal evaporation in establishing Earth’s volatile budget.
- Yuan Li
-
Article |
 Sulfur isotopic signature of Earth established by planetesimal volatile evaporation
Sulfur isotopic signature of Earth established by planetesimal volatile evaporation
Earth’s volatile element content was established largely by volatile evaporation from molten planetesimals before Earth’s formation, according to first-principles calculations and examination of sulfur isotope fractionation.
- Wenzhong Wang
- , Chun-Hui Li
- & Shui-Jiong Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Fluvial organic carbon cycling regulated by sediment transit time and mineral protection
Fluvial organic carbon cycling regulated by sediment transit time and mineral protection
Particulate organic carbon oxidation in rivers is regulated by both transit time and mineral protection, according to modelling and analysis of organic matter transported nearly 1,300 km through a lowland river.
- Marisa Repasch
- , Joel S. Scheingross
- & Dirk Sachse
-
Article |
 Delayed and variable late Archaean atmospheric oxidation due to high collision rates on Earth
Delayed and variable late Archaean atmospheric oxidation due to high collision rates on Earth
The oxygenation of Earth may have been delayed due to high late Archaean extraterrestrial impact rates, which acted as a fluctuating sink of atmospheric oxygen, according to a reassessment of past impactor fluxes and atmospheric chemistry modelling.
- S. Marchi
- , N. Drabon
- & T. Lyons
-
Matters Arising |
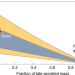 No 182W evidence for early Moon formation
No 182W evidence for early Moon formation
- Thomas S. Kruijer
- , Gregory J. Archer
- & Thorsten Kleine
-
Matters Arising |
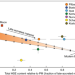 Reply to: No 182W evidence for early Moon formation
Reply to: No 182W evidence for early Moon formation
- Maxwell Marzban Thiemens
- , Jonas Tusch
- & Carsten Münker
-
Article |
 Temperature control on CO2 emissions from the weathering of sedimentary rocks
Temperature control on CO2 emissions from the weathering of sedimentary rocks
The release of carbon dioxide during oxidative weathering of sedimentary rocks acts as a positive feedback to warming, according to 2.5 years of CO2 flux measurements from the Draix-Bléone Critical Zone Observatory, France.
- Guillaume Soulet
- , Robert G. Hilton
- & Caroline Le Bouteiller
-
Article |
 Global chemical weathering dominated by continental arcs since the mid-Palaeozoic
Global chemical weathering dominated by continental arcs since the mid-Palaeozoic
Earth’s surface temperature is stabilized by the drawdown of CO2 owing to weathering of continental arcs, whose length is shown to be a primary control on global weathering fluxes, according to a probabilistic analysis of interdependencies.
- Thomas M. Gernon
- , Thea K. Hincks
- & R. Dietmar Müller
-
Article |
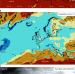 Muted multidecadal climate variability in central Europe during cold stadial periods
Muted multidecadal climate variability in central Europe during cold stadial periods
Central European multidecadal climate variability was subdued during cold stadials through the last glacial cycle due to atmospheric and oceanic circulation shifts, according to almost annual-resolution terrestrial climate proxy records from varved maar lakes in Germany.
- Frank Sirocko
- , Alfredo Martínez-García
- & Gerald H. Haug
-
Article |
 Oceanic transform fault seismicity and slip mode influenced by seawater infiltration
Oceanic transform fault seismicity and slip mode influenced by seawater infiltration
Seawater infiltration into oceanic transform faults may control their seismicity extent and slip mode variations, according to numerical models of the mechanical and thermal structure of these faults that account for hydration effects.
- Arjun Kohli
- , Monica Wolfson-Schwehr
- & Jessica M. Warren
-
Article |
 Carbon concentration increases with depth of melting in Earth’s upper mantle
Carbon concentration increases with depth of melting in Earth’s upper mantle
The carbon concentration of Earth’s upper mantle increases with depth, indicating a role for carbon in melt formation, according to data on magmatic gases and volcanic rocks from ocean island and continental rift settings around the world.
- Alessandro Aiuppa
- , Federico Casetta
- & Giancarlo Tamburello
-
Article |
 Eocene to Oligocene terrestrial Southern Hemisphere cooling caused by declining pCO2
Eocene to Oligocene terrestrial Southern Hemisphere cooling caused by declining pCO2
Terrestrial Southern Hemisphere cooling through the Eocene–Oligocene transition points to decreasing atmospheric CO2 dominantly driving global change, according to biomarker records from southeast Australian coals and palaeoclimate modelling.
- Vittoria Lauretano
- , Alan T. Kennedy-Asser
- & B. David A. Naafs
-
Article
| Open Access Possible link between Earth’s rotation rate and oxygenation
Possible link between Earth’s rotation rate and oxygenation
Rotational deceleration has increased daylength on Earth, potentially linking the increased burial of organic carbon by cyanobacterial mats and planetary oxygenation, according to experiments and modelling of Precambrian benthic ecosystems.
- J. M. Klatt
- , A. Chennu
- & G. J. Dick
-
Article |
 Rapid recycling of subducted sedimentary carbon revealed by Afghanistan carbonatite volcano
Rapid recycling of subducted sedimentary carbon revealed by Afghanistan carbonatite volcano
Sedimentary carbon is subducted to, and returned from, mantle depths in less than 27 million years, according strontium isotope analysis and geochronology of lavas from southern Afghanistan.
- Forrest Horton
-
Article |
 Dry metastable olivine and slab deformation in a wet subducting slab
Dry metastable olivine and slab deformation in a wet subducting slab
Transformation kinetics of olivine may be a cause of deep-focus earthquakes even in wet slabs, according to water-partitioning experiments, which show that olivine remains relatively dry even under wet subducting slab conditions.
- Takayuki Ishii
- & Eiji Ohtani
-
Article
| Open Access Large subglacial source of mercury from the southwestern margin of the Greenland Ice Sheet
Large subglacial source of mercury from the southwestern margin of the Greenland Ice Sheet
Meltwaters from the southwestern margin of the Greenland Ice Sheet contain exceptionally high concentrations of mercury, exporting up to more than 200 kmol of dissolved mercury every year, suggest mercury measurements from three glacial catchments.
- Jon R. Hawkings
- , Benjamin S. Linhoff
- & Robert G. M. Spencer
-
Article |
 Microbial methylation potential of mercury sulfide particles dictated by surface structure
Microbial methylation potential of mercury sulfide particles dictated by surface structure
The environmental behaviour of mercury and other toxic soft elements is in part dictated by the surface structure of nanoparticulates, according to a combination of microcosm bioassays and theoretical calculations.
- Li Tian
- , Wenyu Guan
- & Tong Zhang
-
Article |
 Bedrock weathering contributes to subsurface reactive nitrogen and nitrous oxide emissions
Bedrock weathering contributes to subsurface reactive nitrogen and nitrous oxide emissions
Weathering of deep bedrock releases reactive nitrogen into the subsurface, which contributes to the flux of nitrous oxide to the atmosphere, according to a field study that combines soil, rock and groundwater data within a river catchment.
- Jiamin Wan
- , Tetsu K. Tokunaga
- & Kenneth H. Williams
-
Article |
 Heinrich Stadial aridity forced Mediterranean-wide glacier retreat in the last cold stage
Heinrich Stadial aridity forced Mediterranean-wide glacier retreat in the last cold stage
Mountain glacier growth around the Mediterranean repeatedly stalled during cold, dry Heinrich Stadials, according to an analysis of cosmogenic isotope-dated glacial landforms from across the region.
- James L. Allard
- , Philip D. Hughes
- & Jamie C. Woodward
-
News & Views |
 Intermittent warmth on young Mars
Intermittent warmth on young Mars
Warm and wet conditions could have episodically punctuated a generally cold early climate on Mars, according to a multidisciplinary modelling approach that potentially solves a five-decade long debate regarding warm conditions on early Mars.
- Nicolas Mangold

 Decadal warming events extended into central North America during the last glacial period
Decadal warming events extended into central North America during the last glacial period Look between the grains
Look between the grains