Featured
-
-
Article |
 Mapping peat thickness and carbon stocks of the central Congo Basin using field data
Mapping peat thickness and carbon stocks of the central Congo Basin using field data
Field surveys suggest peatlands in the central Congo Basin are globally significant carbon stocks, storing approximately 28% of the world’s tropical peat carbon.
- Bart Crezee
- , Greta C. Dargie
- & Simon L. Lewis
-
Article |
 Global mapping reveals increase in lacustrine algal blooms over the past decade
Global mapping reveals increase in lacustrine algal blooms over the past decade
Algal blooms are occurring more frequently, as seen in a global database compiled from satellite imagery from the past few decades.
- Xuejiao Hou
- , Lian Feng
- & Chunmiao Zheng
-
Review Article |
 Anthropogenic stresses on the world’s big rivers
Anthropogenic stresses on the world’s big rivers
Stressors such as large-scale damming, hydrological change, pollution, the introduction of non-native species and sediment mining are challenging the integrity and future of large rivers, according to a synthesis of the literature on the 32 biggest rivers.
- Jim Best
-
News & Views |
 Stream metabolism heats up
Stream metabolism heats up
Higher stream temperatures as the climate warms could lead to lower ecosystem productivity and higher CO2 emissions in streams. An analysis of stream ecosystems finds that such changes will be greatest in the warmest and most productive streams.
- James B. Heffernan
-
Article |
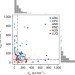 Continental-scale decrease in net primary productivity in streams due to climate warming
Continental-scale decrease in net primary productivity in streams due to climate warming
An increase in stream temperature leads to a convergence of metabolic balance, overall decline in net ecosystem productivity, and higher CO2 emissions from streams, according to analyses of temperature sensitivity of stream metabolism across six biomes.
- Chao Song
- , Walter K. Dodds
- & Ford Ballantyne IV
-
-
News & Views |
 Cleaner Chinese lakes
Cleaner Chinese lakes
Phosphorus loading can cause eutrophication of lakes. Analyses of lake chemistry in China reveal that policies have led to lower phosphorus levels overall, but increasing trends in some lakes suggest that expanded policies may be needed.
- Jessica Corman
-
Article |
 Thermodynamically controlled preservation of organic carbon in floodplains
Thermodynamically controlled preservation of organic carbon in floodplains
Anoxic carbon decomposition is thought to depend on the energetics of electron acceptors. Mass spectrometry measurements of floodplain sediments reveal that the energetics of organic compounds can also determine whether they are decomposed.
- Kristin Boye
- , Vincent Noël
- & Scott Fendorf
-
Letter |
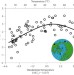 Impact of warming on CO2 emissions from streams countered by aquatic photosynthesis
Impact of warming on CO2 emissions from streams countered by aquatic photosynthesis
Aquatic CO2 emissions are expected to increase if warming reduces photosynthesis relative to respiration. An analysis of streams across a 41 °C temperature gradient reveals that the thermal responses of respiration and photosynthesis are similar.
- Benoît O. L. Demars
- , Gísli M. Gíslason
- & Thomas E. Freitag
-
News & Views |
 It's a gas
It's a gas
Climate change is causing widespread permafrost thaw in the Arctic. Measurements at 33 Arctic lakes show that old carbon from thawing permafrost is being emitted as methane, though emission rates have not changed during the past 60 years.
- Torben R. Christensen
-
News & Views |
 The fate of phosphorus
The fate of phosphorus
Phosphorus is essential for food production, but it is also a key cause of eutrophication. Estimates of phosphorus flux for the past 40–70 years reveal that large river basins can experience phases of phosphorus accumulation and depletion.
- Julien Némery
- & Josette Garnier
-
Letter |
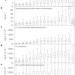 Significant fraction of CO2 emissions from boreal lakes derived from hydrologic inorganic carbon inputs
Significant fraction of CO2 emissions from boreal lakes derived from hydrologic inorganic carbon inputs
Lakes are a large source of CO2. An analysis of chemical and physical data from 5,118 boreal lakes reveals that a majority emit CO2 originating primarily from terrestrial sources rather than CO2 produced within the lakes.
- Gesa A. Weyhenmeyer
- , Sarian Kosten
- & Fabio Roland
-
Letter |
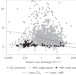 Sources of and processes controlling CO2 emissions change with the size of streams and rivers
Sources of and processes controlling CO2 emissions change with the size of streams and rivers
Rivers and streams are key sources of CO2. Estimated emissions and aquatic productivity from across the US show that small streams predominantly emit CO2 produced in soils, but the contribution from aquatic metabolism increases with river size.
- E. R. Hotchkiss
- , R. O. Hall Jr
- & J. Karlsson
-
Letter |
 Persistence of dissolved organic matter in lakes related to its molecular characteristics
Persistence of dissolved organic matter in lakes related to its molecular characteristics
Organic matter’s molecular structure has been thought to influence its decomposition. Analyses of dissolved organic carbon in Swedish lakes found that aliphatic and N-containing compounds persisted, while oxidized aromatic compounds were lost.
- Anne M. Kellerman
- , Dolly N. Kothawala
- & Lars J. Tranvik
-
News & Views |
 Old carbon mobilized
Old carbon mobilized
Soil contains aged organic carbon that can be hundreds or thousands of years old. Human disturbance in small and large watersheds is mobilizing some of this fossil carbon from soils to aquatic systems.
- Chris Evans
-
Letter |
 Predator-induced reduction of freshwater carbon dioxide emissions
Predator-induced reduction of freshwater carbon dioxide emissions
Predators can potentially influence the exchange of carbon dioxide between ecosystems and the atmosphere. Predator manipulation experiments with fish and invertebrates in a range of freshwater systems suggest that freshwater carbon dioxide emissions are reduced in the presence of predators.
- Trisha B. Atwood
- , Edd Hammill
- & John S. Richardson
-
Letter |
 Hotspots of anaerobic ammonium oxidation at land–freshwater interfaces
Hotspots of anaerobic ammonium oxidation at land–freshwater interfaces
Anammox, anaerobic ammonium oxidation, accounts for over 50% of nitrogen loss in marine ecosystems. A field study in north China reveals hotspots of anammox activity in sediments sampled from land–lake interfaces.
- Guibing Zhu
- , Shanyun Wang
- & Chengqing Yin
-
Feature |
 Freshwater in flux
Freshwater in flux
A surprising fraction of Earth's element cycling takes place in inland waters. Jonathan Cole suggests that interactions between these water bodies and the terrestrial biosphere are more extensive and interesting than previously thought.
- Jonathan Cole
-
-
Letter |
 Abiotic nitrous oxide emission from the hypersaline Don Juan Pond in Antarctica
Abiotic nitrous oxide emission from the hypersaline Don Juan Pond in Antarctica
Nitrous oxide is a potent atmospheric greenhouse gas that is thought to be produced in soils through biological processes. Field measurements reveal nitrous oxide fluxes near Don Juan Pond, Antarctica — of comparable magnitude to those found in tropical soils — which may result from abiotic water–rock reactions.
- Vladimir A. Samarkin
- , Michael T. Madigan
- & Samantha B. Joye

 Rewetting global wetlands effectively reduces major greenhouse gas emissions
Rewetting global wetlands effectively reduces major greenhouse gas emissions Arctic streams in murky waters
Arctic streams in murky waters Complex water future
Complex water future