Featured
-
-
Article |
 Site-specific reactivity of stepped Pt surfaces driven by stress release
Site-specific reactivity of stepped Pt surfaces driven by stress release
Stress release at stepped platinum surfaces is shown to influence the strain experienced by atoms near the steps, resulting in effects on the catalytic activity of the whole surface.
- Guangdong Liu
- , Arthur J. Shih
- & Zhenhua Zeng
-
Article |
 Establishing reaction networks in the 16-electron sulfur reduction reaction
Establishing reaction networks in the 16-electron sulfur reduction reaction
We investigate the mechanism underlying the sulfur reduction reaction that plays a central role in high-capacity lithium sulfur batteries, highlighting the electrocatalytic approach as a promising strategy for tackling the fundamental challenges associated with these batteries.
- Rongli Liu
- , Ziyang Wei
- & Xiangfeng Duan
-
Article |
 Three-dimensional atomic structure and local chemical order of medium- and high-entropy nanoalloys
Three-dimensional atomic structure and local chemical order of medium- and high-entropy nanoalloys
Atomic electron tomography is used to determine the 3D atomic positions and chemical species of medium- and high-entropy alloy nanoparticles and quantitatively characterize the local lattice distortion, strain tensor, twin boundaries, dislocation cores and chemical short-range order.
- Saman Moniri
- , Yao Yang
- & Jianwei Miao
-
Article |
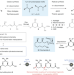 Complex molecule synthesis by electrocatalytic decarboxylative cross-coupling
Complex molecule synthesis by electrocatalytic decarboxylative cross-coupling
We report a radical-based Ni/Ag-electrocatalytic cross-coupling of substituted carboxylic acids, enabling an approach to accessing complex molecular architectures, which relies on a silver additive that forms an active Ag nanoparticle-coated electrode surface along with carefully chosen ligands.
- Benxiang Zhang
- , Jiayan He
- & Phil S. Baran
-
Article |
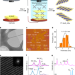 Phase-dependent growth of Pt on MoS2 for highly efficient H2 evolution
Phase-dependent growth of Pt on MoS2 for highly efficient H2 evolution
We report the production of MoS2 nanosheets with high phase purity, showing that the 2H-phase templates facilitate epitaxial growth of Pt nanoparticles, whereas the 1T′ phase supports single-atomically dispersed Pt atoms.
- Zhenyu Shi
- , Xiao Zhang
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article |
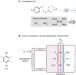 Quinone-mediated hydrogen anode for non-aqueous reductive electrosynthesis
Quinone-mediated hydrogen anode for non-aqueous reductive electrosynthesis
A quinone-mediated hydrogen anode design shows that hydrogen can be used as the electron source in non-aqueous reductive electrosynthesis, for a more sustainable way to make molecules at larger scale.
- Jack Twilton
- , Mathew R. Johnson
- & Shannon S. Stahl
-
Article |
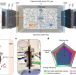 Continuous carbon capture in an electrochemical solid-electrolyte reactor
Continuous carbon capture in an electrochemical solid-electrolyte reactor
By combining O2/H2O redox electrolysis with a modular solid-electrolyte reactor, a design for continuous electrochemical carbon capture showing high capture rates, high Faradaic efficiencies and low energy consumption is demonstrated.
- Peng Zhu
- , Zhen-Yu Wu
- & Haotian Wang
-
Article |
 CO2-mediated organocatalytic chlorine evolution under industrial conditions
CO2-mediated organocatalytic chlorine evolution under industrial conditions
A study shows that an organocatalyst with an amide functional group, and carbon dioxide, can efficiently and selectively produce chlorine, potentially offering a low-cost and less energy intensive alternative to the chlor-alkali process.
- Jiarui Yang
- , Wen-Hao Li
- & Yadong Li
-
Article |
 Constrained C2 adsorbate orientation enables CO-to-acetate electroreduction
Constrained C2 adsorbate orientation enables CO-to-acetate electroreduction
A study using a copper-in-silver dilute alloy catalyst in a high-pressure gas flow reactor reports highly selective electrosynthesis of acetate from carbon monoxide.
- Jian Jin
- , Joshua Wicks
- & Yuanjie Pang
-
Article |
 Water splitting with silicon p–i–n superlattices suspended in solution
Water splitting with silicon p–i–n superlattices suspended in solution
The simplicity of particle suspension reactors and the precise synthetic control afforded by silicon nanowire growth are used to develop a system that can produce hydrogen fuel by splitting water with sunlight.
- Taylor S. Teitsworth
- , David J. Hill
- & James F. Cahoon
-
Article |
 Electrophotocatalytic oxygenation of multiple adjacent C–H bonds
Electrophotocatalytic oxygenation of multiple adjacent C–H bonds
Installation of multiple C–O bonds by concurrent oxygenation of contiguous C–H bonds in a selective fashion is highly desirable, and this is achieved by repeated operation of a potent oxidative catalyst via electrophotocatalysis.
- Tao Shen
- , Yi-Lun Li
- & Tristan H. Lambert
-
Article |
 Pivotal role of reversible NiO6 geometric conversion in oxygen evolution
Pivotal role of reversible NiO6 geometric conversion in oxygen evolution
An electron transfer mechanism that involves a light-triggered geometric conversion between metal and oxygen redox chemistry shows superior performance compared with approaches that use either metal or oxygen redox chemistry.
- Xiaopeng Wang
- , Shibo Xi
- & Junmin Xue
-
Article |
 Tandem electrocatalytic N2 fixation via proton-coupled electron transfer
Tandem electrocatalytic N2 fixation via proton-coupled electron transfer
Using a molecular catalyst and a proton–electron transfer mediator in tandem delivers efficient electroreduction of nitrogen to ammonia at modest potentials, an approach that could be used to improve other important reactions.
- Pablo Garrido-Barros
- , Joseph Derosa
- & Jonas C. Peters
-
Article |
 Floating perovskite-BiVO4 devices for scalable solar fuel production
Floating perovskite-BiVO4 devices for scalable solar fuel production
This work introduces lightweight, leaf-like photoelectrochemical devices for unassisted water splitting and syngas production, which could be used in the fabrication of floating systems for solar fuel production.
- Virgil Andrei
- , Geani M. Ucoski
- & Erwin Reisner
-
Article |
 Electroreduction of nitrogen with almost 100% current-to-ammonia efficiency
Electroreduction of nitrogen with almost 100% current-to-ammonia efficiency
A high-efficiency, robust process using a high-concentration imide-based lithium-salt electrolyte enables the electroreduction of nitrogen with stabilized ammonia yield rates of 150 ± 20 nmol s−1 cm−2 and a current-to-ammonia efficiency that is close to 100%.
- Hoang-Long Du
- , Manjunath Chatti
- & Alexandr N. Simonov
-
Article |
 Electrocatalytic metal hydride generation using CPET mediators
Electrocatalytic metal hydride generation using CPET mediators
Concerted proton–electron transfer mediators enable facile electrochemical metal hydride formation and thus improve CO2 reduction to useful chemicals, and could benefit a range of catalytic reactions involving metal hydride intermediates.
- Subal Dey
- , Fabio Masero
- & Victor Mougel
-
Article |
 Cobalt-electrocatalytic HAT for functionalization of unsaturated C–C bonds
Cobalt-electrocatalytic HAT for functionalization of unsaturated C–C bonds
A perspective is given on how an electrocatalytic approach, inspired by decades of energy storage studies, can be used in the context of efficient cobalt-hydride generation with a variety of applications in modern organic synthesis.
- Samer Gnaim
- , Adriano Bauer
- & Phil S. Baran
-
Article |
 Ni-electrocatalytic Csp3–Csp3 doubly decarboxylative coupling
Ni-electrocatalytic Csp3–Csp3 doubly decarboxylative coupling
An Ni-electrocatalytic system can couple two different carboxylates using doubly decarboxylative cross-coupling, tolerating a range of functional groups, being scalable, used for the synthesis of 32 known compounds and reducing overall step counts by 73%.
- Benxiang Zhang
- , Yang Gao
- & Phil S. Baran
-
Article |
 In situ Raman spectroscopy reveals the structure and dissociation of interfacial water
In situ Raman spectroscopy reveals the structure and dissociation of interfacial water
Interfacial water consists of hydrogen-bonded water and Na·H2O, its structure changes at hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) potentials, and when structurally ordered it aids interfacial electron transfer, resulting in higher HER rates.
- Yao-Hui Wang
- , Shisheng Zheng
- & Jian-Feng Li
-
Article |
 Mastering the surface strain of platinum catalysts for efficient electrocatalysis
Mastering the surface strain of platinum catalysts for efficient electrocatalysis
By depositing platinum shells on palladium-based nanocubes, the strain can be controlled by through phosphorization and dephosphorization, making it possible to tune the electrocatalytic activity of the platinum shells.
- Tianou He
- , Weicong Wang
- & Mingshang Jin
-
Perspective |
 Designing the next generation of proton-exchange membrane fuel cells
Designing the next generation of proton-exchange membrane fuel cells
This Perspective reviews the recent technical developments in the components of the fuel cell stack in proton-exchange membrane fuel cell vehicles and outlines the road towards large-scale commercialization of such vehicles.
- Kui Jiao
- , Jin Xuan
- & Michael D. Guiver
-
Article |
 Correlative operando microscopy of oxygen evolution electrocatalysts
Correlative operando microscopy of oxygen evolution electrocatalysts
Mapping the operational chemical, physical and electronic structure of an oxygen evolution electrocatalyst at the nanoscale links the properties of the material with the observed oxygen evolution activity.
- J. Tyler Mefford
- , Andrew R. Akbashev
- & William C. Chueh
-
Article |
 Key role of chemistry versus bias in electrocatalytic oxygen evolution
Key role of chemistry versus bias in electrocatalytic oxygen evolution
Spectroscopic studies and theoretical calculations of the electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction establish that reaction rates depend on the amount of charge stored in the electrocatalyst, and not on the applied potential.
- Hong Nhan Nong
- , Lorenz J. Falling
- & Travis E. Jones
-
Article |
 Accelerated discovery of CO2 electrocatalysts using active machine learning
Accelerated discovery of CO2 electrocatalysts using active machine learning
Machine learning predicts Cu-Al electrocatalysts provide better efficiency and productivity than copper when using intermittent renewable electricity to convert carbon dioxide to useful chemicals and fuels.
- Miao Zhong
- , Kevin Tran
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article |
 Domino electroreduction of CO2 to methanol on a molecular catalyst
Domino electroreduction of CO2 to methanol on a molecular catalyst
Individual cobalt phthalocyanine derivative molecules immobilized on carbon nanotubes effectively catalyse the electroreduction of CO2 to methanol via a domino process with high activity and selectivity and stable performance.
- Yueshen Wu
- , Zhan Jiang
- & Hailiang Wang
-
Letter |
 PdMo bimetallene for oxygen reduction catalysis
PdMo bimetallene for oxygen reduction catalysis
PdMo bimetallene, a highly curved and sub-nanometre-thick nanosheet of a palladium–molybdenum alloy, is an efficient and stable electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction and evolution reactions under alkaline conditions.
- Mingchuan Luo
- , Zhonglong Zhao
- & Shaojun Guo
-
Letter |
 Hindered dialkyl ether synthesis with electrogenerated carbocations
Hindered dialkyl ether synthesis with electrogenerated carbocations
A route to the synthesis of hindered ethers is developed, in which electrochemical oxidation is used to liberate high-energy carbocations that are then captured by an alcohol.
- Jinbao Xiang
- , Ming Shang
- & Phil S. Baran
-
Letter |
 A rigorous electrochemical ammonia synthesis protocol with quantitative isotope measurements
A rigorous electrochemical ammonia synthesis protocol with quantitative isotope measurements
A protocol for the electrochemical reduction of nitrogen to ammonia enables isotope-sensitive quantification of the ammonia produced and the identification and removal of contaminants.
- Suzanne Z. Andersen
- , Viktor Čolić
- & Ib Chorkendorff
-
Letter |
 Direct instrumental identification of catalytically active surface sites
Direct instrumental identification of catalytically active surface sites
Scanning tunnelling microscopy is used to distinguish between different active sites of a catalyst—such as boundaries between different materials—during a reaction, allowing the contributions of these sites to be evaluated.
- Jonas H. K. Pfisterer
- , Yunchang Liang
- & Aliaksandr S. Bandarenka
-
Letter |
 Enhanced electrocatalytic CO2 reduction via field-induced reagent concentration
Enhanced electrocatalytic CO2 reduction via field-induced reagent concentration
Gold and palladium nanoneedle electrocatalysts benefit from field-induced reagent concentration to improve the efficiency of carbon dioxide reduction in the synthesis of carbon-based fuels using renewable electricity.
- Min Liu
- , Yuanjie Pang
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Letter |
 Cooperative electrocatalytic alcohol oxidation with electron-proton-transfer mediators
Cooperative electrocatalytic alcohol oxidation with electron-proton-transfer mediators
A co-catalyst system for electrochemical alcohol oxidation composed of a bipyridine copper catalyst and an electron-proton-transfer mediator called TEMPO operates at much lower potential and is faster than TEMPO alone.
- Artavazd Badalyan
- & Shannon S. Stahl
-
Letter |
 Electrostatic catalysis of a Diels–Alder reaction
Electrostatic catalysis of a Diels–Alder reaction
Theory suggests that many chemical reactions (not simply, as is often thought, redox reactions) might be catalysed by an applied electric field; experimental evidence for this is now provided from single-molecule studies of the formation of carbon–carbon bonds in a Diels–Alder reaction.
- Albert C. Aragonès
- , Naomi L. Haworth
- & Michelle L. Coote
-
Letter |
 A pentanuclear iron catalyst designed for water oxidation
A pentanuclear iron catalyst designed for water oxidation
A complex containing five atoms of iron is shown to be a highly efficient and robust water oxidation catalyst owing to the presence of redox flexibility, which enables charge accumulation and electron transfer, and the presence of adjacent active sites that enables intramolecular O–O bond formation.
- Masaya Okamura
- , Mio Kondo
- & Shigeyuki Masaoka
-
Letter |
 Sub-particle reaction and photocurrent mapping to optimize catalyst-modified photoanodes
Sub-particle reaction and photocurrent mapping to optimize catalyst-modified photoanodes
Using single-molecule fluorescence imaging of photoelectrocatalysis, the charge-carrier activities on single TiO2 nanorods and the corresponding water-oxidation photocurrent are mapped at high spatiotemporal resolution, revealing the best catalytic sites and the most effective sites for depositing an oxygen evolution catalyst.
- Justin B. Sambur
- , Tai-Yen Chen
- & Peng Chen
-
Letter |
 Uranium-mediated electrocatalytic dihydrogen production from water
Uranium-mediated electrocatalytic dihydrogen production from water
Homogenous electrocatalytic water reduction with formation of dihydrogen is demonstrated with a trisaryloxide U(III) complex, for which the catalytic cycle was elucidated and found to involve rare terminal U(iv)–OH and U(v)=O complexes.
- Dominik P. Halter
- , Frank W. Heinemann
- & Karsten Meyer
-
Letter |
 Partially oxidized atomic cobalt layers for carbon dioxide electroreduction to liquid fuel
Partially oxidized atomic cobalt layers for carbon dioxide electroreduction to liquid fuel
Electroreduction of carbon dioxide into useful fuels helps to reduce fossil-fuel consumption and carbon dioxide emissions, but activating carbon dioxide requires impractically high overpotentials; here a metal atomic layer combined with its native oxide that requires low overpotentials to reduce carbon dioxide is developed, adapted from an existing cobalt-based catalyst.
- Shan Gao
- , Yue Lin
- & Yi Xie
-
Letter |
 Electroreduction of carbon monoxide to liquid fuel on oxide-derived nanocrystalline copper
Electroreduction of carbon monoxide to liquid fuel on oxide-derived nanocrystalline copper
The electrochemical conversion of CO and H2O into liquid fuel is made feasible at modest potentials with the use of oxide-derived nanocystalline Cu as the catalyst.
- Christina W. Li
- , Jim Ciston
- & Matthew W. Kanan
-
Review Article |
 Electrocatalyst approaches and challenges for automotive fuel cells
Electrocatalyst approaches and challenges for automotive fuel cells
Although automotive fuel-cell catalyst development has come a long way in the past fifteen years, more research is needed for oxygen reduction electrocatalysts to be successfully commercialized.
- Mark K. Debe

 Long-term continuous ammonia electrosynthesis
Long-term continuous ammonia electrosynthesis