Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Sequence and entropy-based control of complex coacervates
Sequence and entropy-based control of complex coacervates
Monomer sequence is an emerging tool to precisely encode information (and thus structure and function) into polymer systems. Here the authors use sequence-control in complex coacervates to understand how monomer sequence translates to physical material properties.
- Li-Wei Chang
- , Tyler K. Lytle
- & Sarah L. Perry
-
Article
| Open Access Multifunctional nanocomposite hollow fiber membranes by solvent transfer induced phase separation
Multifunctional nanocomposite hollow fiber membranes by solvent transfer induced phase separation
Coating porous membranes with nanoparticles can enhance their separation and antifouling properties, but methods to do so remain complex. Here, Lee and colleagues use solvent transfer-induced phase separation to prepare nanoparticle-functionalized hollow fiber membranes from bicontinuous interfacially jammed emulsion gels.
- Martin F. Haase
- , Harim Jeon
- & Daeyeon Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular rheotaxis directs DNA migration and concentration against a pressure-driven flow
Molecular rheotaxis directs DNA migration and concentration against a pressure-driven flow
Implementing a nucleic acid preconcentration method can improve the sensitivity of microfluidic analysis systems. Here Friedrich et al. concentrate DNA by many orders of magnitude using pressure-driven flow, which could lead to a simple and practical microanalysis platform.
- Sarah M. Friedrich
- , Jeffrey M. Burke
- & Tza-Huei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Fully inkjet-printed two-dimensional material field-effect heterojunctions for wearable and textile electronics
Fully inkjet-printed two-dimensional material field-effect heterojunctions for wearable and textile electronics
Heterojunction structures based on 2D materials show promise for wearable and textile electronics. Here, the authors demonstrate fully inkjet-printed hetero junctions of graphene and h-BN as a platform for FET-based smart electronics on wearable and washable textile substrates.
- Tian Carey
- , Stefania Cacovich
- & Felice Torrisi
-
Article
| Open Access Large-scale water collection of bioinspired cavity-microfibers
Large-scale water collection of bioinspired cavity-microfibers
Spider-silk-mimicking microfibers often suffer from low efficiency and durability in water collection. Here, the authors fabricate robust microfibers with spindle cavity-knots and different topological fiber-networks with improved water-collecting performance
- Ye Tian
- , Pingan Zhu
- & Liqiu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access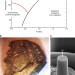 Superelasticity and cryogenic linear shape memory effects of CaFe2As2
Superelasticity and cryogenic linear shape memory effects of CaFe2As2
Shape memory materials are capable of returning to their original form post-deformation, but those with high actuation performances remain scarce. Here the authors reveal that CaFe2As2 exhibits cryogenic linear shape memory behaviour with high recoverable strain and yield strength, owing to a reversible uni-axial phase transformation.
- John T. Sypek
- , Hang Yu
- & Seok-Woo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Bidirectional wavelength-division multiplexing transmission over installed fibre using a simplified optical coherent access transceiver
Bidirectional wavelength-division multiplexing transmission over installed fibre using a simplified optical coherent access transceiver
The signalling scheme used in access networks require electrical bandwidths many times greater than subscribers can utilise. Here, the authors describe a promising approach to achieve bidirectional transmission with bandwidth-efficient yet low-complexity coherent optical network unit transceiver.
- M. S. Erkılınç
- , D. Lavery
- & P. Bayvel
-
Article
| Open Access Origami-based tunable truss structures for non-volatile mechanical memory operation
Origami-based tunable truss structures for non-volatile mechanical memory operation
Origami is a popular method to design building blocks for mechanical metamaterials. Here, the authors assemble a volumetric origami-based structure, predict its axial and rotational movements during folding, and demonstrate the operation of mechanical one- and two-bit memory storage.
- Hiromi Yasuda
- , Tomohiro Tachi
- & Jinkyu Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Inverse poroelasticity as a fundamental mechanism in biomechanics and mechanobiology
Inverse poroelasticity as a fundamental mechanism in biomechanics and mechanobiology
How soft tissues respond to mechanical load is essential to their biological function. Here, the authors discover that – contrary to predictions of poroelasticity – fluid mobility in collagenous tissues induces drastic volume decrease with tensile loading and pronounced chemo-mechanical coupling.
- Alexander E. Ehret
- , Kevin Bircher
- & Edoardo Mazza
-
Article
| Open Access A novel true random number generator based on a stochastic diffusive memristor
A novel true random number generator based on a stochastic diffusive memristor
Memristors can switch between high and low electrical-resistance states, but the switching behaviour can be unpredictable. Here, the authors harness this unpredictability to develop a memristor-based true random number generator that uses the stochastic delay time of threshold switching
- Hao Jiang
- , Daniel Belkin
- & Qiangfei Xia
-
Article
| Open Access Synchronized conductivity modulation to realize broadband lossless magnetic-free non-reciprocity
Synchronized conductivity modulation to realize broadband lossless magnetic-free non-reciprocity
Optical non-reciprocity achieved through refractive index modulation can have its challenges and limitations. Here, Dinc et al. introduce the concept of non-reciprocity based on synchronized spatio-temporal modulation of conductivity to achieve different types of non-reciprocal functionality.
- Tolga Dinc
- , Mykhailo Tymchenko
- & Harish Krishnaswamy
-
Article
| Open Access Neutrophil-inspired propulsion in a combined acoustic and magnetic field
Neutrophil-inspired propulsion in a combined acoustic and magnetic field
Devising effective swimming and propulsion strategies in microenvironments is attractive for drug delivery applications. Here Ahmed et al. demonstrate a micropropulsion strategy in which a combination of magnetic and acoustic fields is used to assemble and propel colloidal particles along channel walls.
- Daniel Ahmed
- , Thierry Baasch
- & Bradley J. Nelson
-
Article
| Open Access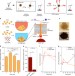 Synthetic microparticles conjugated with VEGF165 improve the survival of endothelial progenitor cells via microRNA-17 inhibition
Synthetic microparticles conjugated with VEGF165 improve the survival of endothelial progenitor cells via microRNA-17 inhibition
Soluble vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) enhances vascular engraftment of transplanted cells but the efficacy is low. Here, the authors show that VEGF-immobilized microparticles prolong survival of endothelial progenitors in vitro and in vivo by downregulating miR17 and upregulating CDKN1A and ZNF652.
- Sezin Aday
- , Janet Zoldan
- & Lino Ferreira
-
Article
| Open Access Frequency-division multiplexer and demultiplexer for terahertz wireless links
Frequency-division multiplexer and demultiplexer for terahertz wireless links
There is growing interest in the development of components to facilitate wireless communications in the terahertz but the characterization of these systems involve an unmodulated input. Here the authors demonstrate multiplexing and demultiplexing of data streams in the terahertz range using a real data link.
- Jianjun Ma
- , Nicholas J. Karl
- & Daniel M. Mittleman
-
Article
| Open Access Organic flash memory on various flexible substrates for foldable and disposable electronics
Organic flash memory on various flexible substrates for foldable and disposable electronics
Flexible flash memory is crucial to modern electronics, but its fabrication is challenging in the absence of suitable dielectric materials. Here, Lee et al. realize organic memory with retention over 10 years using tunneling and blocking dielectric layers prepared by initiated chemical vapor deposition.
- Seungwon Lee
- , Hyejeong Seong
- & Seunghyup Yoo
-
Article
| Open Access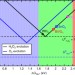 Understanding activity trends in electrochemical water oxidation to form hydrogen peroxide
Understanding activity trends in electrochemical water oxidation to form hydrogen peroxide
Producing hydrogen peroxide via electrochemical oxidation of water is an attractive route to this valuable product. Here the authors theoretically and experimentally investigate hydrogen peroxide production activity trends for a range of metal oxides and identify the optimal bias ranges for high Faraday efficiencies.
- Xinjian Shi
- , Samira Siahrostami
- & Jens K. Nørskov
-
Article
| Open Access Targeted gadofullerene for sensitive magnetic resonance imaging and risk-stratification of breast cancer
Targeted gadofullerene for sensitive magnetic resonance imaging and risk-stratification of breast cancer
Molecular MRI is a powerful clinical tool for non-invasive detection of cancer biomarkers. Here, the authors develop a targeted peptide gadofullerene contrast agent that can sensitively distinguish between breast cancers of different aggressiveness.
- Zheng Han
- , Xiaohui Wu
- & Zheng-Rong Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Physical origins of current and temperature controlled negative differential resistances in NbO2
Physical origins of current and temperature controlled negative differential resistances in NbO2
The development of future computation devices will be aided by a better understanding of the physics underlying material behaviors. Using thermoreflectance and spatially resolved X-ray microscopy, Kumar et al. elucidate the origin of two types of negative differential resistance in NbO2 memristors.
- Suhas Kumar
- , Ziwen Wang
- & R. Stanley Williams
-
Article
| Open Access Heterogeneous multi-compartmental hydrogel particles as synthetic cells for incompatible tandem reactions
Heterogeneous multi-compartmental hydrogel particles as synthetic cells for incompatible tandem reactions
Cells contain isolated compartments where cascade enzymatic biochemical reactions occur to form essential biological products with high efficiency. Here the authors produce functional hydrogel particles with multiple compartments via microfluidics that contain spatially immobilized natural enzymes in distinct domains for one-pot, tandem reactions.
- Hongliang Tan
- , Song Guo
- & Chia-Hung Chen
-
Article
| Open Access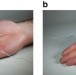 Soft material for soft actuators
Soft material for soft actuators
The development of self-contained electrically driven soft actuators with high strain density is difficult. Here the authors show a single self-contained soft robust composite material that combines the elastic properties of a polymeric matrix and the extreme volume change accompanying liquid vapour transition.
- Aslan Miriyev
- , Kenneth Stack
- & Hod Lipson
-
Article
| Open Access Mergeable nervous systems for robots
Mergeable nervous systems for robots
Robots that can self-assemble into different morphologies are desired to perform tasks that require different physical capabilities. Mathews et al. design robots whose bodies and control systems can merge and split to form new robots that retain full sensorimotor control and act as a single entity.
- Nithin Mathews
- , Anders Lyhne Christensen
- & Marco Dorigo
-
Article
| Open Access 3D calcite heterostructures for dynamic and deformable mineralized matrices
3D calcite heterostructures for dynamic and deformable mineralized matrices
Minerals are rarely explored as building blocks for dynamic inorganic materials. Here, the authors derive inspiration from fish scales to create mutable surfaces based on arrays of calcite crystals, in which one end of each crystal is immobilized in and regenerated from silicone, and the other functional end is left exposed.
- Jaeseok Yi
- , Yucai Wang
- & Bozhi Tian
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo quantitative imaging of tumor pH by nanosonophore assisted multispectral photoacoustic imaging
In vivo quantitative imaging of tumor pH by nanosonophore assisted multispectral photoacoustic imaging
Background optical absorption of several biomolecules impedes an effective in vivo pH imaging in tumors. Here, the authors developed a visible light-based in vivo pH mapping method by coupling photoacoustic imaging and pH-responsive modified nanoparticles that selectively target tumor cells.
- Janggun Jo
- , Chang H. Lee
- & Xueding Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Reactivation of dead sulfide species in lithium polysulfide flow battery for grid scale energy storage
Reactivation of dead sulfide species in lithium polysulfide flow battery for grid scale energy storage
Lithium polysulfide batteries suffer from the precipitation of insoluble and irreversible sulfide species on the surface of carbon and lithium. Here the authors show a reactivation strategy by a reaction with cheap sulfur powder under stirring and heating to recover the cell capacity.
- Yang Jin
- , Guangmin Zhou
- & Yi Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrathin metal–organic framework membrane production by gel–vapour deposition
Ultrathin metal–organic framework membrane production by gel–vapour deposition
MOF-based membranes have shown great promise in separation applications, but producing thin membranes that allow for high fluxes remains challenging. Here, the authors use a gel–vapour deposition strategy to fabricate composite membranes with less than 20 nm thicknesses and high gas permeances and selectivities.
- Wanbin Li
- , Pengcheng Su
- & Eddy Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Conformal metasurface-coated dielectric waveguides for highly confined broadband optical activity with simultaneous low-visibility and reduced crosstalk
Conformal metasurface-coated dielectric waveguides for highly confined broadband optical activity with simultaneous low-visibility and reduced crosstalk
Controlling all the optical properties of dielectric waveguides is a challenging task and often requires complicated core- and cladding designs. Here, Jiang et al. demonstrate that a thin metasurface coating can control several optical properties simultaneously over a broad frequency range.
- Zhi Hao Jiang
- , Lei Kang
- & Douglas H. Werner
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-large single crystals by abnormal grain growth
Ultra-large single crystals by abnormal grain growth
Growing large single crystals cheaply and reliably for structural applications remains challenging. Here, the authors combine accelerated abnormal grain growth and cyclic heat treatments to grow a superelastic shape memory alloy single crystal to 70 cm.
- Tomoe Kusama
- , Toshihiro Omori
- & Ryosuke Kainuma
-
Article
| Open Access Acoustically actuated ultra-compact NEMS magnetoelectric antennas
Acoustically actuated ultra-compact NEMS magnetoelectric antennas
The miniaturization of antennas beyond a wavelength is limited by designs which rely on electromagnetic resonances. Here, Nan et al. have developed acoustically actuated antennas that couple the acoustic resonance of the antenna with the electromagnetic wave, reducing the antenna footprint by up to 100.
- Tianxiang Nan
- , Hwaider Lin
- & Nian Xiang Sun
-
Correspondence
| Open Access Correspondence: The experimental requirements for a photon thermal diode
Correspondence: The experimental requirements for a photon thermal diode
- Bair V. Budaev
-
Correspondence
| Open Access Correspondence: Reply to ‘The experimental requirements for a photon thermal diode’
Correspondence: Reply to ‘The experimental requirements for a photon thermal diode’
- Zhen Chen
- , Carlaton Wong
- & Chris Dames
-
Article
| Open Access Electromagnetic reprogrammable coding-metasurface holograms
Electromagnetic reprogrammable coding-metasurface holograms
Realizing metasurfaces with reconfigurability, high efficiency, and control over phase and amplitude is a challenge. Here, Li et al. introduce a reprogrammable hologram based on a 1-bit coding metasurface, where the state of each unit cell of the coding metasurface can be switched electrically.
- Lianlin Li
- , Tie Jun Cui
- & Shuang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Inverted battery design as ion generator for interfacing with biosystems
Inverted battery design as ion generator for interfacing with biosystems
At the molecular level, biological activities involve the transport of ions in a system. Here the authors demonstrate an ‘electron battery’ by inverting the configuration of a traditional Li-ion battery to generate an ionic current to interact with a biosystem for potential biomedical applications.
- Chengwei Wang
- , Kun (Kelvin) Fu
- & Liangbing Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Physical limits to biomechanical sensing in disordered fibre networks
Physical limits to biomechanical sensing in disordered fibre networks
Cells in the connective tissue are surrounded by a heterogeneous network of biopolymers. Here, the authors investigate how such heterogeneity affects cellular mechanosensing by simulating the deformation response of experimental and modelled biopolymer networks to locally applied forces.
- Farzan Beroz
- , Louise M. Jawerth
- & Ned S. Wingreen
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic-template-directed multiscale assembly for large-area coating of highly-aligned conjugated polymer thin films
Dynamic-template-directed multiscale assembly for large-area coating of highly-aligned conjugated polymer thin films
Controlling macromolecular assembly across length scales during solution coating of semiconducting polymers is still a challenge. Here the authors show a biomineralization inspired dynamic templating method that expedites polymer nucleation and assembly which allows for surface reconfiguration.
- Erfan Mohammadi
- , Chuankai Zhao
- & Ying Diao
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding extreme sea levels for broad-scale coastal impact and adaptation analysis
Understanding extreme sea levels for broad-scale coastal impact and adaptation analysis
Uncertainties in contemporary extreme sea levels (ESL) from mean sea level rise (SLR) projections have been overlooked in broad-scale risk and adaptation studies. Here, the authors quantify the uncertainties in present-day global ESL estimates and find that they exceed those from global SLR projections.
- T. Wahl
- , I. D. Haigh
- & A. B. A. Slangen
-
Article
| Open Access Rewritable ghost floating gates by tunnelling triboelectrification for two-dimensional electronics
Rewritable ghost floating gates by tunnelling triboelectrification for two-dimensional electronics
Once fabricated, the gates of conventional electronic devices are spatially fixed. Here, the authors introduce tunnelling triboelectrification to create, modify and destroy on-demand ghost floating gates underneath 2D materials, with the spatial resolution of an atomic force microscope.
- Seongsu Kim
- , Tae Yun Kim
- & Christian Falconi
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental evidence of Willis coupling in a one-dimensional effective material element
Experimental evidence of Willis coupling in a one-dimensional effective material element
Metamaterials enable the realization of unique material properties such as coupling between strain and momentum in a fluid—known as Willis coupling. Here, Muhlesteinet al. use homogenization theory to better understand Willis coupling in acoustic metamaterials and demonstrate the unusual material response.
- Michael B. Muhlestein
- , Caleb F. Sieck
- & Michael R. Haberman
-
Article
| Open Access Diffusion engineering of ions and charge carriers for stable efficient perovskite solar cells
Diffusion engineering of ions and charge carriers for stable efficient perovskite solar cells
Ion migration in perovskite solar cells are known to cause hysteresis and instability. Biet al., report a charge extraction layer based on graphene, fullerenes and carbon quantum dots which suppresses ion diffusion and enhances charge carrier diffusion leading to efficient devices with improved stability.
- Enbing Bi
- , Han Chen
- & Liyuan Han
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical porous carbons with layer-by-layer motif architectures from confined soft-template self-assembly in layered materials
Hierarchical porous carbons with layer-by-layer motif architectures from confined soft-template self-assembly in layered materials
2D nanomaterials are promising capacitive energy storage materials, but their tendency to restack hinders electrolyte transport. Here, Yamauchi and colleagues introduce 2D ordered mesoporous carbons in between MXene layers, and metal removal affords all-carbon porous 2D–2D heterostructures in which restacking is prevented.
- Jie Wang
- , Jing Tang
- & Yusuke Yamauchi
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum tunnelling and charge accumulation in organic ferroelectric memory diodes
Quantum tunnelling and charge accumulation in organic ferroelectric memory diodes
Organic non-volatile memories based on ferroelectric and semiconductor polymers are one of promising candidates for flexible electronics, yet the relevant device physics remains elusive. Ghittorelliet al. show that quantum tunnelling and charge accumulation govern the ferroelectric memory operation.
- Matteo Ghittorelli
- , Thomas Lenz
- & Fabrizio Torricelli
-
Article
| Open Access Temperature-regulated guest admission and release in microporous materials
Temperature-regulated guest admission and release in microporous materials
Regulating guest access and release in porous materials remains an important goal. Here, May and colleagues elucidate the mechanism by which guest admission can be temperature-regulated in typical microporous materials, and experimentally exploit this process to achieve appreciable and reversible hydrogen storage.
- Gang (Kevin) Li
- , Jin Shang
- & Eric F. May
-
Article
| Open Access Preventing tissue fibrosis by local biomaterials interfacing of specific cryptic extracellular matrix information
Preventing tissue fibrosis by local biomaterials interfacing of specific cryptic extracellular matrix information
Matrix metalloproteinase enzymes are widely known to contribute to the breakdown of tissues. Here, the authors utilise a biomaterial substrate functionalised with a laminin fragment to modulate the expression of these enzymes, subsequently controlling the integrity of tissue.
- Christine-Maria Horejs
- , Jean-Philippe St-Pierre
- & Molly M. Stevens
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic forces enable controlled drug delivery by disrupting endothelial cell-cell junctions
Magnetic forces enable controlled drug delivery by disrupting endothelial cell-cell junctions
The transportation of large molecules through the vascular endothelium presents a major challenge forin vivodrug delivery. Here, the authors demonstrate the potential of using external magnetic fields and magnetic nanoparticles to enhance the local extravasation of circulating large molecules.
- Yongzhi Qiu
- , Sheng Tong
- & Gang Bao
-
Article
| Open Access Compaction of quasi-one-dimensional elastoplastic materials
Compaction of quasi-one-dimensional elastoplastic materials
Principles underlying crumpling of one-dimensional objects may be relevant to both biomolecular processes and to design of mechanical devices. By compacting various wires under rigid confinement and modelling observed geometric features, the authors show how friction, plasticity and torsion enhance disorder and lead to a transition from coiled to folded geometries.
- M. Reza Shaebani
- , Javad Najafi
- & Mehdi Habibi
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional crossbar arrays of self-rectifying Si/SiO2/Si memristors
Three-dimensional crossbar arrays of self-rectifying Si/SiO2/Si memristors
Memristors are key structural units of complex memory and computing systems, yet most currently available memristors are based on materials that are not compatible with silicon technology. Here, the authors demonstrate a CMOS-compatible, self-rectifying memristor and arrays entirely based on p-Si/SiO2/n-Si.
- Can Li
- , Lili Han
- & Qiangfei Xia
-
Article
| Open Access Thermal annihilation of photo-induced radicals following dynamic nuclear polarization to produce transportable frozen hyperpolarized 13C-substrates
Thermal annihilation of photo-induced radicals following dynamic nuclear polarization to produce transportable frozen hyperpolarized 13C-substrates
Hyperpolarized molecules provide unique contrast for MRI but due to their short relaxation time need to be prepared shortly before injection. Here the authors report a method for eliminating the main source of relaxation and producing frozen polarized substances that can be stored and transported.
- Andrea Capozzi
- , Tian Cheng
- & Arnaud Comment
-
Article
| Open Access Hot excited state management for long-lived blue phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes
Hot excited state management for long-lived blue phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes
Large-scale commercialization of organic light-emitting diodes is impeded by the short operational lifetime of blue emitting materials. Leeet al. show a strategy to manage the energy dissipation on molecular dissociation using dopants with high triplet exciton energy that improves device stability.
- Jaesang Lee
- , Changyeong Jeong
- & Stephen R. Forrest
-
Article
| Open Access Neuromorphic device architectures with global connectivity through electrolyte gating
Neuromorphic device architectures with global connectivity through electrolyte gating
Global regulation of synaptic strengths in neural systems is known as homeoplasticity. Here, Gkoupideniset al. use an electrolyte to connect and control an array of organic electrochemical devices, in order to demonstrate behaviour that resembles homeoplasticity phenomena in the brain.
- Paschalis Gkoupidenis
- , Dimitrios A. Koutsouras
- & George G. Malliaras
-
Article
| Open Access Nanogenerator-based dual-functional and self-powered thin patch loudspeaker or microphone for flexible electronics
Nanogenerator-based dual-functional and self-powered thin patch loudspeaker or microphone for flexible electronics
Self-powered nanogenerators by harvesting energy from the environment are desirable for future portable and wearable electronics. Liet al. show the use of ferroelectret nanogenerators to build microphone or loudspeaker, which convert electrical signals to mechanical motions in a reversible manner.
- Wei Li
- , David Torres
- & Nelson Sepúlveda

 Ultra-low and ultra-broad-band nonlinear acoustic metamaterials
Ultra-low and ultra-broad-band nonlinear acoustic metamaterials