News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Self-organization of a biogeomorphic landscape controlled by plant life-history traits
Self-organization of a biogeomorphic landscape controlled by plant life-history traits
Fast-colonizing plants stabilize wetland landscapes, whereas slow-colonizing plants promote channel formation according to biogeomorphic model simulations and field observations.
- Christian Schwarz
- , Olivier Gourgue
- & Stijn Temmerman
-
Article |
 Links among warming, carbon and microbial dynamics mediated by soil mineral weathering
Links among warming, carbon and microbial dynamics mediated by soil mineral weathering
Soil weathering, rather than short-term warming, controls microbial community composition, nutrient availability and soil carbon content, according to observations from a 3-Myr-old soil chronosequence preserved in river terraces in California.
- S. Doetterl
- , A. A. Berhe
- & P. Boeckx
-
Article |
 Highland cropland expansion and forest loss in Southeast Asia in the twenty-first century
Highland cropland expansion and forest loss in Southeast Asia in the twenty-first century
Cultivated areas have expanded at the expense of forests, including primary and protected forests, in Southeast Asian highlands, according to an analysis of satellite imagery of the region.
- Zhenzhong Zeng
- , Lyndon Estes
- & Eric F. Wood
-
Article |
 Improved efficiency of the biological pump as a trigger for the Late Ordovician glaciation
Improved efficiency of the biological pump as a trigger for the Late Ordovician glaciation
Enhanced algal productivity during the Late Ordovician may have led to carbon drawdown and the inception of the Hirnantian glaciation, according to sediment geochemistry and carbon cycle modelling.
- Jiaheng Shen
- , Ann Pearson
- & Yanan Shen
-
Editorial |
 Limits to protection
Limits to protection
Marine protected areas can support ecosystem resilience in the face of environmental stress, but only up to a point.
-
-
News & Views |
 Tree height matters
Tree height matters
Tall trees are more resilient to drought than short trees, suggests a comparison of the sensitivity of photosynthesis to soil moisture in Amazon forests.
- Paulo Brando
-
Article |
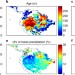 Tall Amazonian forests are less sensitive to precipitation variability
Tall Amazonian forests are less sensitive to precipitation variability
Tall trees are less sensitive to variation in precipitation than short trees, according to analyses of photosynthetic sensitivity to drought in tall and short Amazon forests. The results demonstrate higher resilience of tall trees to drought.
- Francesco Giardina
- , Alexandra G. Konings
- & Pierre Gentine
-
Article |
 Response of the Great Barrier Reef to sea-level and environmental changes over the past 30,000 years
Response of the Great Barrier Reef to sea-level and environmental changes over the past 30,000 years
The Great Barrier Reef has migrated rapidly in response to sea-level changes since the last glacial period, suggesting resilience to environmental stress over this interval, according to a reconstruction of reef accretion.
- Jody M. Webster
- , Juan Carlos Braga
- & Bryan C. Lougheed
-
News & Views |
 Stream metabolism heats up
Stream metabolism heats up
Higher stream temperatures as the climate warms could lead to lower ecosystem productivity and higher CO2 emissions in streams. An analysis of stream ecosystems finds that such changes will be greatest in the warmest and most productive streams.
- James B. Heffernan
-
Article |
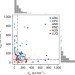 Continental-scale decrease in net primary productivity in streams due to climate warming
Continental-scale decrease in net primary productivity in streams due to climate warming
An increase in stream temperature leads to a convergence of metabolic balance, overall decline in net ecosystem productivity, and higher CO2 emissions from streams, according to analyses of temperature sensitivity of stream metabolism across six biomes.
- Chao Song
- , Walter K. Dodds
- & Ford Ballantyne IV
-
Article |
 A global analysis of terrestrial plant litter dynamics in non-perennial waterways
A global analysis of terrestrial plant litter dynamics in non-perennial waterways
Rewetting of plant litter accumulated in dry riverbeds releases pulses of CO2, reveals a global analysis of intermittent rivers and ephemeral streams.
- T. Datry
- , A. Foulquier
- & A. Zoppini
-
-
News & Views |
 Agroforestry in the Sahel
Agroforestry in the Sahel
West African farmers adjust tree cover to realize the co-benefits of agroforestry, according to analyses of remote sensing data.
- Niall P. Hanan
-
Article |
 Reduction of tree cover in West African woodlands and promotion in semi-arid farmlands
Reduction of tree cover in West African woodlands and promotion in semi-arid farmlands
Farmland management promotes tree cover around villages in the semi-arid Sahel of West Africa, according to analyses of satellite imagery. This implies that a higher population density does not always lead to reduced tree cover.
- Martin Brandt
- , Kjeld Rasmussen
- & Rasmus Fensholt
-
-
Article |
 Dryland photoautotrophic soil surface communities endangered by
global change
Dryland photoautotrophic soil surface communities endangered by
global change
Biocrust coverage of soils could decrease by 25–40% within 65 years, due to climate and land-use changes. Biocrusts, such as lichens and algae, cover 12% of Earth’s land surface but environmental modelling suggests that they are vulnerable to change.
- Emilio Rodriguez-Caballero
- , Jayne Belnap
- & Bettina Weber
-
News & Views |
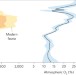 Ordovician oxygen and biodiversity
Ordovician oxygen and biodiversity
Rising oxygen levels may have facilitated the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event according to a reconstruction of atmospheric oxygen concentrations.
- Alycia L. Stigall
-
Article |
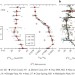 Oxygenation as a driver of the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event
Oxygenation as a driver of the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event
An increase in biodiversity 450 million years ago coincided with a rise in atmospheric oxygen concentrations, suggests a geochemical analysis. Oxygen availability may have thus helped spur the radiation alongside climatic cooling.
- Cole T. Edwards
- , Matthew R. Saltzman
- & David A. Fike
-
Article |
 Unexpected winter phytoplankton blooms in the North Atlantic subpolar gyre
Unexpected winter phytoplankton blooms in the North Atlantic subpolar gyre
Transient winter restratification events can promote phytoplankton blooms in the North Atlantic subpolar gyre, according to float data. Typical winter conditions feature a deep mixed layer that limits phytoplankton activity.
- L. Lacour
- , M. Ardyna
- & D. Iudicone
-
Article |
 The role of microbes in snowmelt and radiative forcing on an Alaskan icefield
The role of microbes in snowmelt and radiative forcing on an Alaskan icefield
Microbes on glacial snow and ice reduce albedo and increase melting. Field experiments show that nutrient and meltwater additions increase microbial abundance and that areas of microbe-covered snow generate increased snowmelt.
- Gerard Q. Ganey
- , Michael G. Loso
- & Roman J. Dial
-
Review Article |
 Metal availability and the expanding network of microbial metabolisms in the Archaean eon
Metal availability and the expanding network of microbial metabolisms in the Archaean eon
Microbial metabolisms depend on enzymes that contain trace metals. A synthesis of molecular and geochemical data shows that these metabolic pathways evolved alongside changing marine availability of trace metals during the Precambrian.
- Eli K. Moore
- , Benjamin I. Jelen
- & Paul G. Falkowski
-
Article |
 Microbial oxidation as a methane sink beneath the West Antarctic Ice Sheet
Microbial oxidation as a methane sink beneath the West Antarctic Ice Sheet
Subglacial lakes contain active microbial ecosystems capable of cycling methane. In a subglacial lake in West Antarctica, methane that is produced is subsequently consumed, limiting the potential for methane emissions during lake drainage.
- Alexander B. Michaud
- , John E. Dore
- & John C. Priscu
-
Article |
 Microbial substrate preference dictated by energy demand rather than supply
Microbial substrate preference dictated by energy demand rather than supply
Microbes are expected to prefer substrates with the highest energy yield. Laboratory experiments demonstrate that a metabolically flexible archaeon exhibits preference for and greater growth from lower energy substrates.
- Maximiliano J. Amenabar
- , Everett L. Shock
- & Eric S. Boyd
-
Article |
 Substantial inorganic carbon sink in closed drainage basins globally
Substantial inorganic carbon sink in closed drainage basins globally
Dissolved inorganic carbon is buried in dryland basins that do not drain to the sea. Based on measurements of sediment chemistry in twelve of these sites, closed basins are estimated to store 0.15 Pg of dissolved inorganic carbon annually.
- Yu Li
- , Chengqi Zhang
- & Wangting Ye
-
News & Views |
 Cleaner Chinese lakes
Cleaner Chinese lakes
Phosphorus loading can cause eutrophication of lakes. Analyses of lake chemistry in China reveal that policies have led to lower phosphorus levels overall, but increasing trends in some lakes suggest that expanded policies may be needed.
- Jessica Corman
-
Article |
 Regionally strong feedbacks between the atmosphere and terrestrial biosphere
Regionally strong feedbacks between the atmosphere and terrestrial biosphere
Understanding biosphere–atmosphere feedback loops can improve forecasts of climate and vegetation resilience. Analyses of satellite observations reveal that feedbacks are strong in regions that determine the net terrestrial carbon balance.
- Julia K. Green
- , Alexandra G. Konings
- & Pierre Gentine
-
Article |
 Decadal soil carbon accumulation across Tibetan permafrost regions
Decadal soil carbon accumulation across Tibetan permafrost regions
Climate change is expected to release carbon stored in permafrost soils. Sampling of sites across the Tibetan Plateau in the early 2000s and early 2010s reveals increased carbon stocks in shallow soils, which may offset losses from deeper soils.
- Jinzhi Ding
- , Leiyi Chen
- & Yuanhe Yang
-
-
Article |
 Thermodynamically controlled preservation of organic carbon in floodplains
Thermodynamically controlled preservation of organic carbon in floodplains
Anoxic carbon decomposition is thought to depend on the energetics of electron acceptors. Mass spectrometry measurements of floodplain sediments reveal that the energetics of organic compounds can also determine whether they are decomposed.
- Kristin Boye
- , Vincent Noël
- & Scott Fendorf
-
Article |
 Microbially driven export of labile organic carbon from the Greenland ice sheet
Microbially driven export of labile organic carbon from the Greenland ice sheet
Glacial systems are important sources of dissolved organic carbon to downstream ecosystems. Observations of carbon dynamics on the Greenland ice sheet reveal substantial melt season production and export of microbial dissolved organic carbon.
- Michaela Musilova
- , Martyn Tranter
- & Alexandre M. Anesio
-
News & Views |
 Warming from freezing soils
Warming from freezing soils
Freezing and thawing of soils leads to large pulses of nitrous oxide release. An empirical model shows that cropland winter nitrous oxide emissions are substantial, calling for a revision of the global nitrous oxide budget.
- Klaus Butterbach-Bahl
- & Benjamin Wolf
-
Article |
 Sensitivity of grassland productivity to aridity controlled by stomatal and xylem regulation
Sensitivity of grassland productivity to aridity controlled by stomatal and xylem regulation
Grass species vary in their regulation of water use. Remote-sensing data reveal that productivity is more sensitive to atmospheric moisture than precipitation deficits, especially in grasslands where plants loosely regulate water use.
- A. G. Konings
- , A. P. Williams
- & P. Gentine
-
Article |
 Carbon sequestration in the deep Atlantic enhanced by Saharan dust
Carbon sequestration in the deep Atlantic enhanced by Saharan dust
Dust-borne nutrients can enhance productivity in the surface ocean. Two years of sediment trap data reveal that dust enhances carbon export to depth by increasing surface nitrogen fixation, productivity and carbon sinking rates in the North Atlantic.
- Katsiaryna Pabortsava
- , Richard S. Lampitt
- & E. Malcolm S. Woodward
-
News & Views |
 Deep ocean iron balance
Deep ocean iron balance
Dissolved iron is mysteriously pervasive in deep ocean hydrothermal plumes. An analysis of gas, metals and particles from a 4,000 km plume transect suggests that dissolved iron is maintained by rapid and reversible exchanges with sinking particles.
- William B. Homoky
-
Article |
 Iron persistence in a distal hydrothermal plume supported by dissolved–particulate exchange
Iron persistence in a distal hydrothermal plume supported by dissolved–particulate exchange
The largest known hydrothermal plume moves dissolved iron halfway across the Pacific. In situ measurements show that dissolved and particulate iron transport is facilitated by reversible exchange of dissolved iron onto organic compounds.
- Jessica N. Fitzsimmons
- , Seth G. John
- & Robert M. Sherrell
-
Article |
 Silicon and zinc biogeochemical cycles coupled through the Southern Ocean
Silicon and zinc biogeochemical cycles coupled through the Southern Ocean
Zinc and silicon distributions co-vary in much of the global oceans. Observations and numerical modelling suggest that this co-variation can arise in the absence of mechanistic links between the uptake of zinc and silicate.
- Derek Vance
- , Susan H. Little
- & Rob Middag
-
Article |
 Warm Mediterranean mid-Holocene summers inferred from fossil midge assemblages
Warm Mediterranean mid-Holocene summers inferred from fossil midge assemblages
Reconstructions of Holocene summer temperatures differ between models and vegetation-based proxies. A quantitative reconstruction for the Mediterranean region based on fossil midge assemblages suggests warm summers, in line with climate models.
- Stéphanie Samartin
- , Oliver Heiri
- & Willy Tinner
-
News & Views |
 Polar merry-go-round
Polar merry-go-round
The dynamics of polar marine ecosystems are poorly understood. A laser-based space-borne sensor captures annual cycles of phytoplankton biomass in seasonally ice-free polar waters, and provides clues on how growth drives these cycles.
- Marcel Babin
-
Article |
 Annual boom–bust cycles of polar phytoplankton biomass revealed by space-based lidar
Annual boom–bust cycles of polar phytoplankton biomass revealed by space-based lidar
Phytoplankton productivity is high in the polar oceans. Lidar observations from 2006–2015 reveal that phytoplankton biomass was characterized by annual cycles influenced by sea-ice extent in the Antarctic and ecological processes in the Arctic.
- Michael J. Behrenfeld
- , Yongxiang Hu
- & Amy Jo Scarino
-
Article |
 Competitive fitness of a predominant pelagic calcifier impaired by ocean acidification
Competitive fitness of a predominant pelagic calcifier impaired by ocean acidification
Ocean acidification can affect growth and calcification rates of calcifying phytoplankton. Mesocosm experiments reveal that acidification can also cause declines in population size and inhibit bloom formation.
- Ulf Riebesell
- , Lennart T. Bach
- & Kai G. Schulz
-
Article |
 N2 production rates limited by nitrite availability in the Bay of Bengal oxygen minimum zone
N2 production rates limited by nitrite availability in the Bay of Bengal oxygen minimum zone
Nitrogen losses have not been observed in the Bay of Bengal, unlike in other ocean oxygen minimum zones. Chemical and molecular analyses reveal that trace levels of oxygen inhibit nitrate formation, largely preventing microbial N2 production.
- L. A. Bristow
- , C. M. Callbeck
- & D. E. Canfield
-
News & Views |
 New pathways in the sand
New pathways in the sand
Organic carbon decomposition in anoxic marine sediments was thought to be dominated by bacteria, but experimental data and microbial culture studies now show that microalgae buried in coastal sands may also play an important role in carbon turnover.
- Alexandra Rao
-
Article |
 Metabolism in anoxic permeable sediments is dominated by eukaryotic dark fermentation
Metabolism in anoxic permeable sediments is dominated by eukaryotic dark fermentation
Bacteria have been assumed to dominate organic matter decomposition in marine sediments. In flow-through reactor experiments, algae were revealed to be primarily responsible for anaerobically metabolizing organic matter in permeable sediments.
- Michael F. Bourke
- , Philip J. Marriott
- & Perran L. M. Cook
-
News & Views |
 Ocean dissolved organics matter
Ocean dissolved organics matter
Large quantities of organic carbon are stored in the ocean, but its biogeochemical behaviour is elusive. Size–age–composition relations now quantify the production of tiny organic molecules as a major pathway for carbon sequestration.
- Rainer M. W. Amon
-
News & Views |
 CO2 and late Palaeozoic glaciation
CO2 and late Palaeozoic glaciation
Large glacial–interglacial fluctuations occurred during the late Palaeozoic. Geochemical and fossil data show these cycles were marked by coincident shifts in the carbon cycle and terrestrial biosphere.
- Timothy S. Myers
-
Letter |
 Climate, pCO2 and terrestrial carbon cycle linkages during late Palaeozoic glacial–interglacial cycles
Climate, pCO2 and terrestrial carbon cycle linkages during late Palaeozoic glacial–interglacial cycles
The late Palaeozoic was marked by a series of glacial–interglacial cycles. Geochemical and fossil data suggest a role for terrestrial vegetation–carbon cycle feedbacks in the climate response to orbital forcing.
- Isabel P. Montañez
- , Jennifer C. McElwain
- & Michael T. Hren
-
Letter |
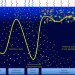 Substantial energy input to the mesopelagic ecosystem from the seasonal mixed-layer pump
Substantial energy input to the mesopelagic ecosystem from the seasonal mixed-layer pump
Life at ocean depths below ∼100 m requires organic carbon from the upper ocean. Analyses of satellite and Argo-float data reveal that seasonal changes in mixed-layer depth supply substantial amounts of carbon to this deep and dark ecosystem.
- Giorgio Dall'Olmo
- , James Dingle
- & Hervé Claustre
-
Progress Article |
 Substantial role of macroalgae in marine carbon sequestration
Substantial role of macroalgae in marine carbon sequestration
Marine macroalgae are dominant primary producers in coastal zones. A review of the published literature suggests that macroalgae may play an important role in carbon sequestration.
- Dorte Krause-Jensen
- & Carlos M. Duarte
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Agroecology
- Animal migration
- Behavioural ecology
- Biodiversity
- Biogeochemistry
- Biogeography
- Biooceanography
- Boreal ecology
- Climate-change ecology
- Community ecology
- Conservation biology
- Ecological epidemiology
- Ecological genetics
- Ecological modelling
- Ecological networks
- Ecophysiology
- Ecosystem ecology
- Ecosystem services
- Environmental economics
- Evolutionary ecology
- Fire ecology
- Forest ecology
- Forestry
- Freshwater ecology
- Grassland ecology
- Invasive species
- Macroecology
- Microbial ecology
- Molecular ecology
- Palaeoecology
- Population dynamics
- Restoration ecology
- Riparian ecology
- Stable isotope analysis
- Theoretical ecology
- Tropical ecology
- Urban ecology
- Wetlands ecology

 Species signatures in landscapes
Species signatures in landscapes The rise and fall of the Great Barrier Reef
The rise and fall of the Great Barrier Reef Arctic streams in murky waters
Arctic streams in murky waters Links between life and landscapes
Links between life and landscapes Accelerating riverbank erosion
Accelerating riverbank erosion